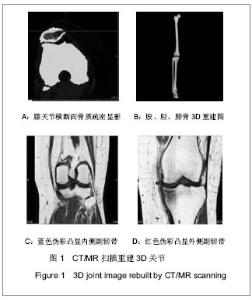
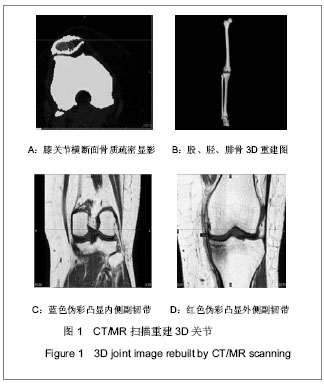
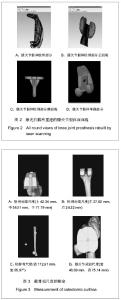
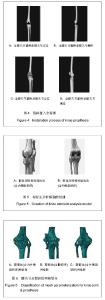
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (52): 8974-8980.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.52.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanics analysis on knee joint after virtual replacement
Matthew Jian-qiao Peng1, Zhang Zhan-lei1, Zhong Shi-zhen2, He Er-xing1
- 1Orthopedic Institute of Guangzhou First Affiliated Hospital at Guangzhou Medical University, Joint Implantation Key Laboratory of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China; 2Clinical Anatomy Institute of Southern Medical University, Medical Biomechanics Key Laboratory of Chinese Liberty Army, Guangzhou 510515, Guangdong Province, China
-
Revised:2013-11-09Online:2013-12-24Published:2013-12-24 -
Contact:He Er-xing, Master, Chief physician, Orthopedic Institute of Guangzhou First Affiliated Hospital at Guangzhou Medical University, Joint Implantation Key Laboratory of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China 18922346634@163.com -
About author:Matthew Jian-qiao Peng☆, Doctor, Senior engineer, Orthopedic Institute of Guangzhou First Affiliated Hospital at Guangzhou Medical University, Joint Implantation Key Laboratory of Guangdong Province, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China PengJQ@gyfyy.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Matthew Jian-qiao Peng, Zhang Zhan-lei, Zhong Shi-zhen, He Er-xing. Mechanics analysis on knee joint after virtual replacement[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(52): 8974-8980.
share this article

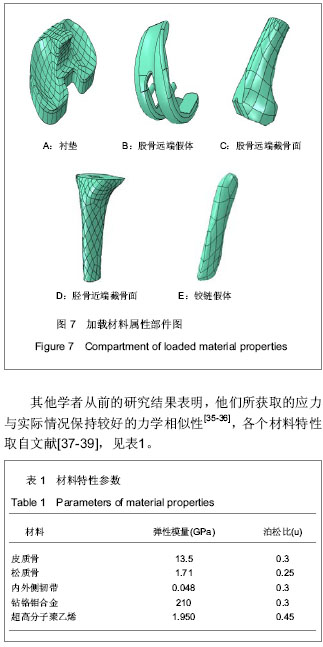
根据以上实验数据归纳出胫/股骨假体位置不良时胫股关节接触面受压状况如下:①股骨假体内外移位对关节面间接触应力的影响:中立位放置股骨假体、内外侧胫股关节间隙接触应力伸直位时为最小,随着膝关节屈曲角度的增加,这种应力均呈逐渐增长趋势;在膝关节伸直位、假体中立位时,内外侧胫股关节最大接触应力为最小,当股骨假体在冠状面上发生了内外移位时均导致内外侧胫股关节间隙接触压峰值的升高。②股骨假体的内外旋植入偏差对关节面间接触应力的影响:股骨假体的内外旋放置对内外侧胫股关节间隙接触应力影响不大,应力的变化主要表现为应力区域在小范围内的变动。③股骨假体的内外翻植入偏差对关节面间接触应力的影响:当股骨假体内翻放置时,内侧胫股关节间隙接触应力反应明显,随着内翻角度的增大,接触应力急剧增加;而股骨假体外翻植入时,外侧胫股关节间隙接触应力也增大,但没有内侧那么明显。④胫骨假体后倾角变化对关节面间接触面积和接触应力的影响:在设置胫骨截骨面垂直于胫骨平台时观察到,无论后倾角如何变化,胫股内侧关节接触面积始终大于外侧关节接触面积,胫骨后倾角在膝关节屈曲45°时胫股关节接触面积均为最小;当受力恒定时,接触面积与接触应力成反比。因此,在膝关节屈曲 45°时胫股关节接触应力最大。 此外,在垂直于下肢机械轴(即后倾角0°)截骨时,应力分布在聚乙烯衬垫接触面的内、外侧不均匀(局部有应力集中现象),随着膝关节屈曲角度的变化,内外侧关节面的最大接触应力也有较大的波动;而在垂直于胫骨平台截骨时,应力分布均匀、无集中现象,主要分布在聚乙烯衬垫接触面的中心,最大接触应力随膝关节屈曲角度的波动较小。"

| [1] Goto K, Tajima N, Chosa E,et al. Mechanical analysis of the lumbar vertebrae in a three-dimensional finite element method model in which intradiscal pressure in the nucleus pulposus was used to establish the model. J Orthop Sci. 2002; 7(2):243-246.[2] Seki N, Itoi E, Shibuya Y,et al. Mechanical environment of the supraspinatus tendon: three-dimensional finite element model analysis.J Orthop Sci. 2008;13(4):348-353.[3] Wagner A, Krach W, Schicho K,et al. A 3-dimensional finite-element analysis investigating the biomechanical behavior of the mandible and plate osteosynthesis in cases of fractures of the condylar process.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94(6):678-686.[4] Wakabayashi I, Itoi E, Sano H,et al. Mechanical environment of the supraspinatus tendon: a two-dimensional finite element model analysis.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(6):612-617.[5] Nabhani F, Sotudeh R, Hart AN, et al. 2D stress analysis of the human patella using the finite element approach. In: Middleton J, Jones ML, Pande GN, editors.Computer methods in biomechanics and biomedical engineering. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers SA.1996:197.[6] Chien WL, Lo CC, Wang CS, et al. Evaluation and analysis of the onlay patellar component in total knee arthroplasty. Adv Materials Res. 2010;97-101:3773.[7] Shashishekar C, Ramesh CS. Finite element analysis of prosthetic knee joint using ANSYS. Biomed Health. 2007; 12: 65.[8] Yosibash Z, Padan R, Joskowicz L,et al. A CT-based high-order finite element analysis of the human proximal femur compared to in-vitro experiments.J Biomech Eng. 2007; 129(3):297-309.[9] Yosibash Z, Trabelsi N, Milgrom C.Reliable simulations of the human proximal femur by high-order finite element analysis validated by experimental observations.J Biomech. 2007;40 (16):3688-3699.[10] Orwoll ES, Marshall LM, Nielson CM,et al. Finite element analysis of the proximal femur and hip fracture risk in older men.J Bone Miner Res. 2009;24(3):475-483. [11] Bougherara H, Zdero R, Miric M,et al.The biomechanics of the T2 femoral nailing system: a comparison of synthetic femurs withfinite element analysis.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2009; 223(3):303-314.[12] Simpson DJ, Brown CJ, Yettram AL,et al. Finite element analysis of intramedullary devices: the effect of the gap between the implant and the bone.Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(3):333-345.[13] Lin CL, Wang JC, Chang SH,et al.Evaluation of stress induced by implant type, number of splinted teeth, and variations in periodontal support in tooth-implant-supported fixed partial dentures: a non-linear finite element analysis.J Periodontol. 2010;81(1):121-130.[14] Kitamura E, Stegaroiu R, Nomura S,et al.Biomechanical aspects of marginal bone resorption around osseointegrated implants: considerations based on a three-dimensional finite element analysis.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004;15(4):401-412.[15] Chang CL, Chen CS, Hsu ML.Biomechanical effect of platform switching in implant dentistry: a three-dimensional finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; 25(2):295-304.[16] Schrotenboer J, Tsao YP, Kinariwala V,et al. Effect of microthreads and platform switching on crestal bone stress levels: a finite element analysis.J Periodontol. 2008;79(11): 2166-2172.[17] Schrotenboer J, Tsao YP, Kinariwala V,et al.Effect of platform switching on implant crest bone stress: a finite element analysis. Implant Dent. 2009;18(3):260-269. [18] Huang CC, Lan TH, Lee HE,et al.The biomechanical analysis of relative position between implant and alveolar bone: finite element method.J Periodontol. 2011;82(3):489-496.[19] Wang TM, Leu LJ, Wang J,et al. Effects of prosthesis materials and prosthesis splinting on peri-implant bone stress around implants in poor-quality bone: a numeric analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002;17(2):231-237.[20] Sütpideler M, Eckert SE, Zobitz M,et al. Finite element analysis of effect of prosthesis height, angle of force application, and implant offset on supporting bone.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2004;19(6):819-825.[21] Geng JP, Tan KB, Liu GR.Application of finite element analysis in implant dentistry: a review of the literature.J Prosthet Dent. 2001;85(6):585-598.[22] Nagasawa S, Hayano K, Niino T,et al.Nonlinear stress analysis of titanium implants by finite element method.Dent Mater J. 2008;27(4):633-639.[23] Qian L, Todo M, Matsushita Y,et al. Effects of implant diameter, insertion depth, and loading angle on stress/strain fields in implant/jawbone systems: finite element analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(5):877-886.[24] Lin CL, Chang SH, Chang WJ,et al. Factorial analysis of variables influencing mechanical characteristics of a single tooth implant placed in the maxilla using finite element analysis and the statistics-based Taguchi method.Eur J Oral Sci. 2007;115(5):408-416.[25] Alikhasi M, Siadat H, Geramy A,et al.Stress distribution around maxillary anterior implants as a factor of labial bone thickness and occlusal load angles: a 3D-finite-element analysis.J Oral Implantol. 2011. [Epub ahead of print][26] Ormianer Z, Palti A, Demiralp B,et al. Implant-supported first molar restorations: correlation of finite element analysis with clinical outcomes.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012;27(1): e1-12.[27] Gupte CM, Bull AM, Thomas RD,et al.The meniscofemoral ligaments: secondary restraints to the posterior drawer. Analysis of anteroposterior and rotary laxity in the intact and posterior-cruciate-deficient knee.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003; 85(5):765-773.[28] Lee KK, Teo EC, Fuss FK,et al. Finite-element analysis for lumbar interbody fusion under axial loading.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2004;51(3):393-400.[29] Polikeit A, Ferguson SJ, Nolte LP,et al.Factors influencing stresses in the lumbar spine after the insertion of intervertebral cages: finite element analysis.Eur Spine J. 2003;12(4):413-420.[30] Li XF, Dai LY.Three-dimensional finite element model of the cervical spinal cord: preliminary results of injury mechanism analysis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(11):1140-1147.[31] García JM, Doblaré M, Seral B,et al.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of several internal and external pelvis fixations. J Biomech Eng. 2000;122(5):516-522.[32] 李孝林.基于CT图像应用Mimics软件快速构建人体胸腰段骨骼有限元模型[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(39): 7619-7622.[33] 唐先智,刘飞,李绪武,等.面向逆向工程的网络化共享应用系统的设计及应用[J].重庆大学学报,2009,32(5):339-356.[34] Feikes JD, O'Connor JJ, Zavatsky AB.A constraint-based approach to modelling the mobility of the human knee joint.J Biomech. 2003;36(1):125-129.[35] Peña E, Calvo B, Martínez MA,et al.A three-dimensional finite element analysis of the combined behavior of ligaments and menisci in the healthy human knee joint.J Biomech. 2006; 39(9):1686-1701.[36] Bendjaballah MZ, Shirazi-Adl A, Zukor DJ.Biomechanical response of the passive human knee joint under anterior-posterior forces.Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1998; 13(8):625-633.[37] LeRoux MA, Setton LA. Experimental and biphasic FEM determinations of the material properties and hydraulic permeability of the meniscus in tension.J Biomech Eng. 2002; 124(3):315-321.[38] Li G, Lopez O, Rubash H.Variability of a three-dimensional finite element model constructed using magnetic resonance images of a knee for joint contact stress analysis.J Biomech Eng. 2001;123(4):341-346.[39] Mesfar W, Shirazi-Adl A. Biomechanics of the knee joint in flexion under various quadriceps forces.Knee. 2005;12(6): 424-434. [40] Brekelmans WA, Poort HW, Slooff TJ.A new method to analyse the mechanical behaviour of skeletal parts.Acta Orthop Scand. 1972;43(5):301-317.[41] Matsuda S, White SE, Williams VG 2nd,et al. Contact stress analysis in meniscal bearing total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 1998;13(6):699-706.[42] Shiramizu K, Vizesi F, Bruce W,et al.Tibiofemoral contact areas and pressures in six high flexion knees.Int Orthop. 2009; 33(2):403-406. [43] 王海鹏,容可,钟砚琳,等.膝关节周围韧带三维有限元模型的建立[J].上海交通大学学报,2008,28(4):367-370. |
| [1] | Liang Xin, Wang Heng, Li Xian-rong. Preoperative application of alprazolam for patients with anxiety and depression and pain after total knee arthroplasty: its safety and effectiveness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 985-992. |
| [2] | Shi Bin, An Jing, Chen Long-gang, Zhang Nan, Tian Ye . Influencing factors for pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 993-997. |
| [3] | Wang Xian-xun. Impact of local compression cryotherapy combined with continuous passive motion on the early functional recovery after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 998-1003. |
| [4] | Lu Yao-jia, Xiong Chuan-zhi, Li Xiao-lei, Hu Han-sheng, Chen Gang, Wang Qiang, Lu Zhi-hua. Comparison of two methods for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1004-1008. |
| [5] | Yuan Wei, Zhao Hui, Ding Zhe-ru, Wu Yu-li, Wu Hai-shan, Qian Qi-rong. Association between psychological resilience and acute mental disorders after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1015-1019. |
| [6] | Xie Qiang. Three-dimensional finite element model for biomechanical analysis of stress in knee inversion and external rotation after posterior cruciate ligament rupture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1036-1040. |
| [7] | He Ze-dong, Zhao Jing, Chen Liang-yu, Li Ke, Weng Jie. Multilevel finite element analysis on the biological tribology damage of water on bone tissue [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1041-1045. |
| [8] | Li Peng, Li Hong-wei, Wang Shuang, Wang Hai-zhou. Digital anatomy of lumbar spinous process tilt angle of adults in northeast China: prodinding reference for pedicle screw insertion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1064-1068. |
| [9] | Li Hui, Ma Jun-yi, Ma Yuan, Zhu Xu . Establishment of a three-dimensional finite element model of ankylosing spondylitis kyphosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1069-1073. |
| [10] | Ling Guan-han, Ou Zhi-xue, Yao Lan, Wen Li-chun, Wang Guo-xiang, Lin Heng-feng. Establishment of simulating three-dimensional model of China-Japan Friendship Hospital Classification for L type osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1074-1079. |
| [11] | Lin Han-wen, Wen Jun-mao, Huang Chao-yuan, Zhou Chi, Tang Hong-yu. Correlation between the changes in lower limb power line and pain area in the knee osteoarthritis patients: imaging evaluation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1110-1114. |
| [12] | Ye Xiang-yang, Sun Xiang, Tang Li-xin, Zhen Ping, Geng Bin, Wang Hua-lei, Zhao Yu-guo. Acetabular liner wear of cross-linked versus conventional polyethylene for total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1143-1148. |
| [13] | Wei Zhi-hui, Zhang Zhong-zu, Zhang Ming-hua. Intravenous combined with topical application of tranexamic acid in primary total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of efficacy and safety [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 464-470. |
| [14] | Tian Hai-tao, Wang Yuan-he, Tian Shao-qi, Zhang Xu-teng, Sun Kang. Effects and safety assessment of methylprednisolone on postoperative nausea and vomiting and pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 335-339. |
| [15] | Chen Lu-yao, Hu Shi-qiang, Wang Xiao-ping, Wu Wei-wei, Wei Zhan-tu, Huang Jian. Accuracy of digital orthopedic three-dimensional reconstruction for thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(3): 373-377. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||