Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (14): 3504-3514.doi: 10.12307/2026.631
Previous Articles Next Articles
Finite element analysis of mechanical properties of porous tantalum implants with different structures and porosities
Wang Ruihao1, 2, Hu Xiaohua3, Wang Yujiao1, 2, Linghu Min1, 2, Yang Xiaohong1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, 3Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Basic Pharmacology, Ministry of Education, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2025-04-09Accepted:2025-06-15Online:2026-05-18Published:2025-09-06 -
Contact:Yang Xiaohong, MD, Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Wang Ruihao, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, Affiliated Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China; Key Laboratory of Basic Pharmacology, Ministry of Education, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563006, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:Project of Postgraduate Research Fund of Zunyi Medical University, No. ZKY202 (to LHM)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Ruihao, Hu Xiaohua, Wang Yujiao, Linghu Min, Yang Xiaohong. Finite element analysis of mechanical properties of porous tantalum implants with different structures and porosities[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3504-3514.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
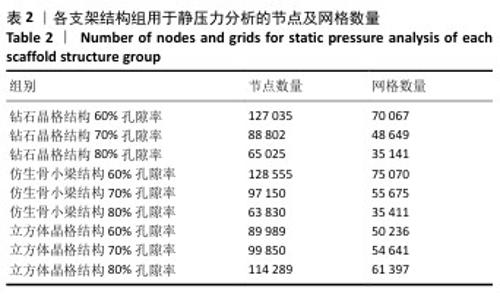
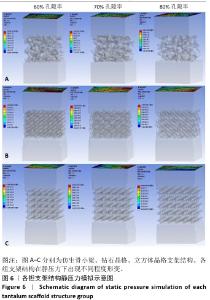
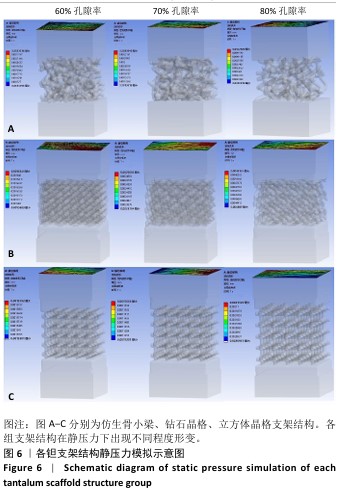
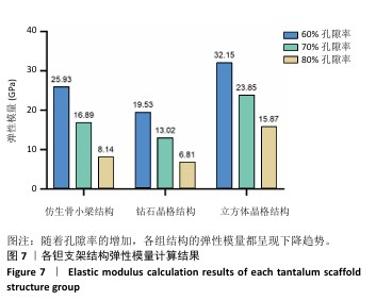
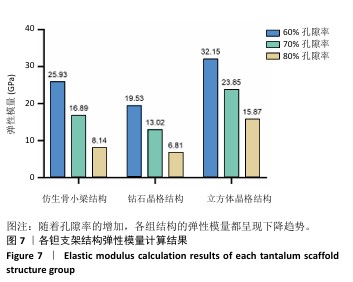
2.1 各组支架结构的弹性模量模拟结果 静压力模拟中使用Ansys软件进行自动网格划分,计算收敛后的各组网格数量及节点数如表2所示。模拟计算结果如图6所示,可以看到各组在静压力下出现不同程度形变。根据公式(2)计算得到弹性模量,其中形变量“dL”为施力面沿受力方向的位移量,计算时取软件中施力面沿Z轴方向的形变量均值。计算得到各组结构的弹性模量如图7所示,可知随着孔隙率的增加,各组结构的弹性模量都呈现下降趋势。有研究指出人下颌骨皮质弹性模量介于12-20 GPa之间[4-7],因此,实验选出各结构中最接近该数值的分组,即钻石晶格结构60%组、仿生骨小梁结构70%组、立方体晶格结构80%组,继续探究它们的早期成骨性能及种植后负载下骨应力表现。"
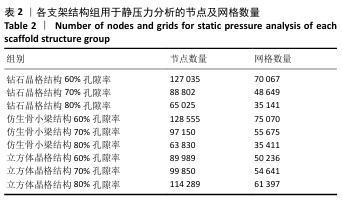
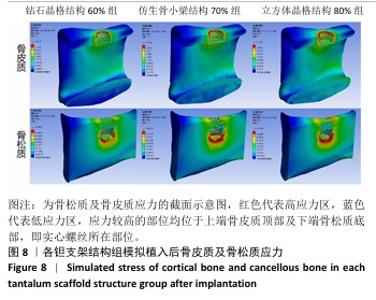
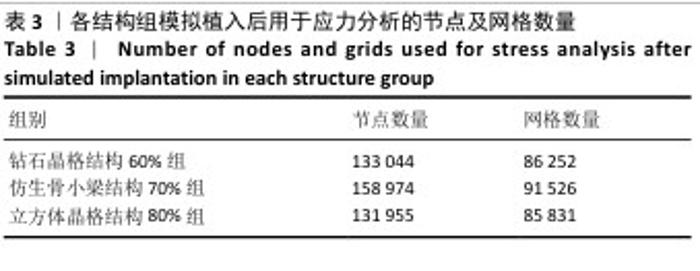
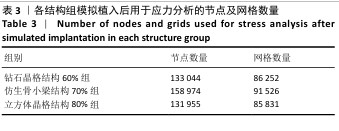
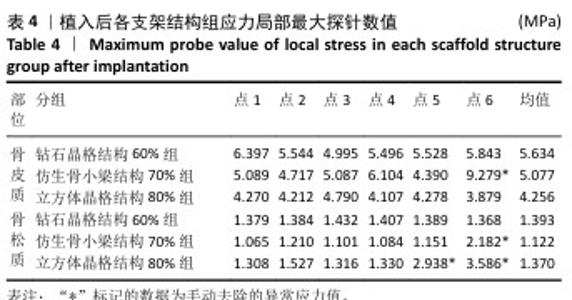
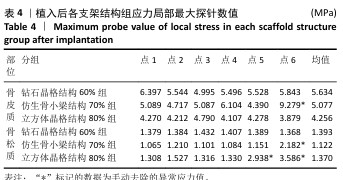
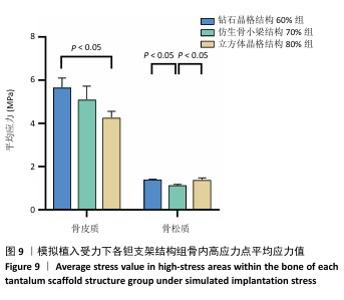
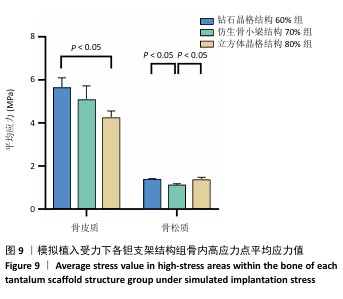
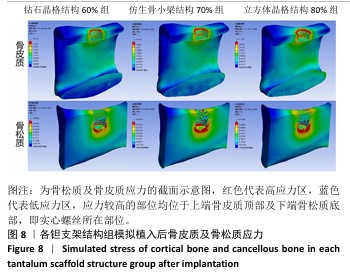
2.2 植入后材料结构对骨应力的影响 由于3种结构均具有弹性模量接近下颌骨皮质的孔隙率分组,因此,实验进一步模拟种植体下颌磨牙区植入,并对外力负载下的骨内应力进行观测,探讨哪一种结构最有利于保护骨组织。种植体植入后压力模拟前软件自动划分网格,单元数及节点数如表3所示。模拟结果如图8所示,为骨松质及骨皮质应力的截面示意图,红色代表高应力区,蓝色代表低应力区,发现应力较高的部位均位于上端骨皮质顶部以及下端骨松质底部,即实心螺丝所在部位,这也印证了多孔支架结构能够降低弹性模量从而保护骨组织的观点。 在制作模型时为了还原真实结构,模型各组成部分间的界面不可避免地会产生尖锐部位,计算中这些尖锐部位会导致应力奇异现象,使应力值异常增大,从而干扰实验结果。若将计算结果中的单个最大应力点作为骨植入后应力观测的评判标准,将导致实验结论明显偏离实际,故使用软件中创建局部最大应力探针功能,自动标记6个最高应力部位数值并进行人工筛选,去除尖锐交界部位的异常应力,剩下的应力值计算均值作为钽支架结构对骨保护作用的评判标准。软件局部最大应力探针选取的各高应力点应力数值如表4所示。各组高应力点平均应力值对比结果,如图9所示,3组骨皮质应力呈依次下降趋势,仿生骨小梁结构70%组骨皮质高应力区平均应力与钻石晶格结构60%组、立方体晶格结构80%组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),但相对的骨松质部分平均应力均值低于钻石晶格结构60%组、立方体晶格结构80%组(P < 0.05);钻石晶格60%组骨皮质平均应力值高于立方体晶格80%组(P < 0.05),两组骨松质平均应力值比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。由于设计的种植体多孔支架部分主要位于骨松质内,因此应该更加关注骨松质内的应力情况,故认为仿生骨小梁结构70%组是保护骨组织效果最佳的结构。 "
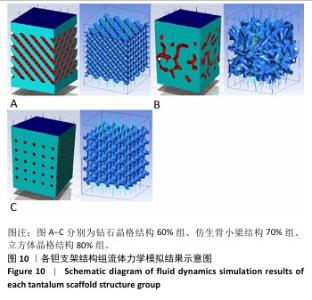
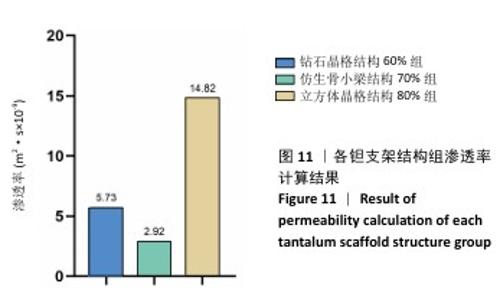
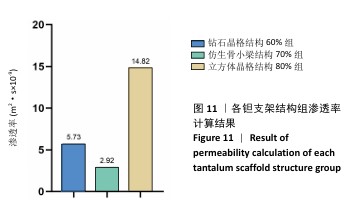
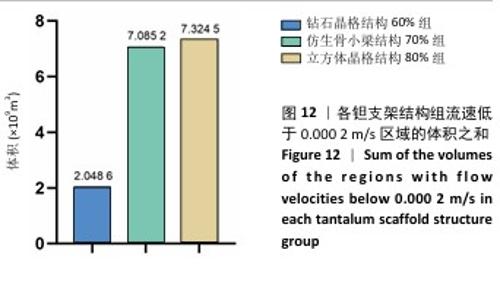
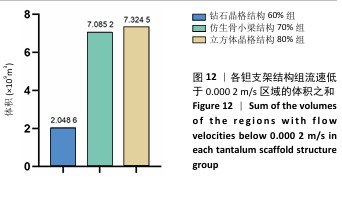
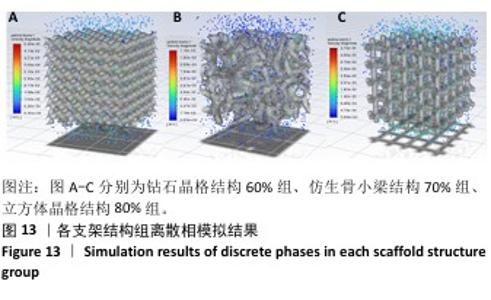
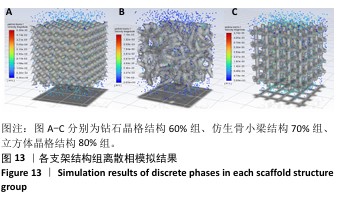
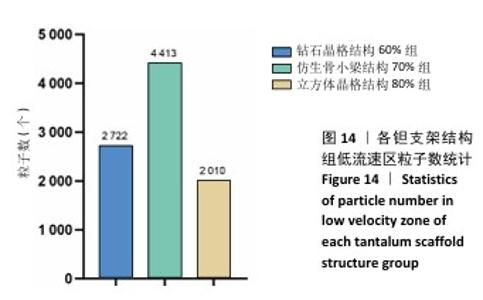
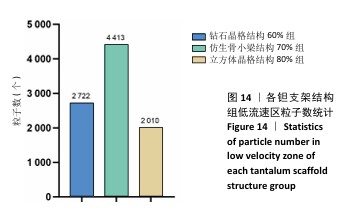
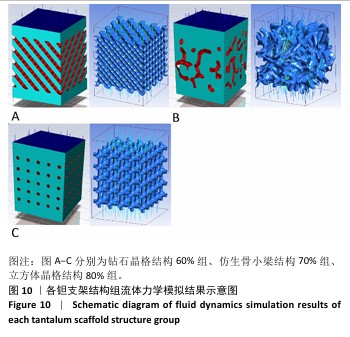
2.3 不同结构对渗透性及早期细胞附着的影响 种植体植入后的远期预后不仅受弹性模量影响,短期内的成骨和愈合过程也与细胞附着速度密切相关,故实验对3个弹性模量优选组进行流体力学性能的进一步探索。由于渗透率是衡量物质交换能力的重要指标,实验首先对渗透率进行了计算分析。模拟前进行体网格划分后,钻石晶格结构60%组、仿生骨小梁结构70%、立方体晶格结构80%组的网格单元数量分别为5 979 760,7 186 003,6 290 150。在软件中模拟向流体区域注入流速0.001 m/s的组织液,结果如图10所示。根据达西定律:K=vμL/Δp,其中已知流体的进出口流速v、行进路程L、液体黏性μ等物理量,现需求得压降Δp。使用软件中的“结果-报告-表面积分-区域权重”功能,可统计进出口的压强均值,进而求得液体进出口压降Δp。渗透率计算结果如图11所示,立方体晶格结构80%组渗透率最高,钻石晶格结构60%组次之,而仿生骨小梁结构70%组渗透率最低。 然而,较高的渗透率虽有助于物质交换、促进成骨,却并不意味着渗透性越高越利于成骨。更高的渗透性常意味着更快的液体流速,而液体流速过快将不利于细胞的黏附和生长;相反,靠近支架区域的低液体流速区域有助于细胞在此区域支架上的停留和附着[33],因此对靠近支架区域低流速区体积之和进行了统计,统计结果如图12所示,立方体晶格结构80%组低流速区体积之和最大,略高于仿生骨小梁结构70%组,而钻石晶格结构60%组低流速区体积之和最小。 为了更加直观地观测不同支架结构对附着难易度的影响,探究最有利于早期细胞黏附生长的一组结构,引入了离散相微粒用于模拟细胞在流体中的运动。在液体中按细胞大小参数将粒子直径设置为25 μm,并将先前的流体模拟设置改为瞬态,模拟结果如图13所示,可观察到粒子在流体中的分布,蓝色表示运动速度低,颜色越接近红色表示运动速度越高。低流速区域的粒子数量统计结果如图14所示,仿生骨小梁结构70%组液体低流速区体积虽略低于立方体晶格结构80%组,但低液体流速区的粒子数量达到立方体晶格结构80%组的2倍多,并且明显高于钻石晶格60%组。表明仿生骨小梁结构70%孔隙率有助于细胞靠近、停留于支架附近,有利于细胞在材料上附着,从而能够提供比另外两组更优秀的早期成骨效果。这可能利于缩短临床中的种植后恢复时间,减少患者等待上部结构修复期间的痛苦。 "
| [1] 田敏.牙列缺损种植固定修复体种植体周围病的影响因素研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2016. [2] MEISCHEL M, HORMANN D, DRAXLER J, et al. Bone-implant degradation and mechanical response of bone surrounding Mg-alloy implants. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;71:307-313. [3] AHN TK, LEE DH, KIM TS, et al. Modification of Titanium Implant and Titanium Dioxide for Bone Tissue Engineering. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1077:355-368. [4] 单验博,乔波,杨烁,等.口腔种植体新材料的研究进展[J].解放军医学院学报,2023,44(1):74-78,85. [5] 宋凯乐.面向即刻种植的根形种植体功能性重建研究[D].济南:山东大学,2021. [6] WANG X, XU S, ZHOU S, et al. Topological design and additive manufacturing of porous metals for bone scaffolds and orthopaedic implants: A review. Biomaterials. 2016;83:127-141. [7] 黄伟.面向性能调控的多孔空间结构骨组织工程支架设计[D].大连:大连交通大学,2021. [8] LIANG D, ZHONG C, JIANG F, et al. Fabrication of Porous Tantalum with Low Elastic Modulus and Tunable Pore Size for Bone Repair. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2023;9(3):1720-1728. [9] KOVÁCS ÁÉ, CSERNÁTONY Z, CSÁMER L, et al. Comparative Analysis of Bone Ingrowth in 3D-Printed Titanium Lattice Structures with Different Patterns. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(10):3861. [10] DENG F, LIU L, LI Z, et al. 3D printed Ti6Al4V bone scaffolds with different pore structure effects on bone ingrowth. J Biol Eng. 2021; 15(1):4. [11] CHEN H, LIU Y, WANG C, et al. Design and properties of biomimetic irregular scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Comput Biol Med. 2021;130:104241. [12] 廖波.胫骨填充多孔钛合金支架仿生设计及服役和骨再生行为研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2022. [13] BENCHARIT S, BYRD WC, ALTARAWNEH S, et al. Development and Applications of Porous Tantalum Trabecular Metal‐Enhanced Titanium Dental Implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2013;16(6):817-826. [14] MA R, LIU Q, ZHOU L, et al. High porosity 3D printed titanium mesh allows better bone regeneration. BMC Oral Health. 2023;23(1):6. [15] 徐伟.基于SLM梯度多孔钛口腔种植体结构设计及应用基础研究[D].北京:北京科技大学,2021. [16] WANG X, NING B, PEI X. Tantalum and its derivatives in orthopedic and dental implants: Osteogenesis and antibacterial properties. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;208:112055. [17] LU MM, WU PS, GUO XJ, et al. Osteoinductive effects of tantalum and titanium on bone mesenchymal stromal cells and bone formation in ovariectomized rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(21): 7087-7104. [18] DOMMETI VK, ROY S, PRAMANIK S, et al. Design and Development of Tantalum and Strontium Ion Doped Hydroxyapatite Composite Coating on Titanium Substrate: Structural and Human Osteoblast-like Cell Viability Studies. Materials (Basel). 2023;16(4):1499. [19] ZHU Y, GU Y, QIAO S, et al. Bacterial and mammalian cells adhesion to tantalum-decorated micro-/nano-structured titanium. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(3):871-878. [20] GUO Y, XIE K, JIANG W, et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Study of 3D-Printed Porous Tantalum Scaffolds for Repairing Bone Defects. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2019;5(2):1123-1133. [21] 王铭.电子束增材制造钛合金组织与力学性能研究[D].淄博:山东理工大学,2019. [22] JAFARI MS, BENDER B, COYLE C, et al. Do Tantalum and Titanium Cups Show Similar Results in Revision Hip Arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(2):459-465. [23] ISOBE D, YANG Q. An integrated finite element analysis and virtual reality system for structural and indoor nonstructural components of buildings under seismic excitations. J Building Eng. 2024;98. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2024.111320. [24] GIA NINH D, TRONG LONG N, VAN VANG T, et al. A new study for aeroplane wing shapes made of boron nitride nanotubes-reinforced aluminium, Part I: review, dynamical analyses and simulation. Compos Struct. 2023;303. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2022.116239. [25] MESLIER QA,SHEFELBINE SJ. Using Finite Element Modeling in Bone Mechanoadaptation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2023;21(2):105-116. [26] 彭琳晶,干耀恺,姚怡飞.多孔钽植入物在骨缺损中的应用进展[J].材料工程,2022,50(11):1-13. [27] 吴先哲.骨科植入用多孔钽激光3D打印成形工艺及生物力学性能研究[D].北京:机械科学研究总院,2021. [28] 王靖.基于SLM的Ti6Al4V梯度多孔牙种植体结构设计及力学特性研究[D].福州:福建工程学院, 2023. [29] ZHANG J, ZHANG X, CHEN Y, et al. Novel Design and Finite Element Analysis of Diamond-like Porous Implants with Low Stiffness. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(22):6918. [30] CHAKRABORTY A, DATTA P, MAJUMDER S, et al. Finite element and experimental analysis to select patient’s bone condition specific porous dental implant, fabricated using additive manufacturing. Comput Biol Med. 2020;124:103839. [31] LIU Z, TAMADDON M, CHEN SM, et al. Determination of an Initial Stage of the Bone Tissue Ingrowth Into Titanium Matrix by Cell Adhesion Model. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021;9:736063. [32] 吴桐.TPMS多孔材料渗透率的评估模型研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2021. [33] 吴其右,崔博宇,夏炜,等.基于细胞黏附的不同微结构3D打印多孔生物支架流体力学有限元分析 [J].组织工程与重建外科,2024, 20(3):293-299. [34] TIAN Y, TONG Z, LU F, et al. Tantalum composite gold coupled on 3D printed Ti6Al4V with a bone-like porous surface structures. Appl Surface Sci. 2025;689. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2025.162532. [35] YU H, XU M, DUAN Q, et al. 3D-printed porous tantalum artificial bone scaffolds: fabrication, properties, and applications. Biomed Mater. 2024;19(4). doi:10.1088/1748-605X/ad46d2. [36] 郭芳,黄硕,胡敏,等.3D打印表面多孔钛根形种植体的生物力学研究[J].医用生物力学,2021,36(1):85-91. [37] CHASTAND V, QUAEGEBEUR P, MAIA W, et al. Comparative study of fatigue properties of Ti-6Al-4V specimens built by electron beam melting (EBM) and selective laser melting (SLM). Mater Charact. 2018;143:76-81. [38] WANG X, ZHANG S, WANG Z Y, et al. 3D printing externally reinforced layers for high-speed railway brake discs: Adaptability of SLM processes for manufacturing gradient materials. Mater Today Commun. 2022;31. doi:org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103778. [39] PALMQUIST A, JOLIC M, HRYHA E, et al. Complex geometry and integrated macro-porosity: Clinical applications of electron beam melting to fabricate bespoke bone-anchored implants. Acta Biomater. 2023;156:125-145. [40] HERRERA P, HERNANDEZ-NAVA E, THORNTON R, et al. Abrasive wear resistance of Ti-6AL-4V obtained by the conventional manufacturing process and by electron beam melting (EBM). Wear. 2023;524-525. [41] CALIGNANO F, GALATI M, IULIANO L, et al. Design of Additively Manufactured Structures for Biomedical Applications: A Review of the Additive Manufacturing Processes Applied to the Biomedical Sector. J Healthc Eng. 2019;2019:9748212. [42] RUPPERT DS, HARRYSSON OLA, MARCELLIN-LITTLE DJ, et al. Osseointegration of Coarse and Fine Textured Implants Manufactured by Electron Beam Melting and Direct Metal Laser Sintering. 3D Print Addit Manuf. 2017;4(2):91-97. [43] MAO S, LIU Y, WANG F, et al. Design and biomechanical analysis of patient-specific porous tantalum prostheses for knee joint revision surgery. Int J Bioprint. 2024;9(4):735. [44] 邓富元.3D打印不同几何形状孔隙的钛合金支架对骨长入影响研究[D].泸州:西南医科大学, 2021. [45] 高媛.舌侧活动翼矫治器内收上前牙的三维有限元研究[D].西安:中国人民解放军空军军医大学,2024. [46] RICHERT R, FARGES JC, TAMIMI F, et al. Validated Finite Element Models of Premolars: A Scoping Review. Materials (Basel). 2020;13(15):3280. [47] ZHAI M, ZHU Y, YANG M, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Enhance Cell-Free Bone Regeneration by Altering Their miRNAs Profiles. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(19):2001334. [48] 徐震超.多孔钽载双抗生素微球支架的构建及成骨和抗菌性能评估[D].长沙:中南大学,2023. [49] BABEY ME, KRAUSE WC, CHEN K, et al. A maternal brain hormone that builds bone. Nature. 2024;632(8024):357-365. [50] WANG R, NI S, MA L, et al. Porous construction and surface modification of titanium-based materials for osteogenesis: A review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:973297. [51] HUANG G, PAN ST, QIU JX. The Clinical Application of Porous Tantalum and Its New Development for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(10):2647. |
| [1] | Zheng Xuying, Hu Hongcheng, Xu Libing, Han Jianmin, Di Ping. Stress magnitude and distribution in two-piece cement-retained zirconia implants under different loading conditions and with varying internal connection shapes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 1979-1987. |
| [2] | Yang Qiongqiong, Liu Wei. Comparison of performance and clinical effects of zirconia and titanium implants [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(8): 2063-2071. |
| [3] | Li Congcong, Wufanbieke·Baheti, Zhao Li, Chen Xiaotao, Kong Chuifan, Yu Min. Physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of hydroxyapatite/graphene oxide/interleukin-4 composite coating materials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 404-413. |
| [4] | Cheng Yanan, Yu Jiazhi, Liu Yinchang, Wu Jie, Yu Tong, Wang Lu, Li Xiaoguang. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of molar distalization with clear aligners with different thicknesses and edges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 310-318. |
| [5] | Zhang Tianwei, Han Xingyuan, Zhang Dianming, Li Ronghua, Zhao Dewei. Structural design and finite element analysis of biodegradable zinc alloy bone plate based on regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3485-3493. |
| [6] | Zhang Junjie, Gegentana. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of influence of different filling methods of the maxillary second premolar on root resistance [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3515-3523. |
| [7] | Du Xue, Luo Siyang, Feng Hongchao, Liu Jianguo, Luo Yi, Sun Jiangling, Chang Xingtao, Li Yuting, Wang Ruijie. Finite element analysis of stress distribution of Schneiderian membrane after maxillary sinus elevation and implantation under different bone quality conditions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3524-3535. |
| [8] | Xie Lili, Zhang Hao, Xun Chunlei. Three-dimensional finite element analysis on distalization of orthodontic maxillary dentition [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(14): 3557-3567. |
| [9] | Mawulanjiang · Abudurenmu, Zilalai · Julaiti, Baibujiafu · Yelisi, Gulizainu · Yibulayin, Nijiati · Tuerxun. Stress analysis of angled abutments of maxillary central incisor implant crown in different implant spacing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3351-3359. |
| [10] | Guan Zhenju, Xie Yonglin, Xiang Shougang, Zhang Chengdong, Li Xiaolong, Li Xingping, Pu Chao, Zhang Bo, Luo Xuwei, Xiao Dongqin. Preparation of polyphenol-mediated copper ion coating on titanium surface and antibacterial and antioxidant properties [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 1997-2005. |
| [11] | Dumanbieke·Amantai, He Huiyu, Han Xiangzhen. Hydroxyapatite-graphene oxide composite coating promotes bone defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2030-2037. |
| [12] | Chen Shaobo, Shuang Feng, Hu Wei, Li Hao, Shao Yinchu. Injectable bone graft for the repair of nonunion of midshaft clavicular fracture after internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5473-5477. |
| [13] | Zhang Bin, Sun Lihua, Zhang Junhua, Liu Tongbin, Liu Yusan, Cui Caiyun, Li Jun. Short-term effect comparison of a modified socket shield technique and conventional flapless immediate implant and immediate restoration in maxillary aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5514-5519. |
| [14] | Shi Qianhui, Wu Chao, Zhou Qian, Cheng Yuting, Li Fang, Huo Hua, Qi Yuhan, Huang Xiaolin, Wang Yong, Liao Jian. Prevention and treatment of implant periapical lesions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5434-5440. |
| [15] | Zhang Suping, Sun Ling, Wan Dingming, Cao Weijie, Li Li, Liu Changfeng, Liu Yufeng, Wang Dao, Guo Rong, Jiang Zhongxing, Xie Xinsheng. Effectiveness of unrelated peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in the treatment of severe aplastic anemia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 4994-5001. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||