Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1159-1167.doi: 10.12307/2025.304
Previous Articles Next Articles
Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats
Zheng Lin1, Jin Wenjun1, Luo Shanshan1, Huang Rui1, Wang Jie1, Cheng Yuting1, An Zheqing1, Xiong Yue1, Gong Zipeng2, Liao Jian1
- 1School/Hospital of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Guizhou Provincial Engineering Research Center for Development and Application of Ethnic Medicines and Traditional Chinese Medicines, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-23Accepted:2024-03-22Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-20 -
Contact:Liao Jian, Chief physician, Professor, School/Hospital of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zheng Lin, Master candidate, School/Hospital of Stomatology, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Project of Guizhou Basic Research Program, No. ZK[2023]037 (to LJ); Science and Technology Fund Project of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission, No. gzwkj2023-439 (to XY)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zheng Lin, Jin Wenjun, Luo Shanshan, Huang Rui, Wang Jie, Cheng Yuting, An Zheqing, Xiong Yue, Gong Zipeng, Liao Jian. Eucommia ulmoides promotes alveolar bone formation in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1159-1167.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
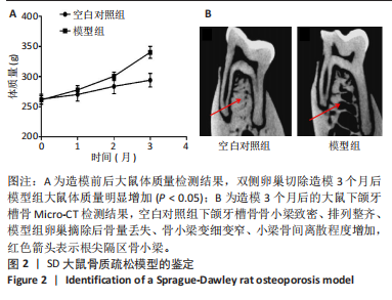
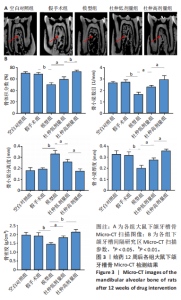
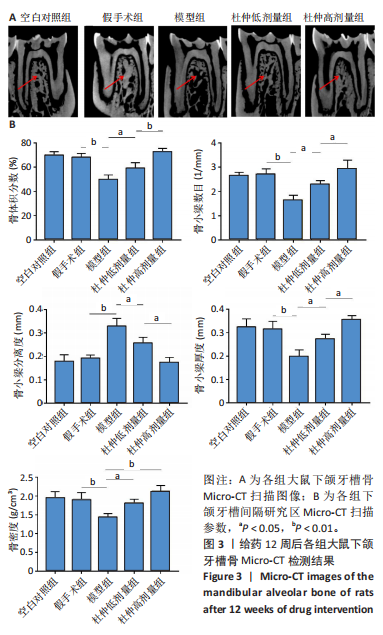
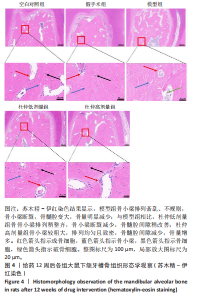
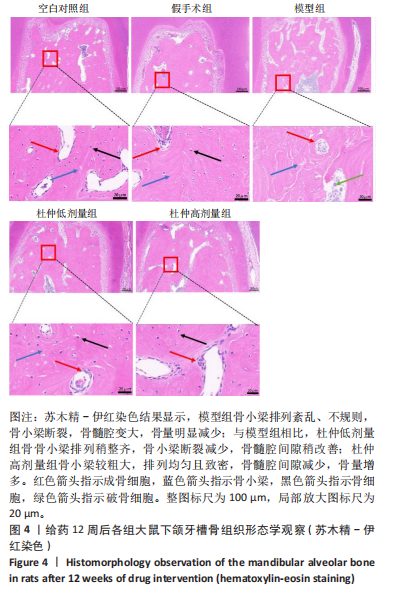
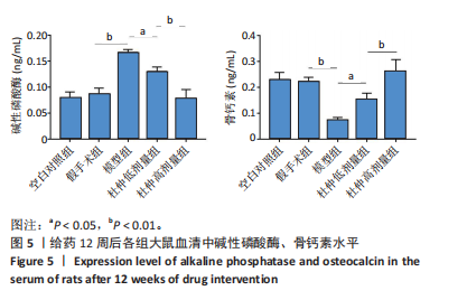
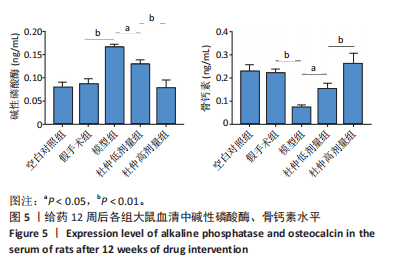
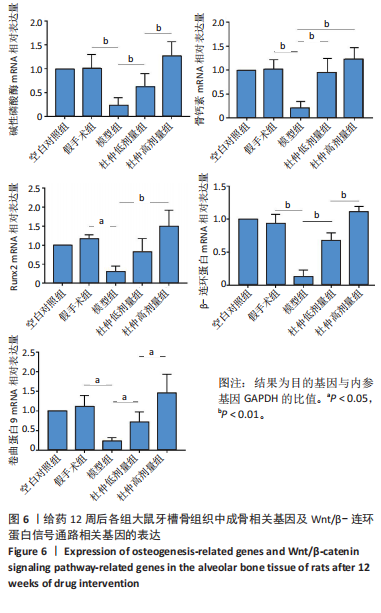
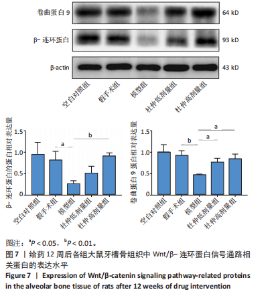
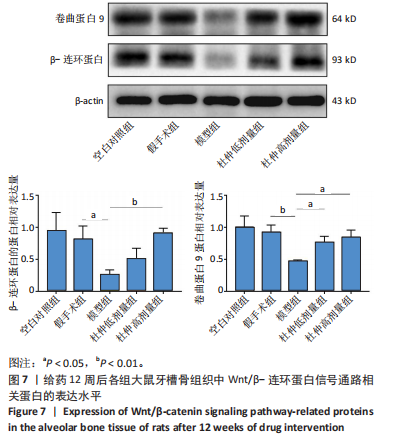
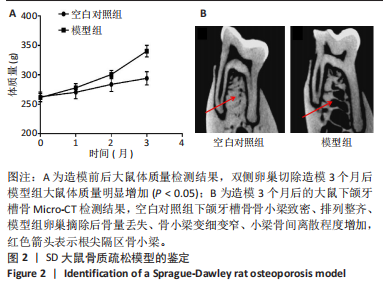
2.1 实验动物数量分析 60只大鼠全部进入结果分析。 2.2 验证骨质疏松动物模型构建成功 2.2.1 SD大鼠造模前后体质量变化 造模前,从空白对照组及模型组各随机抽取5只大鼠称取体质量并记录,摘除双侧卵巢后第1,2,3个月时分别记录体质量。最初各组大鼠体质量、体型相似,体质量在(261.90±7.07) g范围内。卵巢摘除3个月后,相较于空白对照组的(294.10±11.43) g,模型组大鼠体质量明显增加(P < 0.05),为(340.40±9.92) g(图2A)。 2.2.2 Micro-CT验证骨质疏松动物模型构建成功 双侧卵巢摘除术3个月后,Micro-CT检测结果显示空白对照组下颌牙槽骨骨小梁致密,排列整齐;模型组卵巢摘除后骨量丢失,骨小梁变细变窄,小梁骨间离散程度增加(图2B)。 2.3 杜仲对骨质疏松大鼠下颌牙槽骨骨组织结构的影响 Micro-CT检测结果显示各组大鼠下颌第一磨牙根尖隔牙槽骨区域,空白对照组及假手术组下颌牙槽骨骨小梁致密,排列整齐;模型组卵巢摘除后骨量丢失,骨小梁变细窄,小梁骨间离散程度增加;给予低剂量杜仲治疗后部分骨量得以恢复,可见骨小梁数目增加,排列稍致密,离散程度减小;给予高剂量杜仲治疗后骨量恢复明显,骨小梁排列致密,离散程度明显减小,见图3A。 通过 Micro-CT 扫描分析研究区域得出牙槽骨骨微结构参数,与空白对照组及假手术组比较,模型组大鼠牙槽骨骨体积分数、骨小梁数目、骨小梁厚度、骨密度均降低(P < 0.01),骨小梁分离度增加(P < 0.01);与模型组比较,杜仲低、高剂量组大鼠牙槽骨骨体积分数、骨小梁数目、骨小梁厚度、骨密度升高(P < 0.05),骨小梁分离度降低(P < 0.05);与杜仲低剂量组比较,杜仲高剂量组大鼠牙槽骨骨体积分数、骨小梁数目、骨小梁厚度表达升高(P < 0.05),骨小梁分离度降低(P < 0.05),见图3B。 2.4 杜仲对骨质疏松大鼠下颌牙槽骨骨组织形态的影响 苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,空白对照组及假手术组大鼠牙槽骨组织结构完整,骨小梁排列均匀;模型组大鼠牙槽骨骨小梁排列紊乱、不规则,骨小梁断裂,骨小梁变细,骨髓腔变大,破骨细胞数量增多,骨量明显减少;与模型组相比,杜仲低剂量组大鼠牙槽骨骨小梁排列稍整齐,骨小梁断裂减少,骨髓腔间隙稍改善;杜仲高剂量组大鼠牙槽骨骨小梁较粗大,排列均匀且致密,骨髓腔间隙减少,骨细胞增多,骨量增多(图4)。 2.5 杜仲对骨质疏松大鼠血清中碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素的影响 与空白对照组及假手术组比较,模型组大鼠血清中碱性磷酸酶表达水平上升(P < 0.01),骨钙素表达水平下降(P < 0.01);与模型组相比,杜仲低、高剂量组大鼠血清中碱性磷酸酶表达水平下降(P < 0.05),骨钙素表达水平上升(P < 0.05),并且存在剂量依赖性,见图5。表明杜仲可以影响血清中成骨相关因子碱性磷酸酶及骨钙素的表达来改善骨代谢,促进骨生成。 2.6 杜仲对骨质疏松大鼠牙槽骨骨组织中碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、Runx2及β-连环蛋白、卷曲蛋白9 mRNA表达的影响 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与空白对照组及假手术组比较,模型组大鼠牙槽骨组织中碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、Runx2、β-连环蛋白、卷曲蛋白9 的mRNA表达均降低(P < 0.05或P < 0.01);与模型组比较,杜仲低剂量组大鼠牙槽骨组织中碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、β-连环蛋白、卷"
| [1] ALBREKTSSON T, BECKER W, COLI P, et al. Bone loss around oral and orthopedic implants: An immunologically based condition. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(4):786-795. [2] LI Z, GAO S, CHEN H, et al. Micromotion of implant-abutment interfaces (IAI) after loading: correlation of finite element analysis with in vitro performances. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2019;57(5):1133-1144. [3] LU X, TIAN R, LIU S, et al. [Nerve growth factor combined with dental pulp stem cells promotes peri-implant osseointegration in rats]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021;41(9):1304-1309. [4] PEREZ E, SALINAS L, MENDOZA R, et al. Osseointegration of Dental Implants in Patients with Congenital and Degenerative Bone Disorders: A Literature Review. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2023;13(3):167-172. [5] TIAN T, LIU HH, ZHANG ZH, et al. Correlation between bone volume fraction in posterior implant area and initial implant stability. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2022;133(4):396-401. [6] GUO F, YANG Y, DUAN Y, et al. Quality Marker Discovery and Quality Evaluation of Eucommia ulmoides Pollen Using UPLC-QTOF-MS Combined with a DPPH-HPLC Antioxidant Activity Screening Method. Molecules. 2023;28(13):5288. [7] HUANG L, LYU Q, ZHENG W, et al. Traditional application and modern pharmacological research of Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. Chin Med. 2021;16(1):73. [8] 胡倩影,尹瑞林,王一飞,等.杜仲中松脂素二葡萄糖苷和松脂素对成骨细胞中OPG和RANKL表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2018,24(10):181-186. [9] 秧荣昆,关智宇.基于肾主骨理论探讨杜仲通过调控OPG/RANKL/RANK通路对去势骨质疏松大鼠的影响[J].中成药,2023,45(1):70-74. [10] XIONG Y, HUANG CW, SHI C, et al. Quercetin suppresses ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rat mandibles by regulating autophagy and the NLRP3 pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023;248(23):2363-2380. [11] 贺自克,王上增.杜仲水提物上调Nur77表达促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(15):2371-2378. [12] 林奇生,邹学农,曾瑞芬,等.杜仲醇提取物通过RhoA/ROCK信号通路调控大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化作用研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(2):26-30. [13] ZHAO X, WANG Y, NIE Z, et al. Eucommia ulmoides leaf extract alters gut microbiota composition, enhances short-chain fatty acids production, and ameliorates osteoporosis in the senescence-accelerated mouse P6 (SAMP6) model. Food Sci Nutr. 2020;8(9):4897-4906. [14] 李新春,胡万钧,甘发荣,等.杜仲-续断药对通过调控铁死亡途径对去卵巢骨质疏松症大鼠的保护作用及机制研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2023,41(9):103-106. [15] 吴大雷,周守恒,闫健伟,等.杜仲醇提取物可促进根尖周炎模型大鼠骨组织的愈合[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(23):3685-3689. [16] LIU J, XIAO Q, XIAO J, et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):3. [17] CHEN M, SHAN L, GAN Y, et al. Metastasis suppressor 1 controls osteoblast differentiation and bone homeostasis through regulating Src-Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(2):107. [18] SATO A, SHIMIZU M, GOTO T, et al. WNK regulates Wnt signalling and beta-Catenin levels by interfering with the interaction between beta-Catenin and GID. Commun Biol. 2020;3(1):666. [19] GE J, YU YJ, LI JY, et al. Activating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by autophagic degradation of APC contributes to the osteoblast differentiation effect of soy isoflavone on osteoporotic mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2023;44(9):1841-1855. [20] LI H, MENG H, XU M, et al. BMAL1 regulates osteoblast differentiation through mTOR/GSK3beta/beta-catenin pathway. J Mol Endocrinol. 2023;70(4):e220181. [21] XU L, WU J, YU Y, et al. Dok5 regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoblast via canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2022;22(1):113-122. [22] SUTHON S, PERKINS RS, LIN J, et al. GATA4 and estrogen receptor alpha bind at SNPs rs9921222 and rs10794639 to regulate AXIN1 expression in osteoblasts. Hum Genet. 2022;141(12):1849-1861. [23] SHEN J, SUN Y, LIU X, et al. EGFL6 regulates angiogenesis and osteogenesis in distraction osteogenesis via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):415. [24] WANG Y, HANG K, YING L, et al. LAMP2A regulates the balance of mesenchymal stem cell adipo-osteogenesis via the Wnt/beta-catenin/GSK3beta signaling pathway. J Mol Med (Berl). 2023;101(7):783-799. [25] WEN B, HU S, YIN J, et al. Molecular Evolution and Protein Structure Variation of Dkk Family. Genes (Basel). 2023;14(10):1863. [26] ZHENG HL, XU WN, ZHOU WS, et al. Beraprost ameliorates postmenopausal osteoporosis by regulating Nedd4-induced Runx2 ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):497. [27] FELBER K, ELKS PM, LECCA M, et al. Expression of osterix Is Regulated by FGF and Wnt/beta-Catenin Signalling during Osteoblast Differentiation. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e144982. [28] CHEN T, GAO F, LUO D, et al. Cistanoside A promotes osteogenesis of primary osteoblasts by alleviating apoptosis and activating autophagy through involvement of the Wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(2):64. [29] MARINI F, GIUSTI F, PALMINI G, et al. Role of Wnt signaling and sclerostin in bone and as therapeutic targets in skeletal disorders. Osteoporos Int. 2023;34(2):213-238. [30] NOTTMEIER C, LIAO N, SIMON A, et al. Wnt1 Promotes Cementum and Alveolar Bone Growth in a Time-Dependent Manner. J Dent Res. 2021;100(13):1501-1509. [31] REN Y, HAN X, HO SP, et al. Removal of SOST or blocking its product sclerostin rescues defects in the periodontitis mouse model. FASEB J. 2015;29(7):2702-2711. [32] LUO Y, ZHANG L, WANG WY, et al. Alendronate retards the progression of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in ovariectomized rats. Bone. 2013;55(2):439-448. [33] DANIELSEN CC, MOSEKILDE L, SVENSTRUP B. Cortical bone mass, composition, and mechanical properties in female rats in relation to age, long-term ovariectomy, and estrogen substitution. Calcif Tissue Int. 1993;52(1):26-33. [34] 程余婷,伍超,黄晓林,等.低剂量唑来膦酸对去势拔牙大鼠破骨及成骨细胞的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2686-2693. [35] 宋娜,刘官娟,程余婷,等.唑来膦酸促进去势大鼠牙槽骨的成骨作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(28):4494-4501. [36] 霍花,刘官娟,宋娜,等.唑来膦酸干预去势大鼠牙槽骨骨代谢及核苷酸结合寡聚化结构域样受体蛋白3炎症小体表达的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(17):2660-2666. [37] WANG L, CHENG L, ZHANG B, et al. Tanshinone prevents alveolar bone loss in ovariectomized osteoporosis rats by up-regulating phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;376:9-16. [38] ABDUL-FATTAH BN, FATHALLAH AN, ISMAIL HS. The effect of Rutin hydrate on Glucocorticoids induced osteoporosis in mandibular alveolar bone in Albino rats (Radiological, histological and histochemical study). Saudi Dent J. 2022;34(6):464-472. [39] WANG Y, LI X, DENG F, et al. Hydroxy-Safflower Yellow A Alleviates Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Rat Model by Inhibiting Carbonic Anhydrase 2 Activity. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:734539. [40] ZHANG H, JIA Q, PIAO M, et al. Screening of Serum Alkaline Phosphatase and Phosphate Helps Early Detection of Metabolic Bone Disease in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Front Pediatr. 2021;9:642158. [41] 中国骨质疏松杂志骨代谢专家组,张萌萌,马倩倩,等.骨代谢生化指标临床应用专家共识(2023修订版)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2023,29(4):469-476. [42] ZHU J, LIU Y, CHEN C, et al. Cyasterone accelerates fracture healing by promoting MSCs migration and osteogenesis. J Orthop Translat. 2021;28:28-38. [43] 刘焱,陈青宇,高翔,等.胶原蛋白支架对载杜仲叶提取物处理的人牙周膜干细胞增殖和成骨分化的作用[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(16):2537-2543. [44] 刘焱,陈青宇,许凤,等.杜仲叶提取物对人牙周膜干细胞体外增殖及成骨分化的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(18):3970-3974. [45] BAI J, ZHANG W, ZHOU C, et al. MFG-E8 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through GSK3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2023;37(6):e22950. [46] DISHA-IBRAHIMI S, FURLANI B, DREVENSEK G, et al. Olanzapine decreased osteocyte maturation and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during loading of the alveolar bone in rats. Biomol Biomed. 2023;23(1):114-125. [47] CHU Y, GAO Y, YANG Y, et al. beta-catenin mediates fluoride-induced aberrant osteoblasts activity and osteogenesis. Environ Pollut. 2020; 265(Pt A):114734. [48] SHI Q, GUI J, SUN L, et al. Frizzled-9 triggers actin polymerization and activates mechano-transducer YAP to rescue simulated microgravity-induced osteoblast dysfunction. FASEB J. 2023;37(9):e23147. |
| [1] | Liu Xinyue, Li Chunnian, Li Yizhuo, Xu Shifang. Regeneration and repair of oral alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(5): 1247-1259. |
| [2] | Bai Xiangyu, Huo Feng, Hao Yan, Wang Zecheng, Guo Xiaoyu. Platelet-derived growth factor BB-loaded chitosan/reduced graphene oxide scaffold for repairing alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(2): 329-337. |
| [3] | Cai Yaohao, Lang Lyu, Li Hong. Assessing the bone mass of the residual alveolar ridge in the first molar for implant placement by cone-beam computed tomography [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1572-1577. |
| [4] | Lang Mecuo, Zhang Yilin, Wang Li. MiR-338-3p affects proliferation and apoptosis of alveolar bone osteoblasts by targeting receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 899-907. |
| [5] | Lu Xiuli, Xu Huazhen, Chen Yuxing, Yao Nan, Hu Zixuan, Huang Dane. Mechanism of Jiangu Formula in treating osteoporosis based on osteoclast-osteoblast coupling [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(32): 6828-6835. |
| [6] | Akliya·Anwar, Nafisa·Gupur, Baibugafu·Yelisi, Zilalai·Gulaiti, Guzalnur·Emrayim, Nijat·Tursun. Dynamic stress analysis of maxillary sinus lifting without bone grafting and with immediate loading after bone grafting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6416-6425. |
| [7] | Ma Ling, Zhang Zhao. Local application of osteoporosis treatment drugs in oral field [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6547-6555. |
| [8] | Guo Sunlin, Hong Enda, Dai Xinhua, Lin Xi, Peng Zhiyi, Cheng Yingxiong, Fan Linyan. Effect of Bushen Jianpi Formula on bone metabolism and bone microarchitecture in ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5588-5594. |
| [9] | Wei Hexiang, Sun Bin, Liu Hao, Liu Hanqiang, Xia Peng. Effects of nerve growth factor on osteogenesis and bone diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4266-4275. |
| [10] | Liu Zilue, Wang Zhi, Song Wenshang, Li Suna, Cai Shixin. Autogenous bone and platelet-rich fibrin in repair of severe alveolar bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2044-2051. |
| [11] | Xiang Dejian, Liang Xiaoyuan, Wang Shenghong, Chen Changshun, Tian Cong, Yan Zhenxing, Geng Bin, Xia Yayi . Mechanisms by which microgravity causes osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(10): 2132-2140. |
| [12] | Wang Tianqi, Liao Chengcheng, Liu Jianguo, Chen Lulu, Zhao Piao, Xiao Linlin, Guan Xiaoyan. Role of autophagy in orthodontic tooth movement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(34): 5558-5564. |
| [13] | Yuan Ping, Wang Zhihua, Wang Weizhou, Wang Wentong, He Fei. Exosome-derived microRNA with bone and joint diseases: role and mechanism [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 5063-5069. |
| [14] | Zhou Jing, Zhang Zhao. Osteoprotegerin/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B/receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand and the application of relevant target therapy in oral medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3736-3742. |
| [15] | Wang Lu, Xu Jie, Xia Yijing, Zhang Xinsong, Zhao Bin. Preparation and characterization of silk fibroin/bioactive glass composite fiber membrane [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(22): 3457-3463. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||