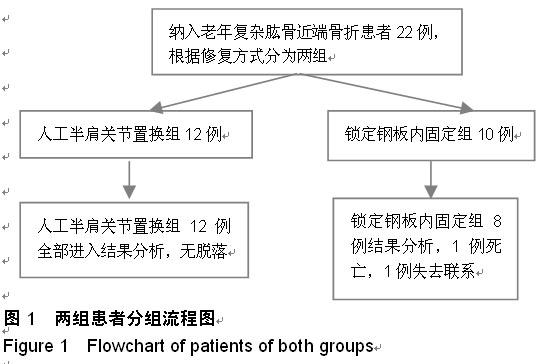
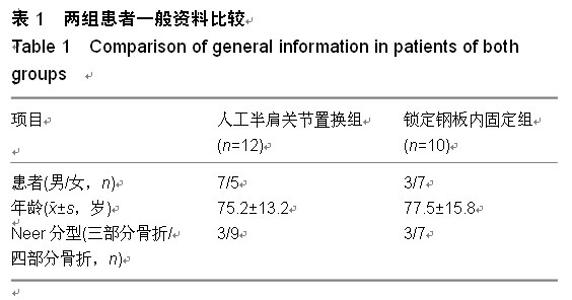
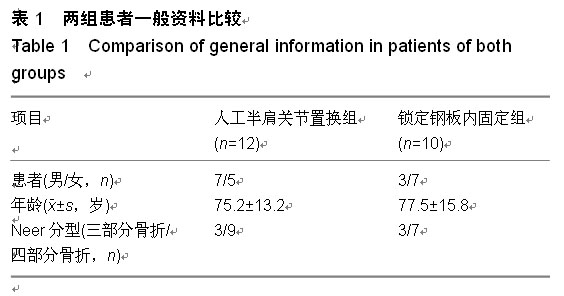
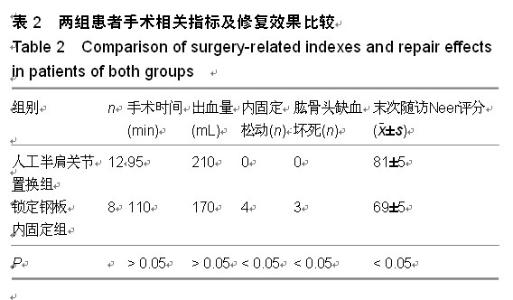
| [1] Marie C. Strength analysis of clavicle fracture fixation devices and fixation techniques using finite element analysis with musculoskeletal force input. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2015.
[2] Mansat P, Bonnevialle N. Treatment of fracture sequelae of the proximal humerus: anatomical vs reverse shoulder prosthesis. Int Orthop. 2015;39(2): 349-354.
[3] Jiang DM, Su B. [Present status and choice of treatment for proximal humeral fractures]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014; 27(12): 975-979.
[4] Maier MW, Zeifang F, Caspers M, et al. Can reverse shoulder arthroplasty in post-traumatic revision surgery restore the ability to perform activities of daily living? Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015; 101(2): 191-196.
[5] Rangan A, Handoll H, Brealey S, et al. Surgical vs nonsurgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus: the PROFHER randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2015;313(10): 1037-1047.
[6] Okike K, Lee OC, Makanji H, et al. Comparison of locked plate fixation and nonoperative management for displaced proximal humerus fractures in elderly patients. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015;44(4): E106-112.
[7] Kumar GN, Sharma G, Sharma V, et al. Surgical treatment of proximal humerus fractures using PHILOS plate. Chin J Traumatol. 2014;17(5): 279-284.
[8] Bandalovi? A, Cukelj F, Kne?evi? J, et al. The Results of Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Osteoporotic Fractures with PHILOS Locking Plate. Psychiatr Danub. 2014;26 Suppl 2:376-381.
[9] Erasmo R, Guerra G, Guerra L. Fractures and fracture-dislocations of the proximal humerus: A retrospective analysis of 82 cases treated with the Philos((R)) locking plate. Injury. 2014;45 Suppl 6: S43-48.
[10] Pearson T, Glyde M, Hosgood G, et al. The effect of intramedullary pin size and monocortical screw configuration on locking compression plate-rod constructs in an in vitro fracture gap model. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2015;28(2): 95-103.
[11] Li Q, Zhao WB, Tu CQ, et al. [Locking compression plate (LCP) combined with minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO) for the treatment of Pilon fracture]. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(12): 1029-1032.
[12] Ferguson PC. CORR Insights((R)): Synthetic Mesh Improves Shoulder Function After Intraarticular Resection and Prosthetic Replacement of Proximal Humerus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(5): 1735-1736.
[13] Mehlhorn AT, Schmal H, Sudkamp NP, et al. Clinical evaluation of a new custom offset shoulder prosthesis for treatment of complex fractures of the proximal humerus. Acta Orthop Belg. 2006;72(4): 387-394.
[14] Castricini R, De Benedetto M, Pirani P, et al. Shoulder hemiarthroplasty for fractures of the proximal humerus. Musculoskelet Surg. 2011;95 Suppl 1: S49-54.
[15] Van Tongel A, Piepers I, De Wilde L. The significance of the clavicle on shoulder girdle function. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015.
[16] Booker S, Alfahad N, Scott M, et al. Use of scoring systems for assessing and reporting the outcome results from shoulder surgery and arthroplasty. World J Orthop. 2015; 6(2):244-251.
[17] Bastian JD, Hertel R. Osteosynthesis and hemiarthroplasty of fractures of the proximal humerus: outcomes in a consecutive case series. J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2009;18(2): 216-219.
[18] Beaudreuil J, Ostertag A, Lasbleiz S, et al. Efficacy of dynamic humeral centering according to Neer test results: a stratified analysis of a randomized-controlled trial. Int J Rehabil Res. 2015;38(1):81-83.
[19] Zhang NJ, Jiang L, Zhou ZB, et al.Case-control study on locking plates fixation for the treatment of Neer 3-and 4-part proximal humerus fractures. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2014;27(1): 38-40.
[20] 刘长路,刘晓民,黄健,等.半肩关节置换治疗复杂肱骨骨折近端骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,52(17):8987-8992.
[21] 陈鹏,田晓滨,胡如印.肱骨近端锁定钢板内固定与人工半肩关节置换治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折63例疗效分析[J].实用医学杂志, 2014,8(30):1296-1298.
[22] 邓磊,白露,张培训,等.213例肤骨近端骨折的Neer分型[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(4):121.
[23] 王亦璁.骨与关节损伤[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:763-767.
[24] 黄强,王满宜,荣国威.复杂肱骨近端骨折的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,3(25):159-164.
[25] 刘长路,刘晓民,黄健,等.半肩关节置换治疗复杂肱骨骨折近端骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,52(17):8987-8992.
[26] 鲁宁,Edward VC.人工肩关节表面置换术的应用[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2010,4(5):70-73.
[27] 陈鹏,田晓滨,胡如印. 肱骨近端锁定钢板内固定与人工半肩关节置换治疗复杂肱骨近端骨折63例疗效分析[J].实用医学杂志, 2014,8(30):1296-1298. |