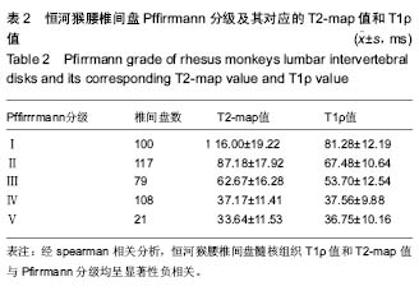
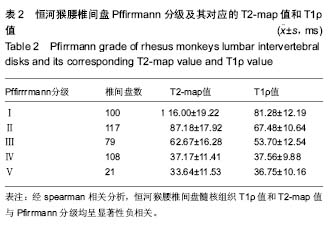
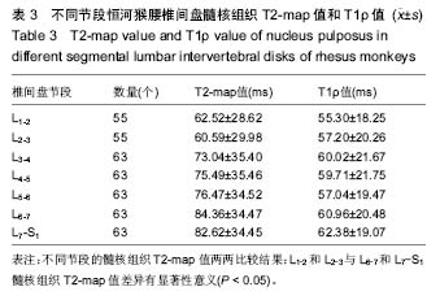
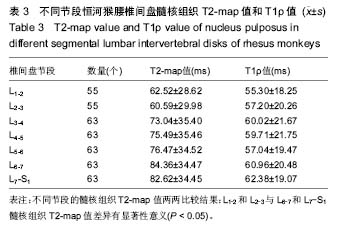
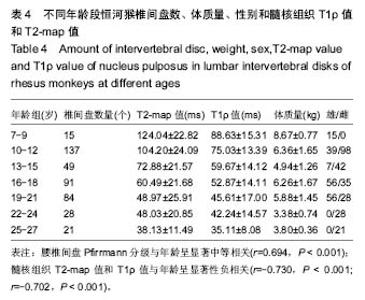
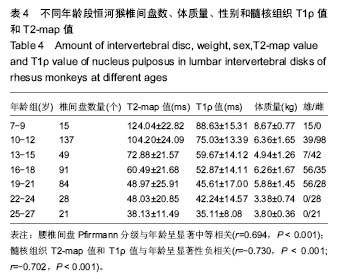
| [1] Webb AA. Potential sources of neck and back pain in clinical conditions of dogs and cats: a review. Vet J.2003;165(3): 193-213.[2] Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R, et al.Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration.Spine.2000;25(4): 487-492. [3] Lotz JC. Animal models of intervertebral disc degeneration: lessons learned. Spine.2004;29(23):2742-2750. [4] Peacock A. Observations on the prenatal development of the intervertebral disc in man. J Anat.1951;85(3):260-274.[5] Roberts S, Menage J, Duance V, et al. 1991 Volvo Award in basic sciences. Collagen types around the cells of the intervertebral disc and cartilage end plate: an immunolocalization study. Spine.1991;16(9):1030-1038. [6] Wei WJ, Zhou ZY, Guo WB, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of T2 mapping in rabbit lumbar intervertebral disc. ZhongguoZuZhiGongchengYanjiu.2013;17(35):6281-6286. [7] Takashima H,Takebayashi T, Yoshimoto M, et al.Correlation between T2 relaxation time and intervertebral disk degeneration.Skeletal Radiol.2012;41(2):163-167. [8] Hoppe S, Quirbach S, Mamisch TC, et al. Axial T2 mapping in intervertebral disc: a new technique for assessment of intervertebral disc degeneration. EurRadiol. 2012;22(9): 2013-2019.[9] Stelzeneder D, Welsch GH, Kovacs BK, et al. Quantitative T2 evaluation at 3.0T compared to morphological grading of the lumbar intervertebral disc: a standardized evaluation approach in patients with low back pain.Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81(2):324-330. [10] Blumenkrantz G, Li X, Han ET, et al. A feasibility study of in vivo T1rho imaging of the intervertebral disc.MagnReson Imaging.2006;24(8):1001-1007 [11] Johannessen W, Auerbach JD, Wheaton AJ, et al. Assessment of human disc degeneration and proteoglycan content using T1 rho-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Spine.2006;31(11):1253-1257.[12] Zobel BB, Vadala G, Del Vescovo R, et al. T1ρ magnetic resonance imaging quantification of early lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in healthy young adults. Spine.2012;37(14):1224-1230.[13] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.[14] Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumber intervertebral disk degeneration.Spine.2001;26(17):1873-1878.[15] Zhou Z,Jiang B, Zhou Z, et al. Intervertebral disk degeneration: T1ρ MR imaging of human and animal models. Radiology. 2013;268(2):492-500.[16] Duncan AE, Colman RJ, Kramer PA. Sex differencesin spinal osteoarthritis in humansand rhesus monkeys (Macacamulatta). Spine. 2012;37(11):915-922. |