Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 1549-1557.doi: 10.12307/2026.575
Previous Articles Next Articles
Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases
Guo Ying1, Tian Feng2, Wang Chunfang1
- 1School of Basic Medicine, 2School of Stomatology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2024-12-18Accepted:2025-03-01Online:2026-02-28Published:2025-07-18 -
Contact:Wang Chunfang, Professor, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China Co-corresponding author: Tian Feng, Experimentalist, School of Stomatology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Guo Ying, Master candidate, School of Basic Medicine, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:Central Government Guided Local Science and Technology Development Fund, No. YDZJSX2022A056 (to WCF); Science and Technology Innovation Program for Higher Education Institutions in Shanxi Province, No. 2023L082 (to TF); Basic Research Program of Shanxi Province (Free Exploration Projects), No. 202203021212373 (to TF)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
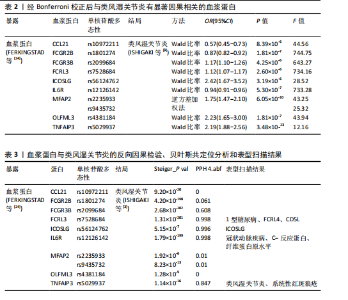
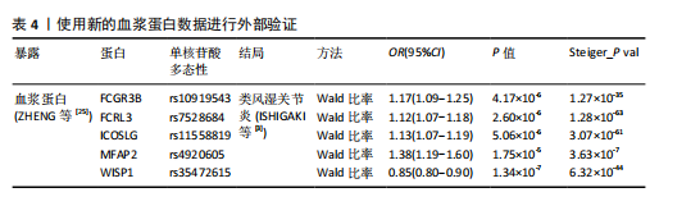
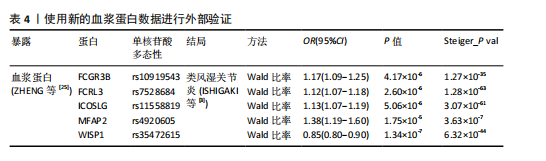
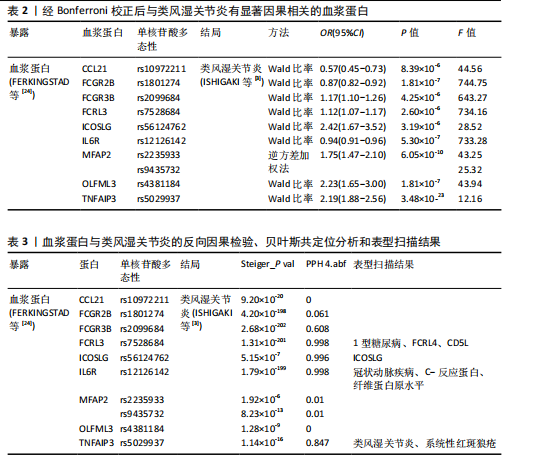
2.1 工具变量的选择 在选择全基因组独立(r2=0.001,window size=10 000 kb)和P < 5×10-8后,1 553个血浆蛋白的1 858个显著单核苷酸多态性被筛选出来,这些单核苷酸多态性的F值最小为19.53,表明弱仪器偏差的概率最小。 2.2 1 553个血浆蛋白对类风湿关节炎的因果影响 根据Bonferroni校正阈值(P=3.22×10-5,< 0.05/1 553),孟德尔随机化分析共筛选出9种与类风湿关节炎存在显著因果关系的蛋白质(表2),分别为:C-C motif chemokine 21(CCL21)、Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor II-b(FCGR2B)、Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-B(FCGR3B)、Fc receptor-like protein 3 (FCRL3)、ICOS ligand (ICOSLG)、Interleukin-6 receptor subunit alpha (IL6R)、Microfibrillar-associated protein 2(MFAP2)、Olfactomedin-like protein 3(OLFML3)和Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 3(TNFAIP3)。 研究结果显示,这9种蛋白与类风湿关节炎的风险存在不同的调控趋势,其中,CCL21、FCGR2B和IL6R与类风湿关节炎呈负向关联,表明这3种蛋白表达水平升高可降低类风湿关节炎的发生风险。在这组蛋白中,CCL21与类风湿关节炎的负相关性最强(OR=0.57),这意味着每增加一个单位的CCL21浓度,类风湿关节炎的相对风险将降低至原来的57%。相反,其余6种蛋白(如ICOSLG、TNFAIP3等)与类风湿关节炎呈正向关联,表明其表达水平升高可能增加类风湿关节炎的发生风险,其中ICOSLG对类风湿关节炎风险的影响最显著(OR=2.42),说明每增加一个单位的ICOSLG浓度,类风湿关节炎的发生风险将增加2.42倍。 需要特别注意的是,表2中的OR值反映了蛋白质水平与类风湿关节炎风险之间的关联方向和强度:OR > 1的蛋白(如ICOSLG、TNFAIP3等)表示其表达水平的增加与疾病风险增加有关;OR < 1的蛋白(如CCL21、IL6R等)则表示其表达水平的增加与疾病风险降低有关。 2.3 蛋白质与类风湿关节炎之间因果关系的敏感性分析结果 表3总结了反向因果分析、贝叶斯共定位分析及表型扫描的主要结果。在反向因果分析中,通过Steiger方向性检验评估类风湿关节炎是否对9种蛋白质存在反向因果影响,结果显示所有蛋白的Steiger检验P < 0.05,表明类风湿关节炎与这些蛋白之间不存在反向因果关系,支持蛋白水平变化先于类风湿关节炎发生。 贝叶斯共定位分析结果进一步验证了蛋白质与类风湿关节炎共享相同遗传变异的可能性,发现有4种蛋白质满足严格的共定位标准,包括FCRL3(PPH 4.abf=0.998)、ICOSLG(PPH 4.abf=0.996)、IL6R(PPH 4.abf=0.998)和TNFAIP3(PPH 4.abf=0.847)。结果表明上述蛋白质与类风湿关节炎共享相同的因果遗传变异位点,进一步支持它们与类风湿关节炎之间存在因果关联。 通过表型扫描分析探索了这些蛋白相关遗传位点与其他表型的关联性,进一步排查可能的混杂因素。例如,FCRL3的关键变异位点rs7528684与1型糖尿病、FCRL4和CD5L有关;IL6R的变异位点rs12126142与冠状动脉疾病、C-反应蛋白水平及纤维蛋白原水平相关;TNFAIP3的变异位点rs5029937与类风湿关节炎和系统性红斑狼疮显著相关。然而,这些性状与类风湿关节炎之间尚无确凿研究证据证明存在因果关系,因此,无法将其作为混杂因素予以排除。 综合各项分析结果,最终确认FCRL3、ICOSLG、IL6R和TNFAIP3为与类风湿关节炎存在可靠因果关系的关键蛋白。 2.4 外部验证结果 为了进一步验证结果的可靠性,减少偶然性带来的影响,在同一数据集中采用不同的遗传变异和显著性策略进行了外部验证分析。根据表4的结果,验证分析显示FCGR3B、FCRL3、ICOSLG和MFAP2与最初因果分析结果一致,表明这些蛋"

白质与类风湿关节炎之间的因果关系具有较高的稳健性。然而,由于新的血浆蛋白数据覆盖范围有限,IL6R和TNFAIP3的相关遗传变异未能在该数据集中找到匹配信息,因此,未能对其进行外部验证。 尽管部分蛋白因数据缺失而未能完全验证,但验证结果支持了最初分析的总体准确性,尤其是FCRL3和ICOSLG等蛋白的显著关联在多种策略下均表现出一致性。这进一步加强了这些蛋白作为类风湿关节炎潜在因果分子的可信度,为后续研究提供了可靠的依据。 2.5 小分子药物的筛选和分子对接 经过一系列分析和鉴定,最终明确了4种与类风湿关节炎存在可靠因果关系的关键蛋白质:FCRL3、IL6R、ICOSLG和TNFAIP3。为了进一步探索其潜在的药物靶点价值,利用DsigDB数据库筛选了针对这4种蛋白的小分子化合物。基于调整后的P值(P < 0.05)进行筛选后,发现一种名为benzo[a]pyrene的小分子化合物能够同时靶向上述4种蛋白质。因此,为进一步评估其结合能力和模式,通过研究方法获取了benzo[a]pyrene与4种蛋白质的三维结构,并依次计算了它们之间的结合能,分析结果见表5,benzo[a]pyrene与FCRL3、IL6R、ICOSLG和TNFAIP3的最高结合能分别为-7.6,-9.2,-7.1,-7.2 kJ/mol,这些结合能均达到分子对接的有效阈值,表明benzo[a]pyrene与上述蛋白之间具有良好的结合稳定性。另外,通过三维分子对接分析直观呈现了benzo[a]pyrene与每种蛋白结合时的最佳构象,见图2。"
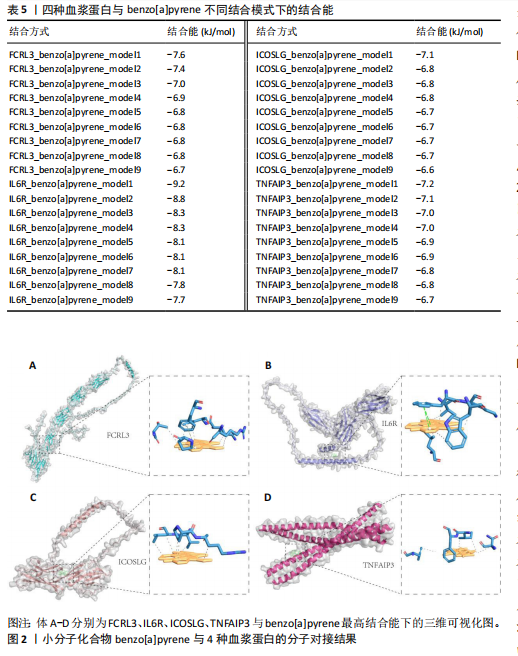
| [1] CARRIÓN M, FROMMER KW, PÉREZ-GARCÍA S, et al. The Adipokine Network in Rheumatic Joint Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(17):4091. [2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, MCINNES IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016; 388(10055):2023-2038. [3] ISHIGAKI K, SAKAUE S, TERAO C, et al. Multi-ancestry genome-wide association analyses identify novel genetic mechanisms in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet. 2022; 54(11):1640-1651. [4] SHAMS S, MARTINEZ JM, DAWSON JRD, et al. The Therapeutic Landscape of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current State and Future Directions. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:680043. [5] HUANG J, FU X, CHEN X, et al. Promising Therapeutic Targets for Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:686155. [6] 赵泽良.类风湿性关节炎的治疗研究进展[J].临床医学进展,2023,13(4):6993-6998. [7] SUN BB, MARANVILLE JC, PETERS JE, et al. Genomic atlas of the human plasma proteome. Nature. 2018;558(7708):73. [8] EMILSSON V, GUDMUNDSDOTTIR V, GUDJONSSON A, et al. Coding and regulatory variants are associated with serum protein levels and disease. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):481. [9] NYS G, COBRAIVILLE G, SERVAIS AC, et al. Targeted proteomics reveals serum amyloid A variants and alarmins S100A8-S100A9 as key plasma biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis. Talanta. 2019;204:507-517. [10] POPE JE, CHOY EH. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021;51(1):219-229. [11] ZHOU J, DAI Y, LIN Y, et al. Association between serum amyloid A and rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;52: 151943. [12] SCHERER HU, HÄUPL T, BURMESTER GR. The etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102400. [13] IRURE-VENTURA J, DÍAZ-TOLEDO M, PALAZUELOS-CAYÓN N, et al. Impact of Likelihood Ratios of Rheumatoid Factor and Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody in Clinical Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis by Two Available Platforms. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025;15(2):135. [14] DÍAZ-GONZÁLEZ F, HERNÁNDEZ-HERNÁNDEZ MV. Rheumatoid arthritis. Med Clin (Barc). 2023;161:533-542. [15] SANTOS SAVIO A, MACHADO DIAZ AC, CHICO CAPOTE A, et al. Differential expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-15Ralpha, IL-15, IL-6 and TNFalpha in synovial fluid from Rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015; 16:51. [16] ANDERSON NL. The clinical plasma proteome: a survey of clinical assays for proteins in plasma and serum. Clin Chem. 2010;56(2):177-185. [17] GU Y, JIN Q, HU J, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites and metabolic pathways on osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):357. [18] PIERCE BL, BURGESS S. Efficient design for Mendelian randomization studies: subsample and 2-sample instrumental variable estimators. Am J Epidemiol. 2013; 178(7):1177-1184. [19] HARTWIG FP, DAVIES NM, HEMANI G, et al. Two-sample Mendelian randomization: avoiding the downsides of a powerful, widely applicable but potentially fallible technique. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45:1717-1726. [20] TERCIC D, BOZIC B. The basis of the synovial fluid analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2001;39:1221-1226. [21] REAY WR, CAIRNS MJ. Advancing the use of genome-wide association studies for drug repurposing. Nat Rev Genet. 2021; 22(10):658-671. [22] EMDIN CA, KHERA AV, KATHIRESAN S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA. 2017;318: 1925-1926. [23] Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621. [24] FERKINGSTAD E, SULEM P, ATLASON BA, SVEINBJORNSSON G, et al. Large-scale integration of the plasma proteome with genetics and disease. Nat Genet. 2021;53:1712-1721. [25] ZHENG J, HABERLAND V, BAIRD D, et al. Phenome-wide Mendelian randomization mapping the influence of the plasma proteome on complex diseases. Nature genetics. 2020;52(10):1122-1131. [26] ZHANG J, DUTTA D, KÖTTGEN A, et al. Plasma proteome analyses in individuals of European and African ancestry identify cis-pQTLs and models for proteome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2022;54(5): 593-602. [27] WANG Q, DAI H, HOU T, et al. Dissecting Causal Relationships Between Gut Microbiota, Blood Metabolites, and Stroke: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J Stroke. 2023;25(3):350-360. [28] YAN W, JIANG M, HU W, et al. Causality Investigation between Gut Microbiota, Derived Metabolites, and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4544. [29] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol. 2016; 145(6):1961-1974. [30] CHENG J, YANG L, YE Y, et al. Mendelian Randomisation Analysis of Causal Association between Lifestyle, Health Factors, and Keratoconus. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024;11:221. [31] ZHANG Y, XIE J, WEN S, et al. Evaluating the causal effect of circulating proteome on the risk of osteoarthritis-related traits. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023;82(12):1606-1617. [32] BURGESS S, BUTTERWORTH A, THOMPSON SG. Mendelian Randomization Analysis With Multiple Genetic Variants Using Summarized Data. Genet Epidemiol. 2013;37(7):658-665. [33] HEMANI G, TILLING K, DAVEY SMITH G. Orienting the causal relationship between imprecisely measured traits using GWAS summary data. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(11):e1007081. [34] WALLACE C. A more accurate method for colocalisation analysis allowing for multiple causal variants. PLoS Genet. 2021; 17(9):e1009440. [35] GIAMBARTOLOMEI C, VUKCEVIC D, SCHADT EE, et al. Bayesian Test for Colocalisation between Pairs of Genetic Association Studies Using Summary Statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(5):e1004383. [36] KAMAT MA, BLACKSHAW JA, YOUNG R, et al. PhenoScanner V2: an expanded tool for searching human genotype-phenotype associations. Bioinformatics. 2019;35(22):4851-4853. [37] BURLEY SK, BHIKADIYA C, BI C, et al. RCSB Protein Data Bank: powerful new tools for exploring 3D structures of biological macromolecules for basic and applied research and education in fundamental biology, biomedicine, biotechnology, bioengineering and energy sciences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D437-451. [38] MCGOWAN LM, DAVEY SMITH G, GAUNT TR, et al. Integrating Mendelian randomization and multiple-trait colocalization to uncover cell-specific inflammatory drivers of autoimmune and atopic disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2019;28(19):3293-2300. [39] MONTGOMERY SB, DERMITZAKIS ET. From expression QTLs to personalized transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(4): 277-282. [40] LI FJ, SCHREEDER DM, LI R, et al. FCRL3 promotes TLR9-induced B-cell activation and suppresses plasma cell differentiation. Eur J Immunol. 2013;43(11):2980-2992. [41] AGARWAL S, KRAUS Z, DEMENT-BROWN J, et al. Human Fc Receptor-like 3 Inhibits Regulatory T Cell Function and Binds Secretory IgA. Cell Rep. 2020;30(5):1292-1299.e3. [42] BAJPAI UD, SWAINSON LA, MOLD JE, et al. A functional variant in FCRL3 is associated with higher Fc receptor-like 3 expression on T cell subsets and rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(8):2451-2459. [43] CHALAYER E, GRAMONT B, ZEKRE F, et al. Fc receptors gone wrong: A comprehensive review of their roles in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 2022;21(3):103016. [44] LIN X, ZHANG Y, CHEN Q. FCRL3 gene polymorphisms as risk factors for rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 2016; 77(2):223-229. [45] TANAKA T, NARAZAKI M, MASUDA K, et al. Regulation of IL-6 in Immunity and Diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;941:79-88. [46] EDWARDS CJ, WILLIAMS E. The role of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis-associated osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2010;21(8):1287-1293. [47] KHAN AW, FAROOQ M, HWANG MJ, et al. Autoimmune Neuroinflammatory Diseases: Role of Interleukins. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(9):7960. [48] MARINOU I, WALTERS K, WINFIELD J, et al. A gain of function polymorphism in the interleukin 6 receptor influences RA susceptibility. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69(6):1191-1194. [49] HER M, KIM D, OH M, et al. Increased expression of soluble inducible costimulator ligand (ICOSL) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2009;18(6):501-507. [50] HUO FF, ZOU XY, ZHANG Y, et al. Aire attenuate collagen-induced arthritis by suppressing T follicular helper cells through ICOSL. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025;144: 113732. [51] MOONEY EC, SAHINGUR SE. The Ubiquitin System and A20: Implications in Health and Disease. J Dent Res. 2021;100(1):10-20. [52] RAMOS PS, CRISWELL LA, MOSER KL, et al. A Comprehensive Analysis of Shared Loci between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Sixteen Autoimmune Diseases Reveals Limited Genetic Overlap. PLoS Genet. 2011;7(12):e1002406. [53] GRAHAM RR, COTSAPAS C, DAVIES L, et al. Genetic Variants Near TNFAIP3 on 6q23 are Associated with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Nat Genet. 2008; 40(9):1059-1061. [54] CICCACCI C, LATINI A, PERRICONE C, CONIGLIARO P, et al. TNFAIP3 Gene Polymorphisms in Three Common Autoimmune Diseases: Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Primary Sjogren Syndrome—Association with Disease Susceptibility and Clinical Phenotypes in Italian Patients. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:6728694. [55] LEE YH, SONG GG. Associations between TNFAIP3 Polymorphisms and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Update with Trial Sequential Analysis. Public Health Genomics. 2022: 1-11. doi: 10.1159/000526212. |
| [1] | Cao Xinyan, Yu Zifu, Leng Xiaoxuan, Gao Shiai, Chen Jinhui, Liu Xihua. Effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current stimulation on motor function and gait in children with cerebral palsy: a network meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1539-1548. |
| [2] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [3] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [4] | Zheng Yin, Wu Zhenhua, Zhang Cheng, Ruan Kexin, Gang Xiaolin, Ji Hong. Safety and efficacy of immunoadsorption therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: a network meta-analysis and systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1260-1268. |
| [5] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [6] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [7] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [8] | Yang Zhijie, Zhao Rui, Yang Haolin, Li Xiaoyun, Li Yangbo, Huang Jiachun, Lin Yanping, Wan Lei, HuangHongxing. Postmenopausal osteoporosis: predictive values of muscle mass, grip strength, and appendicular skeletal muscle index [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1073-1080. |
| [9] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [10] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [11] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [12] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [13] | Bao Zhuoma, Hou Ziming, Jiang Lu, Li Weiyi, Zhang Zongxing, Liu Daozhong, Yuan Lin. Effect and mechanism by which Pterocarya hupehensis skan total flavonoids regulates the proliferation, migration and apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 816-823. |
| [14] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [15] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||