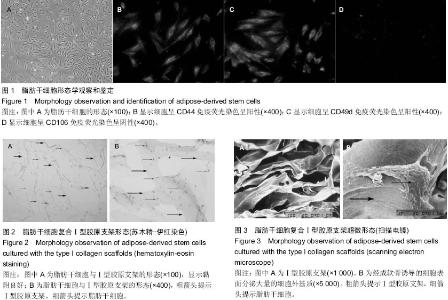
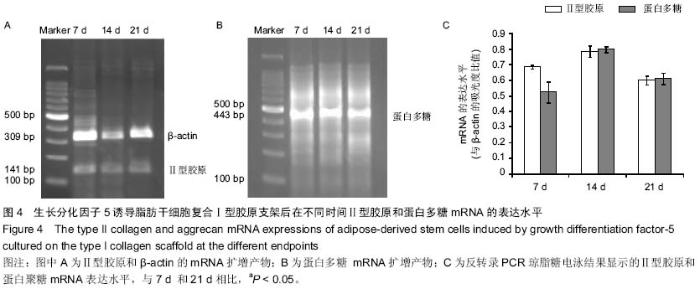
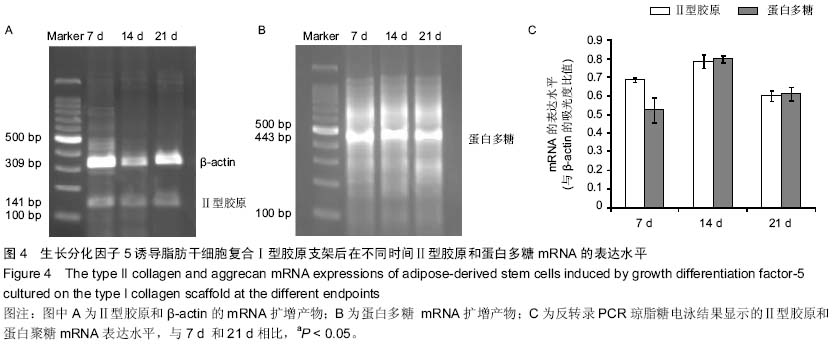
| [1] Kon E, Roffi A, Filardo G, et al. Scaffold-Based Cartilage Treatments: With or Without Cells? A Systematic Review of Preclinical and Clinical Evidence. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(4): 767-775.
[2] Filardo G, Kon E, Roffi A, et al. Scaffold-based repair for cartilage healing: a systematic review and technical note. Arthroscopy. 2013;29(1):174-186.
[3] Solheim E, Hegna J, Inderhaug E, et al. Results at 10-14 years after microfracture treatment of articular cartilage defects in the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014. in press.
[4] Ortved KF, Begum L, Mohammed HO, et al. Implantation of rAAV5-IGF-I transduced autologous chondrocytes improves cartilage repair in full-thickness defects in the equine model. Mol Ther. 2015;23(2):363-373.
[5] Makris EA, Gomoll AH, Malizos KN, et al. Repair and tissue engineering techniques for articular cartilage. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):21-34.
[6] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228.
[7] Faroni A, Smith RJ,Reid AJ.Adipose derived stem cells and nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(14): 1341-1346.
[8] Hötten G, Neidhardt H, Jacobowsky B, et al. Cloning and expression of recombinant human growth/differentiation factor 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994;204(2): 646-652.
[9] 刘振宁,贾长青,韩长旭,等.生长分化因子5诱导兔脂肪干细胞成软骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009, 23(4):483-489.
[10] Im GI, Jung NH, Tae SK. Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells isolated from patients in late adulthood: the optimal conditions of growth factors. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(3):527-536.
[11] Huang X, Yang D, Yan W, et al. Osteochondral repair using the combination of fibroblast growth factor and amorphous calcium phosphate/poly(L-lactic acid) hybrid materials. Biomaterials. 2007;28(20):3091-3100.
[12] 赵明璨,刘畅.脂肪干细胞在软骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中国生物医学工程学报.2014,33(4):475-481.
[13] Nickel J, Kotzsch A, Sebald W, et al. A single residue of GDF-5 defines binding specificity to BMP receptor IB. J Mol Biol. 2005;349(5):933-947.
[14] Yoon HH, Bhang SH, Shin JY, et al. Enhanced cartilage formation via three-dimensional cell engineering of human adipose-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18 (19-20):1949-1956.
[15] Lehmann M, Martin F, Mannigel K, et al. Three-dimensional scaffold-free fusion culture: the way to enhance chondrogenesis of in vitro propagated human articular chondrocytes. Eur J Histochem. 2013;57(4):e31.
[16] Wang PY, Tsai WB. Modulation of the proliferation and matrix synthesis of chondrocytes by dynamic compression on genipin-crosslinked chitosan/collagen scaffolds. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013;24(5):507-519.
[17] Huselstein C, Li Y, He X. Mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage engineering. Biomed Mater Eng. 2012;22(1-3): 69-80.
[18] 张文元,杨亚冬,李颖,等.蚕丝/聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物支架降解液与骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(25):4676-4683.
[19] Heidemann W, Jeschkeit-Schubbert S, Ruffieux K, et al. pH-stabilization of predegraded PDLLA by an admixture of water-soluble sodiumhydrogenphosphate--results of an in vitro- and in vivo-study. Biomaterials. 2002;23(17):3567-3574.
[20] Wang Y, Kim UJ, Blasioli DJ, et al. In vitro cartilage tissue engineering with 3D porous aqueous-derived silk scaffolds and mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2005;26(34): 7082-7094.
[21] Ragetly GR, Griffon DJ, Lee HB, et al. Effect of chitosan scaffold microstructure on mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2010;6(4):1430-1436.
[22] Buma P, Pieper JS, van Tienen T, et al. Cross-linked type I and type II collagenous matrices for the repair of full-thickness articular cartilage defects--a study in rabbits. Biomaterials. 2003; 24(19):3255-3263.
[23] 张军鹏.运动性软骨损伤与组织工程化软骨及生物支架材料的修复[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15 (8):1491-1494.
[24] Wakitani S, Goto T, Pineda SJ, et al. Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(4):579-592.
[25] Schlegel W, Nürnberger S, Hombauer M, et al. Scaffold-dependent differentiation of human articular chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2008;22(5):691-699. |