| [1] 杜哲,李明,张元凯,等.双膝人工关节同期置换与选择性单膝置换近期临床效果分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2013, 12(3):150-154.
[2] Rao C, Fitzpatrick CK, Rullkoetter PJ, et al. A statistical finite element model of the knee accounting for shape and alignment variability. Med Eng Phys. 2013.
[3] Myers H, Davis A, Lazicki R, et al. Sex differences in rectus femoris morphology across different knee flexion positions. Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013;8(2): 84-90.
[4] Liebs TR, Kloos SA, Herzberg W, et al. The significance of an asymmetric extension gap on routine radiographs after total knee replacement: A new sign and its clinical significance. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(4): 472-477.
[5] Reeboonlap N, Kulkamthorn N, Charakorn K, et al. Tibial footprint for single anatomical anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction by the meniscal reference point: the cadaveric study. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012;95 (Suppl 10):S163-166.
[6] Burkhart TA, Asa B, Payne MW, et al. Anatomy of the proximal tibiofibular joint and interosseous membrane, and their contributions to joint kinematics in below-knee amputations. J Anat. 2015,226(2): 143-149.
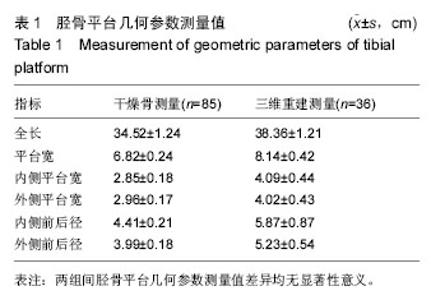
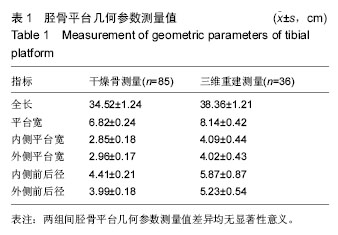
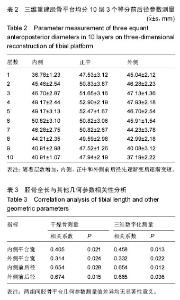
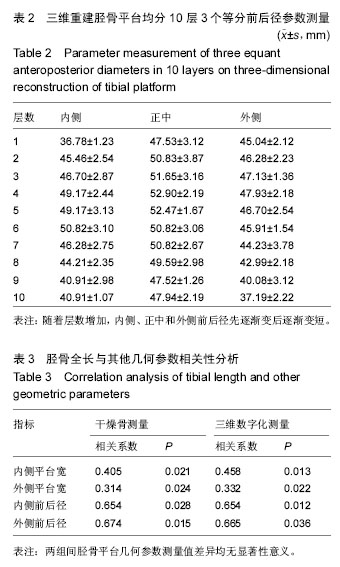
[7] 徐勃兴,王伟,张力,等.三维数字化重建在中国人胫骨近端形态学研究中的应用[J]中国组织工程研究,2012,16(44): 8218-8222.
[8] Moore SR, Milz S, Knothe Tate ML. Periosteal thickness and cellularity in mid-diaphyseal cross-sections from human femora and tibiae of aged donors. J Anat. 2014;224(2):142-149.
[9] 徐勃兴,王伟,张力,等.三维数字化重建技术在156例胫骨近端形态学研究中的应用[J].辽宁医学院学报,2012, 33(3):211-215.
[10] Yu B, Huang G, George JT, et al. Single incision technique for the internal fixation of distal fractures of the tibia and fibula: a combined anatomic and clinical study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013;133(12):1631-1637.
[11] 汪海涵,龙腾河,崔惠勤,等.胫骨近端的形态学测量与膝关节置换[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(52): 9847-9850.
[12] 赵斌修,王坤正,王春生,等.中国西北地区汉族人群胫骨近端截面线性参数的测量与分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(22):4006-4010.
[13] 刘峰,李士春,云才.胫骨平台线性几何参数再CT三维重建中的测量及其意义[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2013,31(3): 265-268.
[14] Botchu R, Douis H, Davies AM, et al. Post-traumatic heterotopic ossification of distal tibiofibular syndesmosis mimicking a surface osteosarcoma. Clin Radiol. 2013;68(12):e676-679.
[15] Halley SE, Bey MJ, Haladik JA, et al. Three dimensional, radiosteriometric analysis (RSA) of equine stifle kinematics and articular surface contact: a cadaveric study. Equine Vet J. 2014;46(3):364-369.
[16] He X, Zhang HL, Hu YC. limb salvage by distraction osteogenesis for distal tibial osteosarcoma in a young child: a case report. Orthop Surg. 2016;8(2):253-256.
[17] Kim CY, Wiznia DH, Averbukh L, et al. PROMIS Computer Adaptive Tests Compared with Time To Brake in Patients with Complex Lower Extremity Trauma. J Orthop Trauma. 2016.
[18] Johnson ZA, Ryan PM, Anderson CD. arthroscopic stabilization for chronic latent syndesmotic instability. Arthrosc Tech. 2016;5(2):e263-e268.
[19] Outani H, Hamada K, Takenaka S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma using a three-dimensional navigation system. J Orthop Sci. 2016.
[20] Cointry GR, Nocciolino L, Ireland A, et al. Structural differences in cortical shell properties between upper and lower human fibula as described by pQCT serial scans. A biomechanical interpretation. Bone. 2016.
[21] Gupta G, Ahmad S, Zahid M, et al. Management of traumatic tibial diaphyseal bone defect by "induced-membrane technique". Indian J Orthop. 2016;50(3):290-296.
[22] Chávez-Martínez P, Ortega-Palma A, Castrejón-Caballero JL, et al Equations to estimate fetal age at the moment of death in the Mexican population. Forensic Sci Int. 2016.
[23] Liu Q, Miao J, Lin B, et al. Development of a new type elastic syndesmosis hook plate. Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi. 2016;40(1):33-34.
[24] Vasanad GH, Antin SM, Akkimaradi RC, et al. the role of fibular fixation in distal tibial fractures. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(4):RC12-RC14.
[25] Tevanov I, Enescu DM, B?l?nescu R, et al. Negative pressure wound therapy (npwt) to treat complex defect of the leg after electrical burn. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2016;111(2):175-179.
[26] D'Amato Gutiérrez M, Palacio Díaz FA. A case report of a patient with FATCO syndrome: fibular aplasia, tibial campomelia and oligosyndactyly. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2016;114(3):e167-e170.
[27] Lee HJ, Min WK, Kim JS, et al. Transfibular ankle arthrodesis using burring, curettage, multiple drilling, and fixation with two retrograde screws through a single lateral incision. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2016;24(1):101-105.
[28] Wang ZY, Wu XB .Anterior dislocation of the fibula resulting from surgical malreduction: a case report. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016;48(2):361-365.
[29] Taylor GI, Corlett RJ, Ashton MW. The evolution of free vascularized bone transfer: a 40-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;137(4):1292-1305.
[30] Seo SG, Lee DY, Kim YS, et al. Foot and ankle function at maturity after ilizarov treatment for atrophic-type congenital pseudarthrosis of the tibia: a comprehensive outcome comparison with normal controls. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(6):490-498.
[31] Rochcongar G, Pillet H, Bergamini E, et al. A new method for the evaluation of the end-to-end distance of the knee ligaments and popliteal complex during passive knee flexion. Knee. 2016;23(3):420-425. |