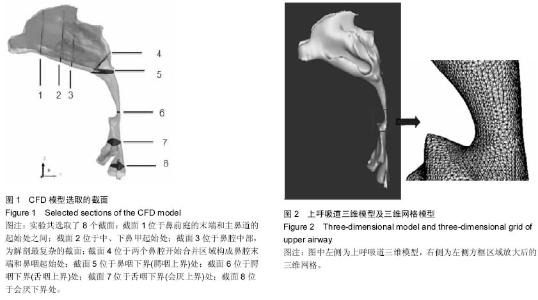
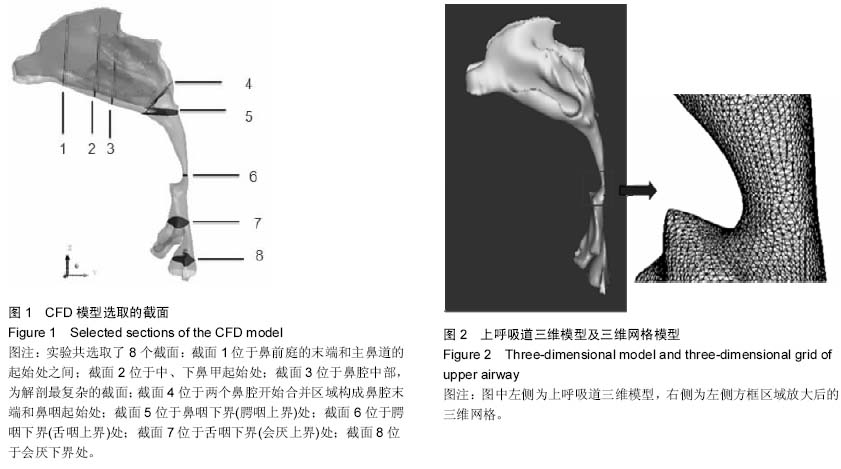
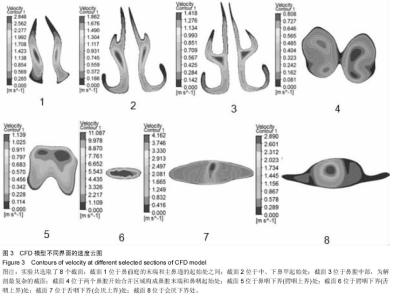
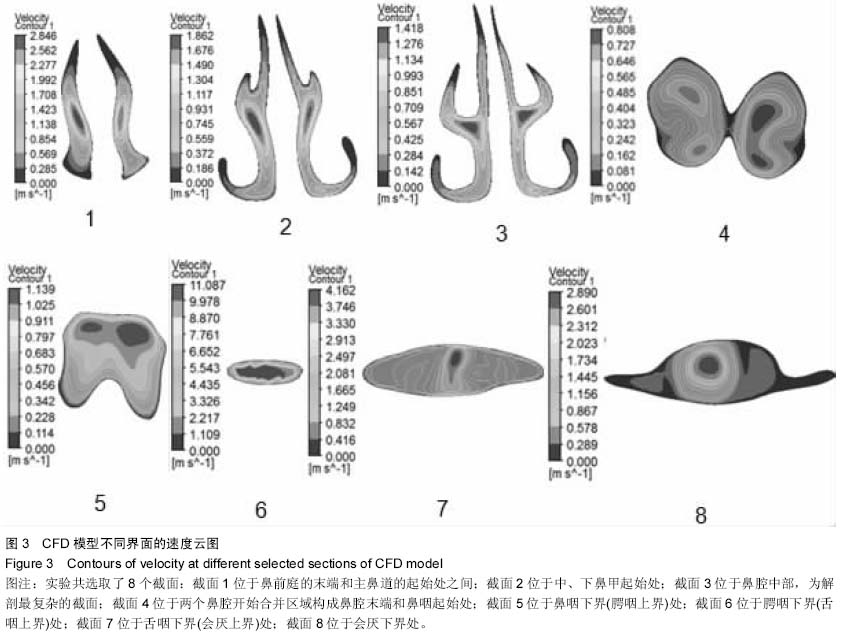
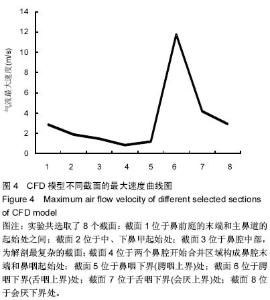
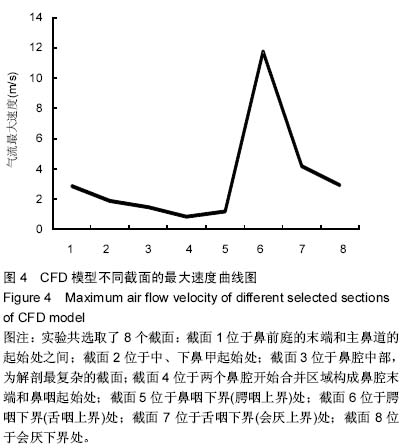
| [1] 李永明.下颌前移式矫治器治疗鼾症和阻塞型睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2009,25(6):910-913.
[2] Montesi SB, Edwards BA, Malhotra A, et al. The effect of continuous positive airway pressure treatment on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Sleep Med. 2012;8(5): 587-596.
[3] 高雪梅,曾祥龙,傅民魁,等.阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征上气道阻塞点的磁共振研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2000,14(3):185-187.
[4] 吕毛古,罗伟,缪东生,等.阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征上气道螺旋CT测量[J].中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志,2009(1):35-38.
[5] 孙秀珍,于申,刘迎曦,等.鼻腔结构的三维重建与气体流场数值模拟[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2006,23(6):1162-1165.
[6] Rhee JS, Pawar SS, Garcia GJ, et al. Toward personalized nasal surgery using computational fluid dynamics. Arch Facial Plast Surg. 2011;13(5):305-310.
[7] Chen XB, Leong SC, Lee HP, et al. Aerodynamic effects of inferior turbinate surgery on nasal airflow--a computational fluid dynamics model. Rhinology. 2010;48(4):394-400.
[8] 钱玉梅,陈丽萍,吴亚东,等.人体上呼吸道三维数值模型的建立与气体流场数值模拟分析[J].上海口腔医学,2010,19(3):310-314.
[9] Proctor DF. The upper airways. I. Nasal physiology and defense of the lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977;115(1):97- 129.
[10] Schwab RJ. Upper airway imaging. Clin Chest Med. 1998; 19(1):33-54.
[11] Hahn I, Scherer PW, Mozell MM. Velocity profiles measured for airflow through a large-scale model of the human nasal cavity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1993;75(5):2273-2287.
[12] Kelly JT, Prasad AK, Wexler AS. Detailed flow patterns in the nasal cavity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2000;89(1):323-337.
[13] Schreck S, Sullivan KJ, Ho CM, et al. Correlations between flow resistance and geometry in a model of the human nose. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1993;75(4):1767-1775.
[14] Keyhani K, Scherer PW, Mozell MM. Numerical simulation of airflow in the human nasal cavity. J Biomech Eng. 1995; 117(4): 429-441.
[15] Sung SJ, Jeong SJ, Yu YS, et al. Customized three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics simulation of the upper airway of obstructive sleep apnea. Angle Orthod. 2006;76(5):791-799.
[16] Mylavarapu G, Murugappan S, Mihaescu M, et al. Validation of computational fluid dynamics methodology used for human upper airway flow simulations. J Biomech. 2009;42(10): 1553-1559.
[17] Xu C, Sin S, McDonough JM, et al. Computational fluid dynamics modeling of the upper airway of children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in steady flow. J Biomech. 2006;39(11):2043-2054. |