Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (15): 2248-2254.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.15.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of sarcopenia and exercise training on muscle satellite cells: current status and prospects
Yu Qun1, Weng Xi-quan2, Wang Li-ping1
- 1Anshun University, Anshun 561000, Guizhou Province, China; 2Key Physical Biochemistry Teaching Laboratory, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou 510075, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2016-01-16Online:2016-04-08Published:2016-04-08 -
About author:Yu Qun, Master, Associate professor, Anshun University, Anshun 561000, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Foundation for Distinguished Talents in Higher Education of Guizhou, China, No. KY-2013-149
Cite this article
Yu Qun, Weng Xi-quan, Wang Li-ping. Effects of sarcopenia and exercise training on muscle satellite cells: current status and prospects[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(15): 2248-2254.
share this article
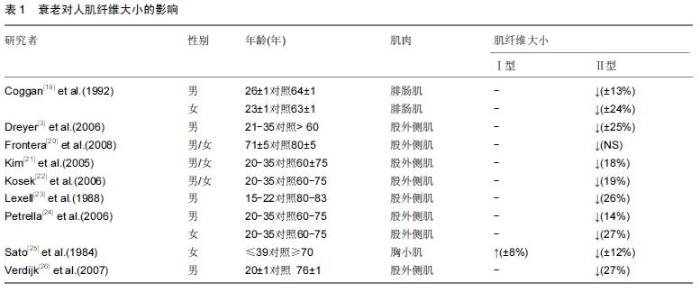
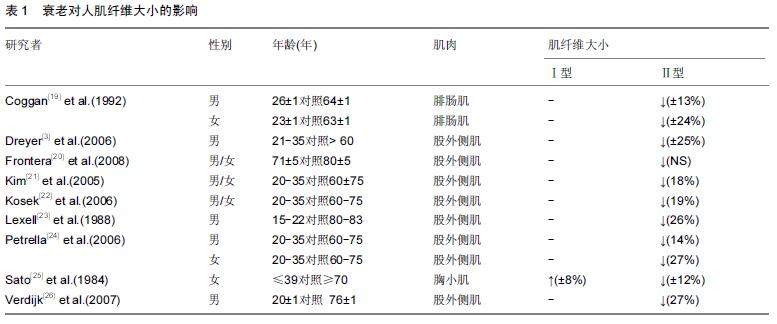
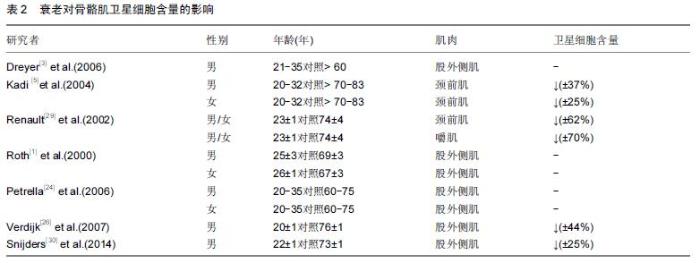
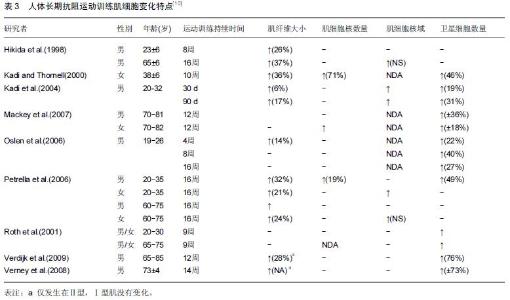
| [1] Roth SM, Martel GF, Ivey FM, et al. Skeletal muscle satellite cell populations in healthy young and older men and women. Anat Rec.2000;260:351-358. [2] Porter MM, Vandervoort AA, Lexell J. Aging of human muscle: structure, function and adaptability. Scand J Med Sci Sports.1995;5:129-142. [3] Dreyer HC, Blanco CE, Sattler FR, et al. Satellite cell numbers in young and older men 24 hours after eccentric exercise. Muscle Nerve.2006;33:242-253. [4] Hawke TJ, Garry DJ. Myogenic satellite cells: physiology to molecular biology. J Appl Physiol.2001;91:534-551. [5] Kadi F, Charifi N, Denis C, et al.Satellite cells and myonuclei in young and elderly women and men. Muscle Nerve.2004;29:120-127. [6] Martel GF, Roth SM, Ivey FM,et al.Age and sex affect human muscle fibre adaptations to heavy-resistance strength training. Exp. Physiol.2006;91:457-464. [7] Paulsen G, Mikkelsen UR, Raastad T, et al.Leucocytes, cytokines and satellite cells: what role do they play in muscle damage and regeneration following eccentric exercise? Exerc Immunol Rev. 2012;18:42-97. [8] Mu X, Urso ML, Murray K, et al. Relaxin regulates MMP expression and promotes satellite cell mobilization during muscle healing in both young and aged mice. Am J Pathol.2010;177:2399-410. [9] Wada KI, Takahashi H, Katsuta S, et al. No decrease in myonuclear number after long-term denervation in mature mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2002;283: C484-C488. [10] Kadi F, Charifi N, Denis C, et al. The behaviour of satellite cells in response to exercise: what have welearned from human studies? Pflugers Arch. 2005; 451(2):319-327. [11] Petrella JK, Kim JS, Mayhew DL,et al.Potent myofiber hypertrophy during resistance training in humans is associated with satellite cell-mediated myonuclear addition: a cluster analysis. J Appl Physiol.2008;104: 1736-1742. [12] Marzetti E,Calvani R,DuPree J,et al.Late-life enalapril administration induces nitric oxide-dependent and independent metabolic adaptations in the rat skeletal muscle.Age (Dordrecht, Netherlands).2013;35: 1061-1075. [13] Crameri RM,Langberg H, Magnusson P, et al. Changes in satellite cells in human skeletal muscle after a single bout of high intensity exercise.J Physiol. 2004;558(Pt 1):333-340. [14] Anderson JE.A role for nitric oxide in muscle repair: nitric oxide-mediated activation of muscle satellite cells.Mol Biol Cell.2000;11:1859-1874. [15] Pisconti A, Brunelli S, Di Padova M, et al. Follistatin induction by nitric oxide through cyclic GMP: a tightly regulated signaling pathway that controls myoblast fusion. J Cell Biol.2006;172:233-244. [16] Amthor H, Macharia R, Navarrete R,et al. Lack of myostatin results in excessive muscle growth but impaired force generation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 2007;104: 1835-1840. [17] Hawke TJ. Muscle stem cells and exercise training. Exerc Sport Sci Rev.2005; 33, 63-68. [18] Lovering RM, Brooks SV. Eccentric exercise in aging and diseased skeletal muscle: good or bad? J Appl Physiol.2014;116:1439-1445. [19] Coggan AR, Spina RJ, King DS, et al. Histochemical and enzymatic comparison of the gastrocnemius muscle of young and elderly men and women. J Gerontol. 1992; 47:B71-76. [20] Frontera WR, Reid KF, Phillips EM, et al. Muscle fiber size and function in elderly humans: a longitudinal study. J Appl Physiol. 2008;105:637-642. [21] Kim JS, Cross JM,Bamman MM.Impact of resistance loading on myostatin expression and cell cycle regulation in young and older men and women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol. Metab. 2005;288:E1110-1119. [22] Kosek DJ, Kim JS, Petrella JK, et al. Efficacy of 3 days/wk resistance training on myofiber hypertrophy and myogenic mechanisms in young vs. older adults. J Appl Physiol.2006; 101, 531-544. [23] Lexell J, Taylor CC, Sjostrom M. What is the cause of the ageing atrophy? Total number, size and proportion of different fiber types studied in whole vastus lateralis muscle from 15- to 83-year-old men. J Neurol Sci. 1988; 84:275-294. [24] Petrella JK, Kim JS, Cross JM,et al. Efficacy of myonuclear addition may explain differential myofiber growth among resistance-trained young and older men and women. Am J Physiol. Endocrinol Metab. 2006; 291:E937-E946. [25] Sato T, Akatsuka H, Kito K, et al. Age changes in size and number of muscle fibers in human minor pectoral muscle. Mech Ageing Dev.1984;28:99-109. [26] Verdijk LB,Koopman R, Schaart G,et al. Satellite cell content is specifically reduced in type II skeletal muscle fibers in the elderly. Am J Physiol Endocrinol. Metab.2007;292:E151-157. [27] Kararizou E, Manta P, Kalfakis N, et al.Age-related morphometric characteristics of human skeletal muscle in male subjects.J Pathol.2009;60:186-188. [28] Nagata Y,Partridge TA,Matsuda R,et al.Entry of muscle satellite cells into the cell cycle requires sphingolipid signaling.J Cell Biol.2006;174:245-253. [29] Renault V, Thornell LE, Eriksson PO,et al. Regenerative potential of human skeletal muscle during aging. Aging Cell.2002;1:132-139. [30] Snijders T, Verdijk LB, Smeets JS, et al.The skeletal muscle satellite cell response to a single bout of resistance-type exercise is delayed with aging in men.Age (Dordr).2014;4: 9693-9699. [31] Dedkov EI, Borisov AB, Wernig A,et al.Aging of skeletal muscle does not affect the response of satellite cells to denervation.J Histochem Cytochem. 2003;51:853-863. [32] Verney J,Kadi F,Charifi N,et al.Effects of combined lower body endurance and upper body resistance training on the satellite cell pool in elderly subjects. MuscleNerve.2008;38:1147-1154. [33] Conboy IM,Conboy MJ,Smythe GM,et al. Notch-mediated restoration of regenerative potential to aged muscle. Science.2003;302;1575-1577. [34] Delgado-Diaz DC, Gordon BS, Dompier T.Therapeutic ultrasound affects IGF-1 splice variant expression in human skeletal muscle.Am J Sports Med.2011; 39: 2233-2241. [35] Nofziger D, Miyamoto A, Lyons KM, et al. Notch signaling imposes two distinct blocks in the differentiation of C2C12 myoblasts. Development. 1999;126:1689–1702. [36] Carey KA, Farnfield MM, Tarquinio SD, et al.Impaired expression of Notch signaling genes in aged human skeletal muscle. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.2007; 62:9-17. [37] Toth MJ, Miller MS, VanBuren P. Resistance training alters skeletal muscle structure and function in human heart failure: effects at the tissue, cellular and molecular levels. J Physiol.2012;590:1243-59. [38] Bunprajun T,Yimlamai T,Soodvilai S.Stevioside enhances satellite cell activation by inhibiting of NF-κB signaling pathway in regenerating muscle after cardiotoxin-induced injury. J Agric Food Chem.2012; 60:2844-2851. [39] Appell HJ, Forsberg S, Hollmann W. Satellite cell activation in human skeletal muscle after training: evidence for muscle fiber neoformation. Int J Sports Med. 1988;9:297-299. |
| [1] | Zhang Yuantong. Body composition and bone mineral density of juvenile basketball players versus ordinary middle school students: data from a middle school [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 341-347. |
| [2] | Lan Qingshi. Participation degree and control ability of human latissimus dorsi, trapezius, triceps, musculus and deltoid during cross support of hand ring: analysis on contribution rate of major muscle group [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(3): 361-366. |
| [3] | Kong Lingyao, Li Tao, Zeng Xinglin, Li Jian, Xiong Yan. Synovial chondromatosis: how to improve the diagnosis accuracy and clearance rate of tumor cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4570-4575. |
| [4] | Yu Hong, Liu Yan. Strength of knee flexor and extensor in football athletes after vibration training [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2327-2331. |
| [5] | Zhu Yaojia1, Huo Hongfeng1, 2. Balance ability and foot type characteristics during different postures of standing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2345-2349. |
| [6] | Li Xintong1, Pan Weimin2, Qin Huasheng1, Qu Lei1, Zhang Hengyin1, Zhu Xinrui1. Blood flow restriction training: a new method for accelerating musculoskeletal rehabilitation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2415-2420. |
| [7] | Wang Minjia1, Qi Ziyi2, Zhu Weihua1, Sun Junzhi1. Mechanism and clinical research advance of muscle atrophy: thinking based on the 65th Annual Meeting of American College of Sports Medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(15): 2421-2426. |
| [8] | Yuan Yiwen, Gui Zhu, Zhang Hongchao. Changes in muscle injury and pulse wave velocity after exercise with compression leg cuffs in college students without fitness habits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(11): 1687-1692. |
| [9] | Xie Hao-dong1, 2, Luo Jiong1, 2. Stiffness of the lower extremities during landing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(8): 1306-1312. |
| [10] | Wang Zhao-feng1, Gong Ming-ming2, Chen Jia-qun2, Mo Wei-bin3. Effects of Glycyrrhiza Flavone on the pathological changes of quadriceps and expression of fatty acid translocase/CD36 in training rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 529-534. |
| [11] | Ma Tao, Li Jian, Jin Jia-peng . Effects of different sports events on bone mineral density in the recent decade: a bibliometric analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(4): 631-634. |
| [12] | Lei Bingkai1, 2, Sun Junzhi1, Zhao Xiaoqin3, Ding Haili1, Liu Yong2, Wang Ruiyuan2, Li Junping2. Role of Omi/Beclin-1 signaling pathway in the eccentric exercise-induced skeletal muscle autophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5791-5796. |
| [13] | Wang Dandan, Zhang Lei, Wu Xueping . Physical activity of people with intellectual disability measured by motion sensor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(36): 5889-5896. |
| [14] | Chen Zhen-yong. Correlation of bone mineral density with sports ability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4452-4456. |
| [15] | Li Lin, Yu Liang. Biological role of myonectin and its correlation with exercise [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(28): 4566-4573. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||