Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (20): 4205-4214.doi: 10.12307/2025.707
Previous Articles Next Articles
Molecular mechanism of allicin-targeted regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor and kynureninase in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Xu Liang, Gulimila·Muhetaer, Ju Bowei, Li Ruoning
- The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-07-22Accepted:2024-08-29Online:2025-07-18Published:2024-12-19 -
Contact:Li Ruoning, MS, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Xu Liang, MS, Pharmacist-in-charge, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang 830000, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, No. 2022D01C580 (to XL)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Liang, Gulimila·Muhetaer, Ju Bowei, Li Ruoning. Molecular mechanism of allicin-targeted regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor and kynureninase in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4205-4214.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
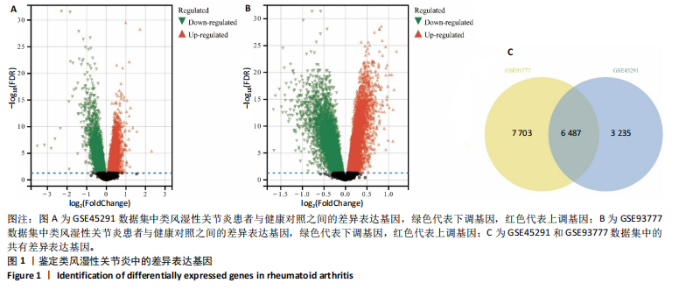
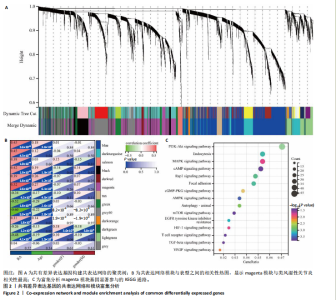
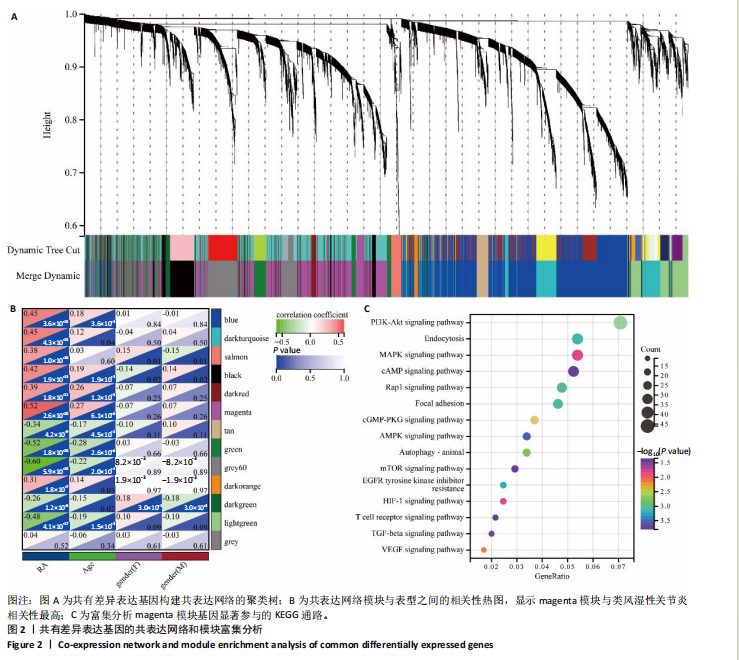
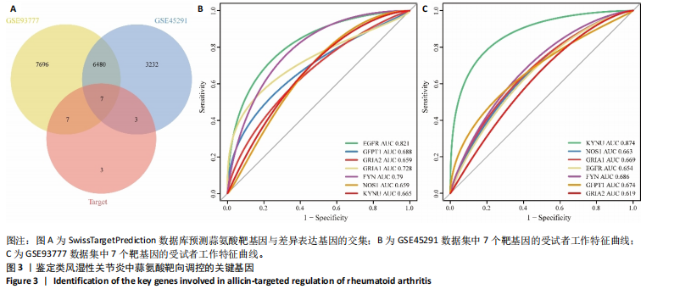
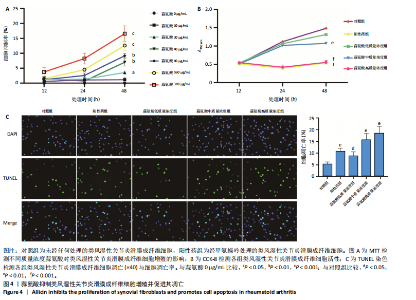
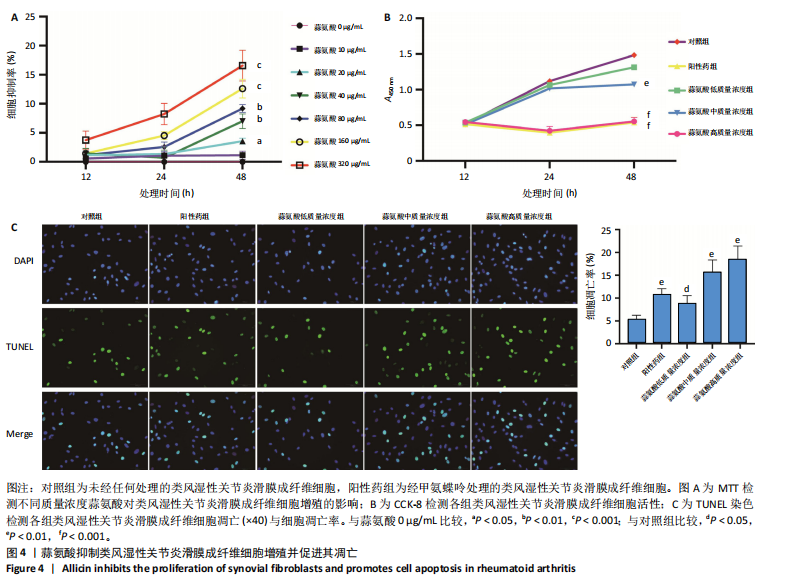
2.1 类风湿性关节炎的差异表达基因及共表达网络 通过对类风湿性关节炎患者和健康对照人群外周血样本之间进行差异表达分析,在GSE45291数据集中鉴定出9 722个差异表达基因(图1A),在GSE93777数据集中鉴定出14 190个差异表达基因(图1B),交集分析结果在两套数据集中鉴定了6 487个共有差异表达基因(图1C)。 通过WGCNA在共有差异表达基因中识别出12个基因共表达模块,见图2A。相关性分析显示magenta模块与类风湿性关节炎相关性最高,其与类风湿性关节炎的相关系数为0.52(P < 0.001),见图2B。富集分析显示magenta模块基因显著参与PI3K/AKT、内分泌等信号通路(图2C)。 2.2 蒜氨酸靶基因的预测 通过SwissTargetPrediction数据库预测蒜氨酸的靶向调控基因,共预测出20个潜在靶基因,其中发现7个基因在共有差异表达基因中(图3A)。通过计算7个基因的AUC值发现,表皮生长因子受体在GSE45291数据集中的AUC值最高,为0.821,见图3B;犬尿氨酸酶在GSE93777数据集中的AUC值最高,为0.874,见图3C,表明这2个基因在区分类风湿性关节炎患者和健康对照中具有较高的特异性。 2.3 蒜氨酸对类风湿性关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞增殖和活性的影响 MTT检测结果显示,20 μg/mL及以上质量浓度的"
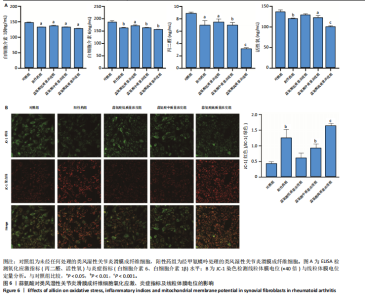
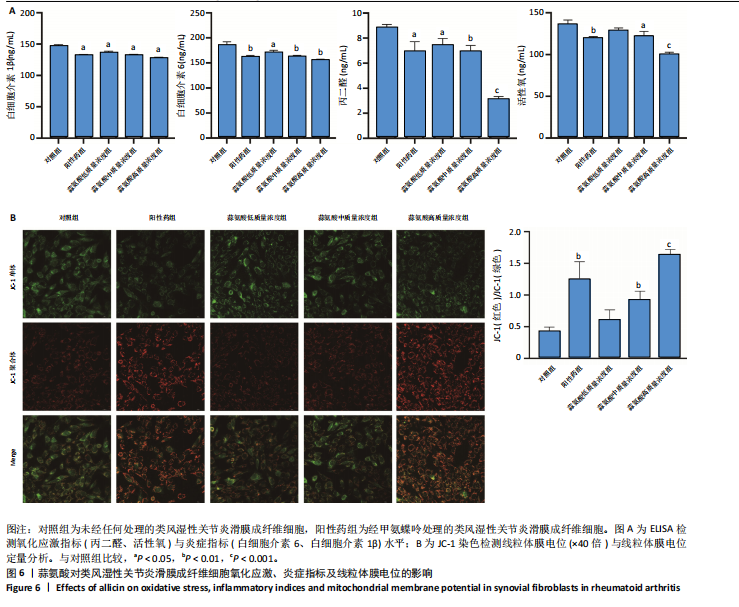
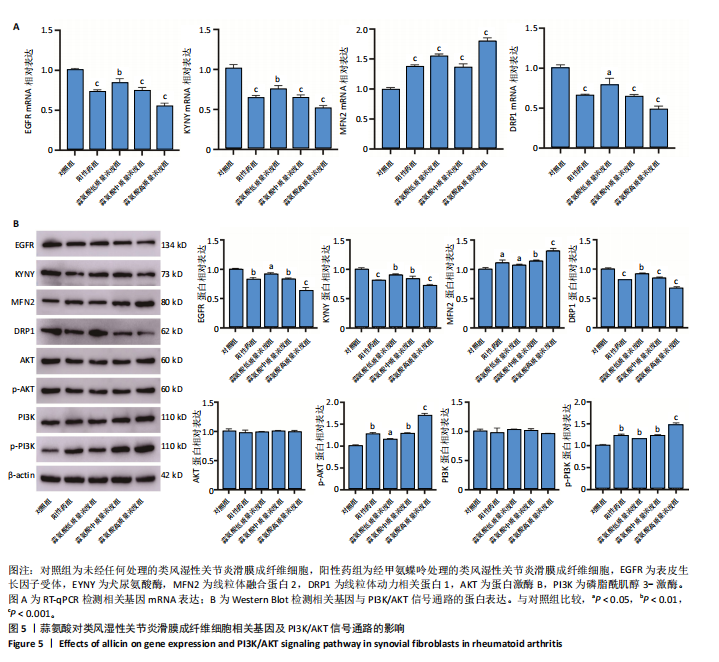
高质量浓度组类风湿性关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞凋亡数量增加,见图4C;定量分析结果显示,与对照组比较,其他4组类风湿性关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞的凋亡率均增加 (P < 0.05,P < 0.01),见图4C。 2.4 蒜氨酸对类风湿性关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞相关基因及PI3K/AKT信号通路的影响 RT-qPCR检测结果显示,与对照组比较,其他4组表皮生长因子受体、犬尿氨酸酶、线粒体动力相关蛋白1 mRNA表达均降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001),线粒体融合蛋白2 mRNA表达均升高(P < 0.001),见图5A。Western Blot检测结果显示,与对照组比较,其他4组表皮生长因子受体、犬尿氨酸酶、线粒体动力相关蛋白1蛋白表达均降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001),线粒体融合蛋白2 蛋白表达均升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01, P < 0.001),见图5B。5组AKT、PI3K蛋白表达比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05),与对照组比较,其他4组p-AKT、p-PI3K蛋白表达均升高(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001),见图5B。 2.5 蒜氨酸对类风湿性关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞氧化应激和炎症指标的影响 与对照组比较,其他4组白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6及丙二醛水平均降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01,P < 0.001),阳性药组及蒜氨酸中、高质量浓度组活性氧水平均降低(P < 0.01,P < 0.05,P < 0.001),见图6A。 2.6 蒜氨酸对类风湿性关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞线粒体膜电位的影响 JC-1染色结果显示,与对照组比较,阳性药组及蒜氨酸中、高质量浓度组线粒体膜电位均升高(P < 0.01,P < 0.01,P < 0.001),见图6B。"
| [1] LA R, ZHOU L, YIN Y, et al. Association between oxidative balance score and rheumatoid arthritis in female: a cross-sectional study. BMC Womens Health. 2024;24(1):225. [2] Collaborators GBDRA. Global, regional, and national burden of rheumatoid arthritis, 1990-2020, and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023;5(10):e594-e610. [3] DING Q, HU W, WANG R, et al. Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):68. [4] MAISHA JA, EL-GABALAWY HS, O’NEIL LJ. Modifiable risk factors linked to the development of rheumatoid arthritis: evidence, immunological mechanisms and prevention. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1221125. [5] GUSKI LS, JURGENS G, PEDDER H, et al. Monotreatment With Conventional Antirheumatic Drugs or Glucocorticoids in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Network Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(10): e2335950. [6] SHARMA SD, BLUETT J. Towards Personalized Medicine in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Open Access Rheumatol. 2024;16:89-114. [7] LONG Z, XIANG W, HE Q, et al. Efficacy and safety of dietary polyphenols in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 47 randomized controlled trials. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1024120. [8] MOOSAVIAN SP, PAKNAHAD Z, HABIBAGAHI Z, et al. The effects of garlic (Allium sativum) supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers, fatigue, and clinical symptoms in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res. 2020;34(11):2953-2962. [9] ARELLANO BUENDIA AS, JUAREZ ROJAS JG, GARCIA-ARROYO F, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of allicin in the kidney of an experimental model of metabolic syndrome. PeerJ. 2023;11:e16132. [10] GONG Q, WANG X, LIU Y, et al. Potential Hepatoprotective Effects of Allicin on Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Toxics. 2024;12(5):328. [11] XIANG Q, CHENG Z, WANG J, et al. Allicin Attenuated Advanced Oxidation Protein Product-Induced Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Apoptosis in Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6685043. [12] 姜玥,刘宵达,吴素琴. anti-IL-33对类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞增殖与凋亡的影响[J].医学信息,2021,34(13):81-83. [13] LI M, TIAN F, GUO J, et al. Therapeutic potential of Coptis chinensis for arthritis with underlying mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14: 1243820. [14] ZHU M, DING Q, LIN Z, et al. New Targets and Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis: From Signal Transduction to Epigenetic Aspect. Biomolecules. 2023;13(5):766. [15] HU S, LIN Y, TANG Y, et al. Targeting dysregulated intracellular immunometabolism within synovial microenvironment in rheumatoid arthritis with natural products. Front Pharmacol. 2024;15:1403823. [16] SWANSON CD, AKAMA-GARREN EH, STEIN EA, et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 2012;188(7):3513-3521. [17] NERVIANI A, BOUTET MA, GHIRARDI GM, et al. Axl and MerTK regulate synovial inflammation and are modulated by IL-6 inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2398. [18] ZHAO L, LIU M, ZHENG K, et al. Fufang Duzheng tablet attenuates adjuvant rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting arthritis inflammation and gut microbiota disturbance in rats. Heliyon. 2024;10(12):e32705. [19] KEHRIBAR DY, EMMUNGIL H, TURKMEN NB, et al. EGFR blocker lapatinib inhibits the synthesis of matrix metalloproteinases from synovial fibroblasts. Turk J Med Sci. 2022;52(4):1355-1361. [20] LIANG C, YU Y, TANG Q, et al. Discovering KYNU as a feature gene in hidradenitis suppurativa. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2023;37: 3946320231216317. [21] MU KL, RAN F, PENG LQ, et al. Identification of diagnostic biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis based on machine learning-assisted comprehensive bioinformatics and its correlation with immune cells. Heliyon. 2024;10(15):e35511. [22] RYCHKOV D, NEELY J, OSKOTSKY T, et al. Cross-Tissue Transcriptomic Analysis Leveraging Machine Learning Approaches Identifies New Biomarkers for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:638066. [23] TONG Y, LI X, DENG Q, et al. Advances of the small molecule drugs regulating fibroblast-like synovial proliferation for rheumatoid arthritis. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1230293. [24] SHI H, ZHANG Y, YIN J, et al. Lysine succinylation analysis reveals the effect of Sirt5 on synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2024; 13(2):110-116. [25] JIN L, CHEN Q, HU K, et al. The FTO-CMPK2 Pathway in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes Modulates Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Inflammation and Cartilage Homeostasis via mtDNA Regulation. Int J Biol Sci. 2024; 20(5):1617-1633. [26] QIAN H, DENG C, CHEN S, et al. Targeting pathogenic fibroblast-like synoviocyte subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024;16(6):316-333. [27] NYGAARD G, FIRESTEIN GS. Restoring synovial homeostasis in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(6):316-333. [28] MOOSAVIAN SP, PAKNAHAD Z, HABIBAGAHI Z. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, evaluating the garlic supplement effects on some serum biomarkers of oxidative stress, and quality of life in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Clin Pract. 2020; 74(7):e13498. [29] ZHANG Y, GONG Y. Allicin regulates Treg/Th17 balance in mice with collagen-induced arthritis by increasing the expression of MEKK2 protein. Food Sci Nutr. 2021;9(5):2364-2371. [30] RASLAN MA, RASLAN SA, SHEHATA EM, et al. Different modalities to manage rheumatoid arthritis: an A to Z story. Future Sci OA. 2024; 10:FSO968. [31] LOPEZ-ARMADA MJ, FERNANDEZ-RODRIGUEZ JA, BLANCO FJ. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(6):1151. [32] LI S, HUO C, LIU A, et al. Mitochondria: a breakthrough in combating rheumatoid arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1439182. [33] CLAYTON SA, MACDONALD L, KUROWSKA-STOLARSKA M, et al. Mitochondria as Key Players in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:673916. [34] CUI L, WEIYAO J, CHENGHONG S, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis and mitochondrial homeostasis: The crossroads of metabolism and immunity. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;9:1017650. [35] WANG G, CHEN X, SHAO Y, et al. PINK1/Parkin-Mediated Mitochondrial Autophagy Participates in H2O2-Induced Abnormal Proliferation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Inflamm Res. 2023;16:1271-1282. [36] DING C, NI L, LIU Q, et al. Cold air plasma improving rheumatoid arthritis via mitochondrial apoptosis pathway. Bioeng Transl Med. 2023;8(1):e10366. |
| [1] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [2] | Zhou Ying, Tian Yong, Zhong Zhimei, Gu Yongxiang, Fang Hao. Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 regulates mTORC1/ULK1 signaling and promotes autophagy to improve myocardial injury in sepsis mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6434-6440. |
| [3] | Zhang Songjiang, Li Longyang, Zhou Chunguang, Gao Jianfeng. Central anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism of tea polyphenols in exercise fatigue model mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(30): 6474-6481. |
| [4] | Wu Xiaochou, Wang Huiying, Wang Jie, Zhang Caifeng, Hou Yanyun, Jin Bo. Protective mechanism of tanshinone IIA in mouse ovarian cryopreservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6198-6204. |
| [5] | Song Yuting, Wen Chunlei, Li Yi, Bai Xue, Gao Hong, Hu Tingju, Wang Zijun, Yan Xu. Effects of myocardial extracellular matrix remodeling on connexin 43 and its Ser368 phosphorylation and electrical conduction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6212-6218. |
| [6] | Liu Ruojing, Zhao Xue, Zhu Yizhen, Fu Lingling, Zhu Junde. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates cerebral ischemic injury in mice by regulating microglial polarization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6219-6227. |
| [7] | Sun Rongyan, Xu Luchun, Jiang Guozheng, Song Jiawei, Ma Yukun, Fan Jiaojiao, Wang Guanlong, Yang Yongdong, Yu Xing. Du Meridian electroacupuncture inhibits ferroptosis and promotes neurorepair in rats with acute cervical spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6228-6238. |
| [8] | Chen Lijuan, Gao Xinxue, Wu Jin, Du Ying, Lyu Meijun, Sui Guoyuan, Jia Lianqun, Pan Guowei. Construction and evaluation of spleen-deficiency hyperlipidemia mouse models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6237-6242. |
| [9] | Du Juan, Zhang Yi, Hao Quanshui. Effects of exercise on activation of microglia and astrocytes and neuronal apoptosis in depressed rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6243-6248. |
| [10] | Liu Haowei, Tian Haodong, Huang Li, Yu Hanglin, Peng Li. Acute effects of blood flow restriction resistance exercise on serum metabolites in obese young men [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6249-6259. |
| [11] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [12] | Chen Xiaoqing, Gong Yunzhao, Chen Wei. Association of the controlling nutritional status score and systemic immune-inflammation index with postmenopausal osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5071-5078. |
| [13] | Zhang Yibo, Lu Jianqi, Mao Meiling, Pang Yan, Dong Li, Yang Shangbing, Xiao Xiang. Rheumatoid arthritis and coronary atherosclerosis: data analysis of serum metabolite and inflammatory factor in the European population [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(24): 5263-5271. |
| [14] | Liu Kexin, Ma Chao, Liu Kai, Hao Maochen, Wang Xingru, Meng Lingting, Dong Mei, Wang Jianzhong . Screening and validation of glucose metabolism genes in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(20): 4181-4189. |
| [15] | Tian Yanhu, Huang Xinan, Guo Tongtong, Rusitanmu·Ahetanmu, Luo Jiangmiao, Xiao Yao, Wang Chao, Wang Weishan . Machine learning identification of LRRC15 and MICB as immunodiagnostic markers for rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2411-2420. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||