Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (11): 2411-2420.doi: 10.12307/2025.361
Machine learning identification of LRRC15 and MICB as immunodiagnostic markers for rheumatoid arthritis
Tian Yanhu1, Huang Xinan1, Guo Tongtong1, Rusitanmu·Ahetanmu1, Luo Jiangmiao1, Xiao Yao1, Wang Chao2, Wang Weishan2
- 1Medical College, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University Medical College, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-03-22Accepted:2024-05-22Online:2025-04-18Published:2024-08-13 -
Contact:Wang Weishan, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Tian Yanhu, Master candidate, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82160423 (to WWS)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Tian Yanhu, Huang Xinan, Guo Tongtong, Rusitanmu·Ahetanmu, Luo Jiangmiao, Xiao Yao, Wang Chao, Wang Weishan . Machine learning identification of LRRC15 and MICB as immunodiagnostic markers for rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(11): 2411-2420.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
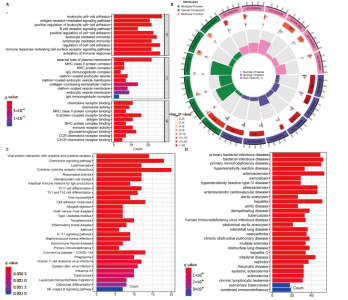
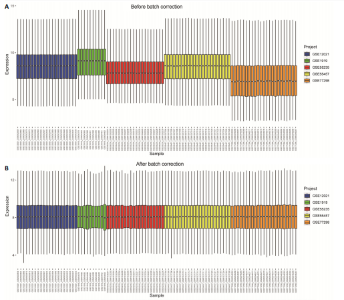
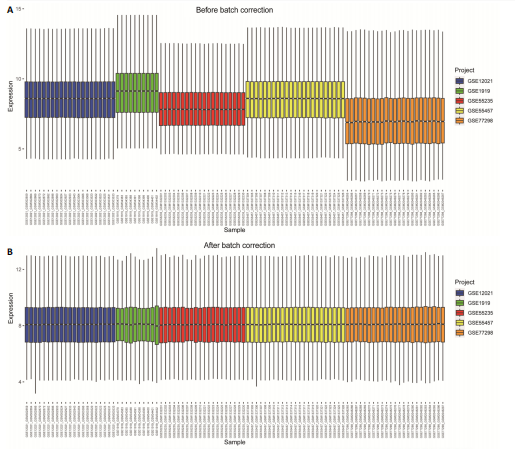
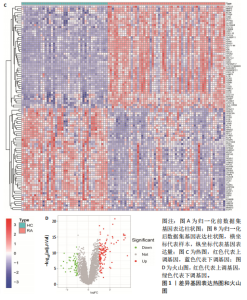
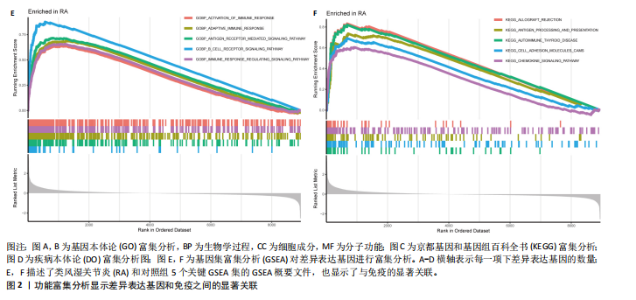
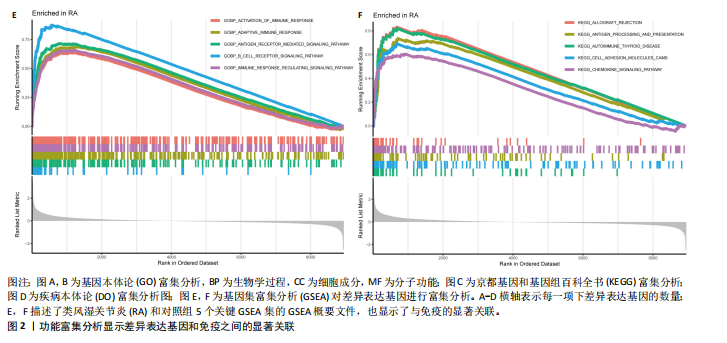
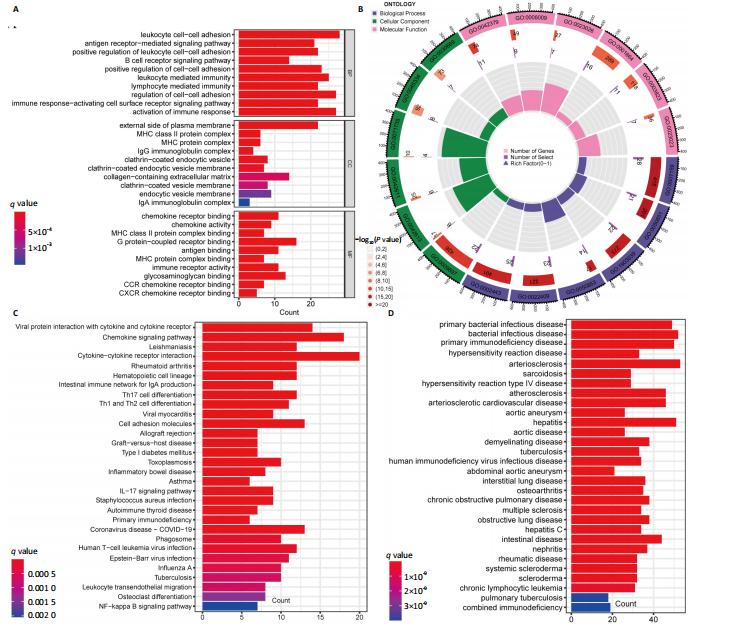
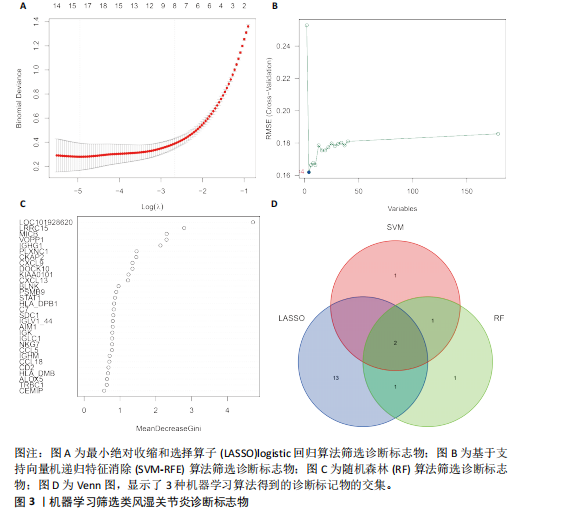
在显著差异。上调最显著的前10个基因分别是MMP1、LOC101928620、CXCL13、IGHM、IGJ、IGLV1-44、IGLC1、CXCL9、IGKC、LRRC15,下调最显著的前10个基因分别是ABCA8、ZBTB16、MAOA、PLIN1、FOSB、RPS4Y1、APOD、FABP4、ADIPOQ、ADH1B。 2.2 富集分析 此次研究进行了功能富集分析,以更深入地了解差异表达基因的生物学功能。GO富集分析结果显示,差异表达基因的生物学过程主要富集在白细胞-细胞黏附、细胞-细胞黏附的调节、免疫反应的激活、单核细胞分化、细胞黏附的正向调节在细胞成分方面,差异表达基因主要与质膜外侧、含胶原蛋白的细胞外基质、内细胞载体相关(图2A,B)。在分子功能方面,差异表达基因主要富集在G 蛋白偶联受体结合、受体配体活性、糖胺聚糖结合方面。 KEGG富集分析显示,差异表达基因在免疫相关通路中显著富集,如细胞因子-细胞因子受体相互作用、趋化因子信号通路和病毒蛋白与细胞因子及细胞因子受体的相互作用、细胞黏附分子(图2C)。DO富集分析显示,差异表达基因主要与动脉硬化、细菌性传染病、肝炎和原发性免疫缺陷相关(图2D)。对合并后的每个滑膜组织基因进行GSEA富集分析,GOBP主要富集在免疫反应的激活、适应性免疫应答、抗原受体介导的信号通路(图2E),B细胞受体信号通路、免疫反应调节信号通路。KEGG主要富集在同种异体移植排斥反应、抗原加工和呈递、甲状腺自身免疫性疾病、细胞黏附分子和趋化因子信号通路(图2F)。 2.3 基于机器学习的诊断标志物筛选 研究使用了3种机器学习算法来识别类风湿关节炎的特征基因,对差异表达基因的表达矩阵进行LASSO回归分析(图3A),模型的二项偏差最小,lambda值为16,选择的预测基因为LRRC15、IGHG1、PSMB9、MICB、AIM1、EDNRB、RRM2、TNFAIP8、SFRP1、QPCT、JUNB、GZMB、FKBP5、GHR、GPR64、CYP4B1;对差异表达基因的表达矩阵进行SVM-RFE算法(图3B),根据算法的迭代过程,具有最小均方根误差(RMSE)的变量"
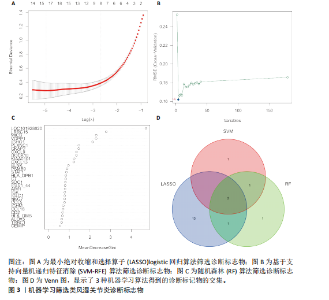
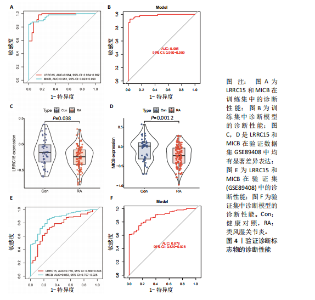
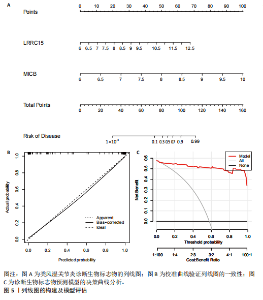
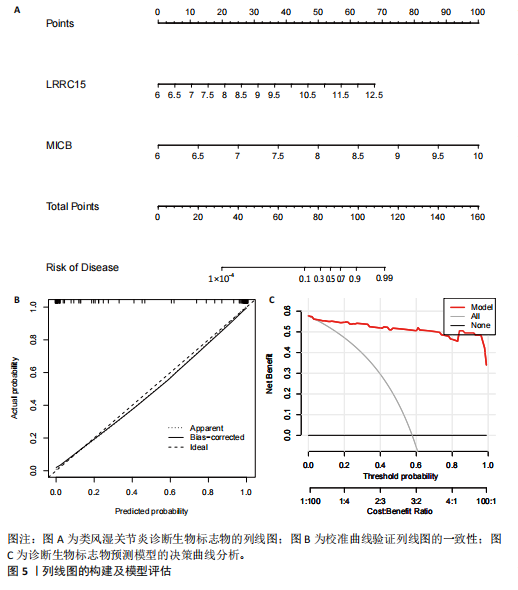
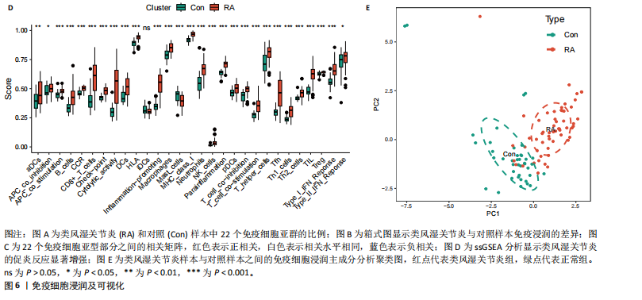
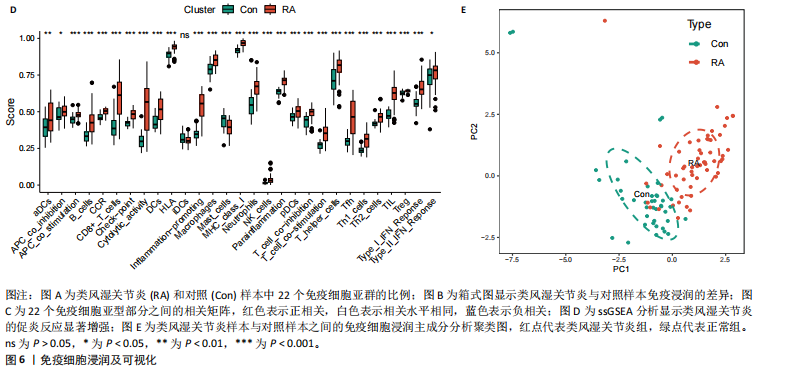
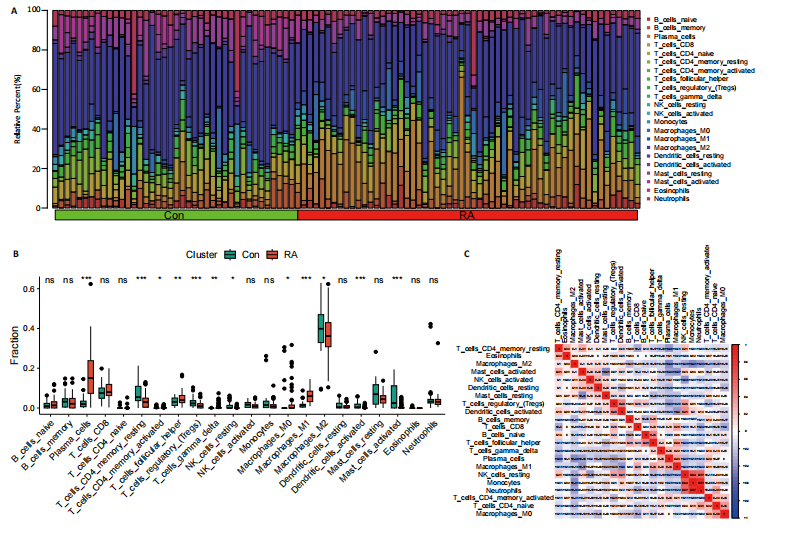
为LRRC15、VOPP1、MICB、CXCL13;利用随机森林结合特征选择,以相对相关性由高到低的顺序,挑选重要性评分大于2的基因(图3C),相关的基因为LOC101928620、LRRC15、MICB、VOPP1、IGHG1,利用维恩图比较差异表达基因和关键模块基因的重叠区域(图3D),可以识别出2个重叠基因区域,这3种机器学习算法确定了LRRC15、MICB为潜在的诊断标志物。 2.4 诊断模型的评估及列线图的构建 在合并后的训练集和验证集中2个潜在标记的基因具有显著的差异表达,并且验证了2个潜在诊断标志物的诊断能力。如图4所示,在训练集中LRRC15曲线下面积为0.964,MICB曲线下面积为0.961(图4A),2种基因合并后诊断模型曲线下面积为0.985;在验证集GSE89408中,用小提琴图展示了LRRC15及MICB的基因表达差异(图4C,D),并且验证2种潜在的诊断标记物的诊断性能,LRRC15曲线下面积为0.759,MICB曲线下面积为0.863(图4E),2种基因合并后诊断模型曲线下面积为0.878,结果表明在验证集中MICB具有良好的诊断能力,但LRRC15在验证集中诊断能力较差,两者合并后的诊断模型仍具有较高的诊断性能。 基于2个筛选的潜在诊断标记物构建列线图来预测类风湿关节炎的发生(图5A),标定曲线验证了模型的准确性(图5B),决策曲线揭示了列线图优异的决策能力(图5C)。这表明构建的列线图具有良好的预测精度和可靠性。 2.5 免疫细胞浸润分析 此次研究分析了类风湿关节炎和正常滑膜组织中免疫细胞的浸润情况,用直方图表示每个样本免疫细胞的组成(图6A),结果表明,类风湿关节炎的滑膜组织中M2巨噬细胞、CD8+ T细胞、静息的肥大细胞、Tfh细胞是主要的浸润性免疫细胞。然后评估类风湿关节炎滑膜组织中免疫细胞的相关性(图6B),例如M2巨噬细胞与浆细胞、单核细胞集中性粒细胞呈负相关,中性粒细胞与静息自然杀伤细胞、单核细胞和幼稚CD4+ T细胞呈正相关,Tfh细胞与记忆B细胞、CD8+ T细胞、幼稚的B细胞和M1巨噬细胞呈正相关。"
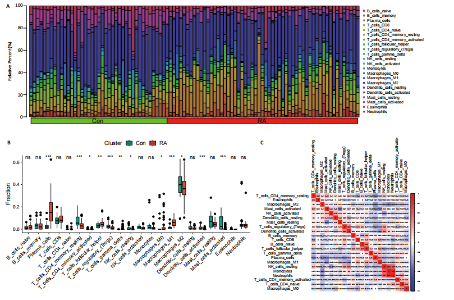
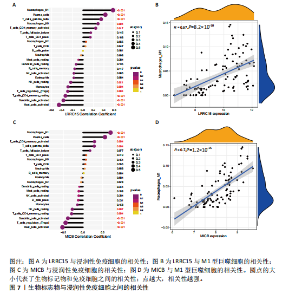
采用Wilcoxon检验对类风湿关节炎和正常滑膜组织的免疫细胞浸润情况进行了显著性识别,结果显示有13种免疫细胞具有显著差异性(P < 0.05)(图6C);ssGSEA分析显示两组免疫细胞功能有显著差异(图6D),类风湿关节炎的滑膜组织激活了大部分促炎功能。通过主成分分析,类风湿关节炎患者和对照组滑膜免疫细胞的比例表现出明显的群体偏聚和个体差异(图6E)。 2.6 诊断标志物与免疫细胞的相关性分析 研究进一步分析LRRC15和MICB的表达与免疫浸润水平的关系,LRRC15与M1型巨噬细胞、浆细胞、γ-T细胞、M0型巨噬细胞、T细胞滤泡辅助细胞、激活的记忆CD4+ T细胞,与静息自然杀伤细胞、单核细胞、调节T细胞、静息的记忆CD4+ T细胞、激活的树突状细胞和激活的肥大细胞成负相关(图7A),其中与M1型巨噬细胞相关性最高(cor=0.57,P=8.2×10-10)(图7B);MICB与M1型巨噬细胞、浆细胞、γ-T细胞、 M0型巨噬细胞、T细胞滤泡辅助细胞、激活的记忆CD4+ T细胞,与静息自然杀伤细胞、单核细胞、调节T细胞、静息的记忆CD4+ T细胞、激活的树突状细胞和激活的肥大细胞成负相关(图7C),其中与M1型巨噬细胞相关性最高(cor=0.7,P=1.2×10-10)(图7D)。"
| [1] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205-2219. [2] DI MATTEO A, BATHON JM, EMERY P. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2023; 402(10416):2019-2033. [3] LEE DM, WEINBLATT ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001;358(9285):903-911. [4] SILMAN AJ, PEARSON JE. Epidemiology and genetics of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. 2002;4 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S265-S272. [5] ALETAHA D, NEOGI T, SILMAN AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569-2581. [6] BARTOK B, FIRESTEIN GS. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes: key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2010; 233(1):233-255. [7] WEYAND CM, GORONZY JJ. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Immunol. 2021; 22(1):10-18. [8] MÜLLER-LADNER U, OSPELT C, GAY S, et al. Cells of the synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(6):223. [9] WU F, GAO J, KANG J, et al. B Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Pathogenic Mechanisms and Treatment Prospects. Front Immunol. 2021;12:750753. [10] FLOUDAS A, NETO N, ORR C, et al. Loss of balance between protective and pro-inflammatory synovial tissue T-cell polyfunctionality predates clinical onset of rheumatoid arthritis [published correction appears in Ann Rheum Dis. 2023; 82(2):e53]. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022;81(2): 193-205. [11] JIANG Q, YANG G, LIU Q, et al. Function and Role of Regulatory T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:626193. [12] ZHONG Y, ZHANG W, HONG X, et al. Screening Biomarkers for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Based on Machine Learning and Exploring Their Expression Correlations With the Ratios of Various Immune Cells. Front Immunol. 2022;13:873787. [13] YANG Y, CAO Y, HAN X, et al. Revealing EXPH5 as a potential diagnostic gene biomarker of the late stage of COPD based on machine learning analysis. Comput Biol Med. 2023;154:106621. [14] UNGETHUEM U, HAEUPL T, WITT H, et al. Molecular signatures and new candidates to target the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Physiol Genomics. 2010;42A(4):267-282. [15] WOETZEL D, HUBER R, KUPFER P, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84. [16] HUBER R, HUMMERT C, GAUSMANN U, et al. Identification of intra-group, inter-individual, and gene-specific variances in mRNA expression profiles in the rheumatoid arthritis synovial membrane. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10(4):R98. [17] BROEREN MG, DE VRIES M, BENNINK MB, et al. Disease-Regulated Gene Therapy with Anti-Inflammatory Interleukin-10 Under the Control of the CXCL10 Promoter for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Hum Gene Ther. 2016;27(3):244-254. [18] GUO Y, WALSH AM, FEARON U, et al. CD40L-Dependent Pathway Is Active at Various Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Progression. J Immunol. 2017;198(11): 4490-4501. [19] WANG H, YANG F, LUO Z. An experimental study of the intrinsic stability of random forest variable importance measures. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016;17:60. [20] LIN X, LI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Selecting Feature Subsets Based on SVM-RFE and the Overlapping Ratio with Applications in Bioinformatics. Molecules. 2017;23(1):52. [21] YANG C, DELCHER C, SHENKMAN E, et al. Machine learning approaches for predicting high cost high need patient expenditures in health care. Biomed Eng Online. 2018; 17(Suppl 1):131. [22] SANZ H, VALIM C, VEGAS E, et al. SVM-RFE: selection and visualization of the most relevant features through non-linear kernels. BMC Bioinformatics. 2018; 19(1):432. [23] ZENG D, YE Z, SHEN R, et al. IOBR: Multi-Omics Immuno-Oncology Biological Research to Decode Tumor Microenvironment and Signatures. Front Immunol. 2021;12:687975. [24] RIVELLESE F, PITZALIS C. Cellular and molecular diversity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Semin Immunol. 2021;58:101519. [25] JANG S, KWON EJ, LEE JJ. Rheumatoid Arthritis: Pathogenic Roles of Diverse Immune Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(2): 905. [26] AN Q, RAHMAN S, ZHOU J, et al. A Comprehensive Review on Machine Learning in Healthcare Industry: Classification, Restrictions, Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors (Basel). 2023; 23(9):4178. [27] TANG H, LIU W, XU Z, et al. Integrated microenvironment-associated genomic profiles identify LRRC15 mediating recurrent glioblastoma-associated macrophages infiltration. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(12):5534-5546. [28] RAY U, PATHOULAS CL, THIRUSANGU P, et al. Exploiting LRRC15 as a Novel Therapeutic Target in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022;82(9):1675-1681. [29] PURCELL JW, TANLIMCO SG, HICKSON J, et al. LRRC15 Is a Novel Mesenchymal Protein and Stromal Target for Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Cancer Res. 2018;78(14):4059-4072. [30] CHEN YJ, CHANG WA, HSU YL, et al. Deduction of Novel Genes Potentially Involved in Osteoblasts of Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatic Approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11):2396. [31] CHEN YJ, CHANG WA, WU LY, et al. Systematic Analysis of Transcriptomic Profile of Chondrocytes in Osteoarthritic Knee Using Next-Generation Sequencing and Bioinformatics. J Clin Med. 2018;7(12):535. [32] WANG Y, LIU Y, ZHANG M, et al. LRRC15 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by modulating p65 cytoplasmic/nuclear translocation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):65. [33] SINGH P, WANG M, MUKHERJEE P, et al. Transcriptomic and epigenomic analyses uncovered Lrrc15 as a contributing factor to cartilage damage in osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):21107. [34] FERRARI DE ANDRADE L, TAY RE, PAN D, et al. Antibody-mediated inhibition of MICA and MICB shedding promotes NK cell-driven tumor immunity. Science. 2018;359(6383):1537-1542. [35] STEPHENS HA. MICA and MICB genes: can the enigma of their polymorphism be resolved? Trends Immunol. 2001;22(7): 378-385. [36] FERRARI DE ANDRADE L, KUMAR S, LUOMA AM, et al. Inhibition of MICA and MICB Shedding Elicits NK-Cell-Mediated Immunity against Tumors Resistant to Cytotoxic T Cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 2020;8(6):769-780. [37] COURAU T, BONNEREAU J, CHICOTEAU J, et al. Cocultures of human colorectal tumor spheroids with immune cells reveal the therapeutic potential of MICA/B and NKG2A targeting for cancer treatment. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7(1):74. [38] ALVES DA SILVA PH, XING S, KOTINI AG, et al. MICA/B antibody induces macrophage-mediated immunity against acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2022;139(2):205-216. [39] LÜ M, XIA B, LI J, et al. MICB microsatellite polymorphism is associated with ulcerative colitis in Chinese population. Clin Immunol. 2006;120(2):199-204. [40] OTA M, KATSUYAMA Y, KIMURA A, et al. A second susceptibility gene for developing rheumatoid arthritis in the human MHC is localized within a 70-kb interval telomeric of the TNF genes in the HLA class III region. Genomics. 2001;71(3):263-270. [41] LÓPEZ-ARBESU R, BALLINA-GARCÍA FJ, ALPERI-LÓPEZ M, et al. MHC class I chain-related gene B (MICB) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(3):426-430. |
| [1] | Li Jiagen, Chen Yueping, Huang Keqi, Chen Shangtong, Huang Chuanhong. The construction and validation of a prediction model based on multiple machine learning algorithms and the immunomodulatory analysis of rheumatoid arthritis from the perspective of mitophagy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(在线): 1-15. |
| [2] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [3] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [4] | Han Haihui, Meng Xiaohu, Xu Bo, Ran Le, Shi Qi, Xiao Lianbo. Effect of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 inhibitor on bone destruction in rats with collagen-induced arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 968-977. |
| [5] | Yang Bin, Tao Guangyi, Yang Shun, Xu Junjie, Huang Junqing . Visualization analysis of research hotspots of artificial intelligence in field of spinal cord nerve injury and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(4): 761-770. |
| [6] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [7] | Chen Ying, Guo Xiaojing, Mo Xueni, Ma Wei, Wu Shangzhi, Li Xiangling, Xie Tingting. Analysis of diagnostic biomarkers for ischemic stroke and experimental validation of targeted cuproptosis related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7562-7570. |
| [8] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| [9] | Li Jing, Lu Guangqi, Zhuang Minghui, Cui Ying, Yu Zhangjingze, Sun Xinyue, Ma Mingming, Zhu Liguo, Yu Jie. Development of a clinical prediction model for cervical instability in young and middle-aged adults based on machine learning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(33): 7203-7210. |
| [10] | Tian Yushi, Fu Qiang, Li Ji . Bioinformatics identification and validation of mitochondrial genes related to acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6697-6707. |
| [11] | Xie Yizi, Lin Xueying, Zhang Xinxin, Huang Xiufang, Zhan Shaofeng, Jiang Yong, Cai Yan. Biological mechanism of mitophagy in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(31): 6708-6716. |
| [12] | Song Haoran, Zhang Yuqiang, Gu Na, Zhi Xiaodong, Wang Wei. Visualization analysis of artificial intelligence in bone trauma research based on Citespace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(3): 493-502. |
| [13] | Zhang Ziyu, Chen Longhao, Sheng Wei, Lyu Hanzhe, Shen Ying, Wang Binghao, Lyu Zhizhen, Lyu Lijiang. Application of artificial intelligence in the diagnosis and treatment of lumbar disc herniation: evolution towards standardization, efficiency, and precision of diagnosis and treatment methods [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6269-6276. |
| [14] | Wang Jiaru, Zhang Ying, Yang Yong, Qi Wen, Xiao Huaye, Ma Qiuping, Yang Lianzhao, Luo Ziwei, He Yaqing, Zhang Jiangyin, Wei Jiawen, Meng Yuan, Tan Silian. Systematic review of machine learning models for predicting functional recovery and prognosis in stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(29): 6317-6325. |
| [15] | Qiu Boyuan, Liu Fei, Tong Siwen, Ou Zhixue, Wang Weiwei. Bioinformatics identification and validation of aging key genes in hormonal osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(26): 5608-5620. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||