Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (26): 5642-5651.doi: 10.12307/2025.688
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mitochondrial dysfunction and brain aging: a bibliometrics analysis based on the Web of Science Core Collection database
Nan Songhua1, Peng Chaojie1, Cui Yinglin2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Henan Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2024-05-21Accepted:2024-08-21Online:2025-09-18Published:2025-02-27 -
Contact:Cui Yinglin, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Henan Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Nan Songhua, MD candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81573919 (to CYL); Special Project for Scientific and Technological Research on Traditional Chinese Medicine, National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. GZY-KJS-2021-017 (to CYL); Henan Province Key Research and Development Special Program, No. 221111310500 (to CYL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Nan Songhua, Peng Chaojie, Cui Yinglin. Mitochondrial dysfunction and brain aging: a bibliometrics analysis based on the Web of Science Core Collection database[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5642-5651.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
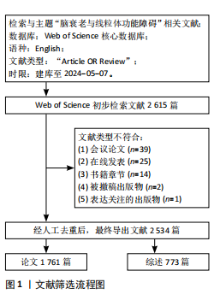
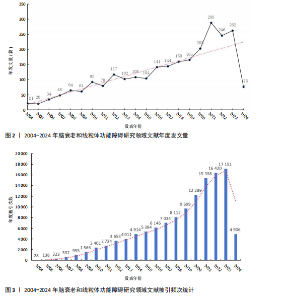
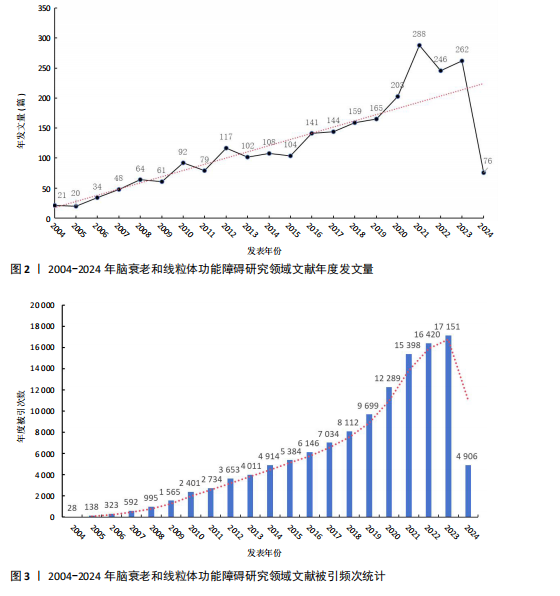
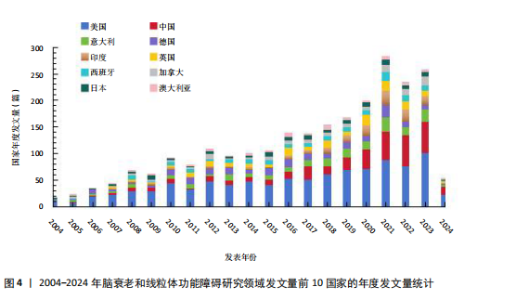
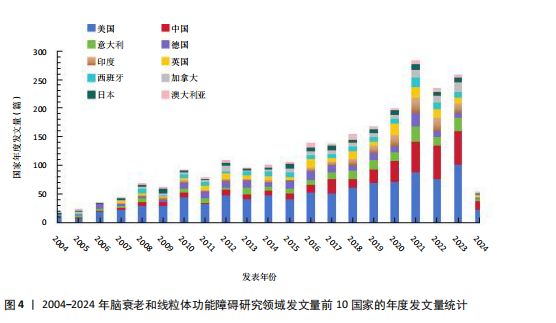
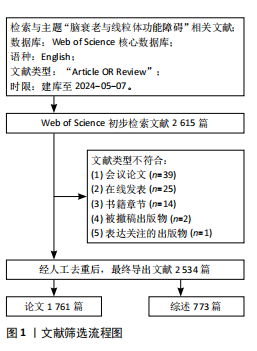
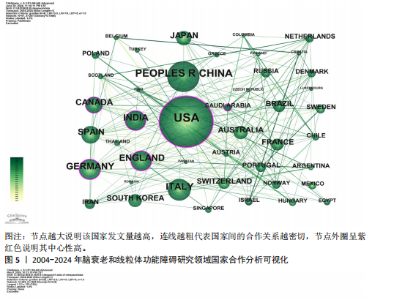
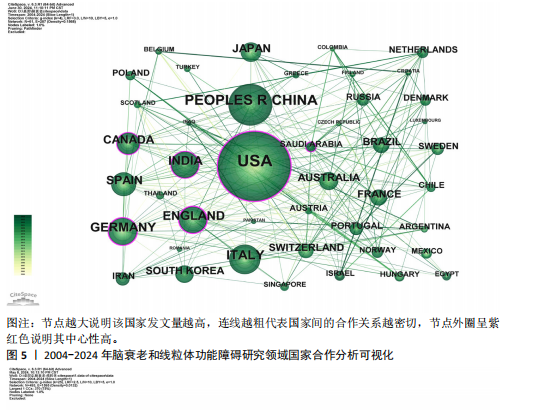
2.1 年度发文量趋势分析 该研究最终纳入2 534篇文献(图1)。年度发文量总体呈增加趋势,但也出现了一些小波动(图2)。年度发文量可分为3个阶段(第一阶段,2004-2007年;第二阶段 2008-2019年;第三阶段,2020-2023年)。在2004-2005年,每年发文量低于30篇;2006-2011年,每年发文量超过30篇,低于100篇;自2012年以来,每年发文量100篇以上,自2020年起年发文量突破200篇,其中2021年度发文量最多(288篇),总的来说近一半的文章是在近5年发表的。其中,2024年度发文量数据仅统计至2024-05-07。文章总被引次数为123 900次,篇均被引频次为48.9次,H指数152(图3)。H指数是一个衡量学者或国家学术产出数量和质量的指标,能够反映一个人的学术成就,指数越高,表明其论文的影响力越大[17]。而文献被引频数能够客观反映文献的实际应用价值,并作为评价个人或国家学术影响力的重要标准[18]。 2.2 国家分析 2004-2024年间,共73个国家参与脑衰老和线粒体功能障"
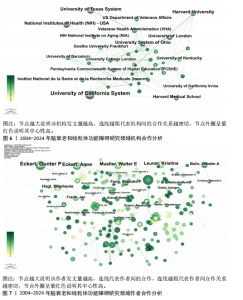
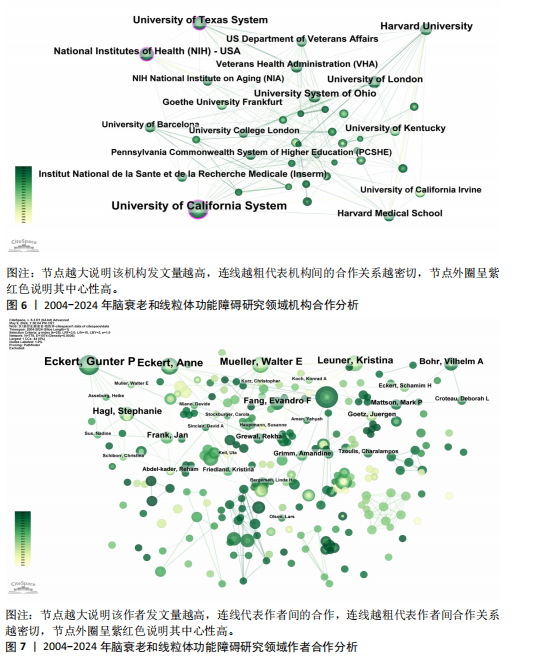
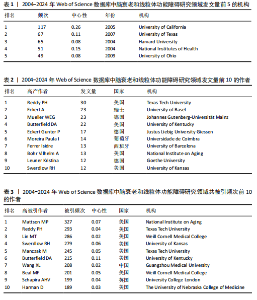
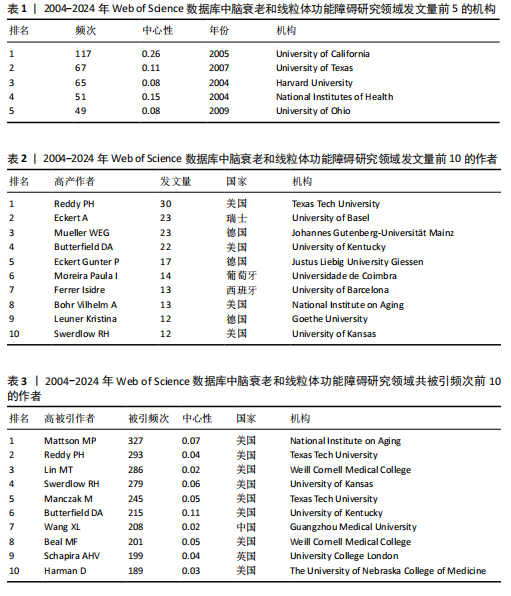
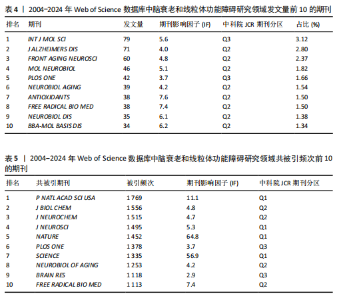
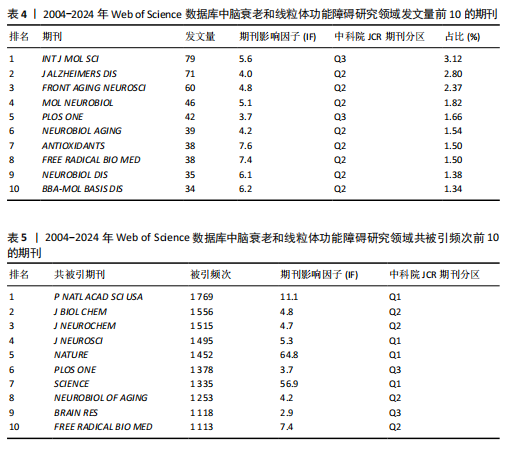
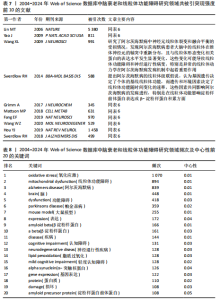
2.3 研究机构分析 运行CiteSpace 6.3.R1软件,选择节点为Institution,绘制脑衰老和线粒体功能障碍研究领域机构协同合作的可视化图谱(图6),共生成493个节点和1 595条连线,图谱密度为 0.013 2。数据分析显示,加利福尼亚大学中心性最高,在该研究领域属于核心机构。由此可知高校是该领域研究的主力军,其中加利福尼亚大学(0.26)、德克萨斯大学(0.11)、哈佛大学(0.08)、美国国立卫生研究院(0.15)、俄亥俄大学(0.08)的发文量排在前5位,分别为117篇、67篇、65篇、51篇、49篇(表1),且这5个机构与其他机构建立了较为广泛的合作关系。 2.4 高影响力作者可视化分析 运行CiteSpace 6.3.R1软件,选择节点为Author,共有203名主要学者对脑衰老和线粒体功能障碍的研究做出了贡献,表2,3列举了发文量和共被引排名前10的作者。由此可知该领域的多个研究群体中,美国研究者占多数,其中德克萨斯理工大学健康科学中心的Reddy P. Hemachandra教授以30篇的发文量排名首位,其次是瑞士巴塞尔大学的Eckert A教授和德国美因茨大学Mueller WEG教授(23篇)。使用CiteSpace 软件绘制作者合作的可视化图谱(图7),共生成778个节点和1 074条连线,图谱密度为0.003 6。其中,美国国家老龄化研究所(National Institute on Aging,NIA)的Mattson M.P教授以共被引327次居于领先地位,但与其他发文量高的作者间的合作甚少,且与其他影响力大的作者间鲜有合作。 2.5 高影响力的期刊分析 共检索到2 534篇文章,来源于677种期刊。表4,5罗列的是高影响力排名前10的期刊,共发表了210篇论文(19.03%),《INT J MOL SCI》是发表最多的期刊(79篇),其次是《J ALZHEIMERS DIS》(71篇) 和《FRONT AGING NEUROSCI》(60篇)。共被引前3名的期刊分别是《P NATL ACAD SCI USA》(1 769次),《J BIOL CHEM》(1 556次),《J NEUROCHEM》(1 515次)。 2.6 文献分析 2.6.1 文献共被引分析 文献共被引分析是统计一篇文献被另外一篇或多篇文献引用的文献计量分析方法,文"

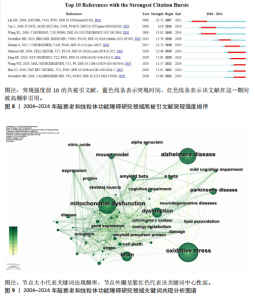
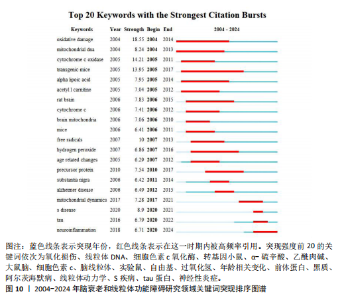
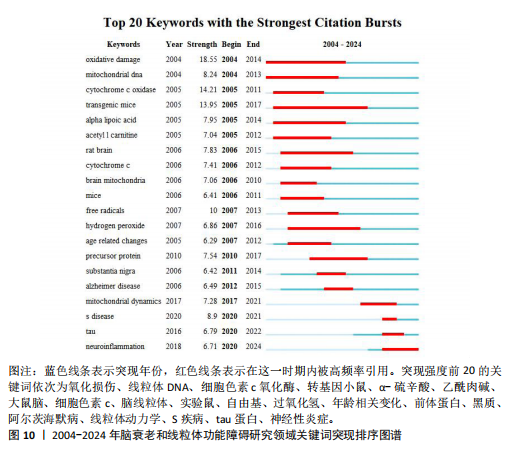
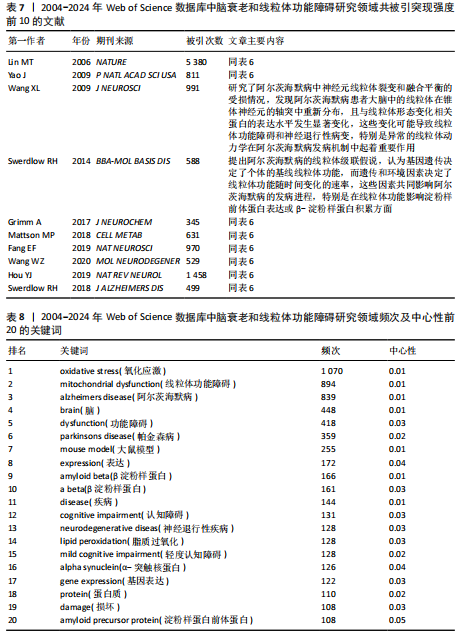
献的被引频率越高说明该文献具有学术价值[19],通过对高被引文献研究内容的分析,可以揭示该领域具有高影响力的研究主体。在检索到的2 534篇文献中,共产生778个节点,1 047条连线,图谱密度为0.003 6,表6是对脑衰老和线粒体功能障碍研究文献被引频次前10的统计和总结。 2.6.2 文献突现分析 利用CiteSpace软件统计出2004-2024年突现强度前10的文献,图8和表7显示突现强度前10的共被引文献,蓝色线条代表突现年份,红色线条代表在这一期间被高频率引用。其中,来自纽约康奈尔大学威尔医学院神经病学和神经科学系的Lin MT教授的文献突现强度最大(23.71),被引频次达5 380次。 2.7 研究热点分析 2.7.1 关键词共现分析 关键词是文章内容的核心要素,通过分析文章中的关键词,可以洞察文章的主旨。深入研究关键词的使用,有助于揭示特定学术领域的研究趋势和热点问题[20]。使用 CiteSpace 软件绘制脑衰老和线粒体功能障碍的研究热点图谱,共生成640个节点,3 662条连线,图谱密度为0.017 9(图9),每个节点代表关键词,节点大小代表关键词出现频率。通过对关键词进行共现分析,表8列出了前20个高频关键词,中心性排名前三的高频关键词分别是“oxidative stress”(1 070,0.01),“mitochondrial dysfunction”(894,0.01),“alzheimers disease”(839,0.01)。 2.7.2 关键词突现分析 关键词突现是指频率急剧增加的关键词,关键词突现是在一段时间内受到相关研究领域学者们特别关注的关键词的一种有用算法,可反映一段时间内该领域的研究前沿及变化趋势,在分析研究前沿、研究趋势和热点以及预测未来研究方向具有重要的价值[21-22]。如图10所示,蓝色线条代表突现年份,红色线条代表在这一期间被高频率引用。突现强度(strength)是对关键词的一种量化表达方式,表示该关键词在短时间内被大量引用[23],其中,氧化损伤(18.55)突现强度最高,爆发起始年份为2004年,说明氧化损伤作为脑衰老过程中一个关键的病理机制,在2004-2014年期间被广泛研究。"

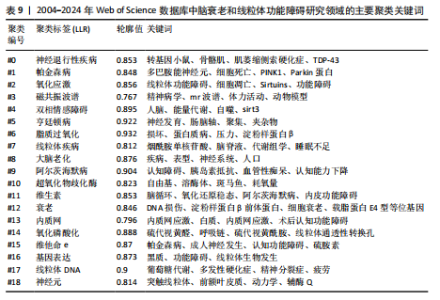
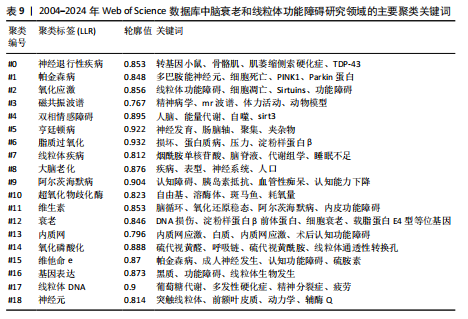
同时,神经炎症(6.71)是近年来新兴的且一直活跃的主题,突现强度虽然不及氧化损伤,但其起始年份较晚且突现强度持续增加,表明这是一个新兴的研究领域。考虑到神经炎症在阿尔茨海默病等神经退行性疾病中的作用,未来的研究可能会集中在炎症反应的调控机制,以及如何通过抗炎治疗来改善疾病进程,这意味着神经炎症将是该领域未来一段时期内的研究热点。 2.7.3 关键词聚类分析 关键词聚类揭示了研究领域内围绕共同主题的关键词所构成的相互关联的网络群体,每个群体的特征由其成员文章中频繁出现的标题词汇来定义。使用CiteSpace 软件对关键词按时间线进行聚类分析,可总结关键词节点间的相似性,采用经典的对数似然率算法得到19个聚类组,聚类从 0 开始编号,即聚类#0 neurodegenerative diseases 是最大的集群。图中共生成640个节点,1 138条连线。其中,Modularity Q(模块值)=0.683 2 > 0.3,Silhouette S(平均轮廓值)=0.859 > 0.7,意味着聚类结构显著,是合理且令人信服的。采用时间轴直观显示关键词聚类的动态时间变化,有助于预测该研究领域在未来的发展趋势,见图11和表9。"
| [1] CAI Y, SONG W, LI J, et al. The landscape of aging. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(12):2354-2454. [2] KENNEDY BK, BERGER SL, BRUNET A, et al. Geroscience: linking aging to chronic disease. Cell. 2014;159(4):709-713. [3] 原新,范文清.人口负增长与老龄化交汇时代的形势与应对[J].南开学报(哲学社会科学版),2022(6):1-10. [4] 原新.全球人口负增长时间可能提前至2065年[J].人口与健康,2020(11):13-16. [5] 郑真真.从全球人口变化看中国人口负增长[J].人口研究,2023,47(2):3-10. [6] BLINKOUSKAYA Y, CAÇOILO A, GOLLAMUDI T, et al. Brain aging mechanisms with mechanical manifestations. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021;200:111575. [7] HOU Y, DAN X, BABBAR M, et al. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(10):565-581. [8] CARDOSO AL, FERNANDES A, AGUILAR-PIMENTEL JA, et al. Towards frailty biomarkers: Candidates from genes and pathways regulated in aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Res Rev. 2018;47: 214-277. [9] WANG H, LAUTRUP S, CAPONIO D, et al. DNA Damage-Induced Neurodegeneration in Accelerated Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(13):6748. [10] CHAN DC. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Its Involvement in Disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 2020;15:235-259. [11] GRIMM A, ECKERT A. Brain aging and neurodegeneration: from a mitochondrial point of view. J Neurochem. 2017;143(4):418-431. [12] FERNANDEZ-MARCOS PJ, AUWERX J. Regulation of PGC-1α, a nodal regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2011;93(4):884S-890S. [13] GAO F, ZHANG J. Mitochondrial quality control and neurodegenerative diseases. Neuronal Signal. 2018;2(4):NS20180062. [14] CHEN C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):5303-5310. [15] 陈挺, 李国鹏, 王小梅.优化科学知识图谱方法绘制全领域科学结构图谱[J].图书情报工作,2022,66(21):107-119. [16] SYNNESTVEDT MB, CHEN C, HOLMES JH. CiteSpace II: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2005;2005:724-728. [17] HIRSCH JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(46):16569-16572. [18] 唐晓娜,曾瑶,陈阳阳,等.基于Web of Science数据库中风病护理的文献计量学分析[J].广西医学,2020,42(7):908-913. [19] 王东浩.文献计量学在图书情报与科技情报中的应用:评《文献计量学》(第二版)[J].领导科学,2022(10):153. [20] AI Y, XING Y, YAN L, et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Depression: A Bibliometric Analysis From 2001 to 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:775329. [21] 史海蛟,丁莉莉,杨珺涵,等.基于Cite Space研究中医药治疗冠心病合并高血压可视化分析[J].辽宁中医药大学学报, 2022,24(12):63-67. [22] ZHOU W, KOU A, CHEN J, et al. A retrospective analysis with bibliometric of energy security in 2000-2017. Energy Reports. 2018;4:724-732. [23] CHEN C, HU Z, LIU S, et al. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: a scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(5):593-608. [24] 肖毅,陈晓萍,许潇丹,等.空间脑科学研究的回顾与展望[J].中国科学:生命科学,2024,54(2):325-337. [25] 朱健椿,魏嘉昕,毛浚彬,等.深度学习在磁共振影像脑疾病诊断中的应用[J].工程科学学报,2024,46(2):306-316. [26] MIWA S, KASHYAP S, CHINI E, et al. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cell senescence and aging. J Clin Invest. 2022; 132(13):e158447. [27] PRADEEPKIRAN JA, BAIG J, SEMAN A, et al. Mitochondria in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease: Focus on Mitophagy. Neuroscientist. 2024;30(4):440-457. [28] REDDY PH, KSHIRSAGAR S, BOSE C, et al. Rlip overexpression reduces oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanistic insights. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2023; 1869(7):166759. [29] BOSE C, KSHIRSAGAR S, VIJAYAN M, et al. The role of RLIP76 in oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: Evidence based on autopsy brains from Alzheimer’s disease patients. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2024;1870(2):166932. [30] PERONE I, GHENA N, WANG J, et al. Mitochondrial SIRT3 Deficiency Results in Neuronal Network Hyperexcitability, Accelerates Age-Related Aβ Pathology, and Renders Neurons Vulnerable to Aβ Toxicity. Neuromolecular Med. 2023;25(1):27-39. [31] YANG B, DAN X, HOU Y, et al. NAD+ supplementation prevents STING-induced senescence in ataxia telangiectasia by improving mitophagy. Aging Cell. 2021; 20(4):e13329. [32] FARR SA, POON HF, DOGRUKOL-AK D, et al. The antioxidants alpha-lipoic acid and N-acetylcysteine reverse memory impairment and brain oxidative stress in aged SAMP8 mice. J Neurochem. 2003; 84(5):1173-1183. [33] MIRSHAFA A, MOHAMMADI H, SHOKRZADEH M, et al. Tropisetron protects against brain aging via attenuating oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation: The role of SIRT1 signaling. Life Sci. 2020;248: 117452. [34] XU TT, LI H, DAI Z, et al. Spermidine and spermine delay brain aging by inducing autophagy in SAMP8 mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(7):6401-6414. [35] RYAN KC, ASHKAVAND Z, NORMAN KR. The Role of Mitochondrial Calcium Homeostasis in Alzheimer’s and Related Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(23):9153. [36] LIANG Y, CUI L, GAO J, et al. Gut Microbial Metabolites in Parkinson’s Disease: Implications of Mitochondrial Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis and Treatment. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(8):3745-3758. [37] LEHMANN S, COSTA AC, CELARDO I, et al. Parp mutations protect against mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in a PARKIN model of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2016; 7(3):e2166. [38] 李政,易波,王国慧,等.基于CiteSpace的机器人结直肠手术临床应用现状与热点可视化分析[J].中国普通外科杂志, 2024,33(4):578-591. [39] PICCA A, GUERRA F, CALVANI R, et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Protein Misfolding and Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s Disease: Roads to Biomarker Discovery. Biomolecules. 2021;11(10):1508. [40] DEOCARIS CC, KAUL SC, WADHWA R. From proliferative to neurological role of an hsp70 stress chaperone, mortalin. Biogerontology. 2008;9(6):391-403. |
| [1] | Zhao Jiyu, Wang Shaowei. Forkhead box transcription factor O1 signaling pathway in bone metabolism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [2] | Liang Haobo, Wang Zeyu, Ma Wenlong, Liu Hao, Liu Youwen. Hot issues in the field of joint revision: infection, rehabilitation nursing, bone defect, and prosthesis loosening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1963-1971. |
| [3] | Lyu Liting, Yu Xia, Zhang Jinmei, Gao Qiaojing, Liu Renfan, Li Meng, Wang Lu. Bibliometric analysis of research process and current situation of brain aging and exosomes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1457-1465. |
| [4] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [5] | Chang Jinxia, Liu Yufei, Niu Shaohui, Wang Chang, Cao Jianchun. Visualization analysis of macrophage polarization in tissue repair process [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1486-1496. |
| [6] |
Li Tian, Ren Yuhua, Gao Yanping, Su Qiang.
Mechanism of agomelatine alleviating anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in APP/PS1 transgenic mice #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1176-1182.
|
| [7] | He Guanghui, Yuan Jie, Ke Yanqin, Qiu Xiaoting, Zhang Xiaoling. Hemin regulates mitochondrial pathway of oxidative stress in mouse chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [8] | He Bo, Chen Wen, Ma Suilu, He Zhijun, Song Yuan, Li Jinpeng, Liu Tao, Wei Xiaotao, Wang Weiwei, Xie Jing . Pathogenesis and treatment progress of flap ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1230-1238. |
| [9] | Lu Ranran, Zhou Xu, Zhang Lijie, Yang Xinling. Dimethyl fumarate alleviates nerve damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 989-994. |
| [10] | Li Huijun, Li Huangyan, Zhang Yeting. Physical activity and cognition in older adults: research hotspot and topic evolution [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1073-1080. |
| [11] | Dang Xiaowen, Huang Hailiang, Huang Lei, Wang Yajie . Research frontiers and hotspots of carbon nanomaterials in biomedical field over the past 10 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 752-760. |
| [12] | Sima Xinli, Liu Danping, Qi Hui. Effect and mechanism of metformin-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell exosomes on regulating chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7728-7734. |
| [13] | Shui Jing, He Yu, Jiang Nan, Xu Kun, Song Lijuan, Ding Zhibin, Ma Cungen, Li Xinyi. Astrocytes regulate remyelination in central nervous system [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7889-7897. |
| [14] | Zhang Xiaoyu, Wei Shanwen, Fang Jiawei, Ni Li. Prussian blue nanoparticles restore mitochondrial function in nucleus pulposus cells through antioxidation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7318-7325. |
| [15] | Su Yongkun, Sun Hong, Liu Miao, Yang Hua, Li Qingsong. Development of novel antioxidants and antioxidant combination carried by nano-hydrogel systems in treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(34): 7376-7384. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||