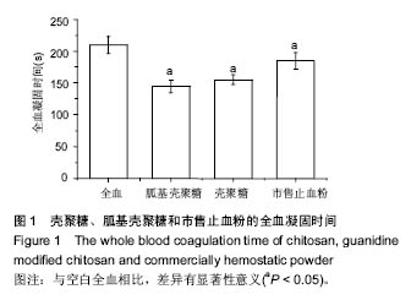
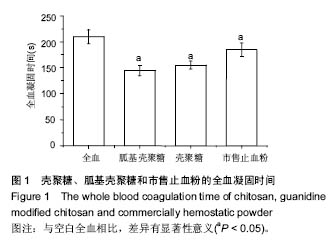
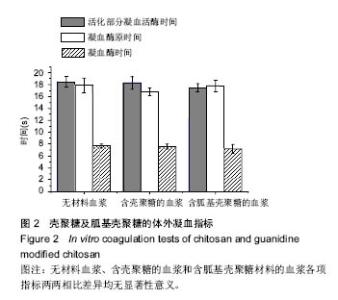
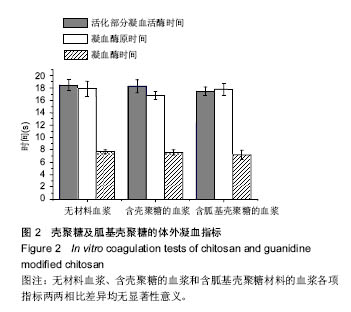
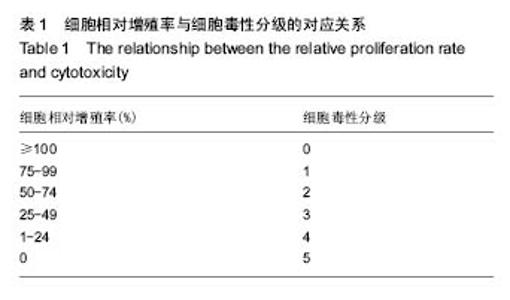
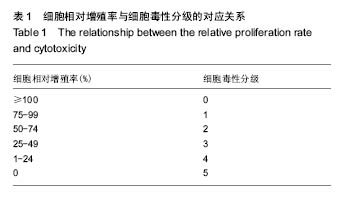
| [1]Elvin CM, Vuocolo T, Brownlee AG, et al. A highly elastic tissue sealant based on photopolymerised gelatin. Biomaterials. 2010;31(32):8323-8331.[2]Wu Y, He J, Cheng W, et al. Oxidized regenerated cellulose-based hemostat with microscopically gradient structure. Carbohydrate Polymers. 2012; 88(3):1023-1032.[3]Eldibany RM. Platelet rich fibrin versus Hemcon dental dressing following dental extraction in patients under anticoagulant therapy. Tanta Dental Journal. 2014; 11(2):75-84.[4]Schmid BC, Rezniczek GA, Rolf N, et al. Postpartum hemorrhage: use of hemostatic combat gauze. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;206(1):e12-13.[5]蒋挺大. 壳聚糖[M]. 2版.北京:化学工业出版社, 2007.[6]蒋小姝, 莫海涛, 苏海佳,等. 甲壳素及壳聚糖在农业领域方面的应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2013, 29(6):170-174.[7]乔德亮. 低聚壳聚糖制备及其在功能食品中应用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2007, 28(4):228-231.[8]程志, 杜娜. 壳聚糖在医药领域应用研究进展[J]. 人民军医, 2013, (2):223-224.[9]刘长岚, 崔文新, 李成彬. 壳聚糖及其衍生物在化工方面应用的研究[J]. 山东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2003, 18(3):73-74.[10]黄勇. 壳聚糖及其胍基化衍生物的合成、表征及抗菌性能研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学, 2013.[11]Martins AF, Facchi SP, Follmann HD, et al. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan derivatives containing N-quaternized moieties in its backbone: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(11): 20800-20832.[12]Baker S, Wiesmann WP, Ryan S. Chitosan-derivative compounds and methods of controlling microbial populations. US, US8658775. 2014.[13]Chan LW, Kim CH, Wang X, et al. PolySTAT-modified chitosan gauzes for improved hemostasis in external hemorrhage. Acta Biomater. 2016;31:178-185.[14]Dowling MB, Smith W, Balogh P, et al. Hydrophobically-modified chitosan foam: description and hemostatic efficacy. J Surg Res. 2015;193(1):316-323.[15]尹刚. 温敏性壳聚糖止血膜止血作用的实验研究[D]. 上海:第二军医大学, 2014.[16]Gu BK, Park SJ, Kim MS, et al. Fabrication of sonicated chitosan nanofiber mat with enlarged porosity for use as hemostatic materials. Carbohydr Polym. 2013;97(1):65-73.[17]奚宏伟, 魏长征, 王文斌, 等. 壳聚糖-三聚磷酸钠纳米粒对于肝组织严重出血模型的止血效果[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2014, 14(15):2831-2834.[18]谭奕哲, 吴国忠, 曾虹燕, 等. 抗菌性壳聚糖双胍醋酸盐的辐照辅助制备及其生物毒性[J]. 功能高分子学报, 2015, 28(2):183-187.[19]Su YR, Yu SH, Chao AC, et al. Preparation and properties of pH-responsive, self-assembled colloidal nanoparticles from guanidine-containing polypeptide and chitosan for antibiotic delivery. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects. 2016; 494:9-20.[20]Sun S, An Q, Li X, et al. Synergistic effects of chitosan-guanidine complexes on enhancing antimicrobial activity and wet-strength of paper.Bioresour Technol. 2010; 101(14):5693-5700.[21]Ryu K, Kim K, Kim TI, et al. Synthesis and characterization of guanidinylated polyethylenimine-conjugated chitosan for gene delivery systems. Macromolecular Research. 2014; 22(3):264-271.[22]He B, Shao Y, Liang M, et al. Biodiesel production from soybean oil by guanidinylated chitosan. Fuel. 2015; 159: 33-39.[23]Luo Y, Zhai X, Ma C, et al. An inhalable β?-adrenoceptor ligand-directed guanidinylated chitosan carrier for targeted delivery of siRNA to lung. J Control Release. 2012;162(1):28-36.[24]Chen CY, Lin HC, Huang YY, et al. ‘One-flask’ transformation of isocyanates and isothiocyanates to guanidines hydrochloride by using sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide. Tetrahedron. 2010; 66(10):1892-1897.[25]Arafa RK, Ismail MA, Munde M, et al. Novel linear triaryl guanidines, N-substituted guanidines and potential prodrugs as antiprotozoal agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2008;43(12):2901-2908.[26]杨健, 田丰, 陈世谦. 壳聚糖的止血机理和应用[J]. 国际生物医学工程杂志, 2001, 24(2):77-80.[27]Di Cera E, Dang QD, Ayala YM. Molecular mechanisms of thrombin function. Cell Mol Life Sci. 1997;53(9):701-730.[28]Matthias R, Wolfram R. Proteinase‐activated receptor activation by coagulation proteinases. Drug Development Research. 2003; 59(4):400-407.[29]Klokkevold PR, Lew DS, Ellis DG, et al. Effect of chitosan on lingual hemostasis in rabbits. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991; 49(8):858-863.[30]Benesch J, Tengvall P. Blood protein adsorption onto chitosan. Biomaterials. 2002;23(12):2561-2568. |