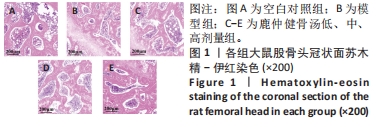
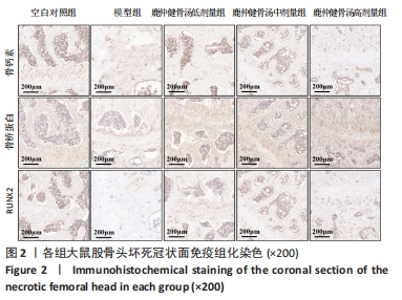
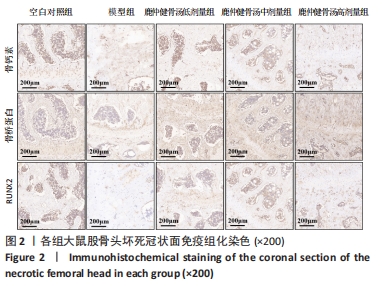
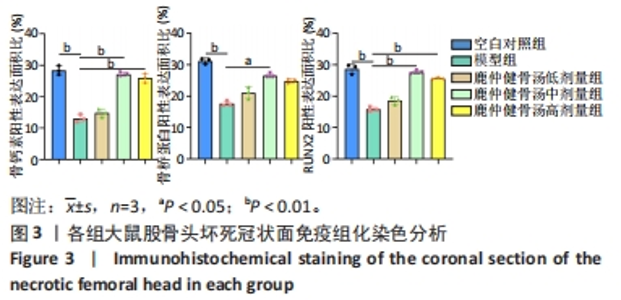
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (35): 5598-5605.doi: 10.12307/2024.550
Previous Articles Next Articles
Luzhongjiangu decoction for the treatment of femoral head necrosis in rats: changes in intestinal flora and serum hormones
Jing Tianyuan1, Wang Ping2, Wang Yi2, Hu Yanan3, Liu Shanxin2, Sun Guodong4, Du Haitao2
- 1Shandong Xiandai University, Jinan 250104, Shandong Province, China; 2Shandong Academy of Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China; 3Jinan Biopharmaceutical Industry Research Institute, Jinan 250000, Shandong Province, China; 4The Third Affiliated Hospital of Shandong first Medical University, Jinan 250031, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2023-08-23Accepted:2023-10-30Online:2024-12-18Published:2024-03-15 -
Contact:Wang Ping, MD, Researcher, Shandong Academy of Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China Du Haitao, Master, Research assistant, Shandong Academy of Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250014, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Jing Tianyuan, Master, Shandong Xiandai University, Jinan 250104, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Shandong Province Key Research & Development Program (Science and Technology Demonstration Project), No. 2021SFGC1205 (to WEP); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, No. ZR2020MH386 (to WP); Special Fund for Centralized Guidance of Local Scientific and Technological Development, No. YDZX2021117 (to WP); "20 New Colleges and Universities" of Jinan City, No. 202228121 (to WP); Centralized Guidance of Local Scientific and Technological Development Fund of Shandong Province, No. YDZX20203700002055 (to WP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jing Tianyuan, Wang Ping, Wang Yi, Hu Yanan, Liu Shanxin, Sun Guodong, Du Haitao. Luzhongjiangu decoction for the treatment of femoral head necrosis in rats: changes in intestinal flora and serum hormones[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5598-5605.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
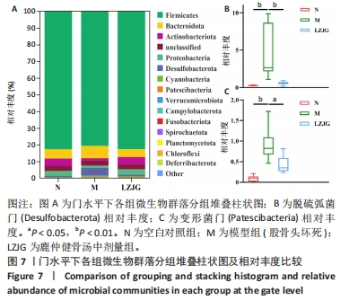
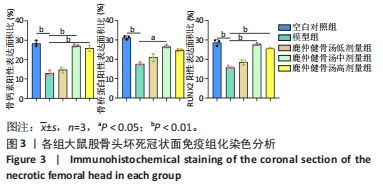
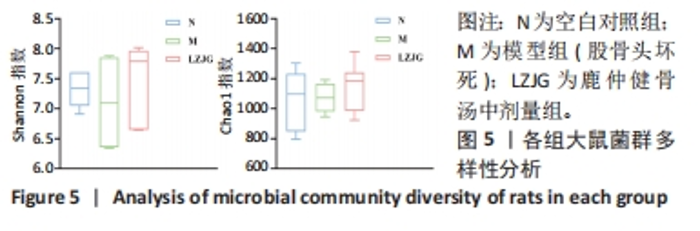
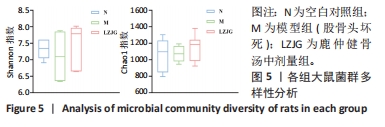
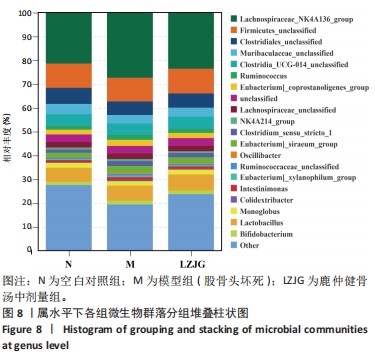
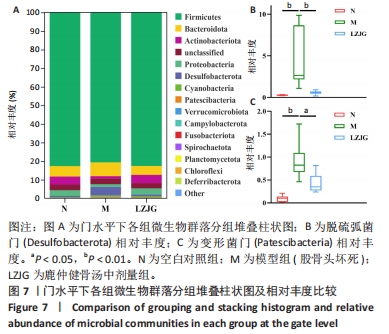
2.5.3 门水平菌群组成分析 如图7所示,各组大鼠的肠道菌群相对丰度发生了改变,在门水平上,各组的优势菌门均为厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidota)、放线菌门(Actinobacteriota)、变形菌门(Proteobacteria)等,其中厚壁菌门丰度最高。如图8所示,与空白对照组相比,模型组大鼠中杆菌门(Patescibacteria)丰度显著上调(P < 0.05),脱硫弧菌门(Desulfobacterota)丰度显著下调(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,鹿仲健骨汤中剂量组髌骨细菌门(Patescibacteria)丰度显著降低(P < 0.05),脱硫弧菌门(Desulfobacterota)丰度显著升高(P < 0.05)。说明ONFH模型大鼠肠道菌群在门水平上出现紊乱,给予鹿仲健骨汤治疗后在一定程度上得到改善。"
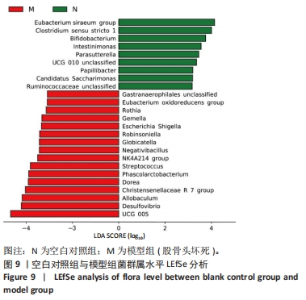
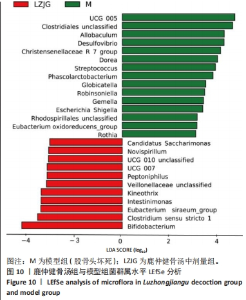
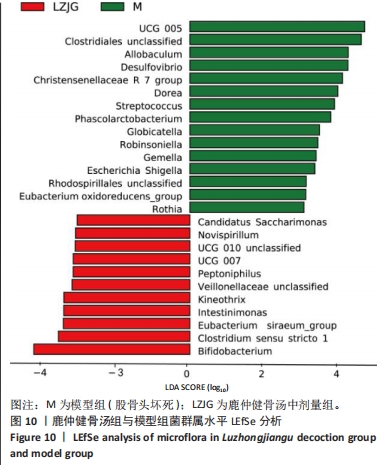
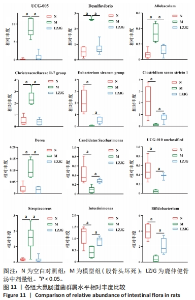
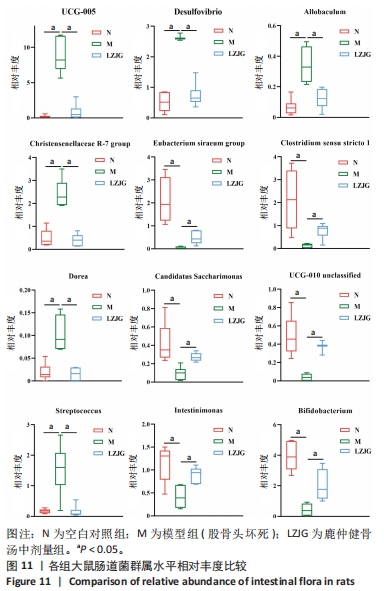
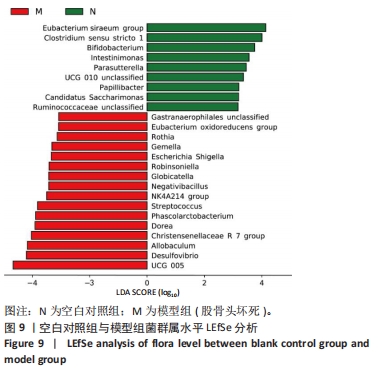
2.5.4 属水平菌群组成分析 由图8可以看出,在属水平上,各组的优势菌门均为毛螺菌科NK4A136属(Lachnospiraceae NK4A136 group)、未分类的厚壁菌(Firmicutes unclassified)、未分类的梭菌属(Clostridiales_unclassified)、未分类的普拉梭菌(Muribaculaceae unclassified)、未分类的梭菌UCG-014菌(Clostridia UCG-014 unclassified)、瘤胃球菌(Ruminococcus)、产粪甾醇真杆菌(Eubacterium coprostanoligenes group unclassified)。 为进一步探究鹿仲健骨汤对ONFH大鼠肠道菌群的影响,对属水平菌群进行细致分析。通过LEfSe分析发现,在属水平上,希拉真杆菌群(Eubacterium siraeum group)、双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)、肠单胞菌属(Intestinimonas)、UCG-005、罗斯氏菌(Rothia)等具有显著差异。与空白对照组相比,模型组UCG-005菌群的LDA分值最大,说明其对空白对照组和模型组之间的差异影响更大,可能是ONFH的标志菌属,而与模型组相比,鹿仲健骨汤组双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)的LDA分值最大,可能是鹿仲健骨汤治疗ONFH的主要菌群,见图9,10。"
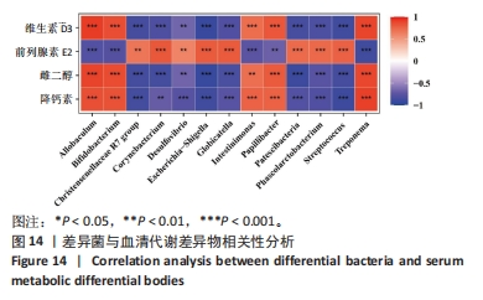
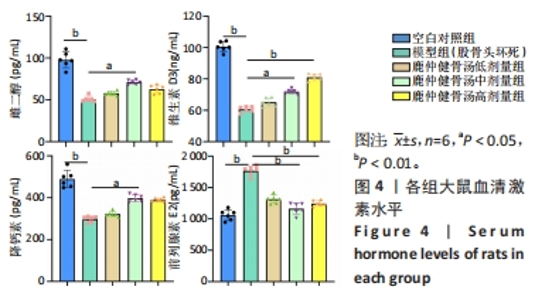
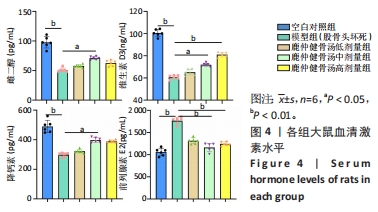
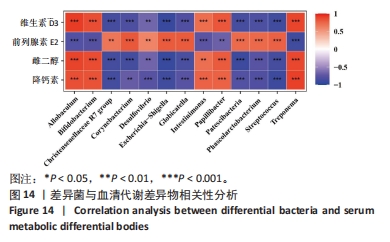
2.7 血清激素水平与差异菌群的相关性分析 为进一步探讨肠道菌群与代谢差异物的相关性,采用Spearman相关系数,将雌二醇、维生素D3、前列腺素E2及降钙素与LDA分析的14个差异菌进行相关性分析,见图14。鹿仲健骨汤中剂量组的差异菌双歧杆菌属(Bifidobacterium)、肠单胞球菌(Intestinimonas)与维生素D3、雌二醇、降钙素呈正相关,与前列腺素E2呈负相关。模型组的差异菌大肠杆菌-志贺氏菌(Escherichia-Shigella)、脱硫孤菌属(Desulfovibrio)、格鲁比卡氏菌属(Globicatella)、链球菌属(Streptococcus)与前列腺素E2呈正相关,与维生素D3、雌二醇、降钙素呈负相关。"
| [1] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today?: A 5-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(12):1084-1099. [2] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110. [3] CHANG C, GREENSPAN A, GERSHWIN ME. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical manifestations of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102460. [4] CUI Q, JO WL, KOO KH, et al. ARCO Consensus on the Pathogenesis of Non-traumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(10):e65. [5] 方祥,周正新,朱磊,等.骨痹通消颗粒干预激素性股骨头坏死小鼠模型的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(16):2599-2604. [6] 林天烨,吴智明,张文胜,等.复方生脉成骨胶囊修复激素性股骨头坏死的作用机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):200-207. [7] 周正新,朱磊,李文华,等.中药骨痹通消颗粒通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路治疗激素性股骨头坏死的实验研究[J].中华中医药学刊,2023,41(1):21-24. [8] KIEFER-HECKER B, BAUER A, DOBENECKER B. Effects of low phosphorus intake on serum calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase activity and parathyroid hormone in growing dogs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018;102(6):1749-1758. [9] KRISHNAN A, MUTHUSAMI S. Hormonal alterations in PCOS and its influence on bone metabolism. J Endocrinol. 2017;232(2):R99-R113. [10] MATIKAINEN N, PEKKARINEN T, RYHÄNEN EM, et al. Physiology of Calcium Homeostasis: An Overview. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2021;50(4):575-590. [11] 赵雨芳,高海红,徐建新,等.促性腺激素释放激素类似物联合生长激素对性早熟女童性激素和骨代谢的影响[J].中国妇幼保健,2023,38(8):1407-1410. [12] LU L, TANG M, LI J, et al. Gut Microbiota and Serum Metabolic Signatures of High-Fat-Induced Bone Loss in Mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021;11:788576. [13] 侯伟.基于“治痿独取阳明”理论探究激素性股骨头坏死患者肠道菌群分布规律的临床研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2022. [14] LI JY, YU M, PAL S, et al. Parathyroid hormone-dependent bone formation requires butyrate production by intestinal microbiota. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(4):1767-1781. [15] 胡亚楠,王平,杜海涛,等.血清蛋白质组学技术发现鹿角胶治疗维甲酸致股骨头坏死模型大鼠的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(14):2243-2251. [16] CHEN S, SUN K, XU B, et al. Akt-mediated mitochondrial metabolism regulates proplatelet formation and platelet shedding post vasopressin exposure. J Thromb Haemost. 2023;21(2):344-358. [17] XIAO W, SU J, GAO X, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis participates in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion by disrupting the metabolism of short-chain fatty acids. Microbiome. 2022;10(1):62. [18] SUN M, CHI G, LI P, et al. Effects of Matrix Stiffness on the Morphology, Adhesion, Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(3):257-268. [19] KOMORI T. Functions of Osteocalcin in Bone, Pancreas, Testis, and Muscle. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7513. [20] ROTEM I, KONFINO T, CALLER T, et al. Osteopontin promotes infarct repair. Basic Res Cardiol. 2022;117(1):51. [21] CHENG H, HUANG H, GUO Z, et al. Role of prostaglandin E2 in tissue repair and regeneration. Theranostics. 2021;11(18):8836-8854. [22] RAISZ LG, ALANDER CB, FALL PM, et al. Effects of prostaglandin F2 alpha on bone formation and resorption in cultured neonatal mouse calvariae: role of prostaglandin E2 production. Endocrinology. 1990;126(2):1076-1079. [23] HAN XG, WANG DW, BI ZG, et al. Regulatory effect of estrogen receptor-α-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway on osteoblast proliferation. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2016;30(2):381-387. [24] 孙晓琪.雌二醇通过G蛋白偶联雌激素受体30 (GPR30)/ERK1/2信号通路调节MC3T3-E1细胞线粒体自噬的分子机制研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2018. [25] 李伟娟,谢保平,石丽颖,等.从ERα/RANK通路探讨淫羊藿苷抑制破骨细胞分化作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(7):121-126. [26] 张萌萌.雌激素与雌激素受体骨代谢调节作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019, 25(5):704-708. [27] 廖二元,曹旭.湘雅代谢性骨病学[M].北京:科学出版社,2013. [28] KARPONIS A, RIZOU S, PALLIS D, et al. Analgesic effect of nasal salmon calcitonin during the early post-fracture period of the distal radius fracture. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2015;15(2):186-189. [29] 张萌萌.生命、骨骼、维生素D3[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(11):1496-1500. [30] 刘昌孝.肠道菌群与健康、疾病和药物作用的影响[J].中国抗生素杂志, 2018,43(1):1-14. [31] CHEVALIER C, KIESER S, ÇOLAKOĞLU M, et al. Warmth Prevents Bone Loss Through the Gut Microbiota. Cell Metab. 2020;32(4):575-590.e7. [32] TYAGI AM, YU M, DARBY TM, et al. The Microbial Metabolite Butyrate Stimulates Bone Formation via T Regulatory Cell-Mediated Regulation of WNT10B Expression. Immunity. 2018;49(6):1116-1131.e7. [33] AUCHTUNG TA, STEWART CJ, SMITH DP, et al. Temporal changes in gastrointestinal fungi and the risk of autoimmunity during early childhood: the TEDDY study. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3151. [34] LAURSEN MF. Gut Microbiota Development: Influence of Diet from Infancy to Toddlerhood. Ann Nutr Metab. 2021:1-14. [35] STOTZER PO, JOHANSSON C, MELLSTRÖM D, et al. Bone mineral density in patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Hepatogastroenterology. 2003;50(53):1415-1418. [36] STEWART CJ, AJAMI NJ, O’BRIEN JL, et al. Temporal development of the gut microbiome in early childhood from the TEDDY study. Nature. 2018;562(7728): 583-588. [37] BUI TP, SHETTY SA, LAGKOUVARDOS I, et al. Comparative genomics and physiology of the butyrate-producing bacterium Intestinimonas butyriciproducens. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2016;8(6):1024-1037. [38] BACH KNUDSEN KE, LÆRKE HN, HEDEMANN MS, et al. Impact of Diet-Modulated Butyrate Production on Intestinal Barrier Function and Inflammation. Nutrients. 2018;10(10):1499. [39] SALVI PS, COWLES RA. Butyrate and the Intestinal Epithelium: Modulation of Proliferation and Inflammation in Homeostasis and Disease. Cells. 2021;10(7):1775. [40] SUN Q, JI YC, WANG ZL, et al. Sodium Butyrate Alleviates Intestinal Inflammation in Mice with Necrotizing Enterocolitis. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:6259381. [41] KAPRAL M, WĘGLARZ L, PARFINIEWICZ B, et al. Quantitative evaluation of transcriptional activation of NF-κB p65 and p50 subunits and IκBα encoding genes in colon cancer cells by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans endotoxin. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2010;55(6):657-661. [42] LODOWSKA J, WOLNY D, JAWORSKA-KIK M, et al. The chemical composition of endotoxin isolated from intestinal strain of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. Scientific World Journal. 2012;2012:647352. [43] RICE TA, BIELECKA AA, NGUYEN MT, et al. Interspecies commensal interactions have nonlinear impacts on host immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30(7): 988-1002.e6. [44] HE X, BAI Y, ZHOU H, et al. Akkermansia muciniphila Alters Gut Microbiota and Immune System to Improve Cardiovascular Diseases in Murine Model. Front Microbiol. 2022;13:906920. [45] PLOTTEL CS, BLASER MJ. Microbiome and malignancy. Cell Host Microbe. 2011; 10(4):324-335. [46] NAKAMURA T, IMAI Y, MATSUMOTO T, et al. Estrogen prevents bone loss via estrogen receptor alpha and induction of Fas ligand in osteoclasts. Cell. 2007; 130(5):811-823. [47] JONES ML, MARTONI CJ, PRAKASH S. Oral supplementation with probiotic L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 increases mean circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013; 98(7):2944-2951. [48] RODRIGUES FC, CASTRO AS, RODRIGUES VC, et al. Yacon flour and Bifidobacterium longum modulate bone health in rats. J Med Food. 2012;15(7):664-670. [49] WHISNER CM, MARTIN BR, NAKATSU CH, et al. Soluble Corn Fiber Increases Calcium Absorption Associated with Shifts in the Gut Microbiome: A Randomized Dose-Response Trial in Free-Living Pubertal Females. J Nutr. 2016;146(7):1298-1306. |
| [1] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [2] | Zhao Rushun, Hao Yangquan, Xu Peng, Zheng Xin, Jiang Yonghong, Zhang Yuting, Wang Mengfei, Lu Chao. Effect of different locations of necrotic focus on the natural course of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 917-921. |
| [3] | Linghu Xitao, Gui Jiaqi, Liang Zhuozhi, Wa Qingde, Huang Shuai. Bioinformatics analysis of m6A-associated genes in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5811-5816. |
| [4] | Wu Zixuan, Sun Shiyi, Zhang Cheng, Zhang Guangyi, Yang Tongjie, He Haijun. Relationship between blood indicators and course of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head in different stages: multiple logistic regression analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(36): 5865-5871. |
| [5] | Xie Yanli, Wei Siang, Zhang Guodong. Effects of treadmill exercise on metabolism and chronic neuroinflammation in type 1 diabetes mice of different sexes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(35): 5577-5583. |
| [6] | Zhao Rushun, Hao Yangquan, Xu Hanbo, Yang Zhi, Xu Peng, Zheng Xin, Zhang Kun, Lu Chao. Natural collapse course of ARCO II stage osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on China-Japan Friendship Hospital classification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4871-4875. |
| [7] | Yu Peng, Meng Dongfang, Li Huiying, Zhang Xiangbei. Bioinformatics identification of CA9 as a signature gene for cartilage-associated ferroptosis in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4293-4299. |
| [8] | Ma Liangchen, Tian Fubao, Xu Yujuan, Tian Xinbao, Tao Ying, Chen Mengying, Lian Jiawei, Lin Ruizhu, Zhu Ning. Mechanisms underlying internal heat-type acupuncture in the treatment of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rabbits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4353-4359. |
| [9] | Gong Gaojin, Huang Haixun. Oleanolic acid alleviates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats by regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4373-4377. |
| [10] | Yang Qihang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Leng Siyi, Song Yongjing, Liu Hui, Du Guangyou. Intestinal flora and osteoporosis and exercise intervention [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(26): 4250-4256. |
| [11] | Ma Wanli, Yang Hongsheng, Qu Bo, Zhang Zhengdong, Gong Kai, Lin Yanshui. Mechanisms by which baicalein protects against steriod-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3661-3668. |
| [12] | Han Jie, Peng Qinglin, Xu Zhiwei, Wu Yukun, Ren Guowu, Xie Xiaozhong, Jin Wanqing, Yang Ling. Active ingredients of Panax notoginseng regulate signaling pathways related to steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(23): 3751-3758. |
| [13] | Li Xun, Zhang Weichao, Li Yingjie, Liu Rong, Tian Xuewen, Zhang Pengyi, Wang Xiaoqiang. Effect of moderate-intensity exercise on the level of autophagy in bone tissue of ovariectomized rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3130-3136. |
| [14] | Zhang Jiahao, Liu Yuhao, Zhou Chi, Mo Liang, Fang Hanjun, Chen Zhenqiu. The pathological progression of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head caused by oxidative stress-induced osteoblast ferroptosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3202-3208. |
| [15] | Yang Qihang, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Leng Siyi, Song Yongjing, Liu Hui, Du Guangyou. Role and mechanism of intestinal flora metabolites in obesity regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(2): 308-314. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||