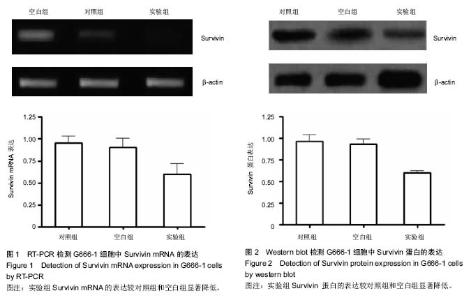
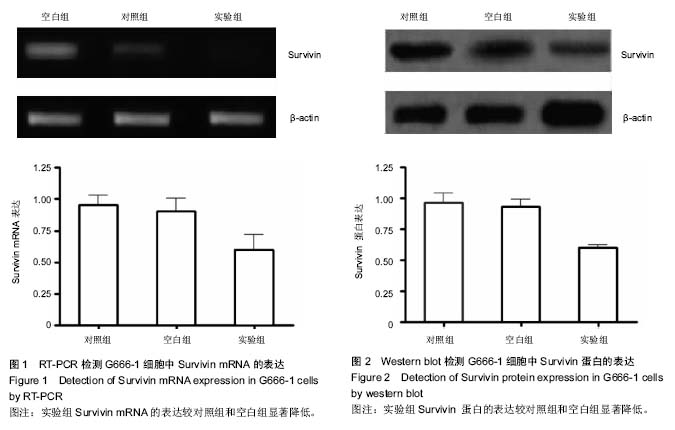
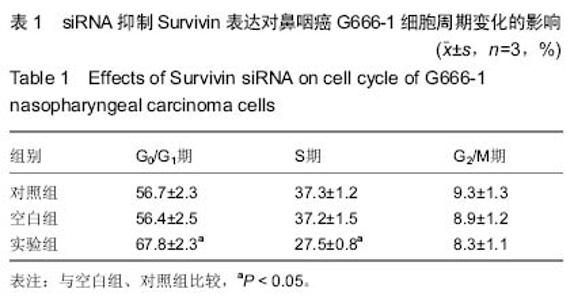
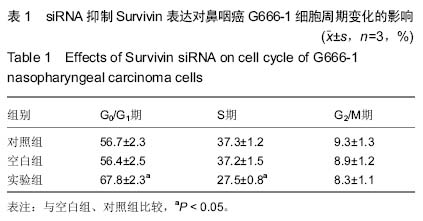
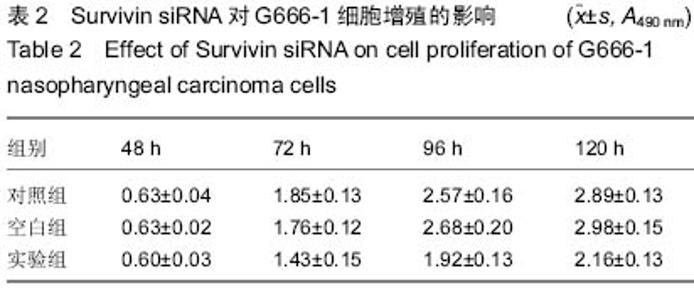
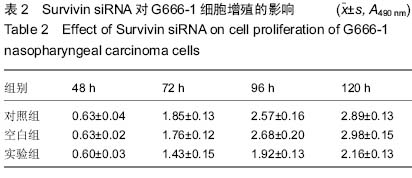
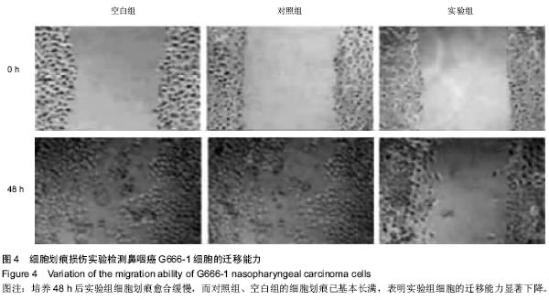
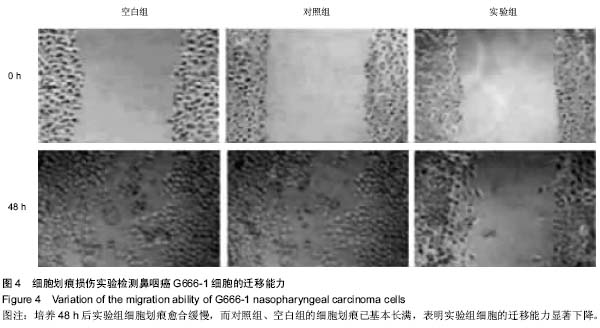
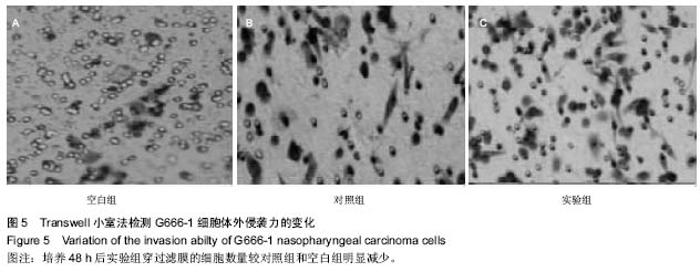
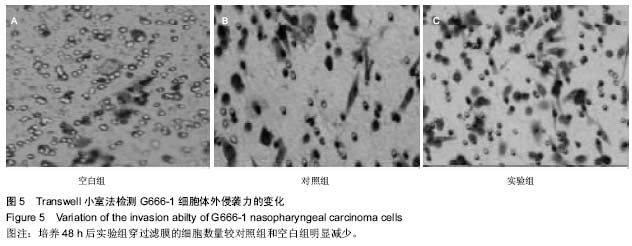
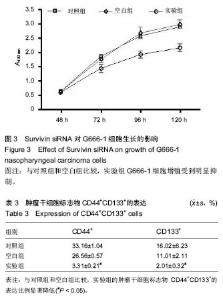
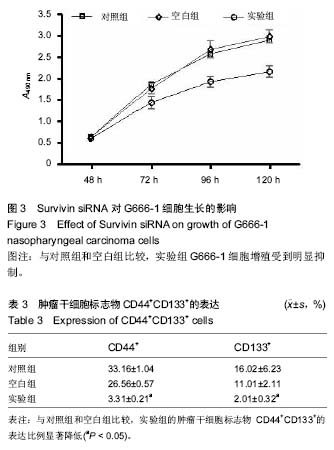
| [1] 尤茜,杨玉成.鼻咽癌肿瘤干细胞的分离筛选及与癌基因相关性的研究进展[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2013,48(3): 254- 257.
[2] 屈永涛,李晓明,徐鸥,等.低氧对Hep-2细胞肿瘤干细胞特性和化疗抵抗的影响及其作用机制[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012,47(3):228-233.
[3] 梁中敏,姚岐,刘维奇,等.鼻咽癌组织中血管内皮生长因子和生存素的表达[J].中国基层医药,2010,17(11):1480-1482.
[4] 张明生,刘萍萍,朱宇,等.肿瘤干细胞在人骨肉瘤细胞株MG63耐顺铂效应中的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2014,31(4):828-831.
[5] 易斌,周欢群,姚润,等.鼻咽癌患者四种血清自身抗体诊断价值的研究[J]. 中华检验医学杂志,2010,33(8):747-751.
[6] 叶明,周岱,周幽心,等.siRNA对人脑胶质瘤细胞Survivin基因表达的影响[J].中华神经外科杂志,2011,27(2):144-147.
[7] 李龄,王安宇,朱小东,等.以CT和MRI颅底骨成像计算鼻咽癌肿瘤靶体积及邻近危及器官照射剂量的对比研究[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2008,28(5):520-522.
[8] 符生苗,王宇田,涂志华,等.Survivin基因mRNA和蛋白在鼻咽癌中的表达[J].中华医学遗传学杂志,2008,25(2):179-182
[9] 李明武,牛朝诗.脑肿瘤干细胞的分布与肿瘤微血管的相关性[J].中华医学杂志,2010,90(5):305-309.
[10] 雷旦生,喻晶,童先丽,等.细胞角蛋白片段19-2G2对鼻咽癌的辅助诊断价值[J].中华病理学杂志,2012,41(7):461-465.
[11] 金亦,邵春奎,唐录英,等.肝细胞癌中Survivin与NF-кB蛋白的表达及其临床意义[J].中华医学杂志,2011,91(36):2542-2545.
[12] 宋英,董明敏,杨海峰,等.RNA同时干扰四个不同基因对鼻咽癌细胞CNE-2Z生长增殖的实验研究[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2010,45(9):751-758.
[13] 吴银艳,黄强,董军,等.原发和复发脑肿瘤干细胞的生物学特征观察[J].中华神经外科杂志,2009,25(8):750-752.
[14] 韩广荣,何丽霞.以复视首诊眼科的鼻咽癌五例分析[J].中国实用眼科杂志, 2007,25(5):491.
[15] 林驰,郑万泉.鼻咽癌放射性脑病16例诊治体会[J].中华神经医学杂志,2010,9(7):736-739.
[16] 李文臣,葛鹏飞,罗毅男. 脑肿瘤干细胞与脑肿瘤耐药[J].中华神经医学杂志,2009,8(1):106-108.
[17] 齐卫卫,胡国清.Survivin蛋白在鼻咽癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志,2004,39(12):759-760.
[18] 高远,阮柏,张卓超,等.CD44:由表及里的肿瘤干细胞标志物[J].国际外科学杂志,2014,41(2):119-122.
[19] 齐瑶,李润美,任秀宝.肿瘤干细胞免疫逃逸机制的研究进展[J].国际免疫学杂志,2011,34(4):270-273.
[20] 姜武忠,卢景琛,文继舫,等.鼻咽癌组织中nm23-H1和survivin蛋白表达及其临床意义[J].中华放射肿瘤学杂志,2005,14(5): 383-387.
[21] 贾茹,孙青.肿瘤干细胞在肿瘤转移过程中的作用[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2012,39(1):22-24.
[22] 吕元景,苗素生,刘伟松,等.重组survivin腺病毒的构建与鉴定[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2011,33(1):13-17.
[23] 朱小东,苏芳,曲颂,等.鼻咽癌放疗前后血清蛋白质谱的变异性研究[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2010,30(4):391-394.
[24] 张璐璐,张月英,张维东.自噬与肿瘤干细胞的研究进展[J].国际肿瘤学杂志,2014,41(4):248-251.
[25] 邹继彬,黄广恩,陈中坚,等.Survivin蛋白和PCNA在鼻咽癌中的表达及其临床意义[J].中国医师杂志,2004,6(12):1636-1638.
[26] 沈汉斌,吴耀辉,龙浩成,等.pEGFP-survivin对GBC-SD细胞生长的抑制及对化疗敏感性的影响[J].中华肝胆外科杂志,2010, 16(1):43-47.
[27] 宁宁,李荣,徐迎新,等.靶向结肠癌肿瘤干细胞的结肠癌治疗研究进展[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(11):2472-2473.
[28] 赵琳,孙克康,申琳棱,等.表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯对人鼻咽癌CNE-1细胞辐射敏感性的影响[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志, 2012,32(3):236-240.
[29] 陈平,唐安洲,张哲,等.鼻咽癌放疗后突发感音神经性聋14例临床分析[J].中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2011,46(9):705-708.
[30] 林炜明,曹毅.细胞表面糖链与肿瘤干细胞[J].中华病理学杂志, 2013,42(9):641-643.
[31] 黄亮,陈志坚,余剑书,等.Survivin和富含亮氨酸重复序列免疫球蛋白2在人膀胱移行细胞癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(8):1595-1597. |