Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (22): 5682-5693.doi: 10.12307/2026.141
Previous Articles Next Articles
Gushukang Granule-containing drug serum improves dexamethasone-induced atrophy of C2C12 myotubes via regulating mitochondrial homeostasis
Wei Wei1, Liu Hongfei2, Qi Xiaonan3, Liu Yantong2, Wang Deyu2, Yu Zhitong2, Qiao Chunlin1, Wang Shixuan1, Teng Hai1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China; 2Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110087, Liaoning Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics 1, Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110031, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2025-03-12Accepted:2025-08-06Online:2026-08-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Teng Hai, MS, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Wei Wei, PhD, Attending physician, Department of Orthopedics, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:Liaoning Provincial Department of Education General Project, No. JYTMS20231832 (to WW); National Natural Science Foundation for the Youth, No. 82305275 (to QXN); Doctoral Research Initiation Fund Program Project of Liaoning Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. 2023-BS-050 (to WW); National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine National Famous Elderly Chinese Medicine Expert Inheritance Workshop: 2022 Wang Shixuan National Elderly Chinese Medicine Expert Inheritance Workshop Construction Project, No. (2022)75 (to WSX)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Wei, Liu Hongfei, Qi Xiaonan, Liu Yantong, Wang Deyu, Yu Zhitong, Qiao Chunlin, Wang Shixuan, Teng Hai. Gushukang Granule-containing drug serum improves dexamethasone-induced atrophy of C2C12 myotubes via regulating mitochondrial homeostasis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5682-5693.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
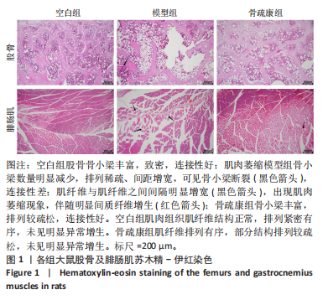
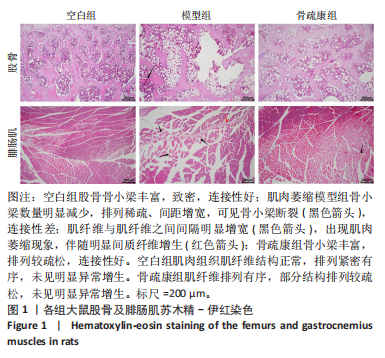
2.1 实验动物数量分析 实验选用SD大鼠36只,造模后无死亡,全部进入结果分析。 2.2 苏木精-伊红染色结果 (1)股骨苏木精-伊红染色结果(图1):在光学显微镜下观察到空白组股骨骨小梁丰富,致密,连接性好;肌肉萎缩的模型组骨小梁数量明显减少,排列稀疏、间距增宽,可见骨小梁断裂(黑色箭头),连接性差;骨疏康组骨小梁丰富,排列较疏松,连接性好。 (2)腓肠肌苏木精-伊红染色结果(图1):在光学显微镜下观察到空白组肌纤维结构正常,排列紧密有序,未见明显异常增生;模型组肌纤维排列稀疏、紊乱,肌纤维与肌纤维之间间隔明显增宽(黑色箭头),出现肌肉萎缩现象,伴随明显间质纤维增生(红色箭头);骨疏康组肌纤维排列有序,部分结构排列较疏松(黑色箭头),未见明显异常增生。"
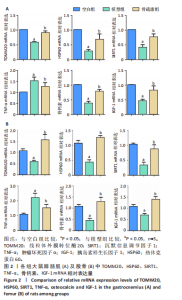
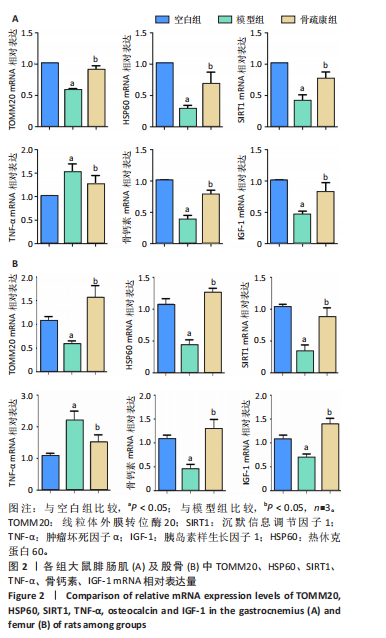
2.3 各组大鼠腓肠肌及股骨中沉默信息调节因子 1、肿瘤坏死因子α、骨钙素、胰岛素样生长因子1、线粒体外膜转位酶20、热休克蛋白60 mRNA表达水平 如图2所示,与空白组相比,模型组肌肉、股骨组织中沉默信息调节因子 1、骨钙素、胰岛素样生长因子1、线粒体外膜转位酶20、热休克蛋白60 mRNA表达降低(P < 0.05);与空白组相比,模型组肌肉、股骨组织中肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05)。与模型组相比,骨疏康组肌肉、股骨组织中沉默信息调节因子 1、骨钙素、胰岛素样生长因子1、线粒体外膜转位酶20、热休克蛋白60 mRNA表达升高(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,骨疏康组肌肉、股骨组织中肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达降低,但仍较空白组稍高(P < 0.05)。"
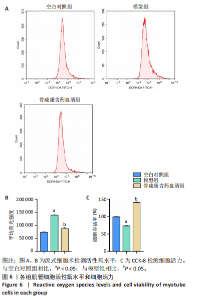
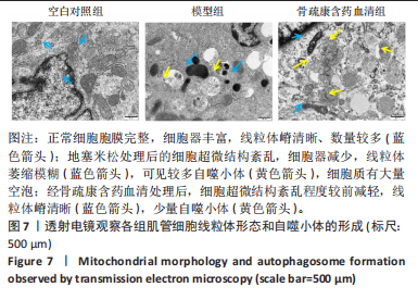
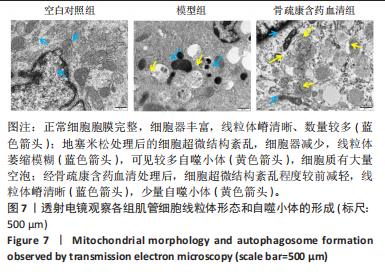
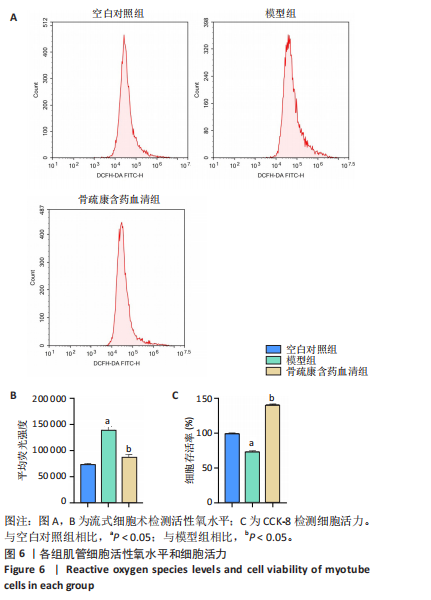
2.7 骨疏康颗粒对地塞米松诱导的C2C12肌萎缩具有抑制作用 流式细胞术和CCK-8结果表明,地塞米松诱导的模型组C2C12细胞活性氧水平显著升高,细胞活力显著降低;经骨疏康含药血清处理后,活性氧水平显著降低,细胞活力显著升高(图6)。透射电镜观察各组细胞线粒体形态和自噬小体的形成,结果显示空白对照组细胞超微结构正常,胞膜完整,细胞器丰富,线粒体嵴清晰、数量较多(蓝色箭头);地塞米松处理后的细胞超微结构紊乱,细胞器减少,线粒体萎缩模糊(蓝色箭头),可见较多自噬小体(黄色箭头),细胞质有大量空泡;经骨疏康含药血清处理后,细胞超微结构紊乱程度较前减轻,线粒体嵴清晰(蓝色箭头),少量自噬小体(黄色箭头)(图7)。"
| [1] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, SAYER AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191): 2636-2646. [2] 孔洁,李树铁,黄攀登,等.中国老年居民肌肉减少症与全因死亡率的关联实证分析[J/OL].上海预防医学,1-14[2025-01-21].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1635.R.20250107.1507.006.html. [3] GILLESPIE LD, ROBERTSON MC, GILLESPIE WJ, et al. Interventions for preventing falls in older people living in the community. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;2012(9):CD007146. [4] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019; 48(4):601. [5] COLETTI C, ACOSTA GF, KESLACY S, et al. Exercise-mediated reinnervation of skeletal muscle in elderly people: An update. Eur J Transl Myol. 2022;32(1):10416. [6] NORDSBORG NB, BONNE TC, BREENFELDT ANDERSEN A, et al. Glucocorticoids Accelerate Erythropoiesis in Healthy Humans-Should the Use in Sports Be Reevaluated? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2023;55(7): 1334-1341. [7] ZHANG L, LI M, WANG W, et al. Celecoxib alleviates denervation-induced muscle atrophy by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress and improving microcirculation. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022; 203:115186. [8] 谢晓婷,何永,马彦韬,等.富血小板血浆结合周期性机械牵拉对C2C12肌管萎缩的影响及机制探讨[J].中国康复医学杂志,2025, 40(1):8-14. [9] 白雪,崔立敏,许佳阳.肌少症筛查、评估工具及干预措施的研究进展[J].吉林医药学院学报,2025,46(4):295-300. [10] 杜倩,李小会,陈丽名,等.中药基于“肠-肌肉轴”及肠道菌群治疗慢性肾脏病肌少症研究进展[J/OL].中医学报,1-8[2024-10-21].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/41.1411.R.20240808.1328.030.html. [11] 侯成志,韩佳童,魏光成,等.骨疏康干预破骨细胞:激活核因子E2相关因子2调控c-Fos/NFATc1通路[J].中国组织工程研究, 2025,29(2):279-285. [12] 唐彬彬,袁一峰,刘康,等.骨疏康颗粒影响破骨细胞外泌体治疗绝经后骨质疏松的机制研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2024,44(3): 339-347. [13] 徐叔云,卞如濂,陈修主编.药理实验方法学[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2002:911-916. [14] 张瑞鹏,李杰.lncRNA GPRC5D-AS1对地塞米松诱导小鼠成肌细胞肌萎缩的抵抗和再生作用及其机制[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2023,49(6):1457-1465. [15] 刘桂敏,孙建辉,李建良,等.肾虚证临床与动物实验研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(23):269-280. [16] GIACOMELLO M, PYAKUREL A, GLYTSOU C, et al. The cell biology of mitochondrial membrane dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(4): 204-224. [17] RAPAPORT D, NEUPERT W, LILL R. Mitochondrial protein import. Tom40 plays a major role in targeting and translocation of preproteins by forming a specific binding site for the presequence. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(30):18725-18731. [18] LÓPEZ-OTÍN C, BLASCO MA, PARTRIDGE L, et al. Hallmarks of aging: An expanding universe. Cell. 2023;186(2):243-278. [19] WANG S, HE F, WU H, et al. Health-Promoting Activities and Associated Mechanisms of Polygonati Rhizoma Polysaccharides. Molecules. 2023;28(3):1350. [20] SHAO S, YE X, SU W, et al. Curcumin alleviates Alzheimer’s disease by inhibiting inflammatory response, oxidative stress and activating the AMPK pathway. J Chem Neuroanat. 2023;134:102363. [21] TIAN X, LIANG T, LIU Y, et al. Extraction, Structural Characterization, and Biological Functions of Lycium Barbarum Polysaccharides: A Review. Biomolecules. 2019;9(9):389. [22] LIU H, ZHEN C, XIE J, et al. TFAM is an autophagy receptor that limits inflammation by binding to cytoplasmic mitochondrial DNA. Nat Cell Biol. 2024;26(6):878-891. [23] ZHANG H, QI G, WANG K, et al. Oxidative stress: Roles in skeletal muscle atrophy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;214:115664. [24] BJØRKØY G, LAMARK T, BRECH A, et al. p62/SQSTM1 forms protein aggregates degraded by autophagy and has a protective effect on huntingtin-induced cell death. J Cell Biol. 2005;171(4):603-614. [25] MIZUSHIMA N, KOMATSU M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011;147(4):728-741. [26] HAJAM YA, RANI R, GANIE SY, et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells. 2022;11(3):552. [27] CHEN C, ZHOU M, GE Y, et al. SIRT1 and aging related signaling pathways. Mech Ageing Dev. 2020;187:111215. [28] OWJFARD M, RAHIMIAN Z, KARIMI F, et al. A comprehensive review on the neuroprotective potential of resveratrol in ischemic stroke. Heliyon. 2024;10(14):e34121. [29] 谭敏,黄丽端,侯艳红,等.补骨脂异黄酮调控SIRT1/NF-κB依赖的信号通路抑制Ang II诱导的心肌肥大[J].中国药理学通报,2025, 41(6):1142-1148. [30] MUNTEANU C, ONOSE G, POȘTARU M, et al. Hydrogen Sulfide and Gut Microbiota: Their Synergistic Role in Modulating Sirtuin Activity and Potential Therapeutic Implications for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024;17(11):1480. [31] SIRELKHATIM A, MAHMUD S, SEENI A, et al. Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism. Nanomicro Lett. 2015;7(3):219-242. [32] 郭孝静,秦欢,项栋良,等.铁死亡在骨关节炎中的作用及中医药干预研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2024,30(19):263-272. [33] OKOYE CN, KOREN SA, WOJTOVICH AP. Mitochondrial complex I ROS production and redox signaling in hypoxia. Redox Biol. 2023;67: 102926. [34] 高松林,韦柳婷,管晓,等.基于生物信息学分析非酒精性脂肪性肝病的线粒体自噬相关基因及防治中药筛选[J].中草药,2024, 55(19):6655-6665. [35] ZHAO L, ZHANG H, LI N, et al. Network pharmacology, a promising approach to reveal the pharmacology mechanism of Chinese medicine formula. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;309:116306. [36] WEI Z, CHEN J, ZUO F, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine has great potential as candidate drugs for lung cancer: A review. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;300:115748. [37] LOCKETT J, INDER WJ, CLIFTON VL. The Glucocorticoid Receptor: Isoforms, Functions, and Contribution to Glucocorticoid Sensitivity. Endocr Rev. 2024;45(4):593-624. [38] ZHANG X, FENG C, YUAN T, et al. Inhibition of protein disulfide isomerase mitigates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by suppressing osteoclast activity through the reduction of cellular oxidative stress. Chem Biol Interact. 2024;404:111263. [39] HUANG M, YAN Y, DENG Z, et al. Saikosaponin A and D attenuate skeletal muscle atrophy in chronic kidney disease by reducing oxidative stress through activation of PI3K/AKT/Nrf2 pathway. Phytomedicine. 2023;114:154766. [40] 商岚清,刘永智,周广智,等.从“骨肉不相亲”探讨牛膝活性成分β-蜕皮甾酮论治骨质疏松的研究进展[J].中华中医药学刊, 2024,42(4):254-258. [41] 朱汉民,王松,肖文琳,等.线粒体自噬调控骨代谢[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(8):1676-1683. [42] 钱琨,李子卿,孙水.内质网应激与常见退行性骨骼疾病的发生与发展[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(6):1285-1295. |
| [1] | Zhou Jian, Zhang Tao, Zhou Weili, Zhao Xingcheng, Wang Jun, Shen Jie, Qian Li, Lu Ming. Effects of resistance training on quadriceps mass and knee joint function in patients with osteoporosis and sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1081-1088. |
| [2] | Li Guangzheng, Li Wei, Zhang Bochun, Ding Haoqin, Zhou Zhongqi, Li Gang, Liang Xuezhen. A prediction model for sarcopenia in postmenopausal women: information analysis based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 849-857. |
| [3] | Sun Jiahe, Shi Jipeng, Zhu Tianrui, Quan Helong, Xu Hongqi. Effect of exercise intervention in elderly individuals with sarcopenia and its comorbidities: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 997-1007. |
| [4] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [5] | Zhang Zheng, Zhang Yibo, Xu Bin, Yan Shichao, Guo Hui. Sarcopenia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: analysis of the gut microbiota [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6000-6009. |
| [6] | Yin Xingxiao, Jiang Yang, Song Yanping, Yao Na, Shen Zhen, Li Yanqi, Song Yueyu, Peng Hao, Chen Qigang. Association between sarcopenia and osteoporosis: a genome-wide data analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6030-6039. |
| [7] | Liao Guibin, Wu Yixuan, Tang Jing, Huang Jinke, Wang Jun, Yan Ziqi, Liu Shujun, Zhang Haiyan. Shared genetic basis and causal relationship between nutrition, nutritional status and inflammatory bowel disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5876-5885. |
| [8] | Wang Siwei, Yao Xiaosheng, Qi Xiaonan, Wang Yu, Cui Haijian, Zhao Jiaxuan. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 mediates mitophagy to regulate osteogenesis and myogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(18): 4557-4567. |
| [9] | Li Xinying, Zhang Wenhua, Li Xun, Zhang Shihua, Wang Xiaoqiang. Regulation of bone metabolism by myokines under resistance exercise intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2475-2483. |
| [10] | Yuan Weiyuan, Lei Qinhui, Li Xiuqi, Lu Tiezhu, Fu Ziwen, Liang Zhili, Ji Shaoyang, Li Yijia, Ren Yu . Therapeutic effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their exosomes on dexamethasone-induced sarcopenia in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(1): 58-67. |
| [11] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei, Zhou Jiatan. Based on Mendelian randomization, the causal relationship between 1400 metabolites and sarcopenia and the correlation analysis of cardiovascular disease were investigated [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-11. |
| [12] | Li Jiatong, Jin Yue, Liu Runjia, Song Bowen, Zhu Xiaoqian, Li Nianhu . Association between thyroid function levels and phenotypes associated with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1312-1320. |
| [13] | Jiang Siqi, Huang Huanhuan, Yu Xinyu, Peng Ying, Zhou Wei, Zhao Qinghua. Meta-analysis of dose-effect of exercise on improving muscle health in community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6295-6304. |
| [14] | Chen Jiayong, Tang Meiling, Lu Jianqi, Pang Yan, Yang Shangbing, Mao Meiling, Luo Wenkuan, Lu Wei. Causal association between metabolites and sarcopenia: a big data analysis of genome-wide association studies in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6369-6380. |
| [15] | Sun Yahui, Wang Yufeng, Guo Chao, Yao Junjie, Ji Yuanyuan, Li Zhongxu, Lou Huijuan, Jiang Jinglei, Sun Yiping, Xu Jing, Cong Deyu. Effect of massage on extracellular matrix collagen deposition in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5549-5555. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||