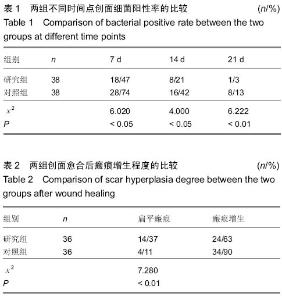
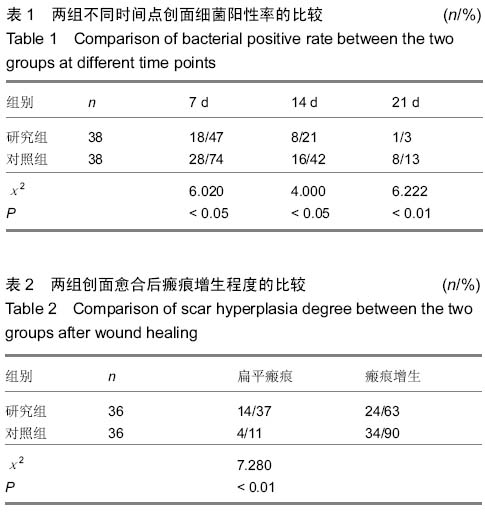
| [1] 滕建英,任园园,徐少骏,等.血竭负载人工真皮支架对猪III度烧伤创面修复中VEGF表达及创面收缩的影响[J].健康研究,2013, 33(6):415-417.
[2] 王世岭,邓诗琳,马建丽,等.不同剂型重组人表皮生长因子对烧伤创面促愈合作用比较[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2011,12(9): 12-14.
[3] 杨景哲,陈凤平,冯欣姝,等. rhGM-CSF、纳米银外用对深Ⅱ°烫伤创面愈合的影响研究[J]. 南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2015, 2(2):56-59.
[4] 陈曦,李峰.重组人生长激素在严重烧伤治疗中的应用[J].健康研究,2010,30(2):101-103.
[5] 段辉辉,杨壮群,白转丽,等.重组人表皮生长因子凝胶联合复方多粘菌素B软膏治疗皮肤创面的疗效观察[J].中国美容医学,2014, 21(12):18-19.
[6] 李晓燕,马国安,丁红炜. 蓝科肤宁联合重组人表皮生长因子治疗激素依赖性皮炎疗效观察[J].现代仪器与医疗,2014, 20(1): 63-65.
[7] Kumari M,Mukherjee A,Chandrasekaran N.Genotoxicity of silvernanoparticles in Allium cepa.Sci Total Environ. 2009; 407(19):5243-5246.
[8] 谢云民,陈梅华,季英,等.重组人表皮生长因子凝胶联合中药坐浴促进肛瘘术后创面愈合疗效观察[J].新中医,2013,11(6): 64-66.
[9] 朱东来,武凤莲,王连英,等.重组人酸性成纤维细胞生长因子与纳米银敷料联合治疗深II度烧伤创面的临床观察[J].中国美容医学, 2013,22(18):1840-1843.
[10] Asha Rani PV,Low Kah Mun G,Hande MP,et al. Gytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. Acs Nano.2009;3(2):279-290.
[11] 晏鹰,黄国雨,王宏伟,等.爱康肤银离子敷料联合重组人表皮生长因子凝胶治疗深II度烧伤残余创面临床疗效观察[J].中国医药导报,2012,9(24):35-38.
[12] 李传禹,靳江波,宋恩,等.重组人表皮生长因子在骨科I类手术切口中的临床应用效果研究[J].当代医药论丛,2014,12(3): 96-99.
[13] Esteban-Tejeda L,Malpartida F,Esteban-Cubillo A,et al. The antibacterial and antifungal activity of a soda-lime glass containing silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology. 2009; 20(8): 85-103.
[14] 陈丽.微晶磨削术联合外用重组人表皮生长因子修复皮肤瘢痕105例疗效观察[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2012,26(4):357-359.
[15] 郭春兰,田玉凤.高锰酸钾溶液联合重组人表皮生长因子凝胶治疗糖尿病足感染性溃疡的疗效[J].中华医院感染学杂志,2011, 21(23):4961-4963.
[16] 何洪彬.重组人表皮生长因子与纳米银敷料联合治疗局部冻伤创面临床观察[J].河北医药,2010,32(18):2556-2558.
[17] Ryu SH,Kang KM,Moon SY,et al.Therapeutic effects of recombinant human epi-dermal growth factor (rhEGF) in a murine model of concur-rentchemo-and radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis.J Radiat Res.2010;51(5):643-645.
[18] Kumari M,Mukherjee A,Chandrasekaran N.Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa.Sci Total Environ.2009; 407(19):5243-5246.
[19] 程景武.重组人表皮生长因子软膏对烧伤创面修复的促进效果观察[J].吉林医学,2014,35(31):6933-6935.
[20] 胡安根.几种生物敷料在临床烧伤中的应用评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(25):4955-4957.
[21] Fumei Z.Moderate senile dementia patients in rehabilitation nursing model on. Contem porary Med.2012;6(142): 105-111.
[22] Akgül EA,Karakaya J,Ayd?n S.Role of comorbidities as limiting factors to the effect of hyperbaric oxygen in diabetic foot patients: a retrospective analysis.Diabetes Ther. 2014; 5(2):535-544.
[23] Doggen K,Van Acker K,Beele H,et al.Implementation of a quality improvement initiative in Belgian diabetic foot clinics: feasibility and initial results.Diabetes Metab Res Rev.2014; 30(5):137-142.
[24] Jacobs E.Mycoplasma pneumoniae: now in the focus of clinicians and epidemiologists.Euro Surveill.2012;17(6):1-3.
[25] 张亮,郭金龙,朱承亮,等. rb-bFGF联合纳米银敷料在小儿非功能部位深II度烧伤创面临床研究[J].青岛医药卫生,2014,46(6): 37-38.
[26] 刘朋飞.重组人表皮生长因子联合磺胺嘧啶锌凝胶治疗深Ⅱ度烧伤创面的临床疗效观察[D].泸州医学院,2014.
[27] 张德清,司民真,刘仁明,等.基于宽表面等离子体吸收带纳米银膜的制备及其SERS活性研究[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2012,32 (9):2438-2441.
[28] Kawai Y,Miyashita N,Kubo M,et al.Therapeutic efficacy of macrolides, minocycline, and tosufloxacin against macrolide-resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in pediatric pa- tients .Antimicrob Agents Chemother.2013;57(5): 2252-2258.
[29] Kang YP,Si MZ,Zhu YQ,et al.Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) spectra of hemoglobin of mouse and rabbit with self-assembled nano-silver film. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2013;108(22):177-180.
[30] Cheng L,Zhang K,Weir MD,et al.Effects of antibacterial primers with quaternary ammonium and nano-silver on Streptococcus mutans impregnated in human dentin blocks. Dent Mater. 2013;29(4):462-472.
[31] Taghiyari HR.Effects of nano-silver and nano-zycosil on mechanical strength of heat, vapor, and dry-ice-treated biscuit and dovetail medium-density fiberboard miter joints. Mater Design.2013;5(1):695-700.
[32] Khazaka R, Mendizabal L, Henry D.Review on Joint Shear Strength of Nano-Silver Pasteand Its Long-Term High Temperature Reliability. J Electron Mater.2014;43(7): 2459-2466.
[33] Tugulea AM,Bérubé D,Giddings M,et al.Nano-silver in drinking water and drinking water sources: stability and influences on disinfection by-product formation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2014;21(20):11823-11831.
[34] Wang C,Huang XB,Deng WL,et al.A nano-silver composite based on the ion-exchange response for the intelligent antibacterial applications. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;41(15):619-628.
[35] Sheehy K, Casey A, Murphy A,et al.Antimicrobial properties of nano-silver: A cautionary approach to ionic interference J Colloid Interface Sci. 2014;33(21):720-728.
[36] Palaniappan P,Sathishkumar G,Sankar R.Fabrication of nano-silver particles using Cymodocea serrulata and its cytotoxicity effect against human lung cancer A549 cells line. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015;138: 885-890.
[37] Waites KB,Duffy LB,Bébéar CM,et al. Standardized methods and quality control limits for agar and broth microdilution susceptibility testing of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Mycoplasma hominis, and Ureaplasma urealyticum.J Clin Microbiol.2012; 50(11):3542-3547.
[38] Shah SS,Test M,Sheffler-Collins S,et al.Macrolide therapy and outcomes in a multicenter cohort of children hospitalized with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Hosp Med.2012; 7(4):311-317.
[39] Sφarensen CM,Schonning K,Rosenfeldt V.Clinical characteristics of children with Mycoplasma pneumonia infection hospitalized during the Danish 2010- 2012 epidemic. Dan Med J.2013;60(5):A4632.
[40] Paes MF,Daltoe RD,Madeira KP,et al.A retrospective analysis of clinicopathological and prognostic characteristics of ovarian tumors in the State of Esp rito Santo,Brazil. J Ovarian Res. 2011;4(4):14-18.
|