Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (18): 3747-3757.doi: 10.12307/2025.704
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics analysis and identification of hub genes and their role in immune infiltration in osteoarthritis
Cai Wei1, Zhu Yukun2, Xu Jianzhong1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Critical Care Medicine, West China Hospital of Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Received:2024-07-24Accepted:2024-08-29Online:2025-06-28Published:2024-11-27 -
Contact:Xu Jianzhong, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China -
About author:Cai Wei, Master candidate, Department of Orthopedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cai Wei, Zhu Yukun, Xu Jianzhong. Bioinformatics analysis and identification of hub genes and their role in immune infiltration in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(18): 3747-3757.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

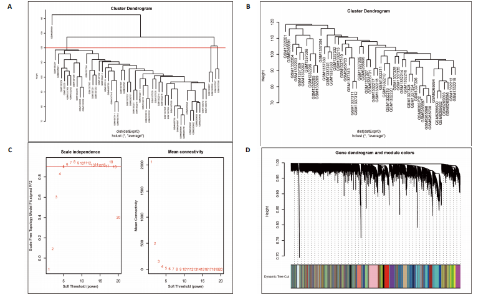
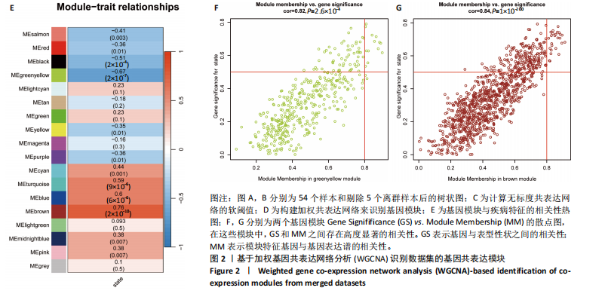
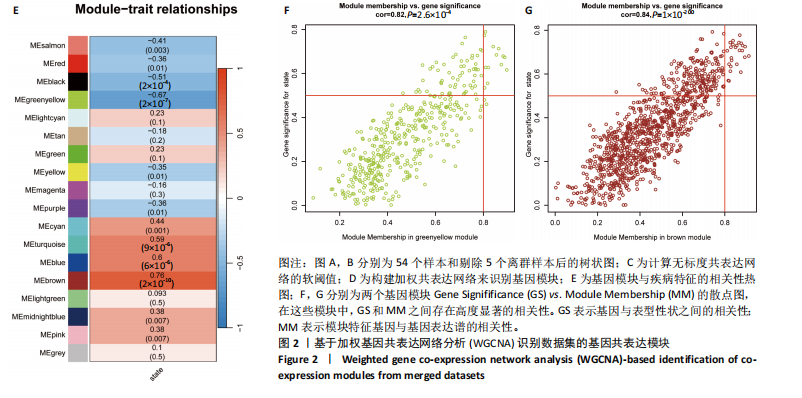
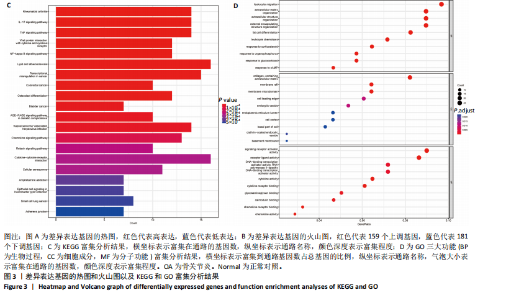
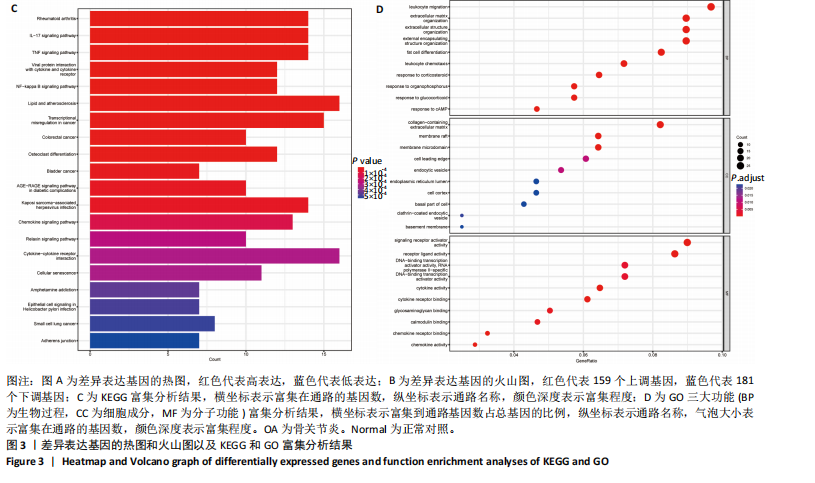
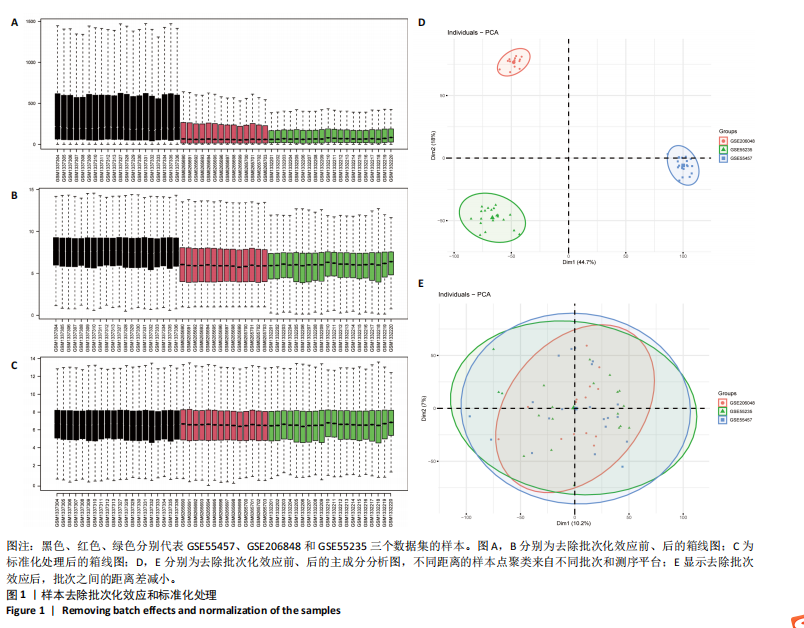
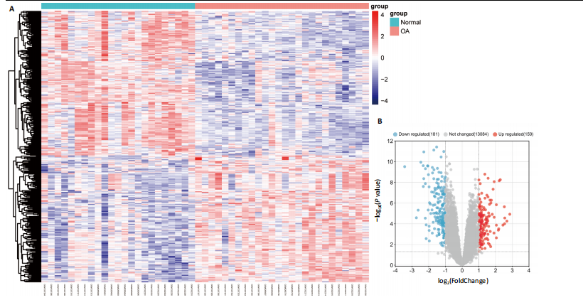
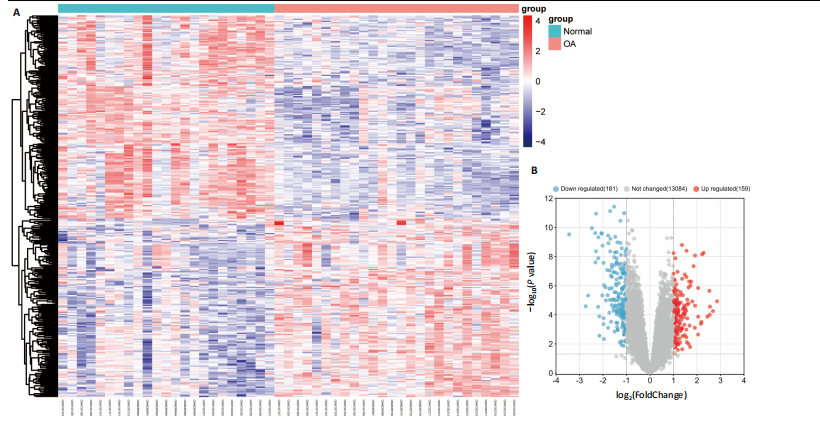
2.1 差异表达基因的筛选 2.1.1 数据集的标准化 使用R软件将3个数据集GSE55235、GSE55457和GSE206848合并去除批次效应,见图1A,B;并标准化处理基因表达数据,见图1C;对处理前后的数据集进行主成分分析(principal component analysis,PCA),见图1D,E。 2.1.2 加权相关网络的构建 利用加权基因共表达网络分析筛选与疾病相关的模块和探索潜在的枢纽基因被认为是一种有效的方法[13]。在R软件中使用加权基因共表达网络分析包来分析合并后数据集中13 424个基因与骨关节炎之间的相关性。对54个样本进行聚类后,剔除5个离群样本,见图2A,B;并确定软阈值为5,见图2C;随后将13 424个基因聚类到18个模块中,见图2D;通过热图展示这些模块与临床信息之间的相关性,见图2E;选择了两个拥有最强相关性的模块,筛选标准为:|GS| > 0.5和|MM| > 0.8,从这两个模块中筛选出了42个基因作为初步得到的枢纽基因,见图2F,G。 2.1.3 差异表达基因的鉴定与富集分析 在消除5个离群样本后,共鉴定出340个差异表达基因,包括159个上调基因和181个下调基因,见图3A,B。根据KEGG通路富集分析,差异表达基因主要富集在与类风湿性关节炎、白细胞介素17信号通路、肿瘤坏死因子信号通路、病毒蛋白与细胞因子及其受体的相互作用、核因子κB信号通路、脂质和动脉粥样硬化、癌症中的转录失调、结直肠癌及破骨细胞分化相关的通路中,见图3C;GO分析结果主要体现在以下3个方面,见图3D。在生物过程方面,差异表达基因在白细胞迁移反应、细胞外基质组织、细胞外结构组织、外包封结构组织、脂肪细胞分化、白细"
胞趋化、皮质类固醇反应、有机磷反应、糖皮质激素反应及cAMP反应中起着重要作用;在细胞组分方面,差异表达基因主要富集在含胶原的细胞外基质、膜筏、膜微域、细胞前缘及内吞小泡中;在分子功能方面,差异表达基因在信号受体激活活性、受体配体活性、DNA结合转录激活活性-RNA聚合酶Ⅱ特异性、细胞因子活性及细胞因子受体结合中显示出最强的相关性。 2.1.4 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络构建与枢纽基因的筛选 使用在线平台STRING(https://string-db.org/)构建了一个可视化的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络,旨在研究差异表达基因之间的关系。使用Cytoscape软件中的MCODE插件,在蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络中筛选出了两个高度显著的模块,分别包含16个基因(score=9.867)和17个基因(score=9.000),见图4A,B;此外,使用"
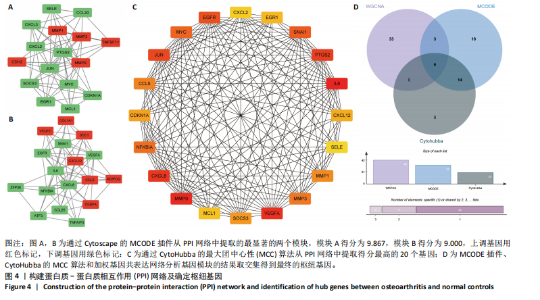
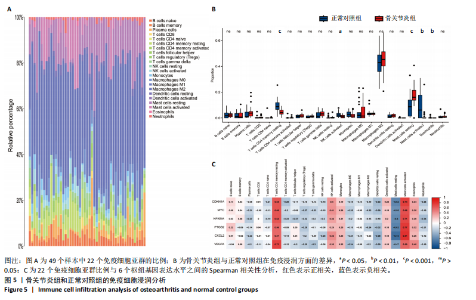
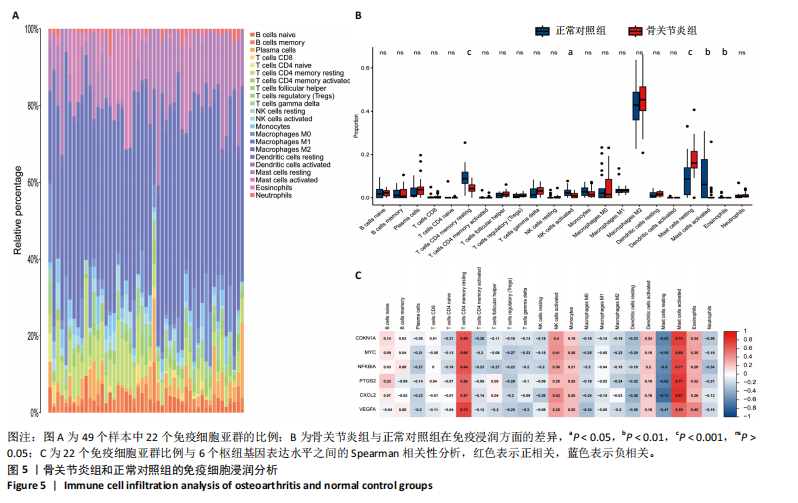
Cytohubba插件中的最大团中心性算法鉴定了蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络中得分最高的前20个基因,见图4C;通过MCODE插件筛选出的33个基因和通过Cytohubba插件筛选获得的20个基因与初步筛选出的42个基因相结合,最终筛选出6个基因,即CDKN1A、MYC、NFKBIA、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶2(prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2,PTGS2)、CXC趋化因子配体2(CXCL2)和血管内皮生长因子A,见图4D。这些基因在骨关节炎组中的表达水平均呈下调趋势。 2.2 免疫细胞浸润及相关性分析 在R软件中使用 CIBERSORT算法计算了骨关节炎组26个样本和正常组23个样本中22种免疫细胞的比例,见图5A。与正常组中的免"
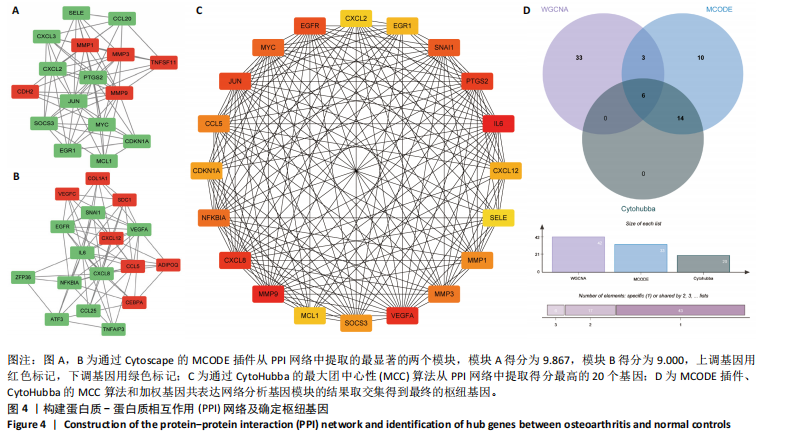

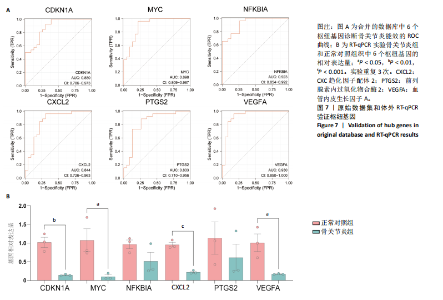
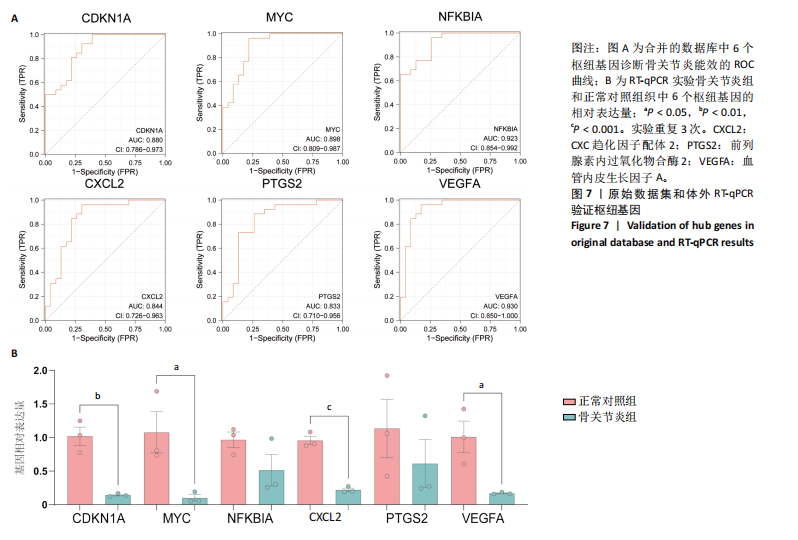
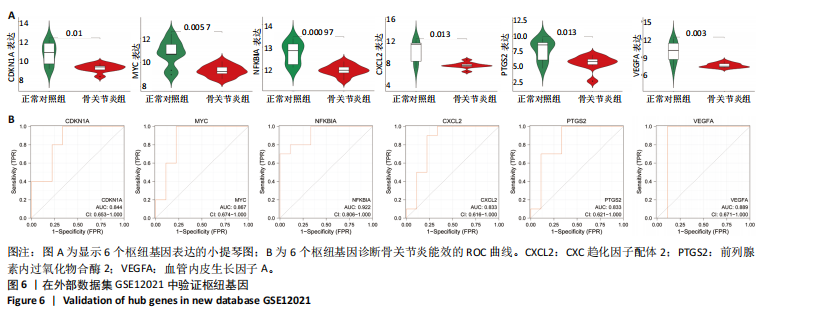
疫细胞比例相比,发现骨关节炎组中的静息记忆CD4+ T细胞(P < 0.001)、活化肥大细胞(P < 0.01)、嗜酸性粒细胞(P < 0.01)和活化NK细胞(P < 0.05)水平较低,而静息肥大细胞的比例较高,见图5B;进一步分析了6个枢纽基因的表达水平与免疫细胞比例之间的相关性,见图5C。结果表明,所有6个枢纽基因的表达水平与静息记忆CD4+ T细胞、活化NK细胞、活化肥大细胞和嗜酸性粒细胞呈正相关,而与静息肥大细胞呈负相关。 2.3 验证枢纽基因的表达 2.3.1 外部独立数据集验证枢纽基因 结果显示,CDKN1A、MYC、NFKBIA、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶2、CXC趋化因子配体2和血管内皮生长因子A在骨关节炎组中呈下调趋势,见图6A,与之前的结果一致。 利用ROC曲线评估枢纽基因在诊断骨关节炎中的临床效能,结果表明,在外部独立数据集GSE12021中,所有6个枢纽基因的AUC值均超过0.8,表明这些枢纽基因均具有很强的区分骨关节炎患者和对照组的能力,见图6B。 2.3.2 体外RT-qPCR实验验证枢纽基因 如图7所示,6个枢纽基因CDKN1A、MYC、NFKBIA、前列腺素内过氧化物合酶2、CXC趋化因子配体2和血管内皮生长因子A的相对表达水平与微阵列杂交的结果一致。但是,NFKBIA和前列腺素内过氧化物合酶2的表达差异未显示出统计学上的显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387. [2] BARNETT R. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2018;391(10134):1985. [3] MARTEL-PELLETIER J, BARR AJ, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16072. [4] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组, 国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心(湘雅医院), 等. 中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(18):1291-1314. [5] ABRAMOFF B, CALDERA FE. Osteoarthritis: Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options.Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(2):293-311. [6] CHO Y, JEONG S, KIM H, et al. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: current status and future directions. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11):1689-1696. [7] YUE L, BERMAN J. What Is Osteoarthritis? JAMA. 2022;327(13):1300. [8] JANSEN MP, MASTBERGEN SC. Joint distraction for osteoarthritis: clinical evidence and molecular mechanisms. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):35-46. [9] MOLNAR V, MATIŠIĆ V, KODVANJ I, et al. Cytokines and Chemokines Involved in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(17):9208. [10] ROBINSON WH, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(10):580-592. [11] ZHANG R, YANG X, WANG J, et al. Identification of potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis between rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis via integrative genome‑wide gene expression profiling analysis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(1):30-40. [12] LOUGHLIN J. Translating osteoarthritis genetics research: challenging times ahead. Trends Mol Med. 2022;28(3):176-182. [13] WANG T, DAI L, SHEN S, et al. Comprehensive Molecular Analyses of a Macrophage-Related Gene Signature With Regard to Prognosis, Immune Features, and Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on WGCNA and the LASSO Algorithm.Front Immunol. 2022;13:843408. [14] POSTLER AE, LÜTZNER C, GORONZY J, et al. When are patients with osteoarthritis referred for surgery?. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2023;37(2):101835. [15] MOSSER DM, EDWARDS JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8(12):958-969. [16] WARMINK K, VINOD P, KORTHAGEN NM, et al. Macrophage-Driven Inflammation in Metabolic Osteoarthritis: Implications for Biomarker and Therapy Development. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(7):6112. [17] YUNNA C, MENGRU H, LEI W, et al. Macrophage M1/M2 polarization.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;877:173090. [18] XIE J, HUANG Z, YU X, et al. Clinical implications of macrophage dysfunction in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019;46:36-44. [19] SCHAIBLE HG.Nociceptive neurons detect cytokines in arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):470. [20] SELLAM J, BERENBAUM F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6(11):625-635. [21] ZHENG W, ZHOU T, ZHANG Y, et al. Simplified α2-macroglobulin as a TNF-α inhibitor for inflammation alleviation in osteoarthritis and myocardial infarction therapy. Biomaterials. 2023;301:122247. [22] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al.Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42. [23] LIAO CR, WANG SN, ZHU SY, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products increase TNF-α and IL-1β expression in chondrocytes via NADPH oxidase 4 and accelerate cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis progression. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101306. [24] LI Z, HUANG Z, BAI L. Cell Interplay in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:720477. [25] RUAL JF, VENKATESAN K, HAO T, et al.Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature. 2005; 437(7062):1173-1178. [26] YAO Q, WU X, TAO C, et al. Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):56. [27] YANG W, LI J, ZHANG M, et al. Elevated expression of the rhythm gene NFIL3 promotes the progression of TNBC by activating NF-κB signaling through suppression of NFKBIA transcription. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):67. [28] KIHARA S, HAYASHI S, HASHIMOTO S, et al. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor-1-Deficient Mice are Susceptible to Osteoarthritis Associated with Enhanced Inflammation. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(5):991-1001. [29] RODRIGUEZ-FONTENLA C, CALAZA M, EVANGELOU E, et al. Assessment of osteoarthritis candidate genes in a meta-analysis of nine genome-wide association studies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):940-949. [30] HAMILTON JL, NAGAO M, LEVINE BR, et al. Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924. [31] YOO SA, BAE DG, RYOO JW, et al. Arginine-rich anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) hexapeptide inhibits collagen-induced arthritis and VEGF-stimulated productions of TNF-alpha and IL-6 by human monocytes. J Immunol. 2005;174(9):5846-5855. [32] LU J, ZHANG H, CAI D, et al. Positive-Feedback Regulation of Subchondral H-Type Vessel Formation by Chondrocyte Promotes Osteoarthritis Development in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):909-920. [33] LIU Y, ZENG Y, SI HB, et al. Exosomes Derived From Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Overexpressing miR-140-5p Alleviate Knee Osteoarthritis Through Downregulation of VEGFA in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105. [34] CHEN Z, WANG W, HUA Y. Identification and validation of BCL6 and VEGFA as biomarkers and ageing patterns correlating with immune infiltrates in OA progression. Sci Rep. 2023;13(1):2558. [35] LI HY, PAN L, KE YS, et al.Daidzein suppresses pro-inflammatory chemokine Cxcl2 transcription in TNF-α-stimulated murine lung epithelial cells via depressing PARP-1 activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014; 35(4):496-503. [36] CAI W, LI H, ZHANG Y, et al. Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics analysis.PeerJ. 2020;8:e8390. [37] DUFFY MJ, O’GRADY S, TANG M, et al. MYC as a target for cancer treatment.Cancer Treat Rev. 2021;94:102154. [38] LIU J, HUANG X, LIU D, et al. Demethyleneberberine induces cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence of NSCLC cells via c-Myc/HIF-1α pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021;91:153678. [39] LI X, ZHANG Z, GAO F, et al. c-Myc-Targeting PROTAC Based on a TNA-DNA Bivalent Binder for Combination Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J Am Chem Soc. 2023;145(16):9334-9342. [40] EZAWA K, YAMAMURA M, MATSUI H, et al. Comparative analysis of CD45RA- and CD45RO-positive CD4+T cells in peripheral blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Acta Med Okayama. 1997;51(1):25-31. [41] QI C, SHAN Y, WANG J, et al. Circulating T helper 9 cells and increased serum interleukin-9 levels in patients with knee osteoarthritis.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016;43(5):528-534. [42] BENIGNI G, DIMITROVA P, ANTONANGELI F, et al. CXCR3/CXCL10 Axis Regulates Neutrophil-NK Cell Cross-Talk Determining the Severity of Experimental Osteoarthritis. J Immunol. 2017;198(5):2115-2124. [43] CHOU CH, JAIN V, GIBSON J, et al. Synovial cell cross-talk with cartilage plays a major role in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):10868. [44] KULKARNI P, HARSULKAR A, MÄRTSON AG, et al. Mast Cells Differentiated in Synovial Fluid and Resident in Osteophytes Exalt the Inflammatory Pathology of Osteoarthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(1):541. [45] ZHAO X, YOUNIS S, SHI H, et al. RNA-seq characterization of histamine-releasing mast cells as potential therapeutic target of osteoarthritis.Clin Immunol. 2022;244:109117. |
| [1] | Deng Keqi, Li Guangdi, Goswami Ashutosh, Liu Xingyu, He Xiaoyong. Screening and validation of Hub genes for iron overload in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [2] | Yin Lu, Jiang Chuanfeng, Chen Junjie, Yi Ming, Wang Zihe, Shi Houyin, Wang Guoyou, Shen Huarui. Effect of Complanatoside A on the apoptosis of articular chondrocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [3] | Liu Lin, Liu Shixuan, Lu Xinyue, Wang Kan. Metabolomic analysis of urine in a rat model of chronic myofascial trigger points [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1585-1592. |
| [4] | Zhao Jiacheng, Ren Shiqi, Zhu Qin, Liu Jiajia, Zhu Xiang, Yang Yang. Bioinformatics analysis of potential biomarkers for primary osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1741-1750. |
| [5] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [6] | Zhang Haojun, Li Hongyi, Zhang Hui, Chen Haoran, Zhang Lizhong, Geng Jie, Hou Chuandong, Yu Qi, He Peifeng, Jia Jinpeng, Lu Xuechun. Identification and drug sensitivity analysis of key molecular markers in mesenchymal cell-derived osteosarcoma [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1448-1456. |
| [7] | Wang Mi, Ma Shujie, Liu Yang, Qi Rui. Identification and validation of characterized gene NFE2L2 for ferroptosis in ischemic stroke [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1466-1474. |
| [8] | Xu Tianjie, Fan Jiaxin, Guo Xiaoling, Jia Xiang, Zhao Xingwang, Liu kainan, Wang Qian. Metformin exerts a protective effect on articular cartilage in osteoarthritis rats by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1003-1012. |
| [9] | Wu Guangtao, Qin Gang, He Kaiyi, Fan Yidong, Li Weicai, Zhu Baogang, Cao Ying . Causal relationship between immune cells and knee osteoarthritis: a two-sample bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1081-1090. |
| [10] | Liu Yani, Yang Jinghuan, Lu Huihui, Yi Yufang, Li Zhixiang, Ou Yangfu, Wu Jingli, Wei Bing . Screening of biomarkers for fibromyalgia syndrome and analysis of immune infiltration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(5): 1091-1100. |
| [11] | Ma Weibang, Xu Zhe, Yu Qiao, Ouyang Dong, Zhang Ruguo, Luo Wei, Xie Yangjiang, Liu Chen. Screening and cytological validation of cartilage degeneration-related genes in exosomes from osteoarthritis synovial fluid [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7783-7789. |
| [12] | Yang Dingyan, Yu Zhenqiu, Yang Zhongyu. Machine learning-based analysis of neutrophil-associated potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(36): 7909-7920. |
| [13] | Jiang Qiyu, Zeng Huiyan. A novel analysis and prediction method for potential mechanisms of traditional Chinese medicine based on artificial intelligence and omics data-driven approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7552-7561. |
| [14] | Chen Ying, Guo Xiaojing, Mo Xueni, Ma Wei, Wu Shangzhi, Li Xiangling, Xie Tingting. Analysis of diagnostic biomarkers for ischemic stroke and experimental validation of targeted cuproptosis related genes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7562-7570. |
| [15] | Gong Yuehong, Wang Mengjun, Ren Hang, Zheng Hui, Sun Jiajia, Liu Junpeng, Zhang Fei, Yang Jianhua, Hu Junping. Machine learning combined with bioinformatics screening of key genes for pulmonary fibrosis associated with cellular autophagy and experimental validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(35): 7679-7689. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||