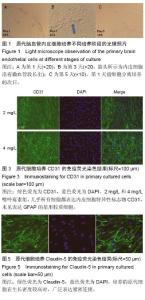
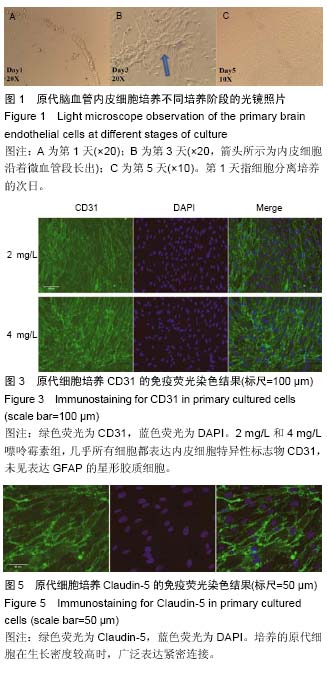
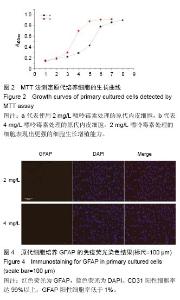
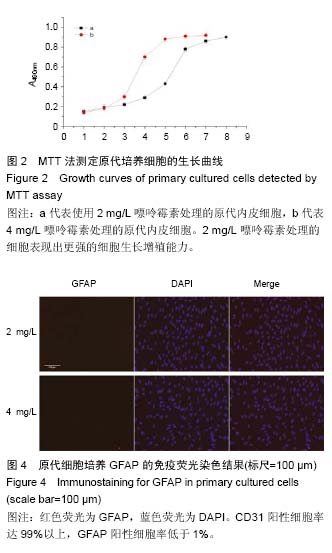
| [1] Mehrotra D,Wu J, Papangeli I, et al.Endothelium as a gatekeeper of fatty acid transport. Trends Endocrinol Metab.2014; 25(2):99-106.[2] Sonveaux P,Copetti T,De Saedeleer CJ,et al.Targeting the lactate transporter MCT1 in endothelial cells inhibits lactate-induced HIF-1 activation and tumor angiogenesis.PLoS One.2012;7(3):e33418.[3] Upadhyay RK. Transendothelial Transport and Its Role in Therapeutics. Int Sch Res Notices.2014; 2014:309404.[4] Fukuhara S,Mochizuki N. [Lymphocytes mobilization into blood regulated by Spns2, a sphingosine 1-phosphate transporter, expressed on endothelial cells]. Seikagaku.2013; 85(4):269-272.[5] Deng D, Xu C, Sun P, et al. Crystal structure of the human glucose transporter GLUT1. Nature. 2014; 510(7503):121-125.[6] Soliman A, Ayele BT ,Daayf F.Biochemical and molecular characterization of barley plastidial ADP-glucose transporter (HvBT1). PLoS One.2014; 9(6):e98524.[7] Dogrukol-Ak D, Kumar VB, Ryerse JS, et al.Isolation of peptide transport system-6 from brain endothelial cells: therapeutic effects with antisense inhibition in Alzheimer and stroke models. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2009; 29(2):411-422.[8] Lindner C, Sigruner A, Walther F, et al. ATP-binding cassette transporters in immortalised human brain microvascular endothelial cells in normal and hypoxic conditions.Exp Transl Stroke Med.2012; 4(1):9.[9] Roy U, Bulot C,Honer zu Bentrup K, et al.Specific increase in MDR1 mediated drug-efflux in human brain endothelial cells following co-exposure to HIV-1 and saquinavir. PLoS One.2013; 8(10):e75374.[10] Chiu C, Miller M C, Monahan R, et al. P-glycoprotein expression and amyloid accumulation in human aging and Alzheimer's disease: preliminary observations. Neurobiol Aging. 2015; 36(9):2475-2482.[11] Jeynes B,Provias J.P-Glycoprotein Altered Expression in Alzheimer's Disease: Regional Anatomic Variability. J Neurodegener Dis.2013;2013:257953.[12] Vogelgesang S,Cascorbi I,Schroeder E,et al. Deposition of Alzheimer's beta-amyloid is inversely correlated with P-glycoprotein expression in the brains of elderly non-demented humans. Pharmacogenetics. 2002; 12(7):535-541.[13] Deo A K, Borson S, Link J M, et al. Activity of P-Glycoprotein, a beta-Amyloid Transporter at the Blood-Brain Barrier, Is Compromised in Patients with Mild Alzheimer Disease.J Nucl Med.2014;55(7): 1106-1111.[14] Kanekiyo T, Cirrito J R, Liu CC, et al. Neuronal clearance of amyloid-beta by endocytic receptor LRP1.J Neurosci.2013; 33(49):19276-19283.[15] Deane R, Bell R D, Sagare A, et al. Clearance of amyloid-beta peptide across the blood-brain barrier: implication for therapies in Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.2009; 8(1):16-30.[16] Kanekiyo T ,Bu G. The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 and amyloid-beta clearance in Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014; 6:93.[17] Gidal BE. P-glycoprotein Expression and Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: Cause or Consequence? Epilepsy Curr.2014;14(3):136-138.[18] Robey RW, Lazarowski A,Bates SE.P-glycoprotein--a clinical target in drug-refractory epilepsy? Mol Pharmacol. 2008; 73(5):1343-1346.[19] Feldmann M, Asselin MC, Liu J, et al.P-glycoprotein expression and function in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol. 2013; 12(8):777-785.[20] Wang GX, Wang DW, Liu Y, et al. Intractable epilepsy and the P-glycoprotein hypothesis. Int J Neurosci. 2016;126(5):385-392.[21] Nakahashi T,Fujimura H,Altar CA,et al.Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett.2000; 470(2):113-117.[22] Seki T,Hosaka K,Lim S,et al.Endothelial PDGF-CC regulates angiogenesis-dependent thermogenesis in beige fat.Nat Commun.2016; 7:12152.[23] da Silva RG, Tavora B, Robinson SD, et al. Endothelial alpha3beta1-integrin represses pathological angiogenesis and sustains endothelial-VEGF.Am J Pathol.2010; 177(3):1534-1548.[24] Wang C, Qin L, Manes TD, et al. Rapamycin antagonizes TNF induction of VCAM-1 on endothelial cells by inhibiting mTORC2. J Exp Med. 2014; 211(3): 395-404.[25] Schmitz B,Vischer P,Brand E,et al.Increased monocyte adhesion by endothelial expression of VCAM-1 missense variation in vitro. Atherosclerosis.2013; 230(2):185-190.[26] Paulis LE, Jacobs I, van den Akker NM, et al. Targeting of ICAM-1 on vascular endothelium under static and shear stress conditions using a liposomal Gd-based MRI contrast agent. J Nanobiotechnology.2012; 10:25.[27] Huang H,Jing G,Wang JJ,et al.ATF4 is a novel regulator of MCP-1 in microvascular endothelial cells. J Inflamm (Lond).2015; 12:31.[28] van Beijnum JR, Rousch M, Castermans K, et al. Isolation of endothelial cells from fresh tissues. Nat Protoc.2008; 3(6):1085-1091.[29] Navone SE, Marfia G, Invernici G, et al.Isolation and expansion of human and mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells. Nat Protoc.2013; 8(9):1680-1693.[30] Perriere N, Demeuse P, Garcia E, et al. Puromycin-based purification of rat brain capillary endothelial cell cultures. Effect on the expression of blood-brain barrier-specific properties. J Neurochem. 2005; 93(2):279-289.[31] Barrand MA, Robertson KJ ,von Weikersthal SF. Comparisons of P-glycoprotein expression in isolated rat brain microvessels and in primary cultures of endothelial cells derived from microvasculature of rat brain, epididymal fat pad and from aorta. FEBS Lett. 1995;374(2):179-183. |