Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2870-2876.doi: 10.12307/2026.037
Previous Articles Next Articles
Carboxypeptidase M: unveiling a new therapeutic target for osteonecrosis based on eQTL Database and Finnish Genetic Big Data
Gao Xinhai1, Tan Huangsheng1, He Shenghua2
- 1The Fourth Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Second Ward of the Orthopedics and Traumatology Department, Shenzhen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2025-01-24Accepted:2025-04-03Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-06 -
Contact:He Shenghua, MS, Chief physician, The Second Ward of the Orthopedics and Traumatology Department, Shenzhen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Gao Xinhai, Physician, The Fourth Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen 518000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:Shenzhen “Healthcare Sanming Project,” No. SZZYSM202211004 (to HSH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Xinhai, Tan Huangsheng, He Shenghua. Carboxypeptidase M: unveiling a new therapeutic target for osteonecrosis based on eQTL Database and Finnish Genetic Big Data[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2870-2876.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
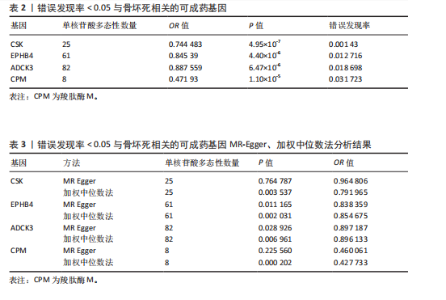
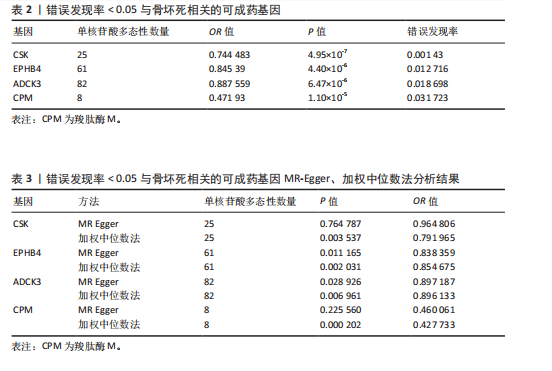
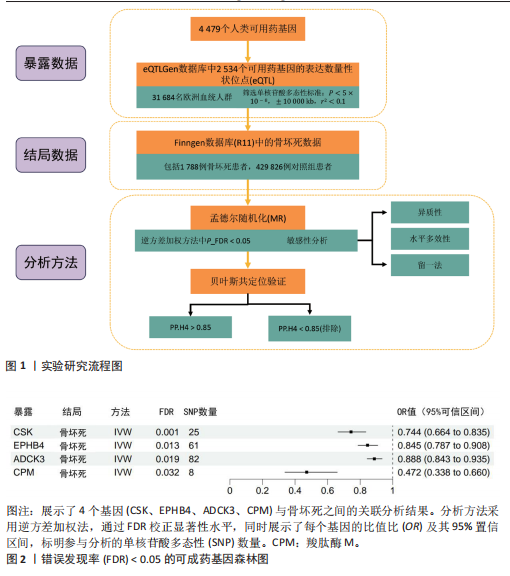
2.1 工具变量筛选与孟德尔随机化分析结果 根据工具变量的选择标准,共筛选出2 534个可成药基因的39 155个单核苷酸多态性作为工具变量,这些单核苷酸多态性与暴露均具有显著的关联性,且所有工具变量的F值均超过20,最低为29.72,平均值为186.39,表明工具变量的效能较强,能够满足孟德尔随机化分析的假设要求。 基于逆方差加权法的孟德尔随机化分析结果显示,有317个可成药基因的表达水平与骨坏死显著相关(P < 0.05)。其中,4个可成药基因通过FDR多重检验校正(FDR < 0.05),分别为CSK、EPHB4、ADCK3和CPM,见表2。此外,采用多种方法评估CPM、CSK、EPHB4和ADCK3基因高表达对骨坏死风险的保护作用。逆方差加权法分析显示,这4个基因的高表达均与骨坏死风险的显著降低相关,其中CPM基因的OR=0.47 (95%CI:0.34-0.66,P=1.10×10-5),CSK基因OR=0.74(95%CI:0.66-0.83,P=4.95×10??),EPHB4基因OR=0.85(95%CI:0.79-0.91,P=4.40×10??),ADCK3基因OR=0.89(95%CI:0.84-0.93,P=6.47×10-6),见图2。为验证结果的稳健性,进一步采用MR-Egger和加权中位数法进行分析。加权中位数法的结果与主要分析一致,4个基因均显示出显著的保护作用,见表3。在CSK、CPM基因中,MR-Egger效应估计值未达到统计显著性。通过留一法对工具变量进行敏感性分析,结果表明,逐一排除每个工具变量后,4个基因的整体效应估计值无明显变化,验证了分析结果的稳健性。 2.2 异常结果处理与敏感性分析 在MR-Egger回归分析中发现,EPHB4基因存在显著水平的多效性,Cochran’s Q检验结果表明,CSK基因可能存在异质性,暗示这些基因未完全满足孟德尔随机化分析的假设要求。因此,为提高分析结果的准确性和稳健性,在后续分析中排除了EPHB4和CSK基因。 2.3 反向孟德尔随机化 在反向孟德尔随机化分析中,以骨坏死为暴露变量、血液中基因表达的cis-eQTL为结局变量,对CPM基因和ADCK3基因"
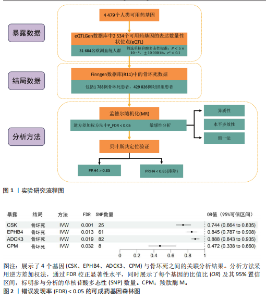
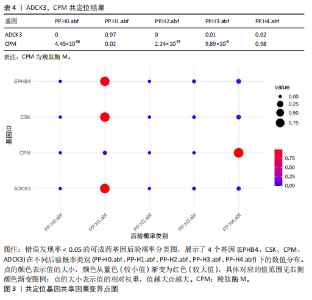
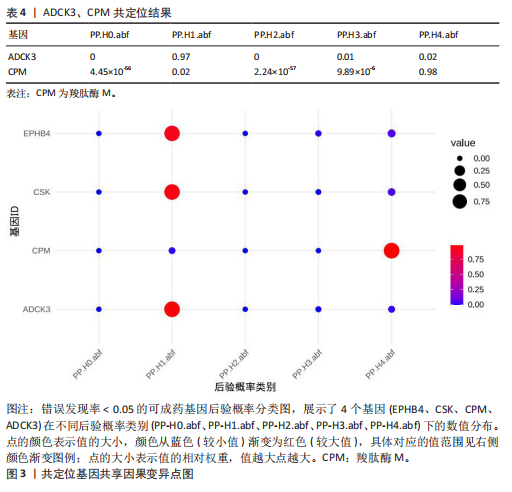
进行了方向性评估。分析结果显示,这2个基因在与骨坏死的反向分析中均未表现出显著的因果关联。这些结果表明,骨坏死对CPM和ADCK3基因表达的潜在因果影响并未得到支持,从因果关系的方向性上进一步验证了正向分析结果的可靠性。 2.4 共定位分析 对于孟德尔随机化分析中通过FDR校正显著的基因,进一步进行了共定位分析,以评估eQTL信号与骨坏死GWAS信号是否共享因果变异。共定位分析结果显示(表4),CPM基因的eQTL信号与骨坏死 GWAS信号具有显著的共定位(后验概率PP.H4 = 98.03%),表明两者共享相同的因果变异,见图3。因此,根据孟德尔随机化分析与共定位分析的综合结果,CPM基因被认为是可能降低骨坏死风险的重要潜在药物靶点。"
| [1] MANKIN HJ. Nontraumatic necrosis of bone (osteonecrosis). N Engl J Med. 1992;326(22): 1473-1479. [2] JONES LC, HUNGERFORD DS. Osteonecrosis: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004;16(4):443-449. [3] RIPAMONTI CI, NAPOLI N. Are We Ready to Use Teriparatide to Treat Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw in Clinical Practice? J Clin Oncol. 2020;38(26):2949-2951. [4] SUN X, CHEN B, QI Y, et al. Multi-omics Mendelian randomization integrating GWAS, eQTL and pQTL data revealed GSTM4 as a potential drug target for migraine. J Headache Pain. 2024;25(1):117. [5] SEKULA P, DEL GRECO MF, PATTARO C, et al. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(11):3253-3265. [6] MAIMAITI A, TURHON M, ABULAITI A, et al. DNA methylation regulator-mediated modification patterns and risk of intracranial aneurysm: a multi-omics and epigenome-wide association study integrating machine learning, Mendelian randomization, eQTL and mQTL data. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):660. [7] LIU Y, LI B, MA Y, et al. Mendelian Randomization Integrating GWAS, eQTL, and mQTL Data Identified Genes Pleiotropically Associated With Atrial Fibrillation. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:745757. [8] SKRIVANKOVA VW, RICHMOND RC, WOOLF BAR, et al. Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology Using Mendelian Randomization: The STROBE-MR Statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614-1621. [9] FINAN C, GAULTON A, KRUGER FA, et al. The druggable genome and support for target identification and validation in drug development. Sci Transl Med. 2017; 9(383):eaag1166. [10] VÕSA U, CLARINGBOULD A, WESTRA HJ, et al. Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression. Nat Genet. 2021;53(9):1300-1310. [11] BIRNEY E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2022;12(4): a041302. [12] ZHANG Y, WANG M, LI Z, et al. An overview of detecting gene-trait associations by integrating GWAS summary statistics and eQTLs. Sci China Life Sci. 2024;67(6):1133-1154. [13] GKATZIONIS A, BURGESS S, NEWCOMBE PJ. Statistical methods for cis-Mendelian randomization with two-sample summary-level data. Genet Epidemiol. 2023;47(1): 3-25. [14] PIERCE BL, AHSAN H, VANDERWEELE TJ. Power and instrument strength requirements for Mendelian randomization studies using multiple genetic variants. Int J Epidemiol. 2011;40(3):740-752. [15] KURKI MI, KARJALAINEN J, PALTA P, et al. FinnGen provides genetic insights from a well-phenotyped isolated population. Nature. 2023;613(7944):508-518. [16] MINTON K. The FinnGen study: disease insights from a ‘bottlenecked’ population. Nat Rev Genet. 2023;24(4):207. [17] YAVORSKA OO, BURGESS S. Mendelian Randomization: an R package for performing Mendelian randomization analyses using summarized data. Int J Epidemiol. 2017;46(6): 1734-1739. [18] BURGESS S, THOMPSON SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the MR-Egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. 2017;32(5):377-389. [19] BURGESS S, DUDBRIDGE F, THOMPSON SG. Combining information on multiple instrumental variables in Mendelian randomization: comparison of allele score and summarized data methods. Stat Med. 2016;35(11):1880-1906. [20] COHEN JF, CHALUMEAU M, COHEN R, et al. Cochran’s Q test was useful to assess heterogeneity in likelihood ratios in studies of diagnostic accuracy. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015; 68(3):299-306. [21] BOWDEN J, DEL GRECO MF, MINELLI C, et al. Assessing the suitability of summary data for two-sample Mendelian randomization analyses using MR-Egger regression: the role of the I2 statistic. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1961-1974. [22] GEORGE NI, BOWYER JF, CRABTREE NM, et al. An Iterative Leave-One-Out Approach to Outlier Detection in RNA-Seq Data. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0125224. [23] SIMOVSKI B, KANDURI C, GUNDERSEN S, et al. Coloc-stats: a unified web interface to perform colocalization analysis of genomic features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(W1):W186-W193. [24] RASOOLY D, PELOSO GM, GIAMBARTOLOMEI C. Bayesian Genetic Colocalization Test of Two Traits Using coloc. Curr Protoc. 2022; 2(12):e627. [25] KANDURI C, SANDVE GK, HOVIG E, et al. Editorial: Genomic Colocalization and Enrichment Analyses. Front Genet. 2021;11: 617876. [26] LIN J, ZHOU J, XU Y. Potential drug targets for multiple sclerosis identified through Mendelian randomization analysis. Brain. 2023;146(8):3364-3372. [27] YUAN N, ZHANG W, YANG W, et al. Exosomes derived from M2 macrophages prevent steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by modulating inflammation, promoting bone formation and inhibiting bone resorption. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):243. [28] WISNIEWSKI P, GANGNUS T, BURCKHARDT BB. Recent advances in the discovery and development of drugs targeting the kallikrein-kinin system. J Transl Med. 2024;22(1):388. [29] BUELLI S, IMBERTI B, MORIGI M. The Complement C3a and C5a Signaling in Renal Diseases: A Bridge between Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Nephron. 2024;148(10):712-723. [30] DEITEREN K, HENDRIKS D, SCHARPÉ S, et al. Carboxypeptidase M: Multiple alliances and unknown partners. Clin Chim Acta. 2009; 399(1-2):24-39. [31] TSAKIRIS I, TOROCSIK D, GYONGYOSI A, et al. Carboxypeptidase-M is regulated by lipids and CSFs in macrophages and dendritic cells and expressed selectively in tissue granulomas and foam cells. Lab Invest. 2012;92(3):345-361. [32] HERNIGOU P, HERNIGOU J, SCARLAT M. Shoulder Osteonecrosis: Pathogenesis, Causes, Clinical Evaluation, Imaging, and Classification. Orthop Surg. 2020;12(5):1340-1349. [33] TAMARI T, KAWAR-JARAISY R, DOPPELT O, et al. The Paracrine Role of Endothelial Cells in Bone Formation via CXCR4/SDF-1 Pathway. Cells. 2020;9(6):1325. [34] MARQUEZ-CURTIS L, JALILI A, DEITEREN K, et al. Carboxypeptidase M expressed by human bone marrow cells cleaves the C-terminal lysine of stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha: another player in hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell mobilization? Stem Cells. 2008;26(5):1211-1220. [35] JALILI A, SHIRVAIKAR N, MARQUEZ-CURTIS L, et al. Fifth complement cascade protein (C5) cleavage fragments disrupt the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis: further evidence that innate immunity orchestrates the mobilization of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Exp Hematol. 2010; 38(4):321-332. [36] KOBAYASHI M, WAKABAYASHI I, SUZUKI Y, et al. Tubulin carboxypeptidase activity of vasohibin-1 inhibits angiogenesis by interfering with endocytosis and trafficking of pro-angiogenic factor receptors. Angiogenesis. 2021;24(1):159-176. [37] ZHANG X, TAN F, BROVKOVYCH V, et al. Carboxypeptidase M augments kinin B1 receptor signaling by conformational crosstalk and enhances endothelial nitric oxide output. Biol Chem. 2013;394(3):335-345. [38] ZHANG X, YANG Z, XU Q, et al. Dexamethasone Induced Osteocyte Apoptosis in Steroid-Induced Femoral Head Osteonecrosis through ROS-Mediated Oxidative Stress. Orthop Surg. 2024;16(3):733-744. [39] CAWLEY NX, YANIK T, WORONOWICZ A, et al. Obese carboxypeptidase E knockout mice exhibit multiple defects in peptide hormone processing contributing to low bone mineral density. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;299(2):E189-E197. [40] XI L, SONG Y, WU W, et al. Investigation of bone matrix composition, architecture and mechanical properties reflect structure-function relationship of cortical bone in glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis. Bone. 2020;136:115334. [41] HARDY E, FERNANDEZ-PATRON C. Destroy to Rebuild: The Connection Between Bone Tissue Remodeling and Matrix Metalloproteinases. Front Physiol. 2020;11:47. [42] LIAO Z, ZHENG X, LI H, et al. Carboxypeptidase M modulates BMSCs osteogenesis-adipogenesis via the MAPK/ERK pathway: An integrated single-cell and bulk transcriptomic study. FASEB J. 2024;38(9):e23657. |
| [1] | Wu Zhilin, , He Qin, Wang Pingxi, Shi Xian, Yuan Song, Zhang Jun, Wang Hao . DYRK2: a novel therapeutic target for rheumatoid arthritis combined with osteoporosis based on East Asian and European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1569-1579. |
| [2] | Zhang Qingfeng, Wang Chaoyi, Yang Jingyan, Li Hanyu, Zhao Yuyang, Hao Huatao, Yu Dong. Potential target genes for spondylolisthesis: drugable genome analysis based on the European population-based biodatabase [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1592-1601. |
| [3] | Liu Hongtao, Wu Xin, Jiang Xinyu, Sha Fei, An Qi, Li Gaobiao. Causal relationship between age-related macular degeneration and deep vein thrombosis: analysis based on genome-wide association study data [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1602-1608. |
| [4] | Guo Ying, Tian Feng, Wang Chunfang. Potential drug targets for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: large sample analysis from European databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(6): 1549-1557. |
| [5] | Gao Zengjie, , Pu Xiang, Li Lailai, Chai Yihui, Huang Hua, Qin Yu. Increased risk of osteoporotic pathological fractures associated with sterol esters: evidence from IEU-GWAS and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1302-1310. |
| [6] | Liu Fengzhi, Dong Yuna, Tian Wenyi, Wang Chunlei, Liang Xiaodong, Bao Lin. Gene-predicted associations between 731 immune cell phenotypes and rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1311-1319. |
| [7] | Zhang Cuicui, Chen Huanyu, Yu Qiao, Huang Yuxuan, Yao Gengzhen, Zou Xu. Relationship between plasma proteins and pulmonary arterial hypertension and potential therapeutic targets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1331-1340. |
| [8] | Zeng Hao, Sun Pengcheng, Chai Yuan, Huang Yourong, Zhang Chi, Zhang Xiaoyun. Association between thyroid function and osteoporosis: genome-wide data analysis of European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1019-1027. |
| [9] | Rong Xiangbin, , Zheng Haibo, Mo Xueshen, Hou Kun, Zeng Ping, . Plasma metabolites, immune cells, and hip osteoarthritis: causal inference based on GWAS data from European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1028-1035. |
| [10] | He Qiwang, , , Chen Bo, Liang Fuchao, Kang Zewei, Zhou Yuan, Ji Anxu, Tang Xialin, . Relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and sarcopenia and body mass index: analysis of GWAS datasets for European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1036-1046. |
| [11] | Ding Yu, Chen Jingwen, Chen Xiuyan, Shi Huimin, Yang Yudie, Zhou Meiqi, Cui Shuai, . Circulating inflammatory proteins and myocardial hypertrophy: large sample analysis of European populations from GWAS Catalog and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(4): 1047-1057. |
| [12] | Zhao Feifan, Cao Yujing. An artificial neural network model of ankylosing spondylitis and psoriasis shared genes and machine learning-based mining and validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 770-784. |
| [13] | Liu Chu, Qiu Boyuan, Tong Siwen, He Linyuwei, Chen Haobo, Ou Zhixue. A genetic perspective reveals the relationship between blood metabolites and osteonecrosis: an analysis of information from the FinnGen database in Finland [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(3): 785-794. |
| [14] | Yan Wenjian, Li Yinghui, Zhang Yong. Daily diet and structural damage of the knee joint: a large-scale genetic analysis based on UK and FinnGen databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2877-2885. |
| [15] | Zhou Xinying, Sun Xinyue, Zhu Wenhao. Insulin-like growth factors and ischemic stroke: a genome-wide association analysis in European populations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2909-2919. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||