Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5632-5641.doi: 10.12307/2025.628
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics screening of key genes for endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritis and experimental validation
Hao Maochen1, Ma Chao2, Liu Kai1, Liu Kexin1, Meng Lingting1, Wang Xingru1, Wang Jianzhong2
- 1Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-06-04Accepted:2024-07-05Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-27 -
Contact:Ma Chao, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China Hao Maochen and Ma Chao contributed equally to this work. Corresponding author: Wang Jianzhong, PhD, Chief physician, Professor, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Hao Maochen, Master’s candidate, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Third-Batch Science and Technology Project of High-level Clinical Specialty Construction of Capital Region Public Hospitals in Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 2023SGGZ143 (to WJZ); Key Project of Inner Mongolia Medical University, No. YKD2024ZD005 (to WJZ); Basic Scientific Research Operational Fees Project of Colleges and Universities under the Direct Subsidiaries of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. YKD2023ZY001 (to LK); Graduate Student Scientific Research Innovation Project in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. S20231189Z (to LK)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hao Maochen, Ma Chao, Liu Kai, Liu Kexin, Meng Lingting, Wang Xingru, Wang Jianzhong. Bioinformatics screening of key genes for endoplasmic reticulum stress in osteoarthritis and experimental validation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5632-5641.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
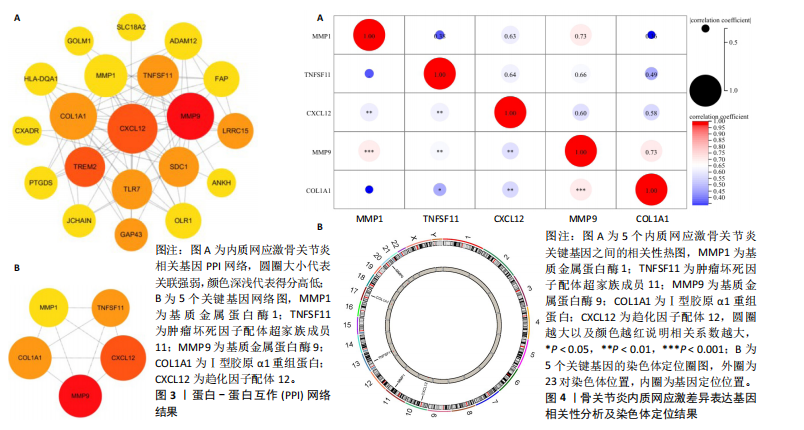
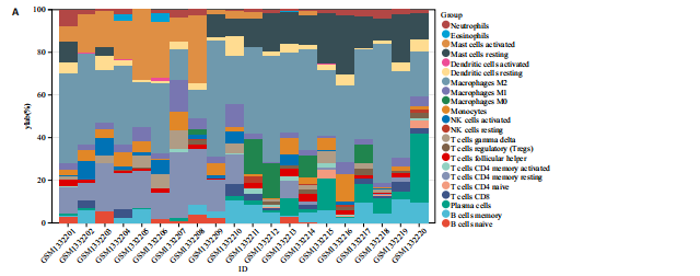
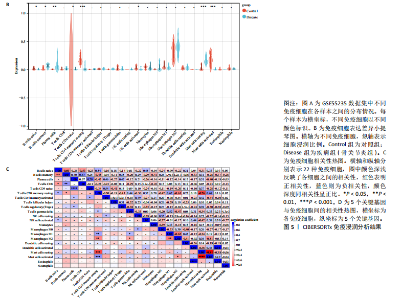
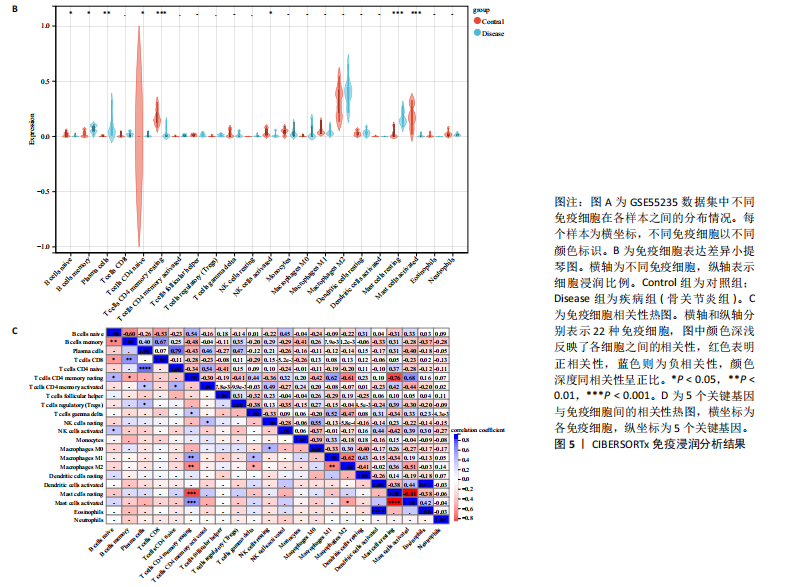
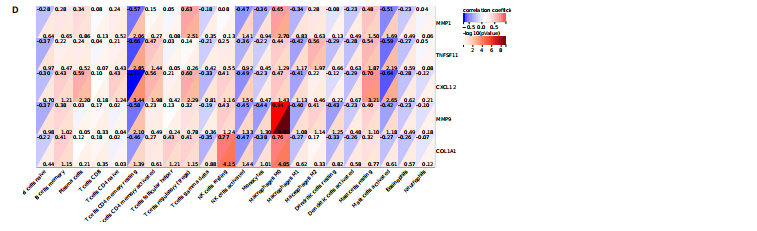
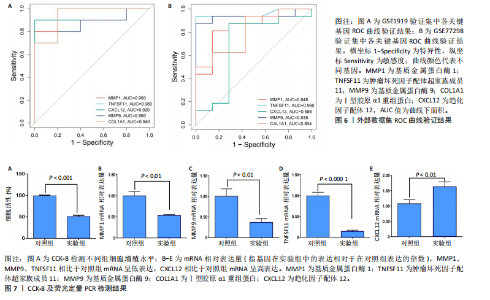
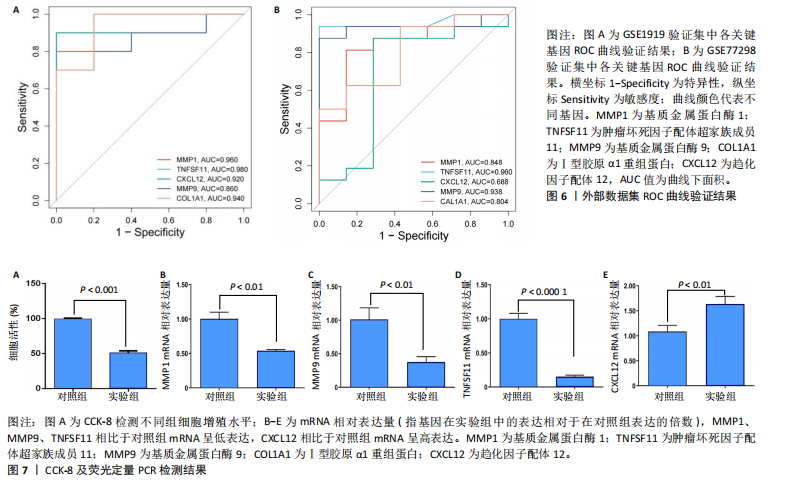
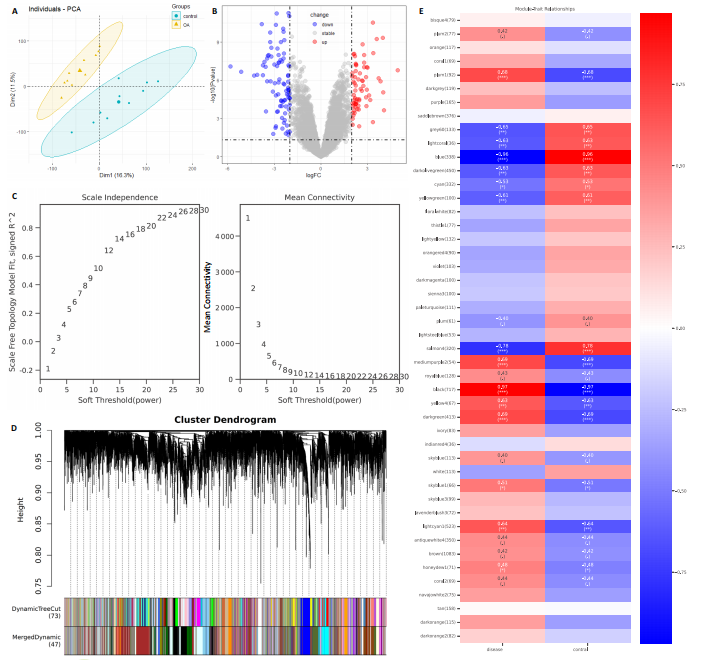
2.1 内质网应激骨关节炎基因的筛选结果 利用GEO2R在线工具中的用R包“limma”对GSE55235数据集进行批次校正及主成分分析后筛选出满足|logFC|> 2且P < 0.05的差异基因,见图1A,共得到153个差异基因(其中67个上调,86个下调,绘制火山图进行可视化分析,见图1B。从GeneCard数据库检索得到10 529个内质网应激相关基因。使用WGCNA算法构建基因共表达网络,过滤表达量变化波动较低(标准偏差≤0.5)的基因后最终剩余8 583个基因,20个样本进行后续分析。为满足无尺度网络分布前提条件,此次分析所用的Power值为22,见图1C。基于选定的Power值,建立加权共表达网络模型,将8 583个基因划分为47个模块,见图1D。通过筛选相关系数的绝对值大于0.3且P < 0.05的情况作为阈值,来选取与各个性状相关的模块,进而分析基因与性状之间的关联程度以及基因与模块之间的关联性,得到与骨关节炎相关性最显著black模块的717个基因。最终,绘制韦恩图为差异基因、WGCNA结果与内质网应激基因取交集得到27个内质网应激骨关节炎相关基因,见1E,F。 2.2 GO富集与KEGG信号通路分析结果 为了分析骨关节炎样本和对照组之间的生物学功能差异,对差异表达基因进行GO功能注释。结果显示这些差异表达基因主要富集在胶原蛋白代谢过程、细胞分泌调节及趋化因子的生成等生物学过程中,见图2A,免疫球蛋白复合物、血液微粒等细胞组分中,见图2B,以及肽聚糖结合、抗原结合、免疫球蛋白受体结合等分子功能中,见图2C。同时这些差异表达基因富集在类风湿性关节炎、松弛肽信号通路相关的KEGG通路中,见图2D。 2.3 PPI网络构建结果 在String数据库中输入27个内质网应激骨关节炎相关基因,构建PPI网络,以探寻蛋白质之间的联系。使用Cytoscape (v3.7.2)软件对STRING数据库中构建的蛋白互作数据可视化,见图3A,然后根据cytohubba插件中Degree算法筛选得分最高的5个基因,包括基质金属蛋白酶1、肿瘤坏死因子配体超家族成员11(tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 11,TNFSF11)、基质金属蛋白酶9、Ⅰ型胶原α1重组蛋白(collagen type I alpha 1,COL1A1)和趋化因子配体12(chemokine C-X-C motif ligand 12,CXCL12),见图3B,为进一步研究骨关节炎的发病机制和治疗靶点提供了重要线索和指导。 2.4 关键基因相关性分析结果 实验观察了5个内质网应激骨关节炎关键基因之间的表达关联情况,并绘制了相关性热图。结果表明这些关键基因整体呈现正相关性,见图4A。其中基质金属蛋白酶9与COL1A1、基质金属蛋白酶1之间的相关性最为显著(相关系数为0.73,P < 0.001),表明它们可能存在正向相互作用。另外,5个关键基因的染色体分布情况如图所示,见图4B。 2.5 免疫浸润分析结果 GO富集和KEGG信号通路分析揭示这些差异基因主要与炎症反应相关,因此文章使用CIBERSORT算法对GSE55235数据集中疾病组与对照组之间的免疫细胞浸润水平进行了评估。结果表明,免疫浸润细胞主要分布于M2型巨噬细胞,见图5A。随后对比了对照组与疾病组中各免疫细胞的含量,结果发现在疾病组中初始B细胞、初始CD4+T细胞、静息的记忆CD4+T细胞、活化的NK细胞、活化的肥大细胞呈低表达;记忆B细胞、浆细胞、调节性T细胞和静息的肥大细胞呈高表达,见图5B。进一步研究各免疫细胞间相关性,发现静息的肥大细胞与活化的肥大细胞、静息的记忆CD4+T细胞与静息的肥大细胞呈显著正相关,而活化的树突状细胞与嗜酸性粒细胞呈显著负相关,见图5C。 文章还绘制了5个差异基因与22种免疫细胞的相关性热图以了解其与骨关节炎免疫微环境的潜在联系。发现CXCL12与静息的肥大细胞呈显著正相关(r=0.70,P < 0.001),与静息的记忆CD4+T细胞呈显著负相关(r=-0.72,P < 0.001);基质金属蛋白酶9与M0巨噬细胞呈显著正相关(r=0.94,P < 0.001);COL1A1与静息的NK细胞(r=0.77,P < 0.001)和M0巨噬细胞(r=0.76,P < 0.001)呈显著正相关,见图5D。 2.6 ROC曲线分析验证结果 为了验证上述5个差异基因的疾病预测效能,在GSE1919和GSE77298验证集中进行了受试者工作曲线分析,见图6。结果显示,训练集中TNFSF11的诊断价值最高,AUC值分别为0.980 (GSE1919)和0.960(GSE77298),其他4个基因AUC值均> 0.6。因此,5个差异基因可作为骨关节炎疾病预测的可靠生物标志物。 2.7 荧光定量PCR结果分析验证结果 为进一步验证各差异基因的表达情况,文章在人原代关节滑膜成纤维细胞中加入脂多糖进行骨关节炎细胞造模,采用CCK-8实验进行细胞活力及增殖水平测试,而后通过荧光定量PCR实验检测各生物标志物的表达水平。CCK-8实验结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组细胞增殖水平均显著降低,见图7A,表明骨关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞模型构建成功。荧光定量PCR实验结果表明,与对照组相比,实验组骨关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞模型中基质金属蛋白酶1、TNFSF11、基质金属蛋白酶9及CXCL12具有显著表达差异,COL1A1表达水平无显著性差异,见图7B-E。"
| [1] HUNTER DJ, MARCH L, CHEW M. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: a Lancet Commission. Lancet. 2020;396(10264): 1711-1172. [2] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [3] DENG H, CHEN Z, KANG J, et al. The mediating role of synovitis in meniscus pathology and knee osteoarthritis radiographic progression. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):12335. [4] ZOU Z, LI H, YU K, et al. The potential role of synovial cells in the progression and treatment of osteoarthritis. Exploration. 2023;3(5):20220132. [5] SADIA K, ASHRAF MZ, MISHRA A. Therapeutic role of sirtuins targeting unfolded protein response, coagulation, and inflammation in hypoxia-induced thrombosis. Front. Physiol. 2021;12:733453. [6] IYER S, ADAMS DJ. Bone and the unfolded protein response: in sickness and in health. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;113(1):96-109. [7] LI Q, WEN Y, WANG L, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced accumulation of advanced glycosylation end products in fibroblast-like synoviocytes promotes knee osteoarthritis. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11):1735-1747. [8] 赵千增,赵振群,刘万林.激素性股骨头缺血坏死过程中内质网应激调控自噬与凋亡的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(29):4685-4690. [9] WANG C, XU S, SUN D, et al. ActivePPI: quantifying protein-protein interaction network activity with Markov random fields. Bioinformatics. 2023;39(9):btad567. [10] FAN X, YUAN J, XIE J, et al. Long non-protein coding RNA DANCR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate osteoarthritis progression via miR-577/SphK2 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(3):658-664. [11] CUI Z, CUI Y, ZANG T, et al. interacCircos: an R package based on JavaScript libraries for the generation of interactive circos plots. Bioinformatics. 2021;37(20):3642-3644. [12] STEEN CB, LIU CL, ALIZADEH AA, et al. Profiling cell type abundance and expression in bulk tissues with CIBERSORTx. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2117:135-157. [13] 付金乐.脂多糖对人滑膜细胞增殖过程中MAPK途径作用机制的研究[D].武汉:武汉大学,2016. [14] YANG T, YANG G, WANG G, et al. Bioinformatics identification and integrative analysis of ferroptosis-related key lncRNAs in patients with osteoarthritis. Biosci Rep. 2023;43(9):BSR20230255. [15] LI Q, TANG X, LI W. Potential diagnostic markers and biological mechanism for osteoarthritis with obesity based on bioinformatics analysis. PLoS One. 2023; 18(12):e0296033. [16] RAHMATI M, MOOSAVI MA, MCDERMOTT MF. ER stress: a therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018;39(7):610-623. [17] WU H, MENG Z, JIAO Y, et al. The endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by tunicamycin affects the viability and autophagy activity of chondrocytes. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020;34(10):e23437. [18] LIU C, CAO Y, YANG X, et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chondrocytes of patients with osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(4):1081-1087. [19] ZHANG Y, LIU D, VITHRAN DTA, et al. CC chemokines and receptors in osteoarthritis: new insights and potential targets. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023;25(1):113. [20] BRYLKA LJ, SCHINKE T. Chemokines in physiological and pathological bone remodeling. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2182. [21] OKAMURA Y, MISHIMA S, KASHIWAKURA JI, et al. The dual regulation of substance P-mediated inflammation via human synovial mast cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Allergol Int. 2017;66s:S9-S20. [22] MUSTONEN AM, NIEMINEN P. Fatty acids and oxylipins in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis-a complex field with significant potential for future treatments. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2021;23(6):41. [23] MALEMUD C J. Matrix metalloproteinases and synovial joint pathology. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2017;148:305-325. [24] KUMAR S, KUMAR H, MITTAL A, et al. Correlation between synovial fluid levels of matrix metalloproteinase’s (MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-9) and TNF-α with the severity of osteoarthritis knee in rural indian population. Indian J Orthop. 2023;57(10):1659-1666. [25] ZENG GQ, CHEN AB, LI W, et al. High MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9 protein levels in osteoarthritis. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(4): 14811-14822. [26] HE L, KANG Q, CHAN KI, et al. The immunomodulatory role of matrix metalloproteinases in colitis-associated cancer. Front Immunol. 2022;13:1093990. [27] BASSIOUNI W, VALENCIA R, MAHMUD Z, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 proteolyzes mitofusin-2 and impairs mitochondrial function during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Basic Res Cardiol. 2023;118(1):29. [28] SINGH S, JINDAL D, KHANNA R. Can serum MMP-3 diagnose early knee osteoarthritis? J Orthop. 2023;38:42-46. [29] WYATT LA, NWOSU LN, WILSON D, et al. Molecular expression patterns in the synovium and their association with advanced symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2019;27(4):667-675. [30] WU Y, TANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. MMP-1 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the JNK and ERK pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2020;129:105880. [31] WANG Y, ZHANG T, XU Y, et al. Suppressing phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases Cγ1 promotes mineralization of osteoarthritic subchondral bone osteoblasts via increasing autophagy, thereby ameliorating articular cartilage degeneration. Bone. 2022;154:116262. [32] BOLLMANN M, PINNO K, EHNOLD LI, et al. MMP-9 mediated Syndecan-4 shedding correlates with osteoarthritis severity. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021;29(2):280-289. [33] UDAGAWA N, KOIDE M, NAKAMURA M, et al. Osteoclast differentiation by RANKL and OPG signaling pathways. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021;39(1):19-26. [34] KOVáCS B, VAJDA E, NAGY EE. Regulatory effects and interactions of the wnt and opg-rankl-rank signaling at the bone-cartilage interface in osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(18):4653. [35] YUE Z, NIU X, YUAN Z, et al. RSPO2 and RANKL signal through LGR4 to regulate osteoclastic premetastatic niche formation and bone metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132(2):e144579. [36] LI J, JIANG M, YU Z, et al. Artemisinin relieves osteoarthritis by activating mitochondrial autophagy through reducing TNFSF11 expression and inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in cartilage. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022;27(1):62. [37] CHEN P, TAO J, ZHU S, et al. Radially oriented collagen scaffold with SDF-1 promotes osteochondral repair by facilitating cell homing. Biomaterials. 2015;39:114-123. [38] CHEN X, LIANG XM, ZHENG J, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α regulates chondrogenic differentiation via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2023;15(5):490-501. [39] LIN C, LIU L, ZENG C, et al. Activation of mTORC1 in subchondral bone preosteoblasts promotes osteoarthritis by stimulating bone sclerosis and secretion of CXCL12. Bone Res. 2019;7:5. [40] THOMSON A, HILKENS CMU. Synovial macrophages in osteoarthritis: the key to understanding pathogenesis? Front Immunol. 2021;12:678757. [41] WU CL, HARASYMOWICZ NS, KLIMAK MA, et al. The role of macrophages in osteoarthritis and cartilage repair. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2020;28(5):544-554. [42] KRIEGOVA E, MANUKYAN G, MIKULKOVA Z, et al. Gender-related differences observed among immune cells in synovial fluid in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2018; 26(9):1247-1256. [43] WARMINK K, RIOS JL, VARDERIDOU-MINASIAN S, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells-derived extracellular vesicles as a potentially more beneficial therapeutic strategy than MSC-based treatment in a mild metabolic osteoarthritis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):137. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [3] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [4] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [5] | Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295. |
| [6] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [7] | Wang Yuru, Li Siyuan, Xu Ye, Zhang Yumeng, Liu Yang, Hao Huiqin. Effects of wogonin on joint inflammation in collagen-induced arthritis rats via the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1026-1035. |
| [8] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [9] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [10] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [11] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [12] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [13] | Li Jing, Lu Guangqi, Zhuang Minghui, Cui Ying, Yu Zhangjingze, Sun Xinyue, Ma Mingming, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie. Development of a clinical prediction model for cervical instability in young and middle-aged adults based on machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7203-7210. |
| [14] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| [15] | Xie Yizi, Lin Xueying, Zhang Xinxin, Huang Xiufang, Zhan Shaofeng, Jiang Yong, Cai Yan. Biological mechanism of mitophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6708-6716. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||