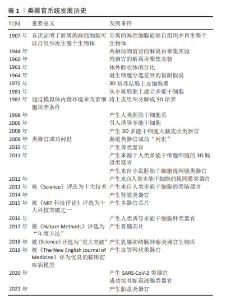
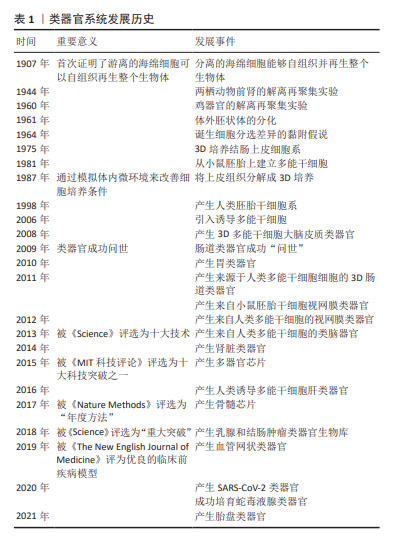
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (1): 202-210.doi: 10.12307/2025.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Application and regulatory challenges of organoid technology in medical field
Cheng Weilu1, Wang Zehua1, Zhang Yidan2, Liu Yinghui1
- 1Department of Clinical and Biostatistics, Center for Medical Device Evaluation, NMPA, Beijing 100081, China; 2GBA Center for Medical Device Evaluation and Inspection, NMPA, Shenzhen 518045, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-30Accepted:2023-12-18Online:2025-01-08Published:2024-05-20 -
About author:Cheng Weilu, PhD, Senior engineer, Department of Clinical and Biostatistics, Center for Medical Device Evaluation, NMPA, Beijing 100081, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Cheng Weilu, Wang Zehua, Zhang Yidan, Liu Yinghui. Application and regulatory challenges of organoid technology in medical field[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(1): 202-210.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
| [1] 刘薇,梅玺丽,陈雨萌,等.3D类器官模型的研究进展及其在化学品毒理学评价中的应用展望[J].生态毒理学报,2021,16(4):32-42. [2] 赵冰.类器官在器官移植领域的应用前景[J].器官移植,2022,13(2): 169-175. [3] KRETZSCHMAR K, CLEVERS H. Organoids: modeling development and the stem cell niche in a dish. Dev Cell. 2016;38(6):590-600. [4] 周永杰,石毓君.类器官研究进展及展望[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2022,29(6):716-718. [5] HAN LH, TONG X, YANG F. Photo-crosslinkable PEG-based microribbons for forming 3D macroporous scaffolds with decoupled niche properties. Adv Mater. 2014;26:1757-1762. [6] CHRISNANDY A, BLONDEL D, REZAKHANI S, et al. Synthetic dynamic hydrogels promote degradation-independent in vitro organogenesis. Nat Mater. 2022;21(4):479-487. [7] GJOREVSKI N, NIKOLAEV M, BROWN TE, et al. Tissue geometry drives deterministic organoid patterning. Science. 2022;375(6576):eaaw9021. [8] CAI H, AO Z, WU Z, et al. Intelligent acoustofluidics enabled mini-bioreactors for human brain organoids. Lab Chip. 2021;21(11):2194-2205. [9] LICATA JP, SCHWAB KH, HAR-EL YE, et al. Bioreactor Technologies for Enhanced Organoid Culture. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(14):11427. [10] SALMON I, GREBENYUK S, FATTAH ARA, et al. Engineering neurovascular organoids with 3D printed microfluidic chips. Lab Chip. 2022;22(8): 1615-1629. [11] WRIGHT CW, LI N, SHAFFER L, et al. Establishment of a 96-well transwell system using primary human gut organoids to capture multiple quantitative pathway readouts. Sci Rep. 2023;13:16357. [12] PECK BC, MAH AT, PITMAN WA, et al. Functional transcriptomics in diverse intestinal epithelial cell types reveals robust microR-NA sensitivity in intestinal stem cells to microbial status. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(7):2586-2600. [13] EVANS GS, FLINT N, SOMERS AS, et al. The development of a method for the preparation of rat intestinal epithelial cell primary cultures. J Cell Sci. 1992;101(Pt1):219-231. [14] 邱广志,喻礼怀,张昌卫,等.肠道类器官模型的构建和应用研究进展[J].动物营养学报,2023,35(7):4231-4237. [15] DERRICOTT H, LUU L, FONG WY, et al. Developing a 3D intestinal epithelium model for livestock species. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;375(2):409-424. [16] SATO T, VRIES RG, SNIPPERT HJ, et al. Single Lgr5 stem cells build crypt-villus structures in vitro without a mesenchymal niche. Nature. 2009;459(7244): 262-265. [17] 林琳.GⅡ.4型人诺如病毒在人肠道类组织中的增殖及转录组研究[D].北京:中国疾病预防控制中心,2019. [18] LI Z, ARAOKA T, WU J, et al. 3D culture supports long-term expansion of mouse and human nephrogenic progenitors. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;19(4): 516-529. [19] TAKEBE T, SEKINE K, ENOMURA M, et al. Vascularized and functional human liver from an iPSC-derived organ bud transplant. Nature. 2013;499(7459): 481-484. [20] SHINOZAWA T, KIMURA M, CAI YQ, et al. High-fidelity drug-induced liver injury screen using human pluripotent stem in organoids. Nat Methods. 2017;14(11):1097-1106. [21] 陈智闻,陈费,刘畅,等.人胆囊类器官培养体系的建立与鉴定[J].海军军医大学学报,2023,44(4):402-408. [22] CARPINO G, CARDINALE V, RENZI A, et al. Activation of biliary tree stem cells within peribiliary glands in primary sclerosing cholangiti. J Hepatol. 2015; 63:1220-1228. [23] 袁波.胆囊良恶性肿瘤类器官培养体系的建立及鉴定[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,海军军医大学,2019. [24] SHIOTA J, SAMUELSON LC, RAZUMILAVA N. Hepatobiliary Organoids and Their Applications for Studies of Liver Health and Disease: Are We There Yet? Hepatology. 2021;74(4):2251-2263. [25] RISS T, KUPCHO K, SHULTZ J, et al. Measuring apoptosis in real-time by linking luciferase fragments to annexin V. Toxicol Lett. 2016;258:S56. [26] 邵云香,黄煜伦.大脑类器官在胶质母细胞瘤中的应用进展[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2020,47(4):453-458. [27] HUBERT CG, RIVERA M, SPANGLER LC, et al. A three-dimensional organoid culture system derived from human glioblastomas recapitulates the hypoxic gradients and cancer stem cell Heterogeneity of Tumors Found In Vivo. Cancer Res. 2016;76(8):2465-2477. [28] EIRAKU M, WATANABE K, MATSUO-TAKASAKI M, et al. Self-organized formation of polarized cortical tissues from ESCs and its active manipulation by extrinsic signals[. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(5):519-532. [29] KIRWAN P, TURNER-BRIDGER B, PETER M, et al. Development and function of human cerebral cortex neural networks from pluripotent stem cells in vitro. Development. 2015;142(18):3178-3187. [30] 卢国庆,孙正宇,康品方,等.心脏类器官的生物构建策略及应用进展[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2023,44(7):664-670. [31] TUVESON D, CLEVERS H. Cancer modeling meets human organoid technology. Science. 2019;364(6444):952-955. [32] ASHOK A, CHOUDHURY D, FANG Y, et al. Towards manufacturing of human organoids. Biotechnol Adv. 2020;39:107460. [33] SHANKARAN A, PRASAD K, CHAUDHARI S, et al. Advances in development and application of human organoids. Biotech. 2021;11(6):257. [34] HOFER M, LUTOLF MP. Engineering organoids. Nat Rev Mater. 2021;6(5): 402-420. [35] TAKEDA M, MIYAGAWA S, FUKUSHIMA S, et al. Development of in vitro drug-induced cardiotoxicity assay by using three-dimensional cardiac tissues derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2018;24:56-67. [36] 刘昕彦,邵瑞,贺爽,等.类器官和立体细胞模型在中药心脏毒性评价中的应用前景[J].药学学报,2019,54(11):1888-1894. [37] 王美佳.皮肤类器官的构建及大面积皮肤损伤的修复研究[D].长春:长春理工大学,2022. [38] ZINK D, CHUAH JKC, YING JY. Assessing toxicity with human cell-based invitro methods. Trends Mol Med. 2020;26(6):570-582. [39] LIU Y, LUO HL, WANG XW, et al. In vitro construction of scaffold-free bilayered tissue-engineered skin containing capillary networks. BioMed Res. Int. 2013;2013:561410. [40] 张艳云,李润芝,姜珊,等.三维表皮模型Epikutis®参考品的研制[J].药物分析杂志,2019,39(12):2117-2125. [41] ALÉPÉE N, GRANDIDIER MH, COTOVIO J, et al. Sub-categorisation of skin corrosive chemicals by the EpiSkinTM reconstructed human epidermis skin corrosion test method according to UN GHS: Revision of OECD Test Guideline 431. Toxicol In Vitro. 2014;28(2):131-145. [42] 刘洋,卢涛,周宙霖,等.HaCaT表皮模型作为皮肤刺激性体外替代实验的可行性研究[J].干细胞与组织工程,2017,31(10):1262-1266. [43] 张劲松,何立成,桑晶,等.EpiskinTM和Epikutis®模型在体外皮肤刺激性和腐蚀性检测应用中的比较[J].中国现代应用药学,2017,34(4): 524-526. [44] 姜珊,陈亮,吴美玉,等.金核/银壳纳米棒在三维表皮模型中的透皮行为和对组织活力的影响[J]. 药物分析杂志,2019,39(3):377-385. [45] 郭正昌,周波.类器官的研究现状及其作为临床前模型的应用[J].安徽医科大学学报,2022,57(3):500-503. [46] BAERT Y, DE KOCK J, ALVES-LOPES JP, et al. Primary human testicular cells self-organize into organoids with testicular properties. Stem Cell Rep. 2017; 8(1):30-38. [47] TURCO MY, GARDNER L, HUGHES J, et al. Long-term,hormone-re-sponsive organoid cultures of human endometrium in a chemically defined medium. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19(5):568-577. [48] DE OLIVEIRA LF, MENDES FILHO D, MARQUES BL, et al. Organoids as a novel tool in modelling infectious diseases. Semin Cell Dev. Biol. 2023;144:87-96. [49] BLUTT SE, ESTES MK. Organoid models for infectious disease. Annu Rev Med. 2022;73:167-182. [50] YIN Y, BIJVELDS M, DANG W, et al. Modeling rotavirus infection and antiviral therapy using primary intestinal organoids. Antiviral Res. 2015;123:120-131. [51] JANOWSKI AB, BAUER IK, HOLTZ LR, et al. Propagation of astrovirus VA1, a neurotropic human astrovirus, in cell culture. J Virol. 2017;91(19):e00740-17. [52] ETTAYEBI K, CRAWFORD SE, MURAKAMI K, et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell–derived human enteroids. Science. 2016;353(6306): 1387-1393. [53] VU DL, BOSCH A, PINTÓ RM, et al. Human astrovirus MLB replication in vitro: persistence in extraintestinal cell lines. J Virol. 2019;93(13):10-1128. [54] KOLAWOLE AO, MIRABELLI C, HILL DR, et al. Astrovirus replication in human intestinal enteroids reveals multi-cellular tropism and an intricate host innate immune landscape. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15(10):e1008057. [55] ZHAO B, NI C, GAO R, et al. Recapitulation of SARS-CoV-2 infection and cholangiocyte damage with human liver ductal organoids. Protein Cell. 2020;11(10):771-775. [56] LESAVAGE BL, SUHAR RA, BROGUIERE N, et al. Next-generation cancer organoids. Nat Mater, 2022;21(2):143-159. [57] DROST J, CLEVERS H. Organoids in cancer research. Nat Rev Cancer. 2018; 18(7):407-418. [58] ABOULKHEYR ES H, MONTAZERI L, AREF AR, et al. Personalized cancer medicine: an organoid approach. Trends Biotechnol. 2018;36(4):358-371. [59] BERTHIAUME F, MAGUIRE TJ, YARMUSH ML. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: history, progress, and challenges. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2011;2:403-430. [60] SUGIMOTO S, KOBAYASHI E, FUJII M, et al. An organoid-based organ repurposing approach to treat short bowel syndrome. Nature. 2021; 592(7852):99-104. [61] SAMPAZIOTIS F, MURARO D, TYSOE OC, et al. Cholangiocyte organoids can repair bile ducts after transplantation in the human liver. Science. 2021; 371(6531):839-846. [62] CUBO N, GARCIA M, DEL CANIZO JF, et al. 3D bioprinting of functional human skin: production and in vivo analysis. Biofabrication. 2016;9(1):015006. [63] VIJAYAVENKATARAMAN S, LU WF, FUH JY. 3D bioprinting of skin: a state-of-the-art review on modelling, materials, and processes. Biofabrication. 2016;8(3):032001. [64] JANG J, PARK HJ, KIM SW, et al. 3D printed complex tissue construct using stem cell-laden decellularized extracellular matrix bioinks for cardiac repair. Biomaterials. 2017;112:264-274. [65] ZHANG YS, ARNERI A, BERSINI S, et al. Bioprinting 3D microfibrous scaffolds for engineering endothelialized myocardium and heart-on-a-chip. Biomaterials. 2016;110:45-59. [66] CHOI WH, BAE DH, YOO J. Current status and prospects of organoid-based regenerative medicine. BMB Rep. 2023;56(1):10-14. [67] LI J, HE L, ZHOU C, et al. 3D printing for regenerative medicine: From bench to bedside. MRS Bull. 2015;40(2):145-154. [68] TARAFDER S, BALLA VK, DAVIES NM, et al. Microwave‐sintered 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regener Med. 2013;7(8):631-641. [69] TARAFDER S, DAVIES NM, BANDYOPADHYAY A, et al. 3D printed tricalcium phosphate bone tissue engineering scaffolds: effect of SrO and MgO doping on in vivo osteogenesis in a rat distal femoral defect model. Biomater Sci. 2013;1(12):1250-1259. [70] LEE CH, MARION NW, HOLLISTER S, et al. Tissue Formation and Vascularization in Anatomically Shaped Human Joint Condyle Ectopically in Vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(12):3923-3930. [71] LEE CH, COOK JL, MENDELSON A, et al. Regeneration of the articular surface of the rabbit synovial joint by cell homing: a proof of concept study. Lancet. 2010;376(9739):440-448. [72] 郭贝贝,胡慧丽.类器官在发育与再生中的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(6):1111-1119. [73] 李潇萌,管若羽,高建军,等.类器官在再生医学中的应用[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2021,43(6):1120-1131. [74] BOUFFI C, WIKENHEISER-BROKAMP KA, CHATURVEDI P, et al. In vivo development of immune tissue in human intestinal organoids transplanted into humanized mice. Nat Biotechnol. 2023;41(6):824-831. [75] VOTANOPOULOS KI, FORSYTHE S, SIVAKUMAR H, et al. Model of Patient-Specific Immune-Enhanced Organoids for Immunotherapy Screening: Feasibility Study. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020;27:1956-1967. [76] FDA.Drug development tool (DDT)qualification programs. 2023-04-06[2023-07-03]. https: //www.Fda.gov/drugs/development-approval-process-drugs/drug-development-tool-ddt-qualification-programs. [77] FDA. FDA’s predictive toxicology roadmap. 2017-12-30 [2023-07-03]. https://www. Fda. Gov/science-research/About-science-research-fda/fdas-predictive-toxicology-Roadmap. [78] 傅丽霞,张秀莉,庞晓丛,等.类器官和器官芯片在新药评价中的应用及国内外监管现状分析[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2023,39(18):2724-2730. [79] UNION E. Directive 2010/63 /EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes Text with EEA relevance. 2019-06-26[2023-07-03]. https://eur-lex.Europa.eu/eli/dir/2010/63/oj. [80] EMA. Reflection paper on the qualification of non - genotoxic impurities. 2018 -11- 15[2023 -07-03].https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/reflection-paper-qualification-non-genotoxic-impurities_en.pdf. [81] EMA. Consolidated 3 - year work plan for the Non - clinical domainincluding the priorities for 2023.2023-01-26[2023-07-03]. https://www.ema. europa.eu/en/documents/otherlconsolidated-3-year-work-plan-non-clinical-do-main-including-priorities-2023_en. pdf. [82] 罗会宇,马永慧.人源类器官的应用前景,伦理风险与治理建议[J].科技导报,2022,40(8): 6-13. [83] 高建超.关于我国细胞治疗产业发展现况和监管思路的浅见(上)[J].中国医药生物技术,2019,14(3):193-198. [84] 高建超.关于我国细胞治疗产业发展现况和监管思路的浅见(下)[J]. 中国医药生物技术,2022,14(4):289-293. [85] 刘家伟,冯佳佳,孔维华,等.我国生物医药领域中生物医学新技术发展及管理现状的思考[J].医学新知,2023,33(2):136-142. [86] 郑颖,邓诗碧,陈方.干细胞与再生医学技术发展态势研究[J].中国生物工程杂志,2022,42(4):111-119. [87] 乐晶晶.类器官应用的伦理问题及治理对策研究[D].厦门:厦门大学, 2020. [88] 杨练,冯海洋,许苑晶.3D打印医疗应用及中心建设现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(13):2110-2115. |
| [1] | Yu Shuai, Liu Jiawei, Zhu Bin, Pan Tan, Li Xinglong, Sun Guangfeng, Yu Haiyang, Ding Ya, Wang Hongliang. Hot issues and application prospects of small molecule drugs in treatment of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [2] | Yu Jingbang, Wu Yayun. Regulatory effect of non-coding RNA in pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1659-1666. |
| [3] | Wang Qiuyue, Jin Pan, Pu Rui . Exercise intervention and the role of pyroptosis in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [4] | Yuan Weibo, Liu Chan, Yu Limei. Potential application of liver organoids in liver disease models and transplantation therapy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(8): 1684-1692. |
| [5] | Hu Taotao, Liu Bing, Chen Cheng, Yin Zongyin, Kan Daohong, Ni Jie, Ye Lingxiao, Zheng Xiangbing, Yan Min, Zou Yong. Human amniotic mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing neuregulin-1 promote skin wound healing in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1343-1349. |
| [6] | Jin Kai, Tang Ting, Li Meile, Xie Yuan. Effects of conditioned medium and exosomes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells on proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1350-1355. |
| [7] | Li Dijun, Jiu Jingwei, Liu Haifeng, Yan Lei, Li Songyan, Wang Bin. Three-dimensional gelatin microspheres loaded human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for chronic tendinopathy repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1356-1362. |
| [8] | Lou Guo, Zhang Min, Fu Changxi. Exercise preconditioning for eight weeks enhances therapeutic effect of adipose-derived stem cells in rats with myocardial infarction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1363-1370. |
| [9] | Liu Qi, Li Linzhen, Li Yusheng, Jiao Hongzhuo, Yang Cheng, Zhang Juntao. Icariin-containing serum promotes chondrocyte proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of stem cells in the co-culture system of three kinds of cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1371-1379. |
| [10] | Huang Ting, Zheng Xiaohan, Zhong Yuanji, Wei Yanzhao, Wei Xufang, Cao Xudong, Feng Xiaoli, Zhao Zhenqiang. Effects of macrophage migration inhibitory factor on survival, proliferation, and differentiation of human embryonic stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1380-1387. |
| [11] | Aikepaer · Aierken, Chen Xiaotao, Wufanbieke · Baheti. Osteogenesis-induced exosomes derived from human periodontal ligament stem cells promote osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells in an inflammatory microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1388-1394. |
| [12] | Zhang Zhenyu, Liang Qiujian, Yang Jun, Wei Xiangyu, Jiang Jie, Huang Linke, Tan Zhen. Target of neohesperidin in treatment of osteoporosis and its effect on osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [13] | Xie Liugang, Cui Shuke, Guo Nannan, Li Aoyu, Zhang Jingrui. Research hotspots and frontiers of stem cells for Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1475-1485. |
| [14] | Peng Hongcheng, Peng Guoxuan, Lei Anyi, Lin Yuan, Sun Hong, Ning Xu, Shang Xianwen, Deng Jin, Huang Mingzhi . Role and mechanism of platelet-derived growth factor BB in repair of growth plate injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1497-1503. |
| [15] | Li Jialin, Zhang Yaodong, Lou Yanru, Yu Yang, Yang Rui. Molecular mechanisms underlying role of mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(7): 1512-1522. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||