Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1592-1601.doi: 10.12307/2026.595
Previous Articles Next Articles
Potential target genes for spondylolisthesis: drugable genome analysis based on the European population-based biodatabase
Zhang Qingfeng1, Wang Chaoyi1, Yang Jingyan1, Li Hanyu1, Zhao Yuyang1, Hao Huatao2, Yu Dong2
- 1The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 2The Third Clinical Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
-
Received:2024-12-23Accepted:2025-02-26Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-19 -
Contact:Yu Dong, MD, Chief physician, Master’s supervisor, The Third Clinical Hospital of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China -
About author:Zhang Qingfeng, MS, The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China Wang Chaoyi, MS candidate, The Third Clinical School of Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China Zhang Qingfeng and Wang Chaoyi contributed equally to this work. -
Supported by:Orthopedics and Traumatology of Traditional Chinese Medicine (OCTCM) - First-Class Discipline Construction Project, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine (BUCM) (to YD)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Qingfeng, Wang Chaoyi, Yang Jingyan, Li Hanyu, Zhao Yuyang, Hao Huatao, Yu Dong. Potential target genes for spondylolisthesis: drugable genome analysis based on the European population-based biodatabase[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1592-1601.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
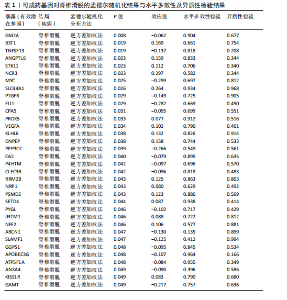
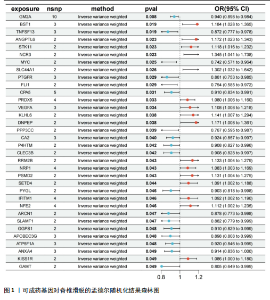
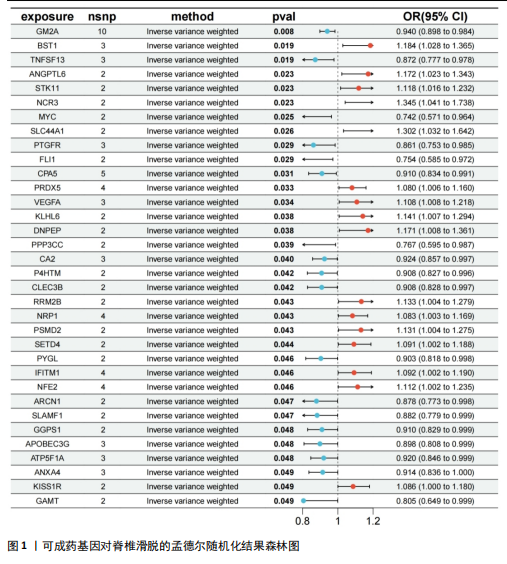
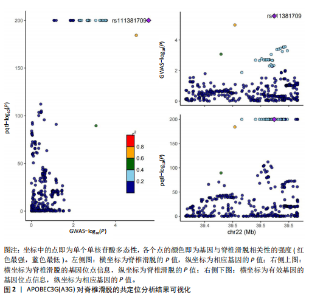
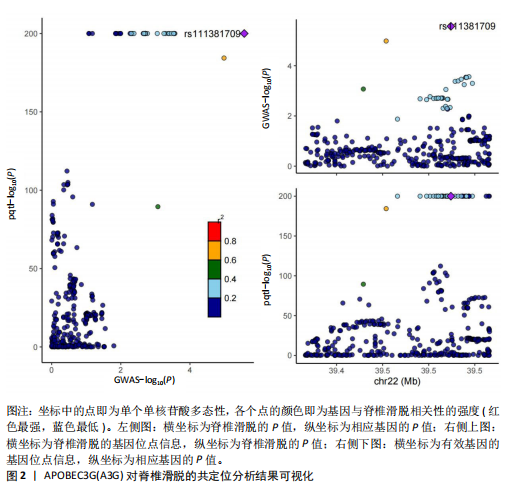
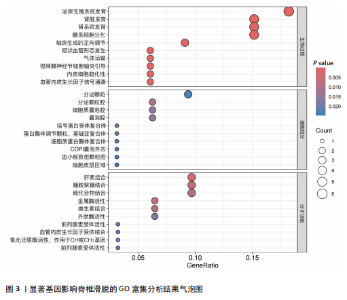
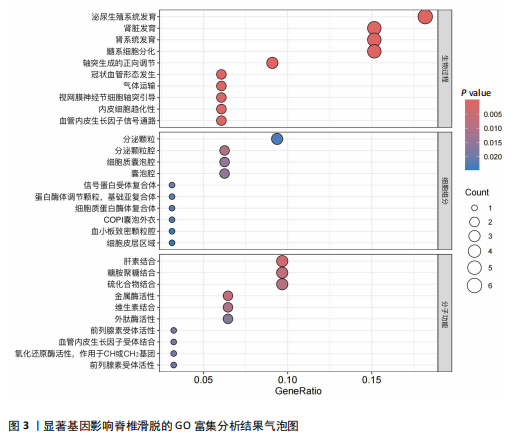
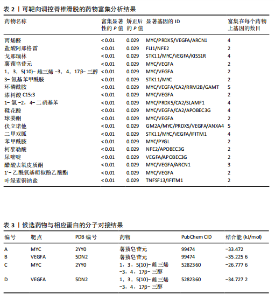
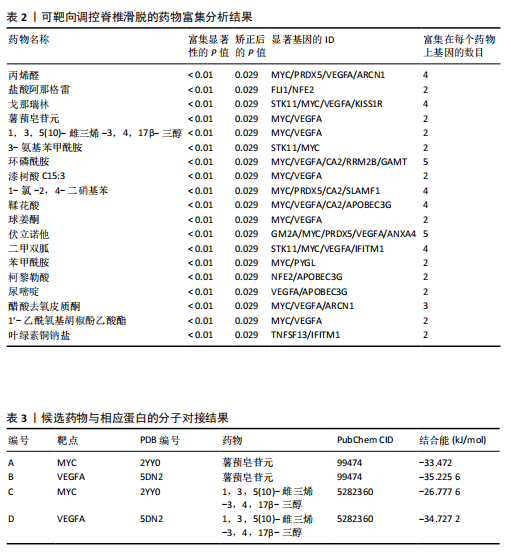
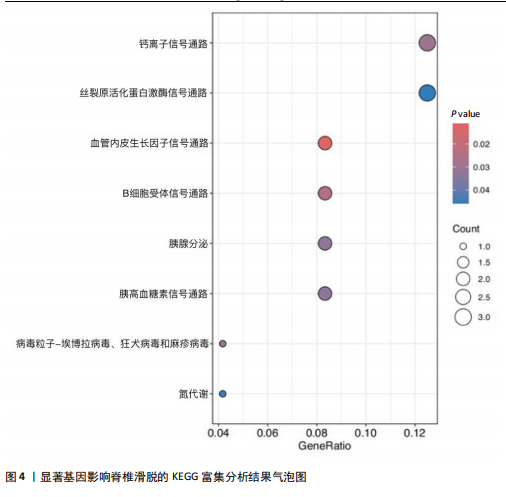
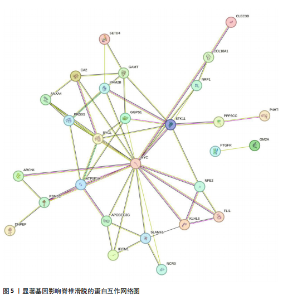
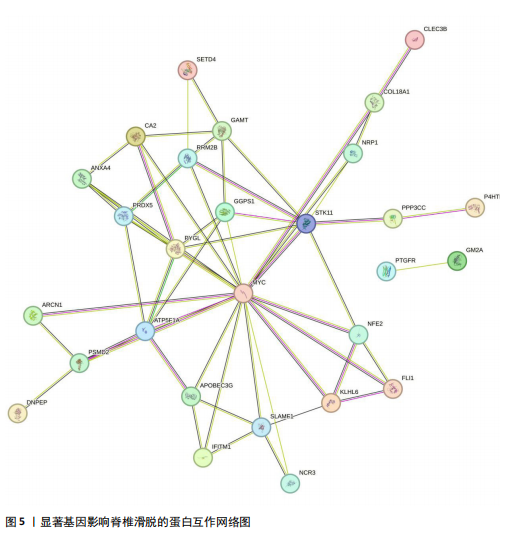
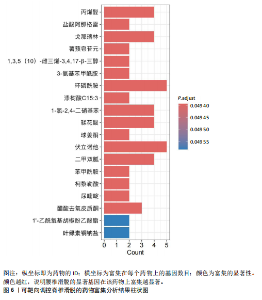
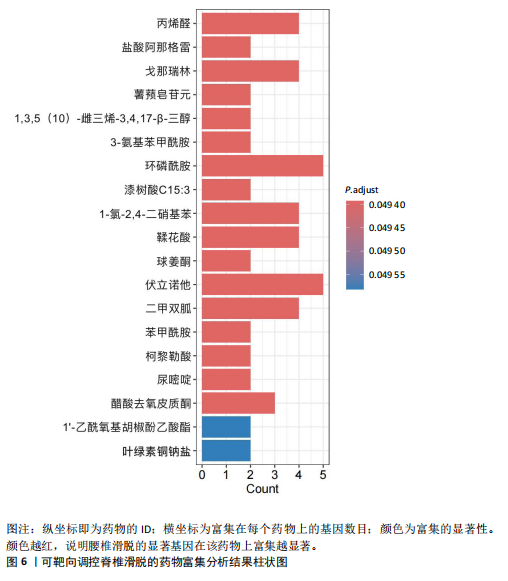
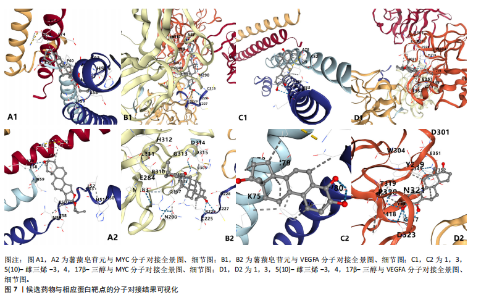
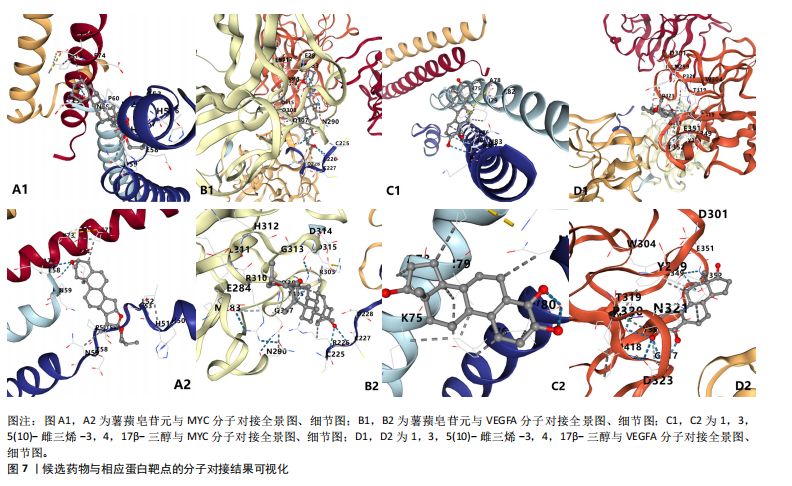
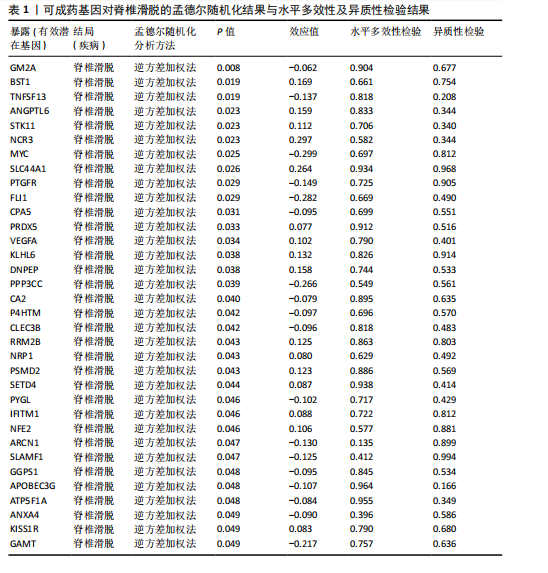
2.1 可成药基因组 从DGIdb获得了5 012个可成药基因。此外,从FINAN等[16]综述中获得了4 463个可成药基因。整合数据后,获得了6 888个由人类基因组组织基因命名委员会命名的独特可成药基因,以供后续分析。 2.2 孟德尔随机化分析及有效基因的筛选 此次研究共筛选出来34个显著潜在基因,具体数据细节见表1,将其进行可视化,见图1。 2.3 共定位分析结果 在34个显著基因中,APOBEC3G的PPH4为0.761,APOBEC3G和脊椎滑脱均可被rs111381709驱动,结果表明APOBEC3G与脊椎滑脱有着较强的关联性,将该结果进行可视化,见图2。 2.4 显著基因功能分析 对34个潜在靶点进行GO富集分析,可以看出这些靶点共参与340项生物过程、涉及19个细胞成分、包括37个分子功能。其中,主要参与的生物过程有泌尿生殖系统发育(GO:0001655)、肾脏发育(GO:0001822、GO:0072001)、骨髓细胞分化(GO:0030099);主要细胞成分有分泌颗粒与分泌颗粒腔(GO:0034774、GO:0030141)、细胞质囊与囊泡腔(GO:0060205、GO:0031983);主要分子功能包括肝素结合(GO:0008201)、糖胺聚糖结合(GO:0005539)、硫化合物结合(GO:1901681),见图3。 KEGG通路富集展示了脊椎滑脱相关的显著可成药基因的8条潜在治疗通路,根据富集在每个药物上基因的数目及显著性,排名前5的是钙离子信号通路、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶信号通路(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)、血管内皮生长因子信号通路(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)、B细胞受体信号通路、胰腺分泌,见图4。 2.5 蛋白互作网络分析 将34个显著基因构建蛋白互作网络,隐藏网络中断开的网络节点后,共得到34个节点和57个边缘,平均节点度:3.35,预期边数:49,蛋白互作富集P值:0.15,网络互动量明显高于预期。将结果导出并进行可视化,见图5。 2.6 药物富集结果 将34个显著基因与DSigDB数据库下载的数据进行富集分析后,得到19个药物,将以上结果进行可视化,见图6,并选取其中2个显著富集的药物进行分子对接,见表2。"
| [1] KONIECZNY MR, JÄGER M. Spondylolisthesis. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2023;52(11):931-940. [2] POLLY DW JR, HASELHUHN JJ, SORIANO PBO, et al. Management of High-Grade Dysplastic Spondylolisthesis. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2023;34(4):567-572. [3] KONIECZNY MR, JÄGER M. Spondylolisthesis. Schmerz. 2024;38(2):157-166. [4] ALOMARI S, JUDY B, SACINO AN, et al. Isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults… A review of the current literature. J Clin Neurosci. 2022;101:124-130. [5] BERNARD F, MAZERAND E, GALLET C, et al. History of degenerative spondylolisthesis: From anatomical description to surgical management. Neurochirurgie. 2019;65(2-3):75-82. [6] KANG WY, LEE JW, LEE E, et al. Efficacy and outcome predictors of fluoroscopy-guided facet joint injection for spondylolysis. Skeletal Radiol. 2018;47(8):1137-1144. [7] JOELSON A. Surgery for spinal stenosis with degenerative spondylolisthesis. BMJ. 2024;386:q1628. [8] QI T, SONG L, GUO Y, et al. From genetic associations to genes: methods, applications, and challenges. Trends Genet. 2024;40(8):642-667. [9] LARSSON SC, BUTTERWORTH AS, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization for cardiovascular diseases: principles and applications. Eur Heart J. 2023;44(47): 4913-4924. [10] STORM CS, KIA DA, ALMRAMHI MM, et al. Finding genetically-supported drug targets for Parkinson’s disease using Mendelian randomization of the druggable genome. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):7342. [11] SCHMIDT AF, FINAN C, GORDILLO-MARAÑÓN M, et al. Genetic drug target validation using Mendelian randomisation. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3255. [12] SU WM, GU XJ, DOU M, et al. Systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomisation identifies therapeutic targets for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023;94(11):954-961. [13] YIN KF, CHEN T, GU XJ, et al. Systematic druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies therapeutic targets for sarcopenia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024;15(4):1324-1334. [14] GAZIANO L, GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, PEREIRA AC, et al. Actionable druggable genome-wide Mendelian randomization identifies repurposing opportunities for COVID-19. Nat Med. 2021;27(4):668-676. [15] 1000 GENOMES PROJECT CONSORTIUM,AUTON A, BROOKS LD, et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526(7571):68-74. [16] FINAN C, GAULTON A, KRUGER FA, et al. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci Transl Med. 2017; 9(383):eaag1166. [17] STALEY JR, BLACKSHAW J, KAMAT MA, et al. PhenoScanner: a database of human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(20):3207-3209. [18] BOWDEN J, DAVEY SMITH G, BURGESS S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44(2):512-525. [19] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014; 10(5):e1004383. [20] KANEHISA M, FURUMICHI M, SATO Y, et al. KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D587-D592. [21] RASOOLY D, PELOSO GM, PEREIRA AC, et al. Genome-wide association analysis and Mendelian randomization proteomics identify drug targets for heart failure. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):3826. [22] YOO M, SHIN J, KIM J, et al. DSigDB: drug signatures database for gene set analysis. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(18):3069-3071. [23] KIM S, CHEN J, CHENG T, et al. PubChem 2023 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023; 51(D1):D1373-D1380. [24] DONG Y, TAO B, XUE X, et al. Molecular mechanism of Epicedium treatment for depression based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021;21(1):222. [25] SHICHIJO T, YASUNAGA JI, SATO K, et al. Vulnerability to APOBEC3G linked to the pathogenicity of deltaretroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121(13):e2309925121. [26] TALLURI S, SAMUR MK, BUON L, et al. Dysregulated APOBEC3G causes DNA damage and promotes genomic instability in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2021; 11(10):166. [27] WANG Y, WU S, ZHENG S, et al. APOBEC3G acts as a therapeutic target in mesenchymal gliomas by sensitizing cells to radiation-induced cell death. Oncotarget. 2017;8(33): 54285-54296. [28] PRABHU P, SHANDILYA SM, BRITAN-ROSICH E, et al. Inhibition of APOBEC3G activity impedes double-stranded DNA repair. FEBS J. 2016;283(1):112-129. [29] KOMOHARA Y, SUEKANE S, NOGUCHI M, et al. Expression of APOBEC3G in kidney cells. Tissue Antigens. 2007;69(1):95-98. [30] GARCÍA-RAMOS CL, VALENZUELA-GONZÁLEZ J, BAEZA-ÁLVAREZ VB, et al. Degenerative spondylolisthesis I: general principles. Acta Ortop Mex. 2020;34(5):324-328. [31] KANG L, ZHANG H, JIA C, et al. Epigenetic modifications of inflammation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2023;87:101902. [32] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60. [33] LI H, WANG C, HE T, et al. Mitochondrial Transfer from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Motor Neurons in Spinal Cord Injury Rats via Gap Junction. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):2017-2035. [34] XU M, FENG T, LIU B, et al. Engineered exosomes: desirable target-tracking characteristics for cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disease therapies. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8926-8944. [35] VIÑAS JL, BURGER D, ZIMPELMANN J, et al. Transfer of microRNA-486-5p from human endothelial colony forming cell-derived exosomes reduces ischemic kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2016;90(6):1238-1250. [36] ZHANG S, TEO KYW, CHUAH SJ, et al. MSC exosomes alleviate temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis by attenuating inflammation and restoring matrix homeostasis. Biomaterials. 2019;200:35-47. [37] WANG T, JIAN Z, BASKYS A, et al. MSC-derived exosomes protect against oxidative stress-induced skin injury via adaptive regulation of the NRF2 defense system. Biomaterials. 2020;257:120264. [38] XING H, ZHANG Z, MAO Q, et al. Injectable exosome-functionalized extracellular matrix hydrogel for metabolism balance and pyroptosis regulation in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):264. [39] GANDHI NS, MANCERA RL. The structure of glycosaminoglycans and their interactions with proteins. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008; 72(6):455-482. [40] SALBACH J, RACHNER TD, RAUNER M, et al. Regenerative potential of glycosaminoglycans for skin and bone. J Mol Med (Berl). 2012;90(6):625-635. [41] LIAN JB, JAVED A, ZAIDI SK, et al. Regulatory controls for osteoblast growth and differentiation: role of Runx/Cbfa/AML factors. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2004; 14(1-2):1-41. [42] BERRIDGE MJ, BOOTMAN MD, RODERICK HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4(7):517-529. [43] CAO Z, LIU D, ZHANG Q, et al. Aluminum Chloride Induces Osteoblasts Apoptosis via Disrupting Calcium Homeostasis and Activating Ca(2+)/CaMKII Signal Pathway. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016;169(2):247-253. [44] HU K, OLSEN BR. Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526. [45] AOKI Y, TAKAHASHI H, NAKAJIMA A, et al. Prevalence of lumbar spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis in patients with degenerative spinal disease. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):6739. [46] HEPWORTH EMW, HINTON SD. Pseudophosphatases as Regulators of MAPK Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12595. [47] FALCICCHIA C, TOZZI F, ARANCIO O, et al. Involvement of p38 MAPK in Synaptic Function and Dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5624. [48] JIA XB, ZHANG Q, XU L, et al. Lotus leaf flavonoids induce apoptosis of human lung cancer A549 cells through the ROS/p38 MAPK pathway. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):7. [49] WU Z, HE D, ZHAO S, et al. IL-17A/IL-17RA promotes invasion and activates MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression via p38 MAPK signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;455(1-2):195-206. [50] REN Y, OUYANG Z, HOU Z, et al. CIC Is a Mediator of the ERK1/2-DUSP6 Negative Feedback Loop. iScience. 2020;23(11): 101635. [51] FU B, LIANG J, HU J, et al. GPCR-MAPK signaling pathways underpin fitness trade-offs in whitefly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024;121(28):e2402407121. [52] WEN X, JIAO L, TAN H. MAPK/ERK Pathway as a Central Regulator in Vertebrate Organ Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3): 1464. [53] HWANG JH, PARK YS, KIM HS, et al. Yam-derived exosome-like nanovesicles stimulate osteoblast formation and prevent osteoporosis in mice. J Control Release. 2023;355:184-198. [54] CONG S, PENG Q, CAO L, et al. Diosgenin prevents periodontitis by inhibiting inflammation and promoting osteogenic differentiation. Oral Dis. 2024;30(4):2497-2510. [55] TOMÉ-BERMEJO F, PIÑERA AR, ALVAREZ L. Osteoporosis and the Management of Spinal Degenerative Disease (II). Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017;5(6):363-374. [56] HASSAN KZ, SHERMAN AL. Epidural Steroids. In: StatPearls[Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, 2025. [57] HERNÁNDEZ N, LÓPEZ-MORATÓ M, PERIANES MJ, et al. 4-Hydroxyestradiol improves mouse embryo quality, epidermal growth factor-binding capability in vitro and implantation rates. Mol Hum Reprod. 2021;27(2):gaaa075. [58] ALANKO J, SIEVI E, LÄHTEENMÄKI T, et al. Catechol estrogens as inhibitors of leukotriene synthesis. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998;55(1):101-104. [59] CHEN Q, TU Z, AI Y, et al. Forearm bone mineral density predicts screw loosening after lumbar fusion similar to lumbar Hounsfield unit value in patients with lumbar spondylolisthesis. Osteoporos Int. 2024;35(3):543-549. [60] LANXIANG W, BIN W, GE X, et al. Long-term exposure of 4-hydroxyestradiol induces the cancer cell characteristics via upregulating CYP1B1 in MCF-10A cells. Toxicol Mech Methods. 2019;29(9):686-692. |
| [1] | Huang Hailun, Wei Yatao, Liu Yongai, Wu Junzhe, Gao Heng, Sun Kui, Cao Zhenwen. Visualization analysis of lumbar spondylolisthesis treatment research from a bibliometric perspective [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2618-2628. |
| [2] | Wang Shoukang, Liang Gang, Liu Xiaolei, Hong Chunbo, Xin Bing. Comparison of imaging findings of paraspinal muscle tissue degeneration in patients with degenerative and isthmic spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(27): 5869-5875. |
| [3] | Song Hanlin, Hu Tianyu, Gao Haoran, Shi Yaozhou, Gao Xiao, Feng Hu. Influence of paravertebral muscles on spinopelvic sagittal plane in patients with isthmic spondylolisthesis: an evaluation of muscle quantity and quality [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(21): 4445-4451. |
| [4] | Shi Haoran, Guan Haishan, Wang Yueyong, Liu Tao. Decompression and fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis affect sagittal disequilibrium of the spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1956-1961. |
| [5] | Liu Changzhen, Sun Ning, Zhu Kai, Liu Xin, Dou Yongfeng, Wang Jianye, Bi Jingwei, Zhu Tengyue, Sun Zhaozhong. Safety of interbody fusion with one-hole split endoscope for L4/5 spondylolisthesis evaluated by three-dimensional CT [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(18): 2884-2891. |
| [6] | Li Yuqiao, Sun Tianwei, Ma Bin, Zhou Zhaohong, Dong Runbei, Wu Haiyang. A comparative study of imaging parameters and quality of life scores between subtypes of lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 943-948. |
| [7] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [8] | Qian Xuankun, Huang Hefei, Wu Chengcong, Liu Keting, Ou Hua, Zhang Jinpeng, Ren Jing, Wan Jianshan. Computer-assisted navigation combined with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spondylolisthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [9] | Wei Yangyang, Chen Jiacheng, Sun Jun, Wang Qiuan, Yuan Feng. Comparison of lumbar-pelvic sagittal parameters after single-level and double-level posterior lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5300-5306. |
| [10] | Zhou Junde, Fan Zhirong, Su Haitao, Peng Jiajie, Zhou Lin, Hong Weiwu, Huang Huida. Comparison of three-dimensional printing-assisted pedicle screw placement and traditional surgery for lumbar spondylolisthesis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(30): 4898-4904. |
| [11] | Wen Wangqiang, Xu Haoxiang, Zhang Zepei, Miao Jun. Related factors and biomechanical characteristics of lumbar facet joint degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3883-3889. |
| [12] | Liu Yang, Xu Baoshan, Xu Haiwei, Li Ning, Jiang Hongfeng, Wang Tao, Liu Yue. Imaging changes in spinal-pelvic sagittal alignment in sitting and standing positions in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(24): 3857-3861. |
| [13] | Li Xianzhou, Wang Qian, Zhang Cunxin . Lumbar spondylolisthesis: status and prospects of implant treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(4): 621-627. |
| [14] |
Rong Feilong, Yin Ruofeng, Feng Mengmeng, Zhang Boyin, Liu Yi, Zhao Baolin.
Correlation between degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis and spinal stenosis and muscle volume around the vertebral body: CT and MRI data analysis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3840-3845.
|
| [15] |
Ma Junfeng, Wang Wei, Wang Zikuo, Jiang Zehua, Long Mingxing, Yuan Jianjun, Zhu Rusen, Hu Wei, Zhang Xueli.
Correlation between facet joint effusion in magnetic resonance imaging and lumbar stability after interspinous and degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(24): 3845-3851.
|
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||