Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (22): 5694-5706.doi: 10.12307/2026.171
Previous Articles Next Articles
Biomarkers for diabetic foot ulcers: single-cell transcriptomics bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation
Yang Wenyan1, 2, Wang Huayu1, Yang Like1, Pang Xue3, Wang Yutao1, 4
- 1First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Ulcer and Vascular Diseases, Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated TCM-WM·HEBEI, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei Province, China; 3Department of Proctology, First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 4Department of Peripheral Vascular Diseases, Guang'anmen Hospital Jinan Hospital (Jinan Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2025-06-26Accepted:2025-10-11Online:2026-08-08Published:2025-12-26 -
Contact:Wang Yutao, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; Department of Peripheral Vascular Diseases, Guang'anmen Hospital Jinan Hospital (Jinan Municipal Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine), China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Jinan 250012, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Yang Wenyan, MS candidate, First Clinical Medical College, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250355, Shandong Province, China; Department of Ulcer and Vascular Diseases, Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated TCM-WM·HEBEI, Cangzhou 061000, Hebei Province, China -
Supported by:The Young Scientists Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82104860 (to WYT); Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Development Program of Shandong Province, China, No. 2019-0559 (to WYT); Health Commission Science and Technology Program Project of Jinan, China, No. 2019-1-23 (to WYT); Zhang Hongxing National Famous Traditional Chinese Medicine Experts Inheritance Studio Construction Project, No. [2022] 75 (to WYT); Shandong Provincial Health and Medical Management Research Center Scientific Research Project of Shandong Province,China, No. 20240430-044 (to PX); Health and Medical Industry High-Level Talent Special Fund Support of Jinan, China, No. 202412 (to WYT)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Wenyan, Wang Huayu, Yang Like, Pang Xue, Wang Yutao. Biomarkers for diabetic foot ulcers: single-cell transcriptomics bioinformatics analysis and experimental validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(22): 5694-5706.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
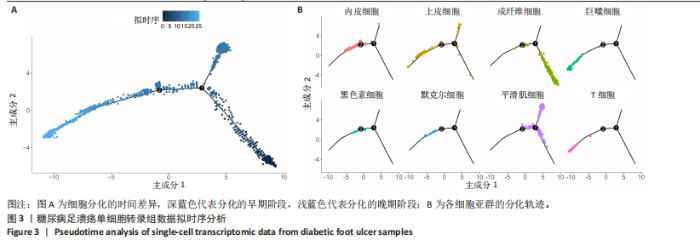
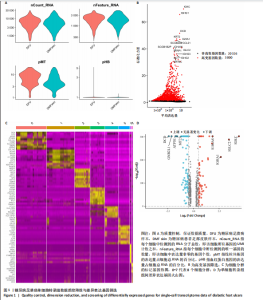
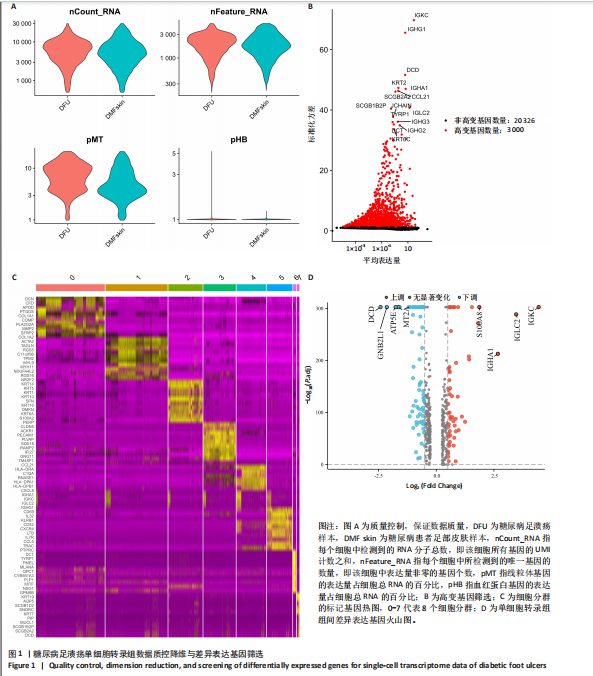
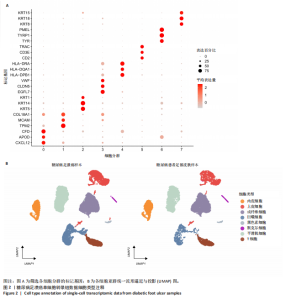
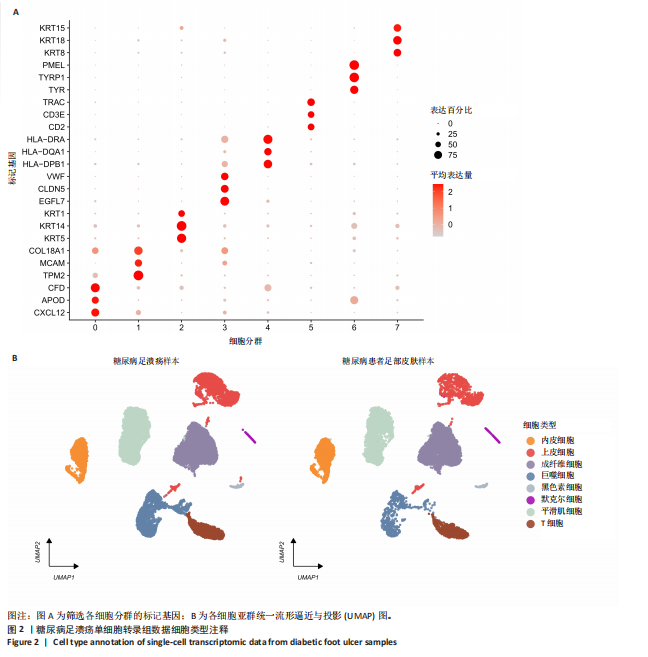
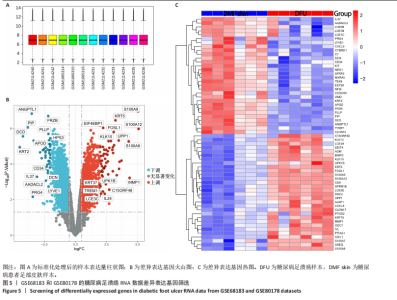
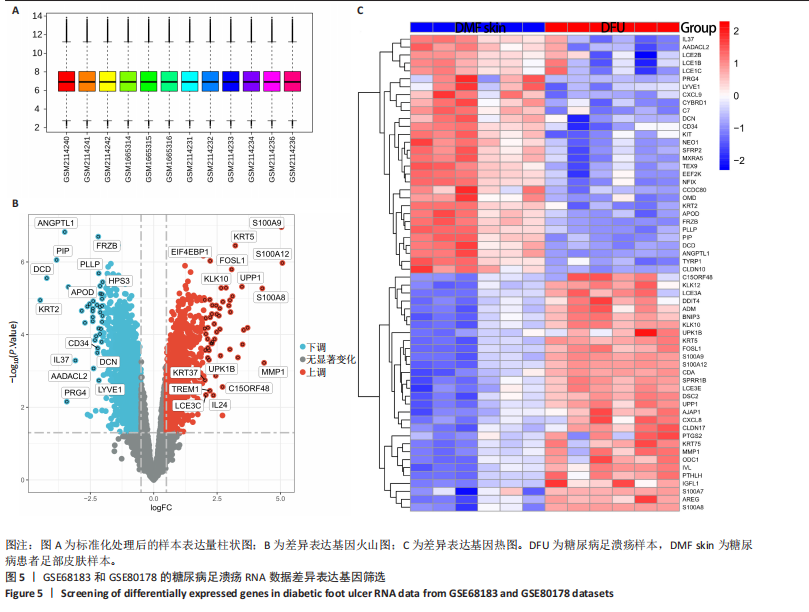
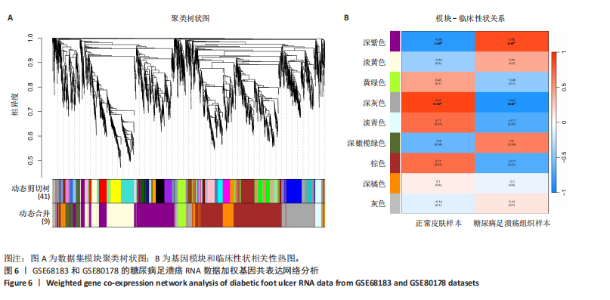
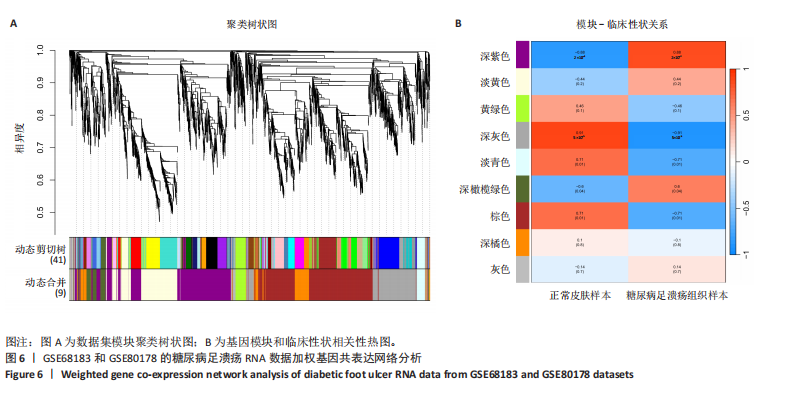
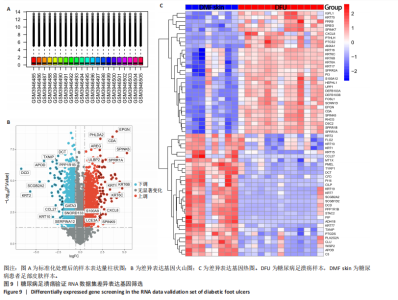
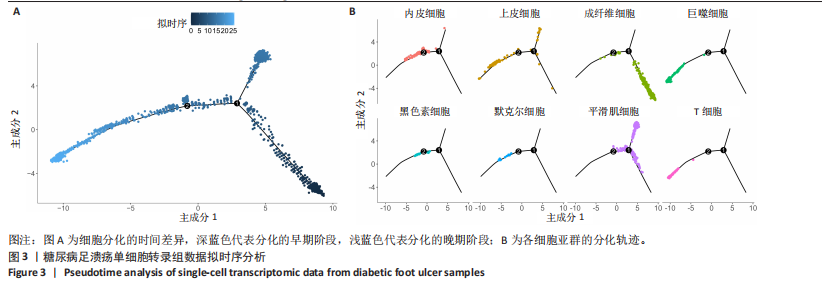
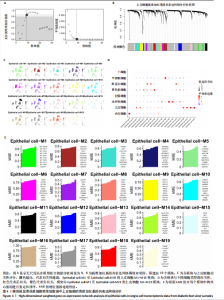
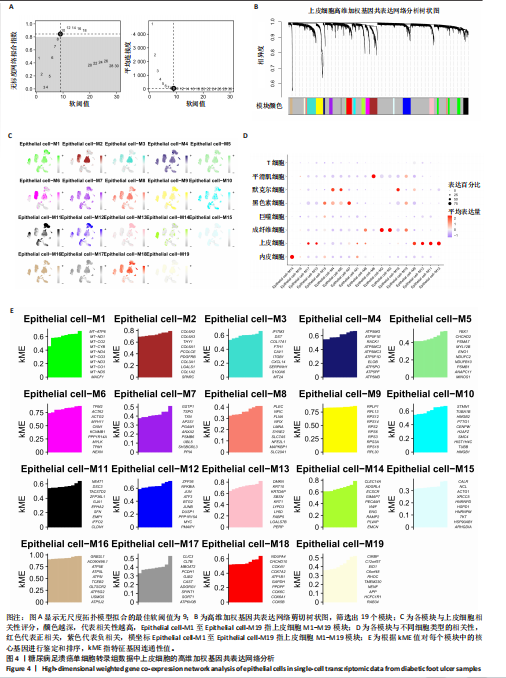
胞分化贯穿了整个病理过程(图3B)。 2.4 高维加权基因共表达网络分析 高维加权基因共表达网络分析与上皮细胞功能显著相关的基因模块,筛选最优软阈值为9 (图4A),合并获得19个基因模块(图4B)。Epithelial M-7、Epithelial M-9、Epithelial M-10、Epithelial M-11、Epithelial M-12和Epithelial M-13模块中的基因与上皮细胞功能呈正相关(图4C,D);根据kME值筛选各模块的核心基因共476个(图4E)。 2.5 转录组数据质控和差异基因筛选 对RNA数据集测序数据进行标准化处理(图5A),获得8 675个表达量大于0的基因,筛选获得913个差异表达基因,其中差异表达上调基因343个、差异表达下调基因570个,绘制差异表达基因火山图和热图(图5B,C)。 2.6 RNA数据加权基因共表达网络分析 使用“WGCNA”包的“pickSoftThreshold”函数对表达量 > 0的基因进行筛选,将软阈值设为30,建立共表达网络,将最优软阈值设为0.25,最小模块基因数设"
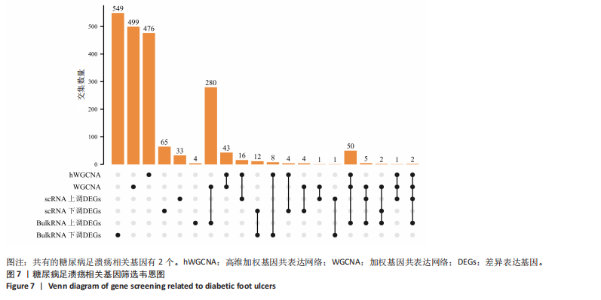
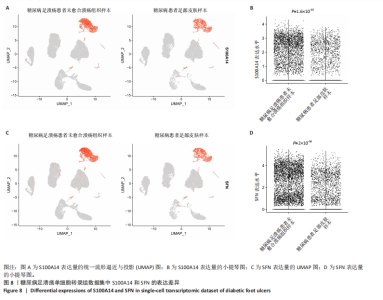
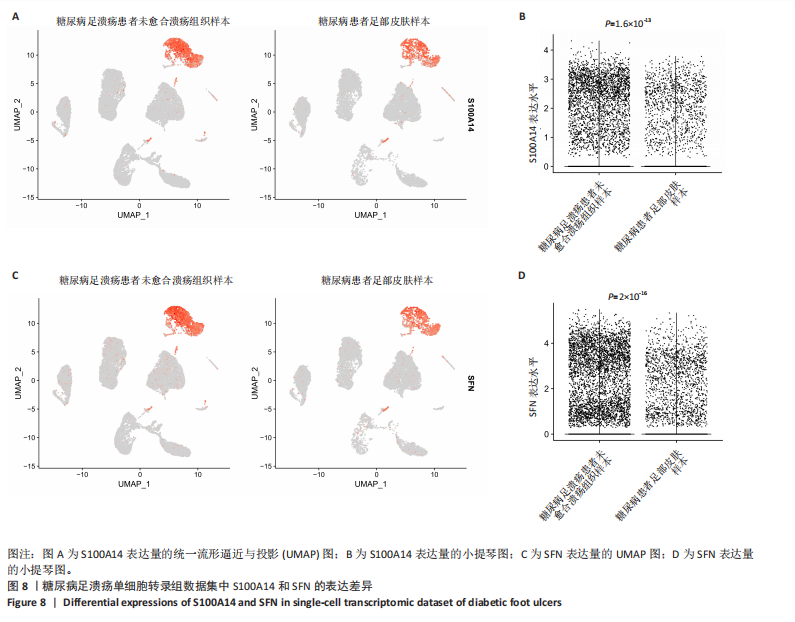
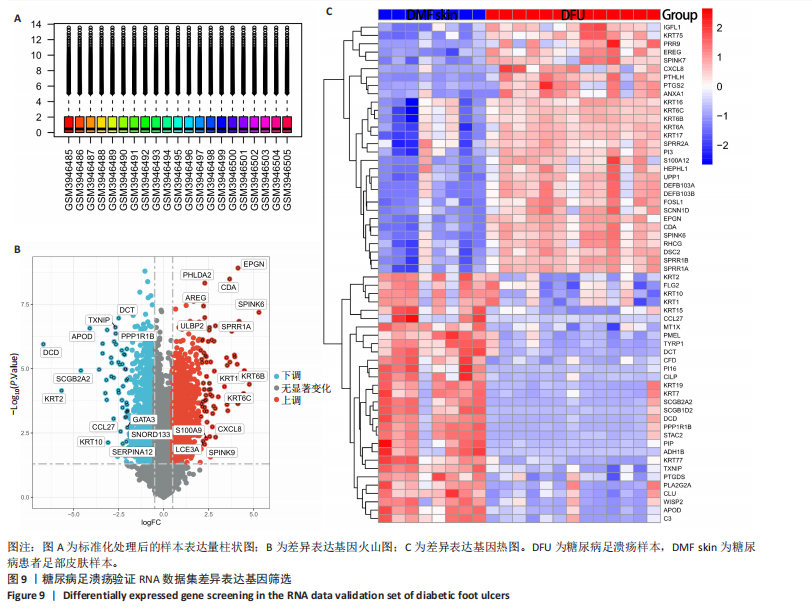
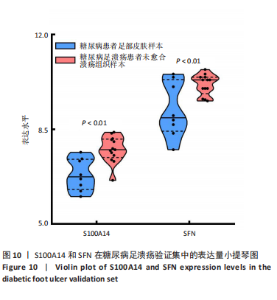
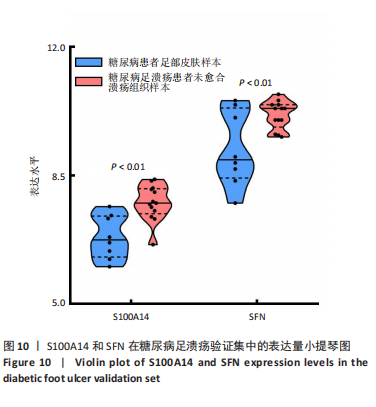
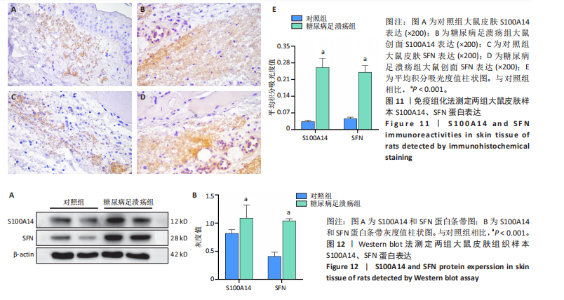
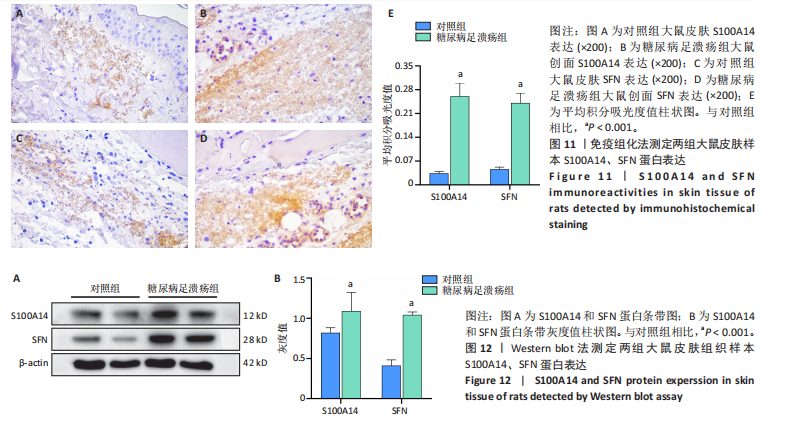
为50,共聚类出9个模块(图6A)。模块-性状关联分析显示深紫色和深橄榄绿色模块与糖尿病足溃疡显著正相关(图6B),包括887个基因。 2.7 潜在生物标志物筛选和验证 将scRNA样本差异表达基因、RNA数据差异表达基因、RNA数据加权基因共表达网络筛选获得的与糖尿病足溃疡病变相关的模块基因以及加权基因共表达网络筛选的模块基因取交集(图7),获得2个糖尿病足溃疡的关键生物标志物,分别为S100A14和SFN。提取scRNA数据集中S100A14和SFN的表达量并进行分析,结果显示S100A14和SFN在糖尿病足溃疡样本及糖尿病患者足部皮肤样本中的上皮细胞亚群中均呈现高表达,且糖尿病足溃疡样本中S100A14和SFN表达水平明显高于糖尿病患者足部皮肤样本(图8)。对验证RNA数据集中糖尿病足溃疡和糖尿病患者足部皮肤样本测序数据进行标准化处理并筛选样本组间差异表达基因(图9),提取S100A14和SFN的表达量,结果显示,S100A14和SFN在糖尿病足溃疡样本中的表达水平显著高于糖尿病患者足部皮肤样本(图10)。 2.8 动物实验 免疫组化结果显示,糖尿病足溃疡组大鼠创面组织S100A14(t=16.130,P < 0.001)、SFN (t=13.830,P < 0.001)表达高于对照组,差异有显著性意义(图11)。Western blot法检测结果显示,糖尿病足溃疡组大鼠创面组织S100A14(t=5.174,P < 0.001)、SFN(t=12.140,P < 0.001)表达高于对照组,差异有显著性意义(t=19.255,P < 0.001)(图12)。"
| [1] ZUBAIR M. Prevalence and interrelationships of foot ulcer, risk‐factors and antibiotic resistance in foot ulcers in diabetic populations: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. World J Diabetes. 2020;11(3):78-89. [2] ARMSTRONG DG, TAN TW, BOULTON AJM, et al. Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. JAMA. 2023;330(1):62-75. [3] AL MAMUN A, SHAO C, GENG P, et al. The Mechanism of Pyroptosis and Its Application Prospect in Diabetic Wound Healing. J Inflamm Res. 2024;17:1481-1501. [4] 滕鹰,祁放,徐广超,等.昼夜节律基因在创面愈合中的作用机制研究进展[J].中华烧伤与创面修复杂志,2024,40(7):689-693. [5] REHMAN ZU, KHAN J, NOORDIN S. Diabetic foot ulcers: contemporary assessment and management. J Pak Med Assoc. 2023;73(7):1480-1487. [6] LI Y, JU S, LI X, et al. Characterization of the microenvironment of diabetic foot ulcers and potential drug identification based on scRNA-seq. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;13:997880. [7] THEOCHARIDIS G, THOMAS BE, SARKAR D, et al. Single cell transcriptomic landscape of diabetic foot ulcers. Nat Commun. 2022; 13(1):181. [8] RAMIREZ HA, PASTAR I, JOZIC I, et al. Staphylococcus aureus Triggers Induction of miR-15B-5P to Diminish DNA Repair and Deregulate Inflammatory Response in Diabetic Foot Ulcers. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138(5):1187-1196. [9] SAWAYA AP, STONE RC, BROOKS SR, et al. Deregulated immune cell recruitment orchestrated by FOXM1 impairs human diabetic wound healing. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):4678. [10] WANG G, ZHANG E, CHEN A, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis revealed the stemness of a specific cluster of B cells in acute lymphoblastic leukemia progression. PeerJ. 2024;12:e18296. [11] HU C, LI T, XU Y, et al. CellMarker 2.0: an updated database of manually curated cell markers in human/mouse and web tools based on scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51(D1):D870-D876. [12] LI X, LIN Z, ZHAO F, et al. Unveiling the cellular landscape: insights from single-cell RNA sequencing in multiple myeloma. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1458638. [13] MORABITO S, REESE F, RAHIMZADEH N, et al. hdWGCNA identifies co-expression networks in high-dimensional transcriptomics data. Cell Rep Methods. 2023;3(6):100498. [14] DENG P, LIANG H, WANG S, et al. Combined metabolomics and network pharmacology to elucidate the mechanisms of Dracorhodin Perchlorate in treating diabetic foot ulcer rats. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1038656. [15] ZHANG Y, LAZZARINI PA, MCPHAIL SM, et al. Global Disability Burdens of Diabetes-Related Lower-Extremity Complications in 1990 and 2016. Diabetes Care. 2020;43(5):964-974. [16] SENNEVILLE É, ALBALAWI Z, VAN ASTEN SA, et al. IWGDF/IDSA guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diabetes-related foot infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024;40(3): e3687. [17] HASSANSHAHI A, MORADZAD M, GHALAMKARI S, et al. Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Skin Wound Healing. Cells. 2022;11(19):2953. [18] BAUER TM, MOON JY, SHADIOW J, et al. Mechanisms of Impaired Wound Healing in Type 2 Diabetes: The Role of Epigenetic Factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025;45(5):632-642. [19] ZHAO X, XU M, TANG Y, et al. Decreased expression of miR-204-3p in peripheral blood and wound margin tissue associated with the onset and poor wound healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Int Wound J. 2023;20(2):413-429. [20] HU SC, LAN CE. High-glucose environment disturbs the physiologic functions of keratinocytes: Focusing on diabetic wound healing. J Dermatol Sci. 2016;84(2):121-127. [21] LAMBERT AW, WEINBERG RA. Linking EMT programmes to normal and neoplastic epithelial stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21(5):325-338. [22] YUAN L, SUN Y, XU M, et al. miR-203 Acts as an Inhibitor for Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Process in Diabetic Foot Ulcers via Targeting Interleukin-8. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2019;26(5):239-249. [23] 郭佳,张江林,黄中峰,等.CD147调控RSK2/Slug/EMT通路影响糖尿病足溃疡的愈合[J].中南大学学报(医学版),2020,45(8):929-934. [24] LIU Z, BIAN X, LUO L, et al. Spatiotemporal single-cell roadmap of human skin wound healing. Cell Stem Cell. 2025;32(3):479-498. [25] DONG Y, WANG M, WANG Q, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq in diabetic foot ulcer wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2024;32(6):880-889. [26] BASNET S, SHARMA S, COSTEA DE, et al. Expression profile and functional role of S100A14 in human cancer. Oncotarget. 2019;10(31):2996-3012. [27] ARIF SH. Correlation of S100A4 and S100A14 Expression With Clinico-Pathological Features and Tumor Location in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cureus. 2024;16(7):e65615. [28] SAPKOTA D, BRULAND O, COSTEA DE, et al. S100A14 regulates the invasive potential of oral squamous cell carcinoma derived cell-lines in vitro by modulating expression of matrix metalloproteinases, MMP1 and MMP9. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47(4):600-610. [29] CHEN H, YUAN Y, ZHANG C, et al. Involvement of S100A14 protein in cell invasion by affecting expression and function of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 via p53-dependent transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(21):17109-17119. [30] ZHU M, WANG H, CUI J, et al. Calcium-binding protein S100A14 induces differentiation and suppresses metastasis in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(7):e2938. [31] HUANG F, LU X, YANG Y, et al. Microenvironment-Based Diabetic Foot Ulcer Nanomedicine. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(2):e2203308. [32] CHEN C, LI X, HU Y, et al. Electrical stimulation promoting the angiogenesis in diabetic rat perforator flap through attenuating oxidative stress-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. PeerJ. 2024;12:e16856. [33] TANG Y, JI H, YAN Y, et al. Enhancing diabetic foot ulcer healing: Impact of the regulation of the FUS and ILF2 RNAbinding proteins through negative pressure wound therapy. Int J Mol Med. 2024;54(5):103. [34] HASHIDA H, COFFEY RJ. Significance of a calcium-binding protein S100A14 expression in colon cancer progression. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022;13(1):149-162. [35] FAN X, CUI L, ZENG Y, et al. 14-3-3 Proteins Are on the Crossroads of Cancer, Aging, and Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(14):3518. [36] ALJABAL G, YAP BK. 14-3-3σ and Its Modulators in Cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020;13(12):441. [37] DU N, LI D, ZHAO W, et al. Stratifin (SFN) Regulates Cervical Cancer Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Cytoskeletal Remodeling and Metastasis Progression Through LIMK2/Cofilin Signaling. Mol Biotechnol. 2024; 66(11):3369-3381. [38] CHEN J, ANANTHANARAYANAN B, SPRINGER KS, et al. Suppression of LIM Kinase 1 and LIM Kinase 2 Limits Glioblastoma Invasion. Cancer Res. 2020;80(1):69-78. [39] HE Y, ZHANG L, HE Y, et al. Involvement of LIMK2 in actin cytoskeleton remodeling during the definitive endoderm differentiation. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2021;57(5):493-500. [40] LY M, SCHIMMER C, HAWKINS R, et al. Integrin-based adhesions promote cell-cell junction and cytoskeletal remodelling to drive embryonic wound healing. J Cell Sci. 2024;137(5):jcs261138. |
| [1] | Lai Jiaming, , Song Yuling, Chen Zixi, Wei Jinghuan, Cai Hao, , Li Guoquan, . Screening of diagnostic markers for endothelial cell Senescence in mice with radiation-induced heart disease and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1450-1463. |
| [2] | Zhang Qian, Huang Dongfeng. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis combined with machine learning to screen and validate biomarkers for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1096-1105. |
| [3] | Gao Minyi, Liu Pinghong, Lin Haixiong. Burn and multi-omic biomarkers: causal relationships with 41 inflammatory factors and 35 blood and urine markers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(23): 6062-6070. |
| [4] | Lin Yong, Yang Xiaoqiang, Lin Kun, Yang Fan, He Mincong, Wei Qiushi. Immune microenvironment and inflammatory repair of cystic degeneration in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a single-cell sequencing analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(17): 4309-4317. |
| [5] | Zhou Man, Long Meiting, Xin Guoyan, Huang Mengjun, Yao Zhenglian, Zhao Huajuan, Shen Linqiang, Wu Xijun, Yang Xiaoyan. Bioinformatics screening and experimental verification of core genes in chronic myeloid leukemia and imatinib resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3331-3342. |
| [6] | Huang Jiayao, Gu Yu. Application of exosomes in the diagnosis and monitoring of oral diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(13): 3392-3401. |
| [7] | Liang Liang, Yan Yulu, Zheng Yang, Zhang Xiaoyun, Wang Lei, Qi Wen . Lactylation-related potential targets and Chinese herbal medicine active ingredients targeting treatment of spinal cord injury: GEO database screening analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(12): 3156-3170. |
| [8] | Tian Meng, Lou Tianwei, Zhang Yongchen, Jia Hongling . Cathepsin F as a potential serum biomarker for stroke risk prediction: GWAS database data analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(10): 2662-2670. |
| [9] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [10] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [11] | Zhang Yixuan, Li Dongna, Liu Chunyan. Pathological processes, inflammatory responses, and related biomarkers of periodontitis: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7601-7610. |
| [12] |
Zhou Rulin, Hu Yuanzheng, Wang Zongqing, Zhou Guoping, Zhang Baochao, Xu Qian, Bai Fanghui.
Exploration of biomarkers for moyamoya disease and analysis of traditional Chinese medicine targets#br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6927-6938.
|
| [13] | Tang Zhi, Shao Yang, Li Shaoshuo, Qi Shubin, Lu Hengyang, Wu Mao, Yang Junfeng, Wang Jianwei. Single-cell sequencing reveals heterogeneity of B cells in osteoporosis patients and their interactions with osteoblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5501-5510. |
| [14] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. Rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy: interaction analysis based on multiple machine learning algorithms [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5595-5607. |
| [15] | Hao Maochen, Ma Chao, Liu Kai, Liu Kexin, Meng Lingting, Wang Xingru, Wang Jianzhong. Bioinformatics screening of key genes for endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritis and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5632-5641. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||