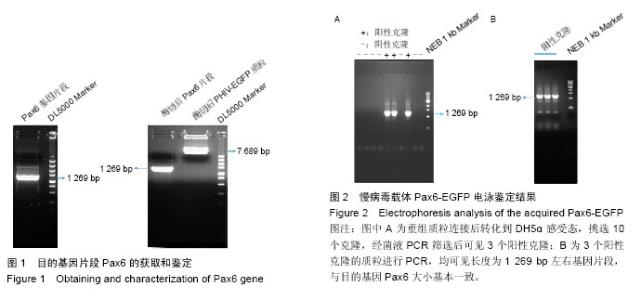
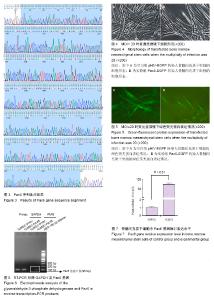
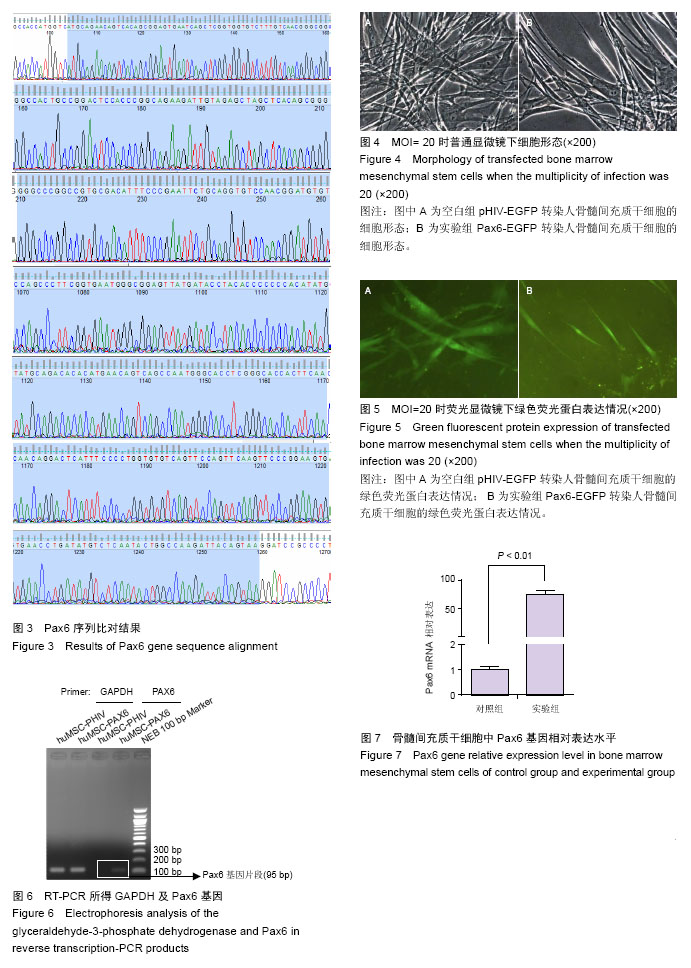
| [1] Yu-Wai-Man P. Traumatic optic neuropathy-Clinical features and management issues. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2015;5(1):3-8.
[2] Wang S, Qu X, Zhao RC.Clinical applications of mesenchymal stem cells.Bone. 2009; 44(5):828-829.
[3] 徐如霞,李静,贾亚丁.骨髓间充质干细胞在眼科疾病中应用研究进展[J].中国实用眼科杂志,2014,32(3):260-263.
[4] Tzameret A, Sher I, Belkin M, et al. Epiretinal transplantation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells rescues retinal and vision function in a rat model of retinal degeneration. Stem Cell Res. 2015; 15(2):387-394.
[5] Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, et al. Therapeutic effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on laser-induced retinal injury in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 15(6):9372-9385.
[6] 郑学栋,徐国兴,侯泽江,等.联合共培养系统诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化为视网膜色素上皮样细胞[J].中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志, 2011,13(2):88-93.
[7] Duan P, Xu H, Zeng Y, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells can differentiate to a retinal pigment epithelial phenotype when co-cultured with pig retinal pigment epithelium using a transwell system. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31(4-5):601-613.
[8] Kicic A, Shen WY, Wilson AS, et al. Differentiation of marrow stromal cells into photoreceptors in the rat eye. J Neurosci. 2003;23(21):7742-779.
[9] 孙旭芳,姜焕荣,杨红.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养及其向视网膜神经样细胞诱导分化的实验研究[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2007,17(16):1974-1976.
[10] 刘东宁,阴正勤,吴楠,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外分化为视网膜神经节样细胞的实验研究[J].眼科研究, 2007, 25(12): 900-903.
[11] 李志清,黄悦,孙慧敏.PAX6基因在眼发育中的调控作用[J].国际眼科杂志,2013,13(4):685-687.
[12] David Wan-Cheng Li.认识人类配对盒基因Pax6,一个控制眼和大脑发育的关键基因[J].中华实验眼科杂志, 2015, 33(7):577-587.
[13] Farhy C, Elgart M, Shapira Z, et al. Pax6 is required for normal cell-cycle exit and the differentiation kinetics of retinal progenitor cells. PLoS One. 2013; 8(9):e76489.
[14] Maruotti J, Wahlin K, Gorrell D, et al. A simple and scalable process for the differentiation of retinal pigment epithelium from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(5):341-354.
[15] Rowland TJ, Blaschke AJ, Buchholz DE, et al. Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells to retinal pigmented epithelium in defined conditions using purified extracellular matrix proteins. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(8):642-653.
[16] Lane A, Philip LR, Ruban L, et al. Engineering efficient retinal pigment epithelium differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014; 3(11):1295-1304.
[17] Dang Y, Zhang C, Zhu Y. Stem cell therapies for age-related macular degeneration: the past, present, and future. Clin Interv Aging. 2015;10:255-264.
[18] Li Y, Tsai YT, Hsu CW, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of human-induced pluripotent stem cell (iPS) grafts in a preclinical model of retinitis pigmentosa. Mol Med. 2012;18:1312-1319.
[19] Duan P, Xu H, Zeng Y, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells can differentiate to a retinal pigment epithelial phenotype when co-cultured with pig retinal pigment epithelium using a transwell system. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;31(4-5):601-613.
[20] Buchholz DE, Pennington BO, Croze RH, et al. Rapid and efficient directed differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into retinal pigmented epithelium. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(5):384-393.
[21] Schwartz SD, Hubschman JP, Heilwell G, et al. Embryonic stem cell trials for macular degeneration: a preliminary report. Lancet. 2012;379(9817):713-720.
[22] He Y, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. Recent advances of stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa.Int J Mol Sci. 2014; 15(8):14456-14474.
[23] Park SS, Bauer G, Abedi M, et al. Intravitreal autologous bone marrow CD34+ cell therapy for ischemic and degenerative retinal disorders: preliminary phase 1 clinical trial findings. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;56(1):81-89.
[24] Mead B, Berry M, Logan A, et al. Stem cell treatment of degenerative eye disease. Stem Cell Res. 2015; 14(3): 243-257.
[25] Pittenger MF, Mbalaviele G, Black M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells. In: Manfred RK, Bernhard OP, John RW. Hum Cell Culture. Vol V. New York: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2002: 189-207.
[26] Kondo T, Johnson SA, Yoder MC, et al. Sonic hedgehog and retinoic acid synergistically promote sensory fate specification from bone marrow-derived pluripotent stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102(13):4789-4794.
[27] 卢建民,马翔.骨髓间充质干细胞及其在眼科应用的研究进展[J].国际眼科杂志,2009,9(10):1952-1956.
[28] Myers TJ, Granero-Molto F, Longobardi L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells at the intersection of cell and gene therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(12): 1663-1679.
[29] 王月丽,魏继楼,程红蕾,等.外源基因转染细胞技术的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展, 2014, 14(7):1382-1384.
[30] de Girolamo L, Lucarelli E, Alessandri G, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a new ''cells as drugs'' paradigm. Efficacy and critical aspects in cell therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(13):2459-2473.
[31] Trapani I, Puppo A, Auricchio A.Vector platforms for gene therapy of inherited retinopathies. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2014;43:108-128.
[32] 方芳,朱平.慢病毒载体的改进为基因治疗带来了新的希望[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2013,21(5):1336-1339.
[33] Pan S, Wan J, Liu S, et al. Lentivirus carrying the Atoh1 gene infects normal rat cochlea. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(17):1551-1559.
[34] Kayama M, Kurokawa MS, Ueda Y, et al. Transfection with pax6 gene of mouse embryonic stem cells and subsequent cell cloning induced retinal neuron progenitors, including retinal ganglion cell-like cells, in vitro. Ophthalmic Res. 2010;43(2):79-91. |