Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 2858-2869.doi: 10.12307/2026.123
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of long-term exercise interventions on appetite-regulating hormones in overweight and obese populations: a meta-analysis
Xin Xianyang, Liu Longyan, Guo Yongqing, Wang Hai, Xie Jun
- Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2025-04-09Accepted:2025-07-02Online:2026-04-18Published:2025-09-06 -
Contact:Xie Jun, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, Beijing 100191, China -
About author:Xin Xianyang, PhD candidate, Capital University of Physical Education and Sports, Beijing 100191, China -
Supported by:Graduate Student Science Popularization Capacity Enhancement Project of China Association for Science and Technology, No. KXYJS2024007 (to XJ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xin Xianyang, Liu Longyan, Guo Yongqing, Wang Hai, Xie Jun. Effects of long-term exercise interventions on appetite-regulating hormones in overweight and obese populations: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(11): 2858-2869.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
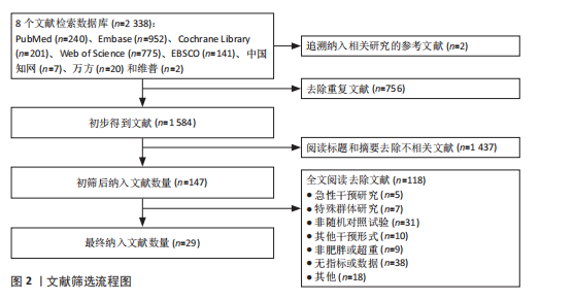
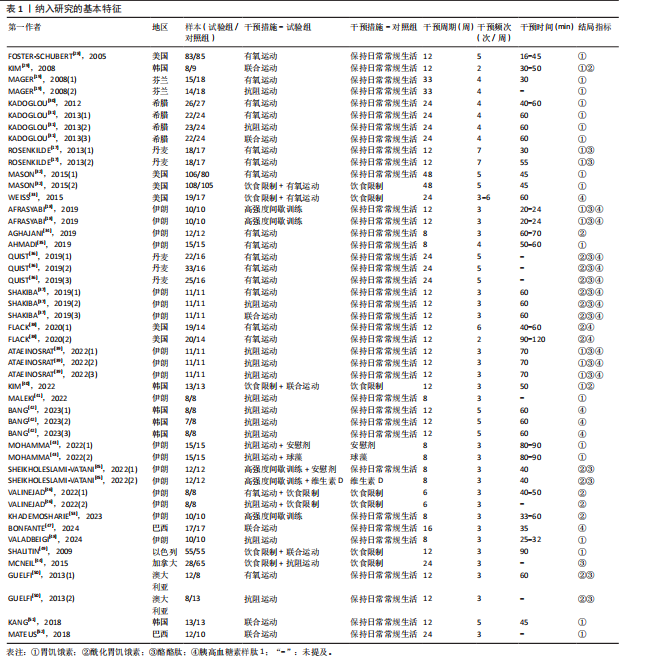
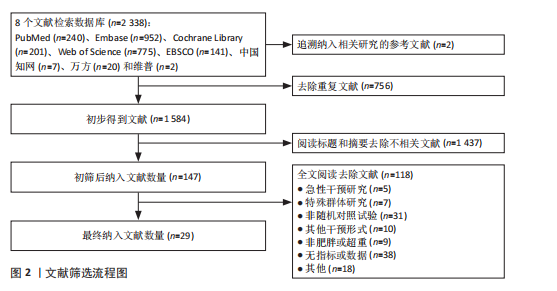
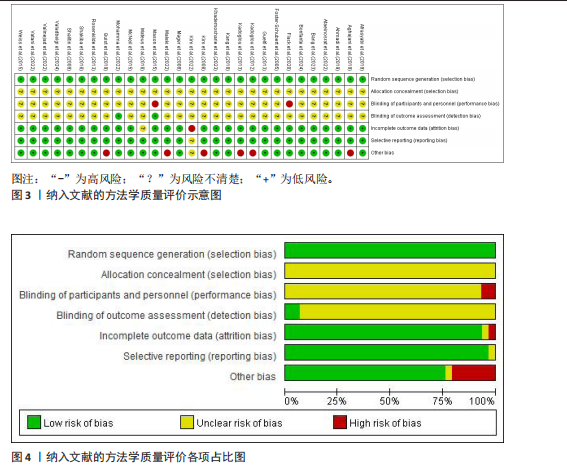
2.1 文献筛选流程 通过数据库检索获得相关文献2 338篇,其中PubMed(n=240)、Embase(n=952)、Cochrane Library(n=201)、Web of Science (n=775)、EBSCO(n=141)、中国知网(n=7)、万方(n=20)和维普(n=2),通过其他途径获得文献2篇。通过导入Endnote 20软件剔除重复文献756篇,2名研究者通过阅读题目和摘要剔除1 437篇,通过全文阅读剔除118篇文献,最后纳入29篇文献,文献筛选流程见图2。 2.2 纳入文献的基本特征 纳入29篇文献,肥胖或超重患者共包含1 758例[17-19,28-53]。其中包含48项研究,即1篇文献中若包含多种研究方法,则每种研究方法算作1项研究。其中,胃饥饿素相关的研究数量最多,共计26项;酰化胃饥饿素、酪酪肽和胰高血糖素样肽1相关研究均为18项。训练干预类型主要有有氧运动、抗阻运动、联合运动、高强度间歇训练,纳入文献基本特征见表1。 2.3 纳入文献的偏倚风险评价结果 纳入研究的偏倚风险评价结果见图3,4。共有27篇文献明确陈述了分组分配的方法,没有文献报告了分配隐藏,2篇文献报告了数据分析盲法。在数据的完整性评价条目中,失访率超过20%且未采用意向性分析则评价为高风险,纳入研究中共1篇失访率"
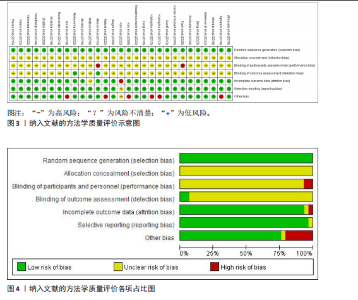
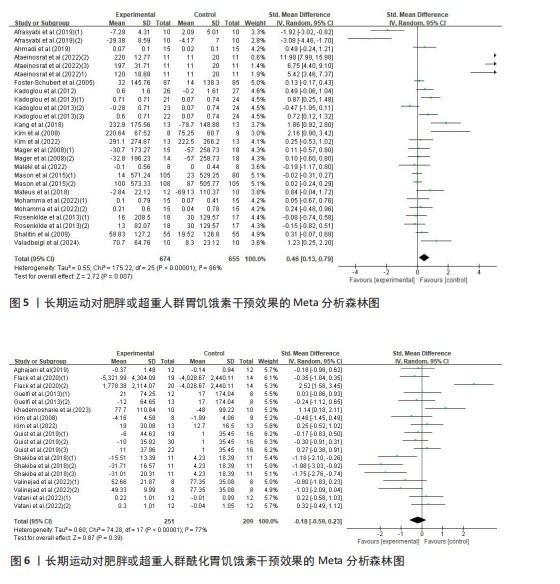
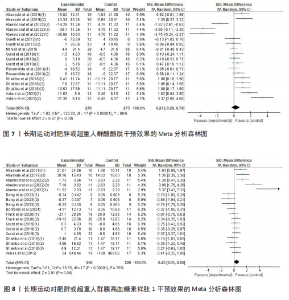
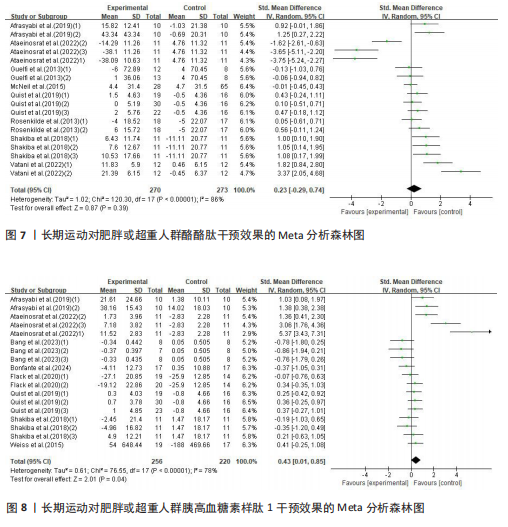
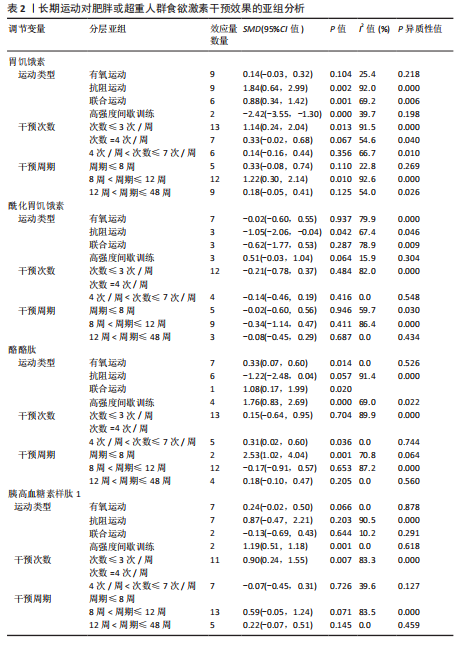
超过20%,28篇文献报告了失访率,试验组和对照组失访数目和原因相似。在其他偏倚中,纳入研究受试者样本量低于10人(小样本量偏倚)、运动干预缺乏监督、存在利益冲突等其中一项因素则评价为高风险,20篇文献不具有其他偏倚。根据每个条目风险评价情况对每一项研究进行综合评级,评级方法参考已有研究[27],高质量文献19篇,中质量文献9篇,低质量文献1篇。 2.4 Meta分析结果 2.4.1 胃饥饿素 运动干预对胃饥饿素激素水平的影响共纳入26项研究,包括1 329名参与者。异质性检验结果(I2=86%,P < 0.000 01)显示存在较高的异质性,因此选择随机效应模型进行效应量的合并分析。合并效应量为 SMD=0.46(95%CI:0.13-0.79,P=0.007),提示效应量具有统计学意义。运动干预对胃饥饿素激素水平具有中等改善作用,提示运动干预在调节胃饥饿素水平方面具有重要意义(图5)。 2.4.2 酰化胃饥饿素 运动干预对酰化胃饥饿素激素水平的影响共纳入18项研究,包括460名参与者。异质性检验结果(I2=77%,P < 0.000 01)显示存在较高的异质性,因此选择随机效应模型进行效应量的合并分析。合并效应量为 SMD=-0.18(95%CI: -0.59-0.23,P=0.39),提示效应量无统计学意义。结果显示,运动干预对酰化胃饥饿素激素水平的总体影响较小且不显著(图6)。 2.4.3 酪酪肽 运动干预对酪酪肽激素水平的影响共纳入18项研究,包括543名参与者。异质性检验结果(I2=86%,P < 0.000 01)显示存在较高的异质性,因此选择随机效应模型进行效应量的合并分析。合并效应量为 SMD=0.23(95%CI:-0.29-0.74,P=0.39),提示效应量无统计学意义。结果显示,运动干预对酪酪肽激素水平的总体影响较小且不显著(图7)。 2.4.4 胰高血糖素肽1 运动干预对胰高血糖素样肽1激素水平的影响共纳入18项研究,包括476名参与者。异质性检验结果(I2=78%,P < 0.000 01)显示存在较高的异质性,因此选择随机效应模型进行效应量的合并分析。合并效应量为 SMD=0.43(95%CI:0.01-0.85,P=0.04),提示效应量具有统计学意义。结果显示,长期运动可能通过提升胰高血糖素样肽1水平,增强饱腹感并促进能量摄入控制,在肥胖管理中具有重要应用潜力(图8)。 2.5 亚组分析结果 各个指标仍然存在着较高的异质性,为进一步探究潜在异质性来源,对潜在的调节变量进行亚组分析,确定各亚组合并效应量。亚组分析结果表明不同运动方案组成要素对肥胖或超重人群食欲激素指标影响效果不同(表2)。 抗阻运动(SMD=1.84)和联合运动(SMD=0.88)对胃饥饿素水平有显著促进作用,而高强度间歇训练有显著抑制作用,有氧运动的效果较弱。较少的干预次数(≤3次/周或4次/周)和中等干预周期(8周<周期≤12周)对胃饥饿素调节最有效。长期干预(12周<周期≤48周)效果不显著,且频次增加到一定程度后效果趋于平缓甚至下降。 抗阻运动是唯一显著降低酰化胃饥饿素水平的运动类型(SMD=-1.05),但异质性较高,提示不同研究间可能"
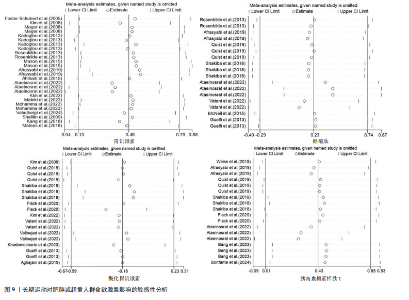
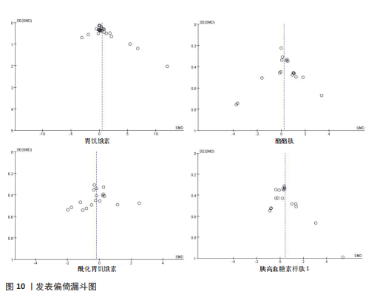
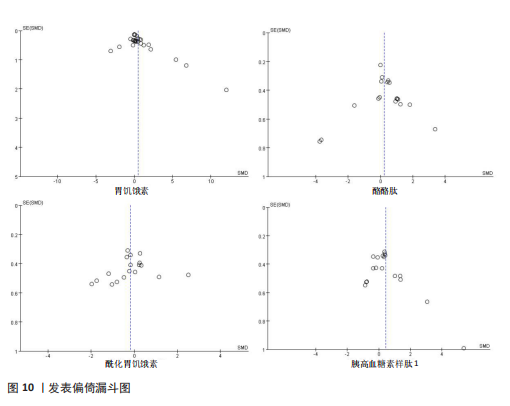
存在设计差异。有氧运动和联合运动对酰化胃饥饿素的效果不显著且异质性较高。高强性间歇运动虽然对酰化胃饥饿素的提升效果不显著,但是酰化胃饥饿素表现出了与其他运动不同的发展趋势。干预次数和干预周期对酰化胃饥饿素的影响结果不显著,研究结果差异不明显。 高强度间歇训练对酪酪肽水平的提升最为显著(SMD=1.76),其次是联合运动和有氧运动。抗阻运动对酪酪肽的作用表现为下降趋势,但未达显著性,且异质性较高。中等频次(4次/周<次数≤7次/周)效果显著且结果一致(异质性为0)。低干预周期(≤ 8周)显著提升酪酪肽水平(SMD=2.53),但异质性较高,中期干预(8周<周期≤12周)提升酪酪肽水平不显著,长期干预(12周<周期≤48周)酪酪肽水平有下降趋势但不显著且异质性较高。 高强度间歇训练显著提升胰高血糖素样肽1水平(SMD=1.19),是最有效的运动类型,且异质性较低;有氧运动效果接近显著,抗阻运动和联合运动效果均不显著。较少的干预次数(≤3次/周)显著提升胰高血糖素样肽1水平,但异质性较高;中等频次干预无显著效果;中期干预(8周<周期≤12周)对胰高血糖素样肽1水平的提升效果接近显著,但异质性较高,长期干预12周<周期≤48周)无显著效果,提示长期干预可能效果有限。 2.6 敏感性分析 为保证Meta分析结果的可靠性,通过敏感性分析探讨是否某一项研究对整体产生较大的影响。通过在整体研究基础上进行逐一剔除的方式来评估每个研究对整体效应量的影响。结果显示各项指标剔除某一研究后对整体效应量及异质性影响不大,表明Meta分析的结果稳定可靠(图9)。 2.7 发表偏倚结果分析 发表偏倚是对系统评价中结果是否存在偏倚的一种检验,该研究联合使用漏斗图、Begg’s检验和Egger’s检验评估纳入研究整体的发表偏倚规模。对食欲激素的4个指标进行定性和定量分析[54]。如图10所示,酰化胃饥饿素、酪酪肽和胰高血糖素样肽1的漏斗图显示两侧基本左右对称分布在漏斗图顶部,形成倒置漏斗形,只有胃饥饿素图形左右侧不十分对称,可能存在部分发表偏倚。Begg’s检验和Egger’s检验结果显示,酰化胃饥饿素、酪酪肽和胰高血糖素样肽1的P均> 0.05。而胃饥饿素Begg’s检验=0.010 6和Egger’s检验=0.020,P均< 0.05,因此进行了剪补法,剪补添加4个研究,合并效应量发生变化,但是仍存在显著差异(SMD= 0.87,95%CI:0.48-1.26,P < 0.05),综合判断结果较为稳健。"
| [1] BRAY GA. Medical consequences of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2583-2589. [2] 中国营养学会肥胖防控分会,中国营养学会临床营养分会,中华预防医学会行为健康分会,等.中国居民肥胖防治专家共识[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022, 43(4):619-631. [3] CUCIUREANU M, CARATAȘU CC, GABRIELIAN L, et al. 360-Degree Perspectives on Obesity. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023;59(6):1119. [4] DRAGANO NRV, FERNØ J, DIÉGUEZ C, et al. Recent Updates on Obesity Treatments: Available Drugs and Future Directions. Neuroscience. 2020;437:215-239. [5] 中国营养学会肥胖防控分会,西安交通大学全球健康研究院,国际肥胖与代谢性疾病研究中心,等.2025年世界肥胖报告[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2025, 46(2):363-379. [6] STENSEL DJ. How can physical activity facilitate a sustainable future? Reducing obesity and chronic disease. Proc Nutr Soc. 2023;82(3):286-297. [7] MILLER WC, KOCEJA DM, HAMILTON EJ. A meta-analysis of the past 25 years of weight loss research using diet, exercise or diet plus exercise intervention. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1997;21(10): 941-947. [8] HOPKINS M, KING NA, BLUNDELL JE. Acute and long-term effects of exercise on appetite control: is there any benefit for weight control? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2010;13(6):635-640. [9] MARTINS C, MORGAN L, TRUBY H. A review of the effects of exercise on appetite regulation: an obesity perspective. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008;32(9):1337-1347. [10] KING NA, CAUDWELL PP, HOPKINS M, et al. Dual-process action of exercise on appetite control: increase in orexigenic drive but improvement in meal-induced satiety. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(4):921-927. [11] STROHACKER K, MCCAFFERY JM, MACLEAN PS, et al. Adaptations of leptin, ghrelin or insulin during weight loss as predictors of weight regain: a review of current literature. Int J Obes (Lond). 2014;38(3):388-396. [12] ALMESBEHI T, HARRIS L, MCGARTY A, et al. Effects of exercise training programmes on fasting gastrointestinal appetite hormones in adults with overweight and obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Appetite. 2023;182:106424. [13] FINLAYSON G, BRYANT E, BLUNDELL JE, et al. Acute compensatory eating following exercise is associated with implicit hedonic wanting for food. Physiol Behav. 2009;97(1):62-67. [14] BECIC T, STUDENIK C, HOFFMANN G. Exercise Increases Adiponectin and Reduces Leptin Levels in Prediabetic and Diabetic Individuals: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Med Sci (Basel). 2018;6(4):97. [15] DORLING J, BROOM DR, BURNS SF, et al. Acute and Chronic Effects of Exercise on Appetite, Energy Intake, and Appetite-Related Hormones: The Modulating Effect of Adiposity, Sex, and Habitual Physical Activity. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1140. [16] GOLBIDI S, LAHER I. Exercise induced adipokine changes and the metabolic syndrome. J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014: 726861. [17] ROSENKILDE M, REICHKENDLER MH, AUERBACH P, et al. Appetite regulation in overweight, sedentary men after different amounts of endurance exercise: a randomized controlled trial. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2013;115(11):1599-1609. [18] AFRASYABI S, MARANDI SM, KARGARFARD M. The effects of high intensity interval training on appetite management in individuals with type 2 diabetes: influenced by participants weight. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2019;18(1):107-117. [19] MAGER U, KOLEHMAINEN M, DE MELLO VD, et al. Expression of ghrelin gene in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and plasma ghrelin concentrations in patients with metabolic syndrome. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;158(4):499-510. [20] MITOIU BI, NARTEA R, MICLAUS RS. Impact of Resistance and Endurance Training on Ghrelin and Plasma Leptin Levels in Overweight and Obese Subjects. Int J Mol Sci. 2024;25(15):8067. [21] XIN X, WANG H, GUO Y, et al. Effect of long-term exercise on circulating ghrelin in overweight and obese individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Nutr. 2025;12:1518143. [22] 中国肥胖问题工作组.中国学龄儿童青少年超重、肥胖筛查体重指数值分类标准[J].中华流行病学杂志,2004,25(2):97-102. [23] Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1995;854:1-452. [24] JACKSON M, FATAHI F, ALABDULJADER K, et al. Exercise training and weight loss, not always a happy marriage: single blind exercise trials in females with diverse BMI. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018;43(4):363-370. [25] MANTHOU E, GILL JM, WRIGHT A, et al. Behavioral compensatory adjustments to exercise training in overweight women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(6):1121-1128. [26] HIGGINS JP, ALTMAN DG, GØTZSCHE PC, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928. [27] CIPRIANI A, FURUKAWA TA, SALANTI G, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2018;391(10128):1357-1366. [28] FOSTER-SCHUBERT KE, MCTIERNAN A, FRAYO RS, et al. Human plasma ghrelin levels increase during a one-year exercise program. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005; 90(2):820-825. [29] KIM HJ, LEE S, KIM TW, et al. Effects of exercise-induced weight loss on acylated and unacylated ghrelin in overweight children. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008;68(3):416-422. [30] KADOGLOU NP, VRABAS IS, KAPELOUZOU A, et al. The impact of aerobic exercise training on novel adipokines, apelin and ghrelin, in patients with type 2 diabetes. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18(5):CR290-295. [31] KADOGLOU NP, FOTIADIS G, KAPELOUZOU A, et al. The differential anti-inflammatory effects of exercise modalities and their association with early carotid atherosclerosis progression in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 2013; 30(2):e41-50. [32] MASON C, XIAO L, IMAYAMA I, et al. The effects of separate and combined dietary weight loss and exercise on fasting ghrelin concentrations in overweight and obese women: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2015;82(3):369-376. [33] WEISS EP, ALBERT SG, REEDS DN, et al. Calorie Restriction and Matched Weight Loss From Exercise: Independent and Additive Effects on Glucoregulation and the Incretin System in Overweight Women and Men. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(7):1253-1262. [34] AGHAJANI R, ZIDASHTI ZH, NEMATI N, et al. Nervous Evaluation Conducted by the Changes of Ghrelin and Obestatin Executed by Aerobic Exercise. Brain-Broad Res Arti. 2019;10(4):101-114. [35] AHMADI SM, FATHI M, RASHIDLAMIR A, et al. Effects of 8 Weeks Aerobic Training on Plasma Ghrelin Level and Ghrelin Lymphocyte Gene Expression in Elderly Men. Iran J Aging. 2019;13(4):494-505. [36] QUIST JS, BLOND MB, GRAM AS, et al. Effects of active commuting and leisure-time exercise on appetite in individuals with overweight and obesity. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(4):941-951. [37] SHAKIBA E, SHEIKHOLESLAMI-VATANI D, ROSTAMZADEH N, et al. The type of training program affects appetite-regulating hormones and body weight in overweight sedentary men. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44(3):282-287. [38] FLACK KD, HAYS HM, MORELAND J, et al. Exercise for Weight Loss: Further Evaluating Energy Compensation with Exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2020; 52(11):2466-2475. [39] ATAEINOSRAT A, HAGHIGHI MM, ABEDNATANZI H, et al. Effects of Three Different Modes of Resistance Training on Appetite Hormones in Males With Obesity. Front Physiol. 2022;13:827335. [40] KIM HJ, TAK YJ, LEE SY, et al. Effects of a 12-Week Diet versus Diet plus Aerobic and Resistance Exercise Program on Acylated and Desacylated Ghrelin, and Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase in Adolescent Girls with Obesity. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(3):1480. [41] MALEKI F, SAFARZADE A. The Effects of Resistance Training on some Inflammatory Markers, Appetite-Regulating Peptides and Insulin Resistance Index in Obese Women. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2022;26(6):524-529. [42] BANG HS. Effect of Resistance Training with Different Set Structures on Neurotrophic Factors and Obesity-Related Biomarkers in Middle-Aged Korean Women with Obesity. J Clin Med. 2023;12(9):3135. [43] MOHAMMAD M, KARIM D, MEHDI M, et al. The Combinatory Effect of Spirulina Supplementation and Resistance Exercise on Plasma Contents of Adipolin, Apelin, Ghrelin, and Glucose in Overweight and Obese Men. Mediators Inflamm. 2022; 2022:9539286. [44] MCNEIL J, SCHWARTZ A, RABASA-LHORET R, et al. Changes in leptin and peptide YY do not explain the greater-than-predicted decreases in resting energy expenditure after weight loss. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(3):E443-452. [45] SHEIKHOLESLAMI-VATANI D, ROSTAMZADEH N. Changes in Appetite-Dependent Hormones and Body Composition After 8 Weeks of High-Intensity Interval Training and Vitamin D Supplementation in Sedentary Overweight Men. Front Nutr. 2022;9:827630. [46] VALINEJAD A, KHODAEI K. Does exercise during a ketogenic diet effectively alter appetite sensation, appetite-regulating hormones, and body composition? Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022;247(21):1898-1906. [47] BONFANTE ILP, DUFT RG, MATEUS KCDS, et al. Combined training and hormones/enzymes with insulinotropic actions in individuals with overweight and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Sport Sci. 2024;24(1):97-106. [48] VALADBEIGI A, AZIZBEIGI K. Elastic resistance training has positive influence on the functional capacity and appetite hormone in overweight men. Sport Sci Health. 2024;20(2):475-481. [49] SHALITIN S, ASHKENAZI-HOFFNUNG L, YACKOBOVITCH-GAVAN M, et al. Effects of a twelve-week randomized intervention of exercise and/or diet on weight loss and weight maintenance, and other metabolic parameters in obese preadolescent children. Horm Res. 2009;72(5):287-301. [50] GUELFI KJ, DONGES CE, DUFFIELD R. Beneficial effects of 12 weeks of aerobic compared with resistance exercise training on perceived appetite in previously sedentary overweight and obese men. Metabolism. 2013;62(2):235-243. [51] KANG SJ, KIM JH, GANG Z, et al. Effects of 12-week circuit exercise program on obesity index, appetite regulating hormones, and insulin resistance in middle-aged obese females. J Phys Ther Sci. 2018;30(1):169-173. [52] MATEUS KC, BRUNELLI DT, GÁSPARI AF, et al. Effects of combined training on total ghrelin and tumor necrosis factor-α in obese middle-aged men. Motriz: Revista de Educação Física. 2018;24:e1018143. [53] KHADEMOSHARIE M, MOLLANOVRUZI A. Effects of High-Intensity Training Upon Appetite, Body Mass, Aerobic Capacity, and Metabolic Hormones in Overweight Women. Endocrinology Research and Practice. 2023;27(1):21-27. [54] EGGER M, DAVEY SMITH G, SCHNEIDER M, et al. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997; 315(7109):629-634. [55] TSCHÖP M, WEYER C, TATARANNI PA, et al. Circulating ghrelin levels are decreased in human obesity. Diabetes. 2001;50(4):707-709. [56] CHEN C, ZHANG D, YE M, et al. Effects of various exercise types on inflammatory response in individuals with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Obes (Lond). 2025;49(2):214-225. [57] CEDERBERG H, RAJALA U, KOIVISTO VM, et al. Unacylated ghrelin is associated with changes in body composition and body fat distribution during long-term exercise intervention. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011;165(2):243-248. [58] RODRÍGUEZ A, GÓMEZ-AMBROSI J, CATALÁN V, et al. Association of plasma acylated ghrelin with blood pressure and left ventricular mass in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Hypertens. 2010;28(3):560-567. [59] LORIA-KOHEN V, FERNÁNDEZ-FERNÁNDEZ C, BERMEJO LM, et al. Effect of different exercise modalities plus a hypocaloric diet on inflammation markers in overweight patients: a randomised trial. Clin Nutr. 2013; 32(4):511-518. [60] YU AP, UGWU FN, TAM BT, et al. One Year of Yoga Training Alters Ghrelin Axis in Centrally Obese Adults With Metabolic Syndrome. Front Physiol. 2018;9:1321. [61] HEISTON EM, EICHNER NZM, GILBERTSON NM, et al. Two weeks of exercise training intensity on appetite regulation in obese adults with prediabetes. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(3):746-754. [62] GUEUGNON C, MOUGIN F, NGUYEN NU, et al. Ghrelin and PYY levels in adolescents with severe obesity: effects of weight loss induced by long-term exercise training and modified food habits. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2012;112(5):1797-1805. [63] CAMPOS RM, DE MELLO MT, TOCK L, et al. Aerobic plus resistance training improves bone metabolism and inflammation in adolescents who are obese. J Strength Cond Res. 2014;28(3):758-766. [64] WU W, ZHU L, DOU Z, et al. Ghrelin in Focus: Dissecting Its Critical Roles in Gastrointestinal Pathologies and Therapies. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024;46(1):948-964. [65] MILLS JG, LARKIN TA, DENG C, et al. Weight gain in Major Depressive Disorder: Linking appetite and disordered eating to leptin and ghrelin. Psychiatry Res. 2019;279:244-251. [66] PAPANDREOU D, KARAVOLIAS C, ARVANITI F, et al. Fasting Ghrelin Levels Are Decreased in Obese Subjects and Are Significantly Related With Insulin Resistance and Body Mass Index. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2017;5(6):699-702. [67] MARTINS C, STENSVOLD D, FINLAYSON G, et al. Effect of moderate- and high-intensity acute exercise on appetite in obese individuals. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(1):40-48. [68] HOLLIDAY A, BLANNIN AK. Very Low Volume Sprint Interval Exercise Suppresses Subjective Appetite, Lowers Acylated Ghrelin, and Elevates GLP-1 in Overweight Individuals: A Pilot Study. Nutrients. 2017; 9(4):362. [69] MORISHIMA T, KURIHARA T, HAMAOKA T, et al. Whole body, regional fat accumulation, and appetite-related hormonal response after hypoxic training. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2014;34(2):90-97. [70] ZOUHAL H, LEMOINE-MOREL S, MATHIEU ME, et al. Catecholamines and obesity: effects of exercise and training. Sports Med. 2013;43(7):591-600. [71] KRAEMER WJ, RATAMESS NA. Hormonal responses and adaptations to resistance exercise and training. Sports Med. 2005; 35(4):339-361. [72] BILSKI J, TELEGŁÓW A, WARZECHA Z, et al. Effects of Exercise on Appetite and Food Intake Regulation. Medicina Sportiva. 2009;13:82-94. [73] BATTERHAM RL, LE ROUX CW, COHEN MA, et al. Pancreatic polypeptide reduces appetite and food intake in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88(8):3989-3992. [74] BATTERHAM RL, COWLEY MA, SMALL CJ, et al. Gut hormone PYY(3-36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002;418(6898):650-654. [75] HANSEN HH, HANSEN G, PAULSEN S, et al. The DPP-IV inhibitor linagliptin and GLP-1 induce synergistic effects on body weight loss and appetite suppression in the diet-induced obese rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;741:254-263. [76] SHAH M, VELLA A. Effects of GLP-1 on appetite and weight. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2014;15(3):181-187. [77] MOHAMMADI A, BIJEH N, MOAZZAMI M, et al. Effect of Exercise Training on Spexin Level, Appetite, Lipid Accumulation Product, Visceral Adiposity Index, and Body Composition in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes. Biol Res Nurs. 2022;24(2):152-162. [78] HOSSEIN N, MEHDI M, KARIM D, et al. Spirulina supplementation and circuit resistance training (CRT) reduce serum asprosin and appetite and improve energy balance in men with obesity and overweight. Hormones (Athens). 2025; 24(1):23-31. [79] ADAM TC, WESTERTERP-PLANTENGA MS. Activity-induced GLP-1 release in lean and obese subjects. Physiol Behav. 2004;83(3):459-466. [80] BRECHET S, PLAISANCIÉ P, DUMOULIN V, et al. Involvement of beta1- and beta2- but not beta3-adrenoceptor activation in adrenergic PYY secretion from the isolated colon. J Endocrinol. 2001;168(1):177-183. [81] ELLINGSGAARD H, HAUSELMANN I, SCHULER B, et al. Interleukin-6 enhances insulin secretion by increasing glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion from L cells and alpha cells. Nat Med. 2011;17(11):1481-1489. [82] SHIRAZI R, PALSDOTTIR V, COLLANDER J, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor induced suppression of food intake, and body weight is mediated by central IL-1 and IL-6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(40):16199-16204. [83] NILSSON A, JOHANSSON E, EKSTRÖM L, et al. Effects of a brown beans evening meal on metabolic risk markers and appetite regulating hormones at a subsequent standardized breakfast: a randomized cross-over study. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e59985. [84] LARSON-MEYER DE, WILLIS KS, WILLIS LM, et al. Effect of honey versus sucrose on appetite, appetite-regulating hormones, and postmeal thermogenesis. J Am Coll Nutr. 2010;29(5):482-493. [85] LIN J, JIANG Y, WANG G, et al. Associations of short sleep duration with appetite-regulating hormones and adipokines: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2020;21(11):e13051. [86] MANDIC I, AHMED M, RHIND S, et al. The effects of exercise and ambient temperature on dietary intake, appetite sensation, and appetite regulating hormone concentrations. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2019; 16:29. [87] 邓潇潇,杨贤罡,李春燕,等.低氧运动和生活方式回归对超重肥胖青年能量摄入和食欲激素的影响[J].北京体育大学学报,2023,46(11):92-101. [88] 吴娜娜,管延飞,朱欢,等.高住低练对肥胖青少年血浆食欲调节激素的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2015,31(3):281-283. [89] HAZELL TJ, ISLAM H, TOWNSEND LK, et al. Effects of exercise intensity on plasma concentrations of appetite-regulating hormones: Potential mechanisms. Appetite. 2016;98:80-88. [90] BEAULIEU K, HOPKINS M, BLUNDELL J, et al. Impact of physical activity level and dietary fat content on passive overconsumption of energy in non-obese adults. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2017;14(1):14. [91] GOLTZ FR, THACKRAY AE, KING JA, et al. Interindividual Responses of Appetite to Acute Exercise: A Replicated Crossover Study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(4): 758-768. |
| [1] | Liu Yu, Lei Senlin, Zhou Jintao, Liu Hui, Li Xianhui. Mechanisms by which aerobic and resistance exercises improve obesity-related cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1171-1183. |
| [2] | Tao Yunfei, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction in low-intensity resistance training on endothelial function-related inflammatory factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1184-1195. |
| [3] | Chen Qiang, Wu Wenjuan, Jiang Shuhua, Huang Da. Physical exercise improves physical function in burn patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1269-1281. |
| [4] | Liao Qing, Zeng Jing, Chen Jun, Yuan Lixia, Liu Gang. Moxibustion alleviates cartilage lesions in rats with knee osteoarthritis through regulating the circPan3/miR-667-5p/Ghrelin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2475-2483. |
| [5] | Li Xiupeng, Su Yuying, Wang Yuetong, Peng Liang, Wang Yida, Jing Wen. Effect of low-volume high-intensity interval training on cardiovascular risk factor in obese or overweight populations: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(12): 2590-2604. |
| [6] | Zhu Xiaofeng, Chen Weiwei, Huang Jian. Effects of maternal high-fat diet and exercise intervention on insulin sensitivity and the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in male offspring mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 556-561. |
| [7] | Dai Xinyu, Yan Jihong, Hua Lingjun, Zheng Xiaohong. Resistance exercise improves body composition in overweight and obese people: an umbrella review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 267-271. |
| [8] | Liu Renfan, Lyu Liting, Wu Yi, Wang Lu. Effects of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on body composition and glucose metabolism in overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes: a Meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(14): 2274-2281. |
| [9] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [10] | Jiang Xiaoyan, Zhu Haifei, Lin Haiqi, Lin Wentao. Cold therapy promotes self-limited recovery of delayed-onset muscle soreness [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3609-3613. |
| [11] | Yang Luyao, Fu Pengyu, Tang Shuning, Zhu Rongxin, Gong Lijing . Change of Ghrelin-GHSR pathway in 4-week intermittent hypoxic exposure improving obesity in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1733-1739. |
| [12] | Lu Qi. Energy consumption and gait characteristics of overweight adults [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(36): 5779-5784. |
| [13] | Yin Lian, Zhao Jin, Lei Xuemei, Li Miaomiao, Wang Kun, Zhang Tingran, Luo Jiong. Effect of exercise-induced irisin on myocardial fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(23): 3730-3736. |
| [14] | Fan Jinqin, Weng Xiquan, Xu Guoqin, Wu Juhua, Lin Wentao. Effects of hypoxic exercise on Nesfatin-1 and Ghrelin in hypothalamus of rats with alimentary obesity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3202-3208. |
| [15] | Chen Yu-feng, Yang Hui-lin, Zou Jun. Ghrelin effects on the growth hormone release, osteoblast proliferation and bone growth [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(32): 5209-5214. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||