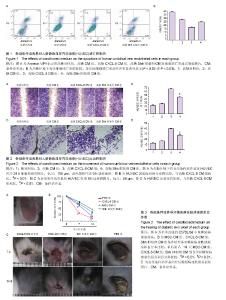
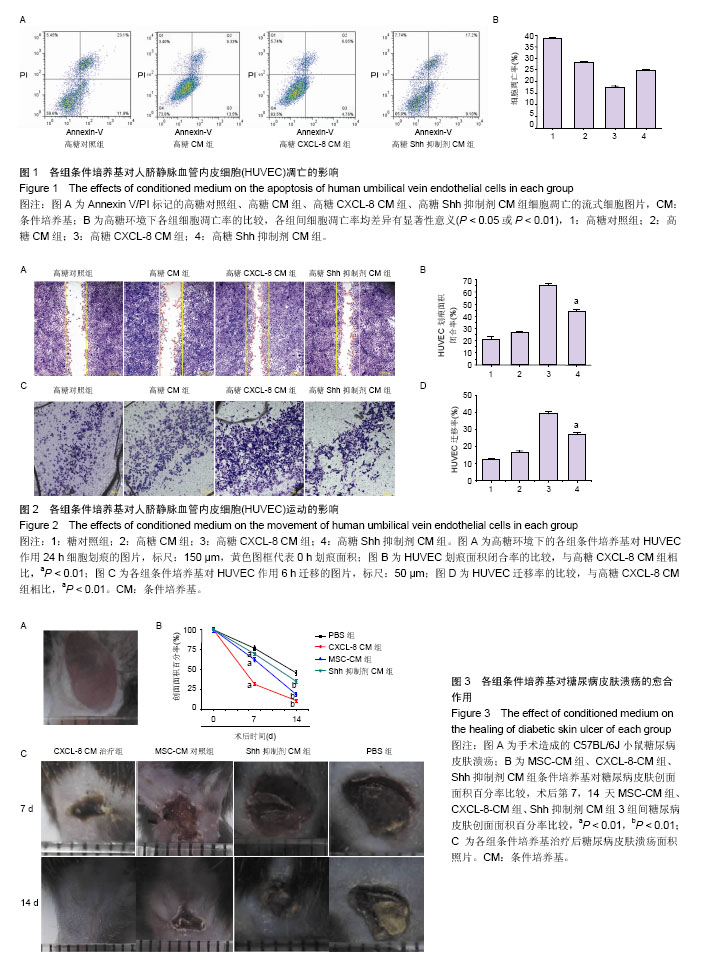
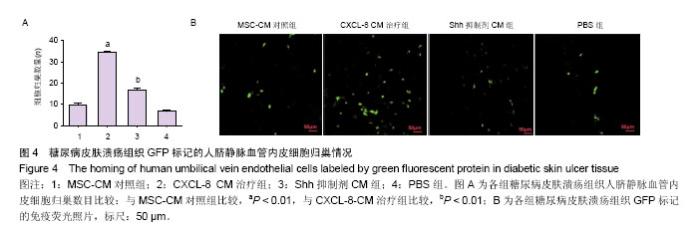
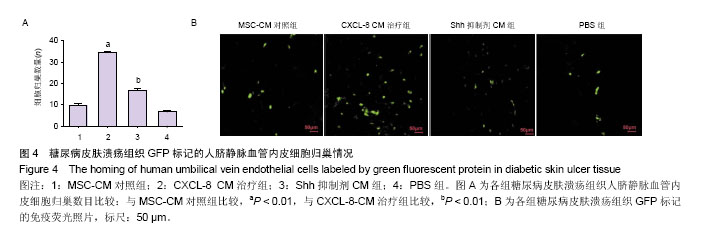
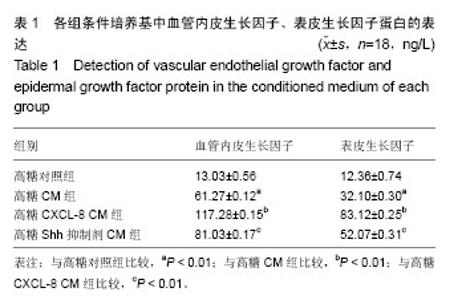
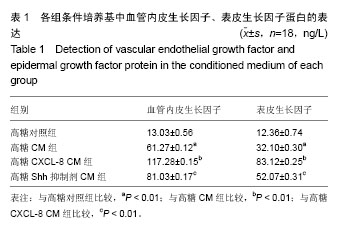
| [1] Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, et al. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103(2):137-149.[2] Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1090- 1101.[3] Hopkins RB, Burke N, Harlock J, et al. Economic burden of illness associated with diabetic foot ulcers in Canada. BMC Health Serv Res. 2015;15:13.[4] Urbán VS, Kiss J, Kovács J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells cooperate with bone marrow cells in therapy of diabetes. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):244-253.[5] Sun BK, Siprashvili Z, Khavari PA. Advances in skin grafting and treatment of cutaneous wounds. Science. 2014; 346 (6212):941-945.[6] Brantley JN, Verla TD. Use of Placental Membranes for the Treatment of Chronic Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Advances in Wound Care. 2015;4(9):545-559.[7] Poittevin M, Bonnin P, Pimpie C, et al. Diabetic microangiopathy: impact of impaired cerebral vasoreactivity and delayed angiogenesis after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion on stroke damage and cerebral repair in mice. Diabetes. 2015;64(3):999-1010.[8] Shestopalov IA, Zon LI. Stem cells: the right neighbour. Nature. 2012;481(7382):453-455.[9] Donà E, Barry JD, Valentin G, et al. Directional tissue migration through a self-generated chemokine gradient. Nature. 2013;503(7475):285-289.[10] 张鹏,张晓东,姜杨,等.趋化因子8对高糖环境下脂肪间充质干细胞迁移能力的影响[J].解剖学报,2015,46(6):764-771.[11] Eming SA, Martin P, Tomic-Canic M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(265):265-256.[12] Wang Y, Chen X, Cao W, et al. Plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells in immunomodulation: pathological and therapeutic implications. Nat Immunol. 2014;15(11):1009-1016.[13] Matusek T, Wendler F, Polès S, et al. The ESCRT machinery regulates the secretion and long-range activity of Hedgehog. Nature. 2014;516(7529):99-103.[14] Battiston KG, Cheung JWC, Jain D, et al. Biomaterials in co-culture systems: Towards optimizing tissue integration and cell signaling within scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2014;35(15): 4465-4476.[15] Alvarez JI, Dodelet-Devillers A, Kebir H, et al. The Hedgehog pathway promotes blood-brain barrier integrity and CNS immune quiescence. Science. 2011;334(6063):1727-1731.[16] Renault MA, Chapouly C, Yao Q, et al. Desert hedgehog promotes ischemia-induced angiogenesis by ensuring peripheral nerve survival. Circ Res. 2013;112(5):762-770.[17] Lewis S. Neural development: Double agent sonic hedgehog. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14(10):666-667.[18] He S, Shen L, Wu Y, et al. Effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on mesenchymal stem cell-seeded electrospinning biomaterial for treating ischemic diabetic ulcers via milieu-dependent differentiation mechanism. Tissue Eng Part A. 2015;21(5-6):928-938.[19] Xu R, Bi C, Song J, et al. Upregulation of miR-142-5p in atherosclerotic plaques and regulation of oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis in macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(5):3229-3234.[20] Shen L, Wang P, Yang J, et al. MicroRNA-217 regulates WASF3 expression and suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 2014;9(10): e109138.[21] Hou C, Shen L, Huang Q, et al. The effect of heme oxygenase-1 complexed with collagen on MSC performance in the treatment of diabetic ischemic ulcer. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(1):112-120.[22] Shen L, Zeng W, Wu YX, et al. Neurotrophin-3 accelerates wound healing in diabetic mice by promoting a paracrine response in mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2013; 22(6):1011-1021.[23] Barcelos LS, Duplaa C, Kränkel N, et al. Human CD133+ progenitor cells promote the healing of diabetic ischemic ulcers by paracrine stimulation of angiogenesis and activation of Wnt signaling. Circ Res. 2009;104(9):1095-1102.[24] Takehara Y, Yabuuchi A, Ezoe K, et al. The restorative effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on damaged ovarian function. Lab Invest. 2013;93(2):181-193.[25] Marzagalli R, Scuderi S, Drago F, et al. Emerging Role of PACAP as a New Potential Therapeutic Target in Major Diabetes Complications. Int J Endocrinol. 2015;2015:160928.[26] Uccelli A, Moretta L, Pistoia V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(9):726-736.[27] Hashemian SJ, Kouhnavard M, Nasli-Esfahani E. Mesenchymal stem cells: rising concerns over their application in treatment of type one diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:675103.[28] Zheng C, Kuang Q, Lao XJ, et al. Differentiation of UC-MSCs into hepatocyte-like cells in partially hepatectomized model rats. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(3):1775-1779.[29] 沈雷,张善强,张晓东,等.缺氧环境下白细胞介素8通过Akt-STAT3通路提高骨髓间充质干细胞自噬和增殖能力[J].生物工程学报,2016,32(10):1422-1432.[30] Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R, et al. Primary role of superoxide anion generation in the cascade of events leading to endothelial dysfunction and damage in high glucose treated HUVEC. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2007;17(4): 257-267. |