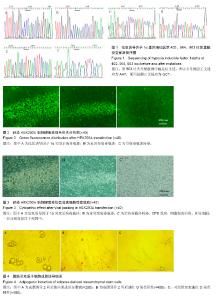
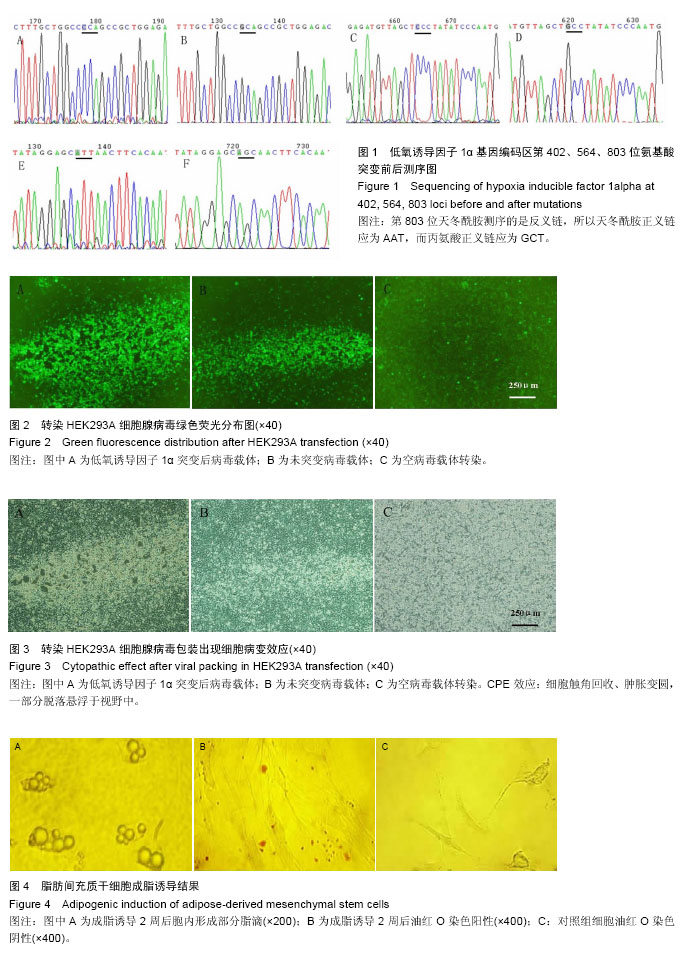
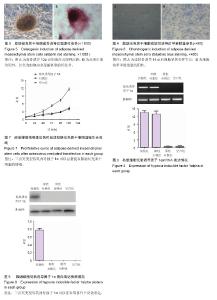
| [1] Lin CY, Chang YH, Sung LY, Long-term tracking of segmental bone healing mediated by genetically engineered adipose-derived stem cells: focuses on bone remodeling and potential side effects. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(9-10): 1392-1402.
[2] Kim H,Choi K,Kweon OK,et al.Enhanced wound healing effect of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with low-level laser therapy in athymic mice. J Dermatol Sci.2012;68(3): 149-156.
[3] Ni X, Sun W, Sun S, et al. Therapeutic potential of adipose stem cells in tissue repair of irradiated skeletal muscle in a rabbit model. Cell Reprogram. 2014;16(2): 140-150.
[4] Zografou A,Tsigris C,Papadopoulos O,et al. Improvement of skin-graft survival after autologous transplantation of adipose-derived stem cells in rats.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.2011;64(12): 1647-1656.
[5] Verseijden F,Posthumus-van Sluijs SJ,van Neck JW, et al. Comparing scaffold-free and fibrin-based adipose-derived stromal cell constructs for adipose tissue engineering: an in vitro and in vivo study.Cell Transplant.2012;21(10): 2283-2297.
[6] Yuan Y,Gao J,Liu L,et al.Role of adipose-derived stem cells in enhancing angiogenesis early after aspirated fat transplantation: induction or differentiation? Cell Biol Int.2013;37(6): 547-550.
[7] Uysal CA,Tobita M,Hyakusoku H,et al.The Effect of Bone-Marrow-Derived Stem Cells and Adipose-Derived Stem Cells on Wound Contraction and Epithelization. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2014;3(6): 405-413.
[8] Strassburg S, Nienhueser H,Stark GB,et al.Human adipose-derived stem cells enhance the angiogenic potential of endothelial progenitor cells, but not of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Tissue Eng Part A.2013;19(1-2): 166-174.
[9] Zhou Y,Sun M,Li H,et al.Recovery of behavioral symptoms in hemi-parkinsonian rhesus monkeys through combined gene and stem cell therapy. Cytotherapy.2013;15(4): 467-480.
[10] Yan A,Avraham T,Zampell JC,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells promote lymphangiogenesis in response to VEGF-C stimulation or TGF-β1 inhibition. Future Oncol. 2011;7(12): 1457-1473.
[11] Semenza GL . Evaluation of HIF-1 inhibitors as anticancer agents. Drug Discov Today.2007;12(19-20): 853-859.
[12] Fiorenzo P,Mongiardi MP,Dimitri D,et al.HIF1-positive and HIF1-negative glioblastoma cells compete in vitro but cooperate in tumor growth in vivo.Int J Oncol. 2010; 36(4): 785-791.
[13] Lando D,Peet DJ,Whelan DA,et al.Asparagine hydroxylation of the HIF transactivation domain a hypoxic switch.Science.2002;295(5556): 858-861.
[14] Yu F,Ji S,Su L, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit activation of hepatic stellate cells in vitro and ameliorate rat liver fibrosis in vivo. J Formos Med Assoc.2015;114(2): 130-138.
[15] Joo HH,Jo HJ,Jung TD,et al.Adipose-derived stem cells on the healing of ischemic colitis: a therapeutic effect by angiogenesis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2012; 27(11): 1437-1443.
[16] Zuk PA.Viral transduction of adipose-derived stem cells. Methods Mol Biol.2011; 702: 345-357.
[17] 赵坤, 梁杰, 彭智.提高自体颗粒脂肪移植成功率的基础研究及临床进展[J].中国实用医药. 2010, 5(5): 238-240.
[18] Bahn JJ,Chung JY,Im W,et al.Suitability of autologous serum for expanding rabbit adipose-derived stem cell populations.J Vet Sci.2012;13(4): 413-417.
[19] Lu CH,Chang YH,Lin SY,et al.Recent progresses in gene delivery-based bone tissue engineering. Biotechnol Adv.2013;31(8): 1695-1706.
[20] Giaccia A,Siim BG,Johnson RS.HIF-1 as a target for drug development.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(10): 803-811.
[21] Lim W, Cho J, Kwon HY, et al.Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha activates and is inhibited by unoccupied estrogen receptor beta. FEBS Lett.2009;583(8): 1314- 1318.
[22] Giatromanolaki A,Fiska A,Pitsiava D,et al. Erythropoietin receptors in endometrial carcinoma as related to HIF1{alpha} and VEGF expression. In Vivo. 2009; 23(5): 699-703.
[23] Simon F,Bockhorn M,Praha C,et al.Deregulation of HIF1-alpha and hypoxia- regulated pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma and corresponding non-malignant liver tissue--influence of a modulated host stroma on the prognosis of HCC. Langenbecks Arch Surg.2010;395(4): 395-405.
[24] Wan C,Gilbert SR,Wang Y,et al.Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1-alpha pathway accelerates. Proc Nat Acad Sci.2008;105(2): 686-691.
[25] Evans CE,Humphries J,Mattock K,et al.Hypoxia and upregulation of hypoxia- inducible factor 1{alpha} stimulate venous thrombus recanalization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2010, 30(12): 2443-2451. |