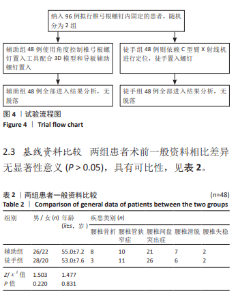
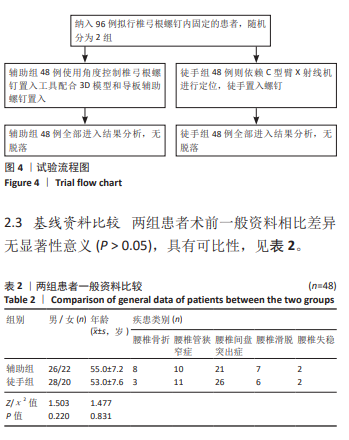
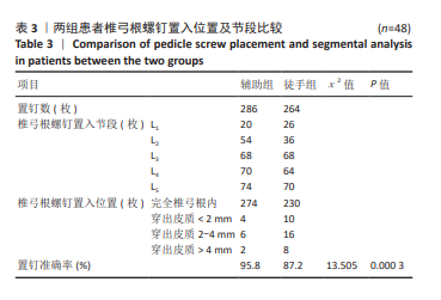
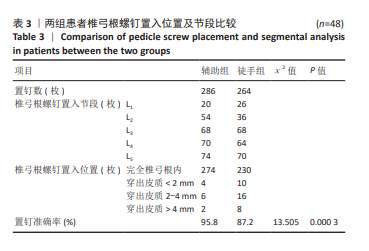
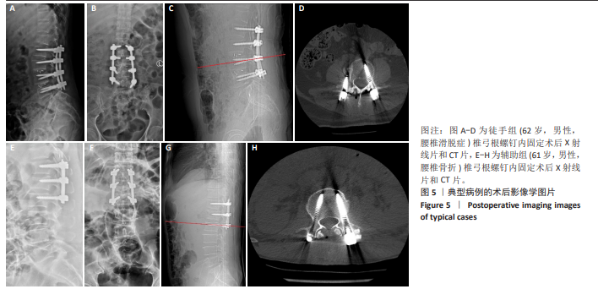
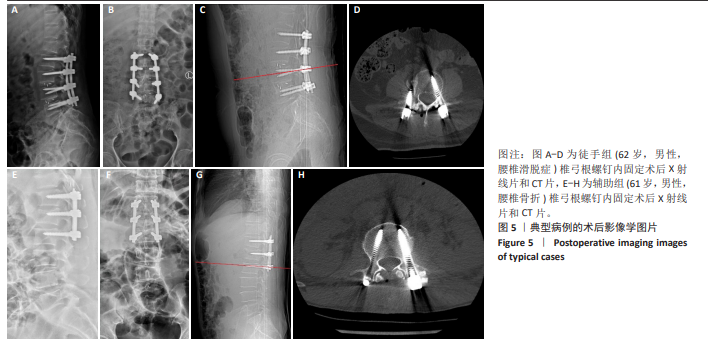
[1] GAUTSCHI OP, SCHATLO B, SCHALLER K, et al. Clinically relevant complications related to pedicle screw placement in thoracolumbar surgery and their management: a literature review of 35 630 pedicle screws. Neurosurg Focus. 2011;31(4):E8.
[2] 王雅辉,刘正蓬,褚立,等.3D打印技术在椎弓根螺钉置入过程中的应用价值[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(6):931-935.
[3] 甘肃省中医院.一种椎弓根螺钉置入方法: CN202011519200.X[P] 2021-04-09.
[4] 杨镇源,邓强,陈文,等.角度控制组合式椎弓根螺钉置入工具的临床应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2018,21(5):545-548.
[5] 杨镇源,邓强,史文宇,等.角度控制组合式椎弓根螺钉置入工具的设计研发[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2015,23(7):71-72.
[6] 张啟维,张耀南,孙常太,等.计算机导航下椎弓根置钉与徒手置钉的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(9):1579-1585.
[7] BOHL MA, ZHOU JJ, MOONEY MA, et al. The Barrow Biomimetic Spine: effect of a 3-dimensional-printed spinal osteotomy model on performance of spinal osteotomies bymedical students and interns. J Spine Surg. 2019;5(1):58-65.
[8] 刘运潮,侯树勋,张宇鹏.脊柱椎弓根螺钉置钉技术研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(8):596-601.
[9] 潘呈,严荣爽,费德锐,等.徒手与辅助技术对于下颈椎椎弓根螺钉置入准确性比较的Meta分析[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2023,44(9): 32-38.
[10] SMITH JS, SHAFFREY CI, AMES CP, et al. Treatment of adult thoracolumbar spinal deformity:past,present,and future. J Neurosurg Spine. 2019;30(5):551-567.
[11] MASON A, PAULSEN R, BABUSKA JM, et al. The accuracy of pedicle screw placement using intraoperative image guidance systems. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;20(2):196-203.
[12] KOKTEKIR E, CEYLAN D, TATARLI N, et al. Accuracy of fluoroscopically-assisted pedicle screw placement: analysis of 1 218 screws in 198 patients. Spine J. 2014;14(8):1702-1708.
[13] 杨睿,李勇奇,张柯,等.天玑骨科机器人辅助椎弓根螺钉置入的临床应用及体会[J].实用骨科杂志,2019,25(10):892-897.
[14] 刘亚军,乐晓峰,郑山,等.计算机导航辅助颈椎椎弓根螺钉内固定技术[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2018,3(3):182-187.
[15] 王雅辉,刘正蓬,褚立,等.3D打印技术在椎弓根螺钉置入过程中的应用价值[J].实用医学杂志,2019,35(6):931-935.
[16] COOL J, VAN SCHUPPEN J, DE BOER MA, et al. Accuracy assessment of pedicle screwinsertion with patient specific 3D‑printed guides through superimpose CT-analysis inthoracolumbar spinal deformity surgery. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(11):3216-3224.
[17] 杨阳,刘林,薛文,等.3D打印技术在重度僵硬性脊柱侧后凸畸形截骨矫形治疗中的辅助作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(31): 4959-4964.
[18] AILI A, MA Y, SUI J, et al. Application of 3D printed models in the surgical treatment ofspinal deformity. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(9): 6341-6348.
[19] 刘爱国,陈朝辉,李东辉,等.下颈椎骨折并脱位手术中3D打印导航模板的有效性与安全性评价[J]. 深圳中西医结合杂志,2022, 32(6):6-9.
[20] 厉彦成,李磊,饶建伟,等.改良3D打印导航模板辅助颈椎后路经椎弓根置钉的效果观察[J]. 浙江临床医学,2023,25(1):89-92.
[21] YANG J, NI P, ZHANG L, et al. Clinical Application of a 3D-Printed Positioning Module and Navigation Template for Percutaneous Vertebroplasty. Surg Innov. 2022;29(6):760-768.
[22] 姜成浩. 脊柱侧凸后路手术中3D打印导航模板与徒手置钉技术的比较研究[D]. 合肥:安徽医科大学,2023.
[23] 牛建雄. 3D打印导航模板与骨科导航机器人辅助置钉在脊柱畸形矫形中的临床研究[D]. 兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2023.
[24] 徐震超,陈刚.3D打印技术在脊柱外科的应用进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2018,38(11):2513-2517.
[25] AZIMI P, YAZDANIAN T, BENZEL EC, et al. 3D-printed navigation template in cervical spine fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2021;30(2):389-401.
[26] XIONG X, CHEN YL, ZHAO L, et al. Individualized 3D-printed navigation template-assisted tension band wiring for olecranon fractures. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023;18(1):407.
[27] HU X, ZHONG M, LOU Y, et al. Clinical application of individualized 3D-printed navigation template to children with cubitus varus deformity. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):111.
[28] JI Z, JIANG Y, SUN H, et al. 3D-printed template and optical needle navigation in CT-guided iodine-125 permanent seed implantation. J Contemp Brachytherapy. 2021;13(4):410-418.
[29] HE K, DONG C, WEI H, et al. A Minimally Invasive Technique Using Cortical Bone Trajectory Screws Assisted by 3D-Printed Navigation Templates in Lumbar Adjacent Segment Degeneration. Clin Interv Aging. 2021;16:1403-1413.
[30] WAN Y, XUE P, YUE J, et al. Comparison of Computer-Assisted Navigation and 3D Printed Patient-Specific Template for the Iliosacral Screw Placement. Orthop Surg. 2023;15(11):2855-2863.
[31] GARCÍA-MATO D, OCHANDIANO S, GARCÍA-SEVILLA M, et al. Craniosynostosis surgery: workflow based on virtual surgical planning, intraoperative navigation and 3D printed patient-specific guides and templates. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):17691.
[32] FAN M, WANG Y, PANG H, et al. Application of three-dimensional printed navigation templates to correct lower limb deformities in children by the guided growth technique. World J Pediatr Surg. 2022; 5(3):e000349.
[33] LIU D, LI Y, LI T, et al. The use of a 3D-printed individualized navigation template to assist in the anatomical reconstruction surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(24):1656.
[34] ZHANG W, MOU L, ZHANG S, et al. 3D-printed individualized navigation template versus the fluoroscopic guide to defining the femoral tunnel for medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023;102(4):e32729.
[35] 杨镇源,张继伟,邓强.3D打印导板辅助经皮微创椎弓根螺钉置入治疗多节段腰椎骨折的疗效[J].实用医学杂志,2022,38(15):1930-1935.
[36] 杨镇源,史文宇.椎弓根螺钉置入导向装置研究现状[J].外科研究与新技术,2017,6(2):110-112.
|