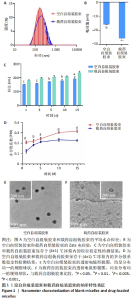
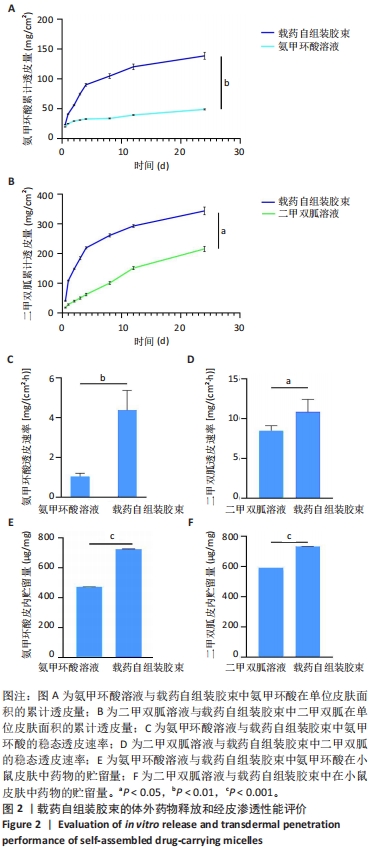
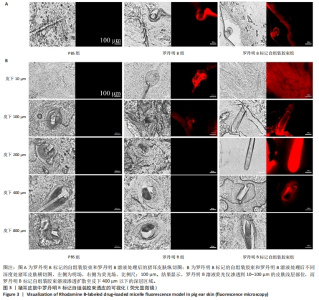
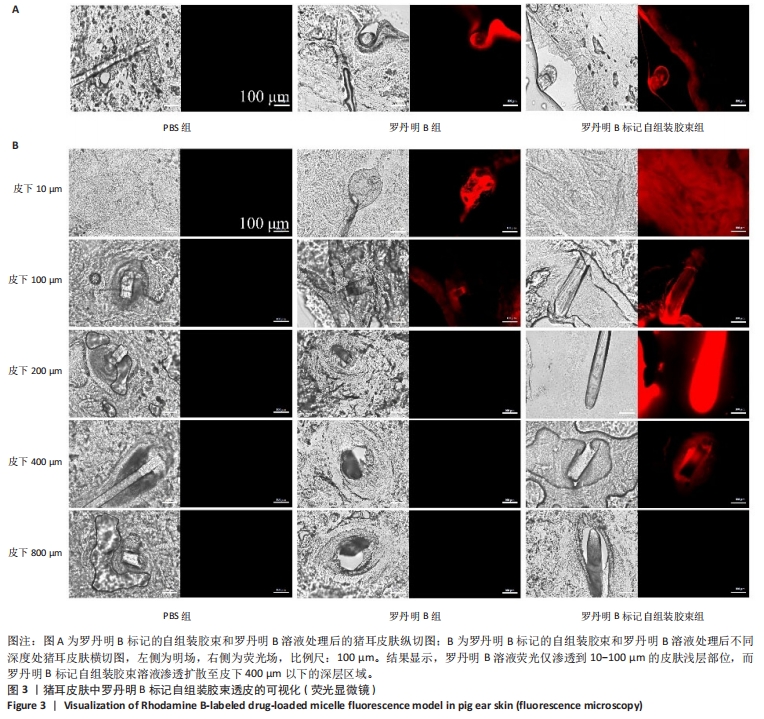
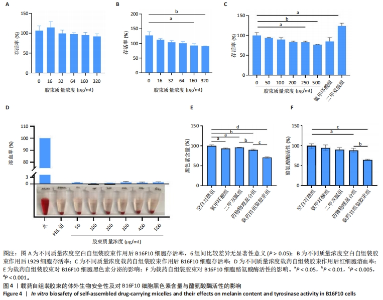
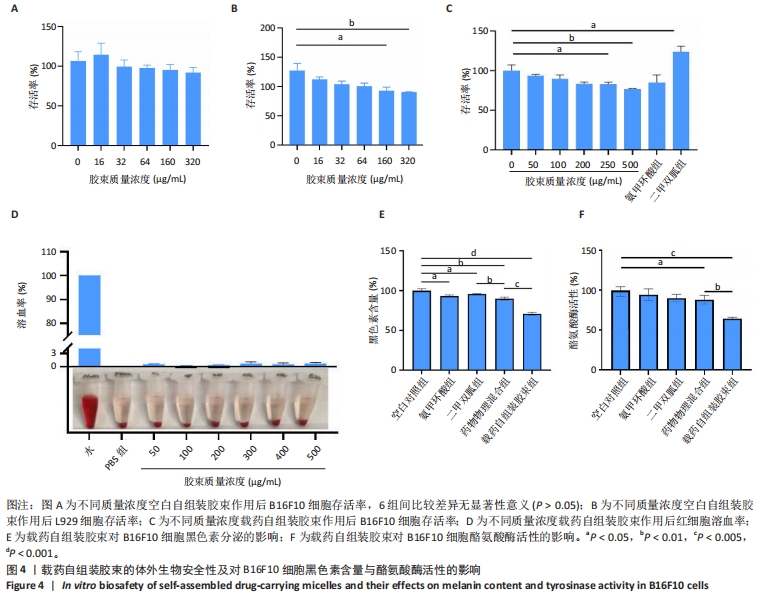
[1] 韩雨晴,李本悦,杨洁,等.身体皮肤色素沉着的常见成因及化妆品原料的应用现状[J].香料香精化妆品,2024(1):43-49.
[2] 陈诗蓉,冯庆媛,谢国勇.皮肤色素沉着的类型及干预策略[J].中国化妆品,2022(12):76-81.
[3] 王铄链,刘毅.烧伤后色素沉着的治疗进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2023,34(4):235-238.
[4] FENG J, HUANG L. Treatment of permanent post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation with medium-fluence medium-spot-size setting in Q-switched Nd: YAG 1064 nm laser: A novel treatment parameters setting strategy. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2021;21(3):1300-1302.
[5] GHIASI M, SAMII R, TOOTOONCHI N, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of tretinoin 0.05% and glycolic acid peeling 70% in axillary and neck lesions of acanthosis nigricans: A single‐blinded, randomized trial. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2024;23(7):2090-2096.
[6] 钱晓莺,赵春华,周宇,等.氨甲环酸不同给药途径治疗黄褐斑的疗效观察[J].中华皮肤科杂志,2013,46(8):598-599.
[7] MAHAJAN VK, PATIL A, BLICHARZ L, et al. Medical therapies for melasma. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2022;21(9):3707-3728.
[8] 王雪.氨甲环酸经皮给药系统的设计与评价[D].南宁:广西中医药大学,2020.
[9] 杨晓霞.氨甲环酸不同给药途径对UVB诱导豚鼠色素沉着的抑制作用[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2023.
[10] MCKESEY J, TOVAR-GARZA A, PA NDYA AG. Melasma treatment: An evidence-based review. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2020;21(2):173-225.
[11] GARG U, JAIN K. Dermal and Transdermal drug delivery through vesicles and particles: preparation and applications. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022;12(1):45-57.
[12] LIU Y, HAN Y, ZHU T, et al. Targeting delivery and minimizing epidermal diffusion of tranexamic acid by hyaluronic acid-coated liposome nanogels for topical hyperpigmentation treatment. Drug Deliv. 2021; 28(1):2100-2107.
[13] 柴云,许凯,常海波,等.聚合物胶束作为药物载体的研究进展[J].化学研究,2018,29(5):522-528.
[14] 丁利营,崔柏宁,王艳,等.光甘草定和氧化白藜芦醇协同治疗黄褐斑作用评价[J].精细化工,2020,37(10):2035-2040.
[15] 孙玮婷,吕丰,董霞.纳米囊泡药物递送载体的研究进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2024,47(2):194-199.
[16] 余胜男,姜伟化,杜子蝶,等.氨甲环酸醇质体的制备及体外评价[J].药学与临床研究,2024,32(1):6-11.
[17] 李媛媛,孙祥科,李伟,等.聚合物胶束载药体系研究进展[J].化学与生物工程,2018,35(5):1-4,10.
[18] ZHU H, MA K, RUAN R, et al. Tumor-targeted self-assembled micelles reducing PD-L1 expression combined with ICIs to enhance chemo-immunotherapy of TNBC. Chin Chem Lett. 2024;35(2):108536.
[19] MONGKHON P, RUENGORN C, AWIPHAN R, et al. Efficacy and safety of metformin for melasma treatment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1281050.
[20] 陈教全,梁碧华,彭丽倩,等.茶多酚在抗皮肤光老化中的作用及研究进展[J].实用皮肤病学杂志,2021,14(6):350-353.
[21] GOFF PS, CASTLE JT, KOHLI JS, et al. Isolation, Culture, and Transfection of Melanocytes. Curr Protoc. 2023;3(5):e774.
[22] 宋开超.基于纳米载药的经皮给药创新制剂的关键技术研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2023.
[23] FILIPCZAK N, PAN J, YALAMARTY SSK, et al. Recent advancements in liposome technology. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;156:4-22.
[24] 史雄喜,李江,邝艳婷,等.聚合物胶束在纳米载药体系的应用研究进展[J].化学与生物工程,2024,41(5):19-24.
[25] CARTER P, NARASIMHAN B, WANG Q. Biocompatible nanoparticles and vesicular systems in transdermal drug delivery for various skin diseases. Int J Pharm. 2019;555:49-62.
[26] REN H, WEI Z, WEI H, et al. Pyridine-containing block copolymeric nano-assemblies obtained through complementary hydrogen-bonding directed polymerization-induced self-assembly in water. Polym Chem. 2022;13(25):3800-3805.
[27] RAYCHAUDHURI R, PANDEY A, HEGDE A, et al. Factors affecting the morphology of some organic and inorganic nanostructures for drug delivery: characterization, modifications, and toxicological perspectives. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2020;17(12):1737-1765.
[28] KONTOGIANNIS O, SELIANITIS D, LAGOPATI N, et al. Surfactant and Block Copolymer Nanostructures: From Design and Development to Nanomedicine Preclinical Studies. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(2):501.
[29] KIRBY SM, ANNA SL, WALKER LM. Effect of surfactant tail length and ionic strength on the interfacial properties of nanoparticle–surfactant complexes. Soft Matter. 2018;14(1):112-123.
[30] PHATALE V, VAIPHEI KK, JHA S, et al. Overcoming skin barriers through advanced transdermal drug delivery approaches. J Control Release. 2022;351:361-380.
[31] MOHD F, TODO H, YOSHIMOTO M, et al. Contribution of the hair follicular pathway to total skin permeation of topically applied and exposed chemicals. Pharmaceutics. 2016;8(4):32.
[32] DENG F, SUN D, YANG S, et al. Comparison of rhodamine 6G, rhodamine B and rhodamine 101 spirolactam based fluorescent probes: A case of pH detection. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2022;268:120662.
[33] 胡杨美晴.pH响应性磁靶向纳米脂质体制备及其抗血栓作用研究[D].沈阳:辽宁大学,2023.
[34] WADHWA R, LI L, SINGH R, et al. Modulation of diacylglycerol-induced melanogenesis in human melanoma and primary melanocytes: role of stress chaperone mortalin. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:9848969.
|