Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (23): 4888-4898.doi: 10.12307/2025.089
Previous Articles Next Articles
Action mechanism by which gambogic acid down-regulates expression of protein C receptor to kill triple negative breast cancer stem cells
Li Su1, Wang Qinghua2, Da Mengting3, Yang Rui2, Chen Daozhen1, 4
- 1Department of Eugenic Genetics Institute, Affiliated Wuxi Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Eugenic Genetics Institute, Jiangnan University Maternity Hospital, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Breast Disease Treatment Center, Medical College of Qinghai University, Xining 810000, Qinghai Province, China; 4Dean’s Office, Second People’s Hospital of Haidong City, Haidong 810600, Qinghai Province, China
-
Received:2023-12-18Accepted:2024-05-17Online:2025-08-18Published:2024-09-27 -
Contact:Chen Daozhen, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Eugenic Genetics Institute, Affiliated Wuxi Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China; Dean’s Office, Second People’s Hospital of Haidong City, Haidong 810600, Qinghai Province, China -
About author:Li Su, Master candidate, Department of Eugenic Genetics Institute, Affiliated Wuxi Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Wuxi 214002, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Qinghai Provincial Natural Science Foundation (General Project), No. 2022-ZJ-912 (to CDZ)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Su, Wang Qinghua, Da Mengting, Yang Rui, Chen Daozhen. Action mechanism by which gambogic acid down-regulates expression of protein C receptor to kill triple negative breast cancer stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(23): 4888-4898.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 藤黄酸抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞的活力及三阴性乳腺癌干细胞的培养 藤黄酸的化学结构式见图2A显示。与对照组相比,藤黄酸在0.16-21 μmol/L浓度范围内能以浓度依赖的方式抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231的细胞活力,半数抑制浓度IC50为(1.18±0.34) μmol/L,见图2B。根据CCK-8实验结果,选取低、中和高浓度(0.5,1.0和2.0 μmol/L)进行后续实验。同时,为研究藤黄酸对三阴性乳腺癌干细胞的杀伤作用,采用三阴性乳腺癌细胞球培养法富集干细胞,干细胞培养基作用后肿瘤球直径逐渐增大,6-8 d后可以观察到3D肿瘤球形成,见图2C,为后续干细胞实验研究奠定了基础。"


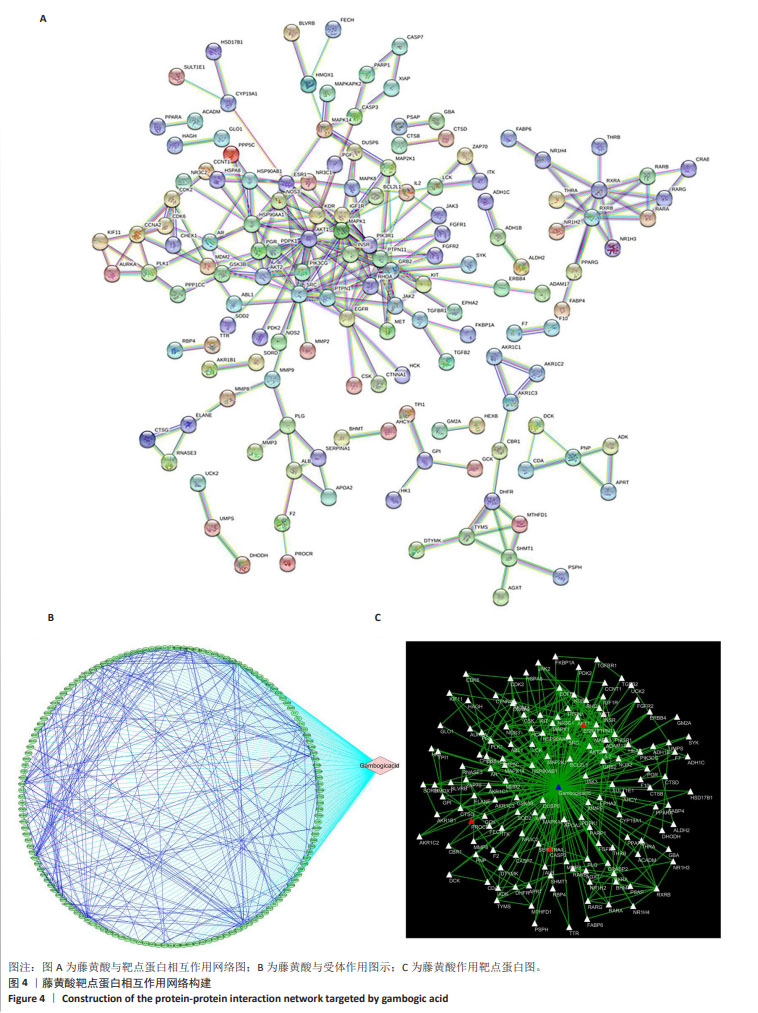
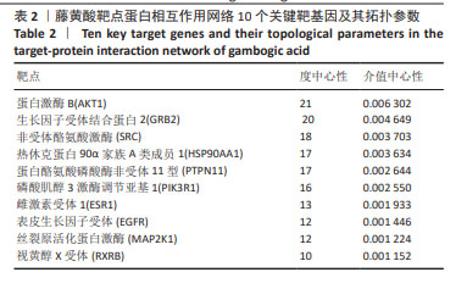
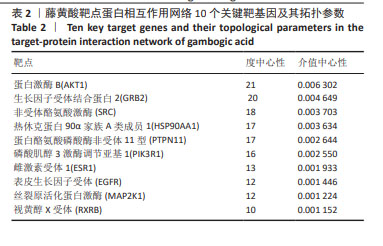
2.2 藤黄酸诱导三阴性乳腺癌干细胞的凋亡作用 TUNEL染色结果显示,藤黄酸以剂量依赖方式诱导三阴性乳腺癌干细胞凋亡,见图3A,表明藤黄酸能够有效杀伤三阴性乳腺癌干细胞。为进一步定量评估藤黄酸诱导三阴性乳腺癌干细胞的凋亡杀伤作用,采用Annexin V-FITC/PI双染法进行流式细胞分析,见图3B,C所示,伴随藤黄酸浓度的增加,三阴性乳腺癌干细胞的凋亡率从30%上升至约80%(P < 0.001)。进一步通过Western blot实验验证凋亡相关蛋白Caspase-3和Cleaved Caspase-3的表达,结果显示,与对照组比较,各浓度藤黄酸干预后三阴性乳腺癌干细胞的凋亡前体蛋白Caspase-3表达降低,活化凋亡蛋白Cleaved Caspase-3升高;与0.5 μmol/L藤黄酸组比较,1.0,2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组Caspase-3蛋白表达降低,Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达升高,具体的组间统计学差异见图3D-F。 2.3 网络药理学证实蛋白C受体是藤黄酸的作用靶点之一 依据藤黄酸反向寻靶PharmMapper(http://lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper/)数据库筛选结果,预测和藤黄酸作用的靶点蛋白,根据匹配度排序,筛选出前10个潜在分子靶点(表1),结果表明,收纳阴性乳腺癌干细胞标记物蛋白C受体是藤黄酸的作用靶点之一且匹配度较高,为藤黄酸靶向杀伤三阴性乳腺癌细胞提供可能。 2.4 藤黄酸药物靶点蛋白相互作用网络与蛋白质相互作用 利用String在线分析各药物靶点蛋白相互作用网络,筛选阈值0.98并去除离散的靶点蛋白,得到靶点蛋白相互作用图,见图4A。此外,进一步将藤黄酸与靶点蛋白信息导入Cytoscape 3.7.1软件构建活性成分-作用靶点网络,见图4B,C所示,共涉及148个节点、397个边。经计算蛋白相互作用网络的2个关键拓扑参数度和介数确认网络中的核心节点,其中蛋白激酶B、生长因子受体结合蛋白2、非受体酪氨酸激酶、热休克蛋白90α家族A类成员1和蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶非受体11型等蛋白度值≥10(表2),表明该节点在网络中越重要。从中可看出藤黄酸药效团可作用于多个靶点基因,充分体现其多靶点的作用特点。"

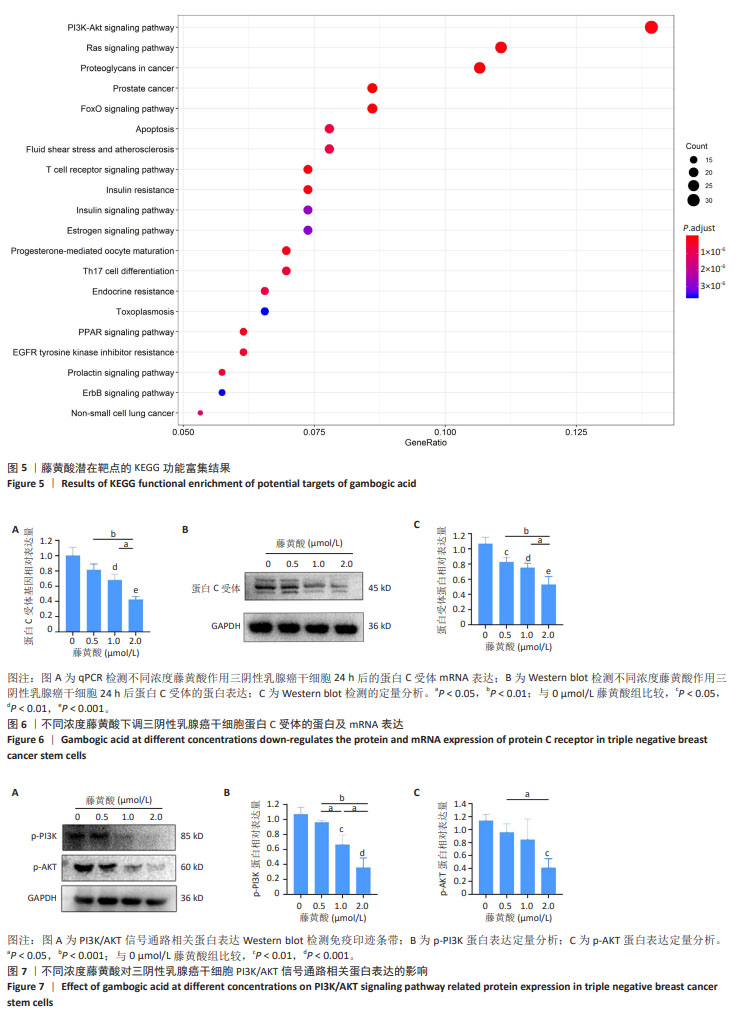
2.5 藤黄酸的KEGG通路富集分析 基于KEGG富集分析藤黄酸作用的138个信号通路,建立了基因通路网络、相应的靶基因,并筛选出P值显著富集的前20个信号通路,如图5显示,包括细胞凋亡、上皮生长因子受体、RAS和PI3K-AKT信号通路等,与癌变信号通路关联的占比约50%;此外,PI3K-AKT信号通路对藤黄酸杀伤作用的贡献最大。 2.6 藤黄酸下调三阴性乳腺癌干细胞中蛋白C受体mRNA和蛋白表达 qPCR检测结果显示,与对照组相比,0.5 μmol/L藤黄酸组蛋白C受体mRNA表达无明显变化(P > 0.05),1.0,2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组蛋白C受体mRNA表达降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.001);0.5,1.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组蛋白C受体mRNA表达高于2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),见图6A,表明藤黄酸可能通过下调蛋白C受体mRNA表达实现对三阴性乳腺癌干细胞的杀伤作用。此外,利用Western blot检测验证藤黄酸作用干细胞后蛋白C受体蛋白表达情况,结果显示:与对照组相比,0.5,1.0,2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组蛋白C受体的蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001);0.5,1.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组蛋白C受体蛋白表达高于2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组(P < 0.01,P < 0.05),见图6B,C。 2.7 藤黄酸对三阴性乳腺癌干细胞PI3K/AKT信号通路磷酸化蛋白表达的影响 根据此前网络药理学的预测结果,PI3K/AKT信号通路在藤黄酸发挥杀伤作用中起到重要作用,因此采用Western blot检测该相关通路磷酸化蛋白表达情况。 Western blot检测结果显示,与对照组相比,各浓度藤黄酸组p-PI3K和p-AKT蛋白表达都呈现了不同程度的下调趋势,见图7A。定量分析结果显示,与对照组相比,0.5 μmol/L藤黄酸组p-PI3K和p-AKT蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05),1.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组p-PI3K蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01)、p-AKT蛋白表达无明显变化(P > 0.05),2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组p-PI3K蛋白与p-AKT蛋白表达降低(P < 0.001, P < 0.01);2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组p-PI3K、p-AKT蛋白表达均低于0.5 μmol/L藤黄酸组(P < 0.001,P < 0.05),1 μmol/L藤黄酸组p-PI3K蛋白表达低于0.5 μmol/L藤黄酸组(P < 0.05)、高于2.0 μmol/L藤黄酸组(P < 0.05),见图7B,C。"
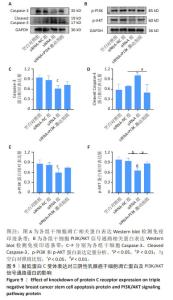
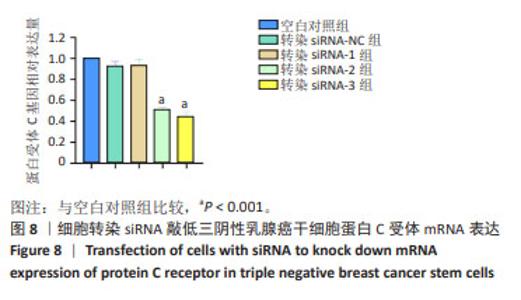
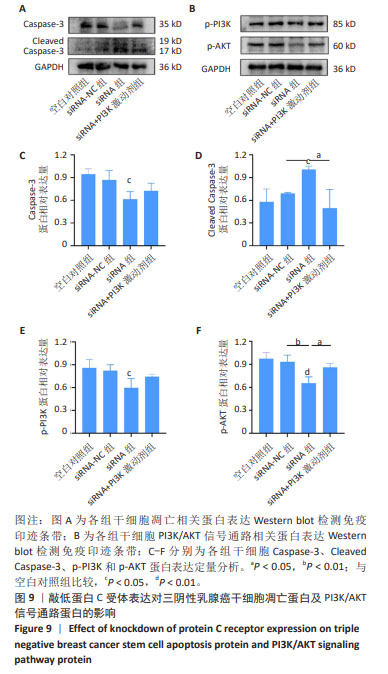
2.9 沉默蛋白C受体对三阴性乳腺癌干细胞凋亡及信号通路的影响 Western blot检测结果显示,与空白对照组比较,siRNA-NC组Caspase-3蛋白、Cleaved Caspase-3、p-PI3K和p-AKT蛋白均无明显变化(P > 0.05),siRNA组Caspase-3、p-PI3K和p-AKT蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与siRNA 组比较,siRNA+PI3K激动剂组Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),p-PI3K蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),见图9。这些实验结果说明,敲低蛋白C受体能够诱导三阴性乳腺癌干细胞发生凋亡,可能机制是抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路的活化。"
| [1] SIEGEL RL, GIAQUINTO AN, JEMAL A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(1):12-49. [2] YIN L, DUAN JJ, BIAN XW, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. 2020;22(1):61. [3] BIANCHINI G, DE ANGELIS C, LICATA L, et al. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer - expanded options, evolving needs. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19(2):91-113. [4] LI Y, ZHANG H, MERKHER Y, et al. Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 2022; 15(1):121. [5] ZHANG Y, DOSTA P, CONDE J, et al. Prolonged local in vivo delivery of stimuli-responsive nanogels that rapidly release doxorubicin in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(4):e1901101. [6] 潘振华,刘红雨,陈军.肺癌干性样细胞与耐药[J].中国肺癌杂志 2022,25(2):111-117. [7] 乌帆,陈国华,张良,等.异黏蛋白调控三阴性乳腺癌细胞干性的机制研究[J].中华乳腺病杂志(电子版),2020,14(4):221-227. [8] HUA Z, WHITE J, ZHOU J. Cancer stem cells in TNBC. Semi Cancer Biol. 2022;82:26-34. [9] GE MH, ZHU XH, SHAO YM, et al. Synthesis and characterization of CD133 targeted aptamer-drug conjugates for precision therapy of anaplastic thyroid cancer. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(4):1313-1324. [10] ZHENG Y, WANG L, YIN L, et al. Lung cancer stem cell markers as therapeutic targets: an update on signaling pathways and therapies. Front Oncol. 2022;12:873994. [11] SHIMOKAWA M, OHTA Y, NISHIKORI S, et al. Visualization and targeting of LGR5+ human colon cancer stem cells. Nature. 2017;545(7653): 187-192. [12] XU H, NIU M, YUAN X, et al. CD44 as a tumor biomarker and therapeutic target. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020;9(1):36. [13] NING ST, LEE SY, WEI MF, et al. Targeting colorectal cancer stem-like cells with anti-CD133 antibody-conjugated sn-38 nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater. 2016;8(28):17793-17804. [14] ZENG Z, FU M, HU Y, et al. Regulation and signaling pathways in cancer stem cells: implications for targeted therapy for cancer. Mol Cancer. 2023;22(1):172. [15] MOHAN RAO LV, ESMON CT, PENDURTHI UR. Endothelial cell protein C receptor: a multiliganded and multifunctional receptor. Blood. 2014; 124(10):1553-1562. [16] YU QC, SONG W, WANG D, et al. Identification of blood vascular endothelial stem cells by the expression of protein C receptor. Cell Res. 2016;26(10):1079-1098. [17] FARES I, CHAGRAOUI J, LEHNERTZ B, et al. EPCR expression marks UM171-expanded CD34+ cord blood stem cells. Blood. 2017;129(25): 3344-3351. [18] SUBRAMANIAM A, TALKHONCHEH MS, MAGNUSSON M, et al. Endothelial protein c receptor (EPCR) expression marks human fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells. Haematologica. 2019;104(2):e47-e50. [19] WANG D, WANG J, BAI L, et al. Long-term expansion of pancreatic islet organoids from resident PROCR+ progenitors. Cell. 2020;180(6): 1198-1211.e19. [20] ALTHAWADI H, ALFARSI H, BESBES S, et al. Activated protein C upregulates ovarian cancer cell migration and promotes unclottability of the cancer cell microenvironment. Oncol Rep. 2015;34(2):603-609. [21] WANG D, LIU C, WANG J, et al. Protein C receptor stimulates multiple signaling pathways in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2018;293(4): 1413-1424. [22] LIU C, LIN C, WANG D, et al. Procr functions as a signaling receptor and is essential for the maintenance and self-renewal of mammary stem cells. Cell Rep. 2022;38(12):110548. [23] WANG D, HU X, LIU C, et al. Protein C receptor is a therapeutic stem cell target in a distinct group of breast cancers. Cell Res. 2019;29(10): 832-845. [24] XU L, MENG X, XU N, et al. Gambogic acid inhibits fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway in erlotinib-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer and suppresses patient-derived xenograft growth. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(3):262. [25] HATAMI E, JAGGI M, CHAUHAN SC, et al. Gambogic acid: a shining natural compound to nanomedicine for cancer therapeutics. BBA-Rev Cancer. 2020;1874(1):188381. [26] ZHANG D, CHU Y, QIAN H, et al. Antitumor activity of thermosensitive hydrogels packaging gambogic acid nanoparticles and tumor-penetrating peptide irgd against gastric cancer. Inter J Nanomed. 2020;15:735-747. [27] MI D, LI J, WANG R, et al. Postsurgical wound management and prevention of triple-negative breast cancer recurrence with a pryoptosis-inducing, photopolymerizable hydrogel. J Control Release. 2023;356:205-218. [28] WEI F, ZHANG T, YANG Z, et al. Gambogic acid efficiently kills stem-like colorectal cancer cells by upregulating zfp36 expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):829-846. [29] YANG R, LU M, MING L, et al. 89Zr-labeled multifunctional liposomes conjugate chitosan for pet-trackable triple-negative breast cancer stem cell targeted therapy. Inter J Nanomed. 2020;15:9061-9074. [30] XU H, ZHANG Y, WANG P, et al. A comprehensive review of integrative pharmacology-based investigation: a paradigm shift in traditional chinese medicine. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(6):1379-1399. [31] NOGALES C, MAMDOUH ZM, LIST M, et al. Network pharmacology: curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms. Trends Pharmacol. 2022;43(2):136-150. [32] CARIATI M, NADERI A, BROWN JP, et al. Alpha-6 integrin is necessary for the tumourigenicity of a stem cell-like subpopulation within the MCF7 breast cancer cell line. Inter J Cancer. 2008;122(2):298-304. [33] LI M, SU F, ZHU M, et al. Research progress in the field of gambogic acid and its derivatives as antineoplastic drugs. Molecules. 2022;27(9): 2937. [34] KIM HH, JEONG SH, HA SE, et al. Cellular regulation of kynurenic acid-induced cell apoptosis pathways in ags cells. Inter J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(16):8894. [35] BAKER SC, SHABIR S, GEORGOPOULOS NT, et al. Ketamine-induced apoptosis in normal human urothelial cells: a direct, n-methyl-d-aspartate receptor-independent pathway characterized by mitochondrial stress. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(5):1267-1277. [36] PORTER AG, JÄNICKE RU. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6(2):99-104. [37] BERNARD A, CHEVRIER S, BELTJENS F, et al. Cleaved caspase-3 transcriptionally regulates angiogenesis-promoting chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Res. 2019;79(23):5958-5970. [38] YANG Q, JIANG W, HOU P. Emerging role of PI3K/AKT in tumor-related epigenetic regulation. Semin Cancer Biol. 2019;59:112-124. [39] UMEMURA S, YOSHIDA S, OHTA Y, et al. Increased phosphorylation of AKT in triple-negative breast cancers. Cancer Sci. 2007;98(12):1889-1892. [40] SHI Z, WULFKUHLE J, NOWICKA M, et al. Functional mapping of AKT signaling and biomarkers of response from the fairlane trial of neoadjuvant ipatasertib plus paclitaxel for triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28(5):993-1003. [41] ARDITO F, GIULIANI M, PERRONE D, et al. The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy (review). Inter J Mol Med. 2017;40(2):271-280. [42] YU JS, CUI W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: the role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development. 2016;143(17):3050-3060. [43] ZHU KY, PALLI SR. Mechanisms, applications, and challenges of insect RNA interference. Annu Rev Entomol. 2020;65:293-311. [44] 徐炎炎,卓倩,汤洋洋,等.EPCR对人乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞增殖、迁移的影响及机制[J].山东医药,2018,58(9):13-16. [45] WANG Q, YANG H, ZHUO Q, et al. Knockdown of EPCR inhibits the proliferation and migration of human gastric cancer cells via the ERK1/2 pathway in a PAR-1-dependent manner. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(4): 1843-1852. |
| [1] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [2] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [3] | Chen Yueping, Chen Feng, Peng Qinglin, Chen Huiyi, Dong Panfeng . Based on UHPLC-QE-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular dynamics simulation to explore the mechanism of Panax notoginseng in treating osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [4] | Yu Ting, Lyu Dongmei, Deng Hao, Sun Tao, Cheng Qian. Icariin pretreatment enhances effect of human periodontal stem cells on M1-type macrophages [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1328-1335. |
| [5] | Yang Zhihang, Sun Zuyan, Huang Wenliang, Wan Yu, Chen Shida, Deng Jiang. Nerve growth factor promotes chondrogenic differentiation and inhibits hypertrophic differentiation of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [6] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [7] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [8] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [9] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [10] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [11] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [12] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [13] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [14] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [15] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||