Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (9): 2162-2171.doi: 10.12307/2026.580
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae
Cheng Qisheng1, Julaiti·Maitirouzi1, Xiao Yang2, Zhang Chenwei1, Paerhati·Rexiti2
- 1College of Intelligent Manufacturing Modern Industry, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Minimally Invasive and Precision Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-12-04Accepted:2025-03-06Online:2026-03-28Published:2025-08-21 -
Contact:Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Associate professor, College of Intelligent Manufacturing Modern Industry, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Cheng Qisheng, Master candidate, College of Intelligent Manufacturing Modern Industry, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830017, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:“Tianshan Talents” Medical and Health High-level Talent Training Program Fund, No. TSYC202301B026 (to PR); Third China Health and Longevity Innovation Competition Fund Project of Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, No. 2022-JKCS-19 (to PR)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Qisheng, Julaiti·Maitirouzi, Xiao Yang, Zhang Chenwei, Paerhati·Rexiti. Finite element analysis of novel variable-diameter screws in modified cortical bone trajectory of lumbar vertebrae[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2162-2171.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
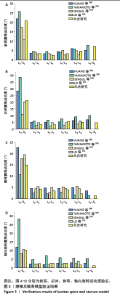
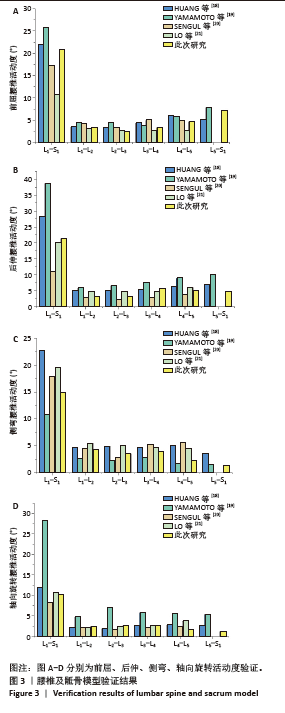
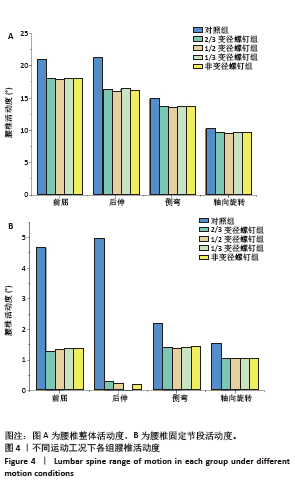
2.2 腰椎活动度 2.2.1 腰椎整体活动度 在前屈、后伸、侧弯、轴向旋转工况下,2/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎整体关节活动度分别降低14.16%,23.75%,8.44%及7.17%;1/2变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎整体活动度分别降低15.24%,25.01%,8.89%及7.50%;1/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎整体活动度分别降低14.46%,23.18%,8.51%及7.14%。非变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎整体活动度分别降低14.45%,23.97%,8.52%及7.07%(图4A)。 2.2.2 腰椎固定节段活动度 在前屈、后伸、侧弯、轴向旋转工况下,2/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎固定节段关节活动度分别降低73.23%,94.35%,35.44%及32.05%;1/2变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎固定节段关节活动度分别降低71.39%,95.62%,37.52%及32.96%;1/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎固定节段关节活动度分别降低70.42%,99.80%,35.16%及33.03%;非变径螺钉组相比对照组,腰椎固定节段关节活动度分别降低70.42%,96.62%,34.70%及32.44%(图4B)。"
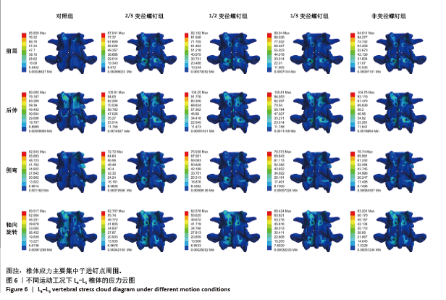
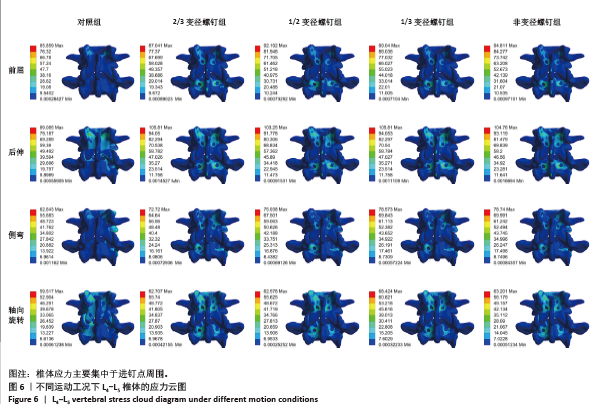
2.4 L4-L5椎体应力 在前屈、后伸、侧弯、轴向旋转工况下,2/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,椎体最大应力分别增加1.38%,18.77%,16.09%及5.36%;相比非变径螺钉组,椎体最大应力分别减少8.20%、增加1.00%、减少7.65%、减少0.78%。1/2变径螺钉组相比对照组,椎体最大应力分别增加7.38%、15.90%,21.22%,5.14%;相比非变径螺钉组,椎体最大应力分别减少2.76%,1.44%,3.56%及0.99%。1/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,椎体最大应力分别增加10.69%,18.77%,25.43%及14.97%;相比非变径螺钉组,椎体最大应力分别增加4.46%、增加1.00%、减少0.21%、增加8.26%。见图6。"
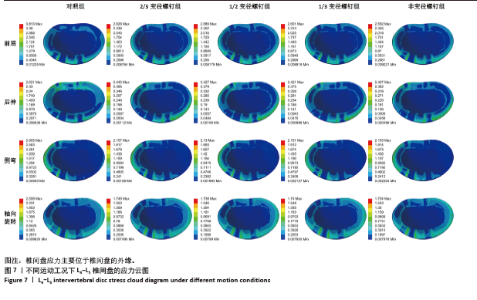
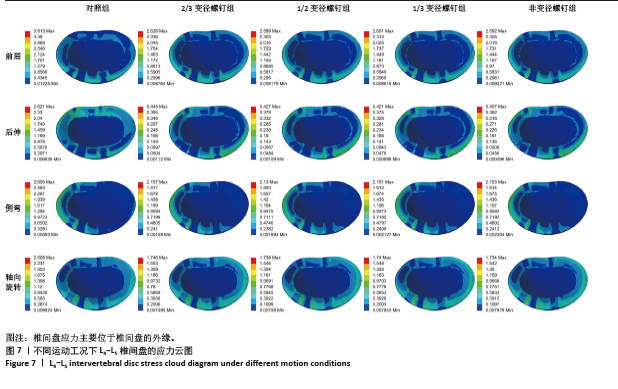
2.5 L4-L5 椎间盘应力 在前屈、后伸、侧弯、轴向旋转工况下,2/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,固定节段椎间盘最大应力分别减少31.13%,83.02%,25.75%及30.38%;相比非变径螺钉组,固定节段椎间盘最大应力分别增加1.31%,9.34%,0.19%,0.69%。1/2变径螺钉组相比对照组,固定节段椎间盘最大应力分别减少32.10%,83.71%,26.68%及30.70%;相比非变径螺钉组,固定节段椎间盘最大应力分别减少0.12%、增加4.91%、减少1.07%、增加0.23%。1/3变径螺钉组相比对照组,固定节段椎间盘最大应力分别减少31.79%,83.94%,25.96%及30.62%;相比非变径螺钉组,固定节段椎间盘最大应力分别增加0.35%、增加3.44%、减少0.09%、增加0.35%。见图7。"
| [1] DE KATER EP, SAKES A, EDSTRÖM E, et al. Beyond the pedicle screw–a patent review. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(6):1553-1565. [2] ODEH K, ROSINSKI A, MITTAL A, et al. Does the Bone Mineral Density of the Lumbar Spine Correlate With Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry T Score? A Cadaveric-Based Analysis of Computed Tomography Densitometry. Int J Spine Surg. 2023;17(1):132-138. [3] PENG SB, YUAN XC, LU WZ, et al. Application of the cortical bone trajectory technique in posterior lumbar fixation. World J Clin Cases. 2023;11(2):255-267. [4] SANTONI BG, HYNES RA, MCGILVRAY KC, et al. Cortical bone trajectory for lumbar pedicle screws. Spine J. 2009;9(5):366-373. [5] 张治豪, 居来提·买提肉孜, 张连鹏, 等. 新型变径全皮质骨螺纹螺钉设计以及在腰椎改良皮质骨轨迹的应用[J]. 医用生物力学,2024, 39(1): 91-97. [6] REXITI P, AIERKEN G, WANG S, et al. Anatomical research on strength of screw track fixation in novel cortical bone trajectory for osteoporosis lumbar spine. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11(11):6850-6859. [7] 罗辉卿, 居来提·买提肉孜, 帕尔哈提热西提,等.不同骨密度轨迹内固定系统对腰椎L4-L5节段的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021, 21(16):6626-6631. [8] 王轶希, 居来提·买提肉孜, 王水泉, 等. 有限元分析腰椎传统椎弓根钉道和改良皮质骨钉道的生物力学性能[J]. 医用生物力学,2022, 37(3):485-491. [9] KAHAER A, ZHOU Z, MAITIROUZI J, et al. Biomechanical Investigation of the Posterior Pedicle Screw Fixation System at Level L4-L5 Lumbar Segment with Traditional and Cortical Trajectories: A Finite Element Study. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:4826507. [10] KAHAER A, MAIMAITI X, MAITIROUZI J, et al. Biomechanical investigation of the hybrid modified cortical bone screw-pedicle screw fixation technique: Finite-element analysis. Front Surg. 2022;9:911742. [11] PASOTO SG, AUGUSTO KL, ALVARENGA JC, et al. Cortical bone density and thickness alterations by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography: association with vertebral fractures in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(12):2200-2211. [12] ZHAO X, DU L, XIE Y, et al. Effect of Lumbar Lordosis on the Adjacent Segment in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Finite Element Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2018;114:e114-e120. [13] MAKAROV SN, NOETSCHER GM, YANAMADALA J, et al. Virtual Human Models for Electromagnetic Studies and Their Applications. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2017;10:95-121. [14] REXITI P, AIKEREMU D, WANG S, et al. Cadaveric study of anatomical measurement of isthmus parameters of lumbar spine to guide cortical bone screw placement. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2022;68(6): 754-758. [15] REXITI P, ABUDUREXITI T, ABUDUWALI N, et al. Measurement of lumbar isthmus parameters for novel starting points for cortical bone trajectory screws using computed radiography. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10(8): 2413-2423. [16] 张连鹏, 居来提·买提肉孜, 张治豪, 等. 有限元分析改良皮质骨轨迹置钉在腰椎翻修术中的力学性能[J]. 医用生物力学,2024,39(3): 413-420. [17] TUOHETI A, XIAO Y, WANG Y, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of modified and traditional cortical bone trajectory technique on adjacent segment degeneration in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion-finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024;25(1):7. [18] HUANG YP, DU CF, CHENG CK, et al. Preserving Posterior Complex Can Prevent Adjacent Segment Disease following Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Surgeries: A Finite Element Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0166452. [19] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1989;14(11):1256-1260. [20] SENGUL E, OZMEN R, YAMAN ME, et al. Influence of posterior pedicle screw fixation at L4-L5 level on biomechanics of the lumbar spine with and without fusion: a finite element method. Biomed Eng Online. 2021;20(1):98. [21] LO HJ, CHEN HM, KUO YJ, et al. Effect of different designs of interspinous process devices on the instrumented and adjacent levels after double-level lumbar decompression surgery: A finite element analysis. PLoS One. 2020;15(12):e0244571. [22] 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心, 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会. 中国骨质疏松症流行病学调查报告(2018)[M]. 北京: 人民卫生岀版社,2021. [23] WANG Y, KAHAER A, MAIMAITI A, et al. Complication, fusion, and revision rate in the lumbar cortical bone trajectory and pedicle screw fixation techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):382. [24] MATSUKAWA K, YATO Y. Lumbar pedicle screw fixation with cortical bone trajectory: A review from anatomical and biomechanical standpoints. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2017;1(4):164-173. [25] WANG Y, MAIMAITI A, XIAO Y, et al. Hybrid cortical bone trajectory and modified cortical bone trajectory techniques in transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion at L4-L5 segment: A finite element analysis. Heliyon. 2024;10(5):e26294. [26] PEREZ-ORRIBO L, KALB S, REYES PM, et al. Biomechanics of lumbar cortical screw-rod fixation versus pedicle screw-rod fixation with and without interbody support. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013;38(8):635-641. [27] 李杰, 曹帅, 郭栋, 等. 聚醚醚酮棒与钛棒在后路腰椎椎间融合中的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(22):3445-3450. [28] 魏源标, 郭惠智, 张顺聪. 皮质骨轨迹螺钉固定对相邻节段影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(18):2799-2804. [29] LI XH, SHE LJ, ZHANG W, et al. Biomechanics of extreme lateral interbody fusion with different internal fixation methods: a finite element analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):134. [30] MCLACHLIN SD, BEATON BJ, SABO MT, et al. Comparing the fixation of a novel hollow screw versus a conventional solid screw in human sacra under cyclic loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(17):1870-1875. [31] CLAESON AA, BAROCAS VH. Computer simulation of lumbar flexion shows shear of the facet capsular ligament. Spine J. 2017;17(1): 109-119. [32] PATEL JY, KUNDNANI VG, MERCHANT ZI, et al. Superior Facet Joint Violations in Single Level Minimally Invasive and Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Comparative Study. Asian Spine J. 2020; 14(1):25-32. [33] ZENG ZL, JIA L, XU W, et al. Analysis of risk factors for adjacent superior vertebral pedicle-induced facet joint violation during the minimally invasive surgery transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a retrospective study. Eur J Med Res. 2015;20:80. [34] ZHANG Q, HAN XG, XU YF, et al. Robot-Assisted Versus Fluoroscopy-Guided Pedicle Screw Placement in Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Disease. World Neurosurg. 2019;125: e429-e434. [35] 王鹏, 王健, 胡勇, 等. 下腰椎融合术后路单、双侧椎弓根固定的有限元比较研究[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2016,34(3):331-337. [36] LOTZ JC, CHIN JR. Intervertebral disc cell death is dependent on the magnitude and duration of spinal loading. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(12):1477-1483. |
| [1] | Liu Wenlong, Dong Lei, Xiao Zhengzheng, Nie Yu. Finite element analysis of tibial prosthesis loosening after fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2191-2198. |
| [2] | Zheng Wangyang, Fei Ji, Yang Di, Zhao Lang, Wang Lingli, Liu Peng, Li Haiyang. Finite element analysis of the force changes of the supraspinatus tendon and glenohumeral joint during the abduction and flexion of the humerus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2199-2207. |
| [3] | Cai Qirui, Dai Xiaowei, Zheng Xiaobin, Jian Sili, Lu Shaoping, Liu Texi, Liu Guoke, Lin Yuanfang. Mechanical effects of Long’s traction orthopedic method on cervical functional units: quantitative analysis of biomechanical model of head and neck [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2208-2216. |
| [4] | Rao Jingcheng, Li Yuwan, Zheng Hongbing, Xu Zhi, Zhu Aixiang, Shi Ce, Wang Bing, Yang Chun, Kong Xiangru, Zhu Dawei. Biomechanical differences between the new proximal femoral stable intramedullary nail and traditional intramedullary nail#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2217-2225. |
| [5] | Chen Long, Wang Xiaozhen, Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin. Biomechanical performance of short-segment screw fixation combined with expandable polyetheretherketone vertebral body replacement in osteoporotic vertebrae [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2226-2235. |
| [6] | Chen Huiting, Zeng Weiquan, Zhou Jianhong, Wang Jie, Zhuang Congying, Chen Peiyou, Liang Zeqian, Deng Weiming. Tail anchoring technique of vertebroplasty in treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with intravertebral cleft: a finite element analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2145-2152. |
| [7] | Zeng Xuan, Weng Rui, Ye Shicheng, Tang Jiadong, Mo Ling, Li Wenchao. Two lumbar rotary manipulation techniques in treating lumbar disc herniation: a finite element analysis of biomechanical differences [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2153-2161. |
| [8] | Liu Jiafu, Ren Ruxia, Liao Zhouwei, Zhou Xiali, Wu Yihong, Zhang Shaoqun. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of cervical spine biomechanical characteristics in a rat model of cervical vertigo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2182-2190. |
| [9] | Zhang Zizheng, Luo Wang, Liu Changlu. Application value of finite element analysis on unicompartmental knee arthroplasty for medial knee compartmental osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2313-2322. |
| [10] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. Risk factors and coping strategies of internal fixation failure in treatment of intertrochanteric fracture with proximal femoral nail antirotation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(9): 2323-2333. |
| [11] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [12] | Hu Xiongke, Liu Shaohua, Tan Qian, Liu Kun, Zhu Guanghui. Shikonin intervention with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells improves microstructure of femur in aged mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(7): 1609-1615. |
| [13] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [14] | Zhang Haiwen, Zhang Xian, Xu Taichuan, Li Chao. Bibliometric and visual analysis of the research status and trends of senescence in osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1580-1591. |
| [15] | Huang Jie, Zeng Hao, Wang Wenchi, Lyu Zhucheng, Cui Wei. Visualization analysis of literature on the effect of lipid metabolism on osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1558-1568. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||