Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (27): 4293-4299.doi: 10.12307/2024.520
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatics identification of CA9 as a signature gene for cartilage-associated ferroptosis in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Yu Peng1, Meng Dongfang2, Li Huiying2, Zhang Xiangbei1
- 1Osteopathy School of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2023-09-18Accepted:2023-10-28Online:2024-09-28Published:2024-01-26 -
Contact:Li Huiying, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
About author:Yu Peng, MD candidate, Osteopathy School of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:Henan Province Chinese Medicine Scientific Research Special Projects, Nos. 2021JDZY009 (to LHY), 2023ZY2029 (to LHY), and 2022JDZX123 (to MDF); 2022 Graduate Student Scientific Research and Innovation Program of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2022KYCX084 (to YP)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Peng, Meng Dongfang, Li Huiying, Zhang Xiangbei. Bioinformatics identification of CA9 as a signature gene for cartilage-associated ferroptosis in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(27): 4293-4299.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
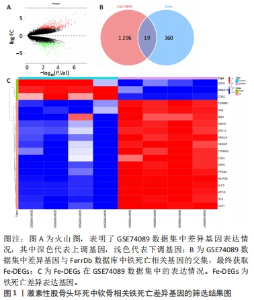
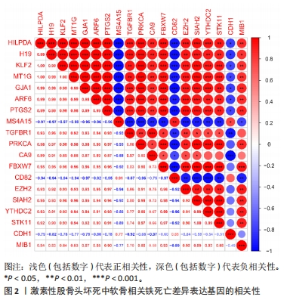
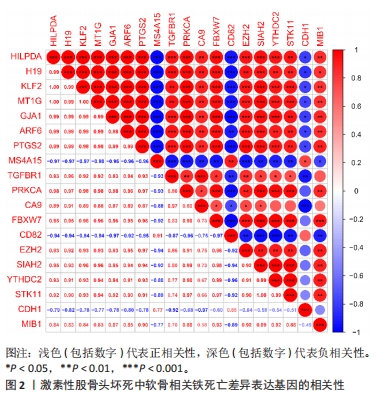
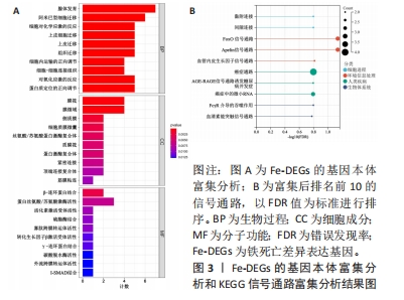
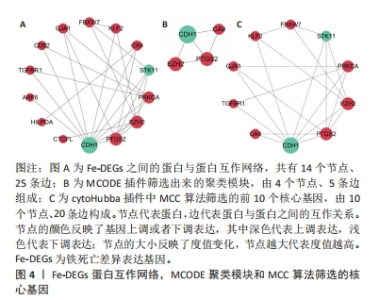
2.1 生物信息学分析结果 2.1.1 筛选铁死亡差异表达基因 从GSE74089数据集中共筛选出1 315个差异表达基因,其中808个上调表达基因,507个为下调表达基因,见图1A。从FerrDb数据库共获取379个已验证的铁死亡相关基因。二者取交集后,最终获得19个在GSE74089数据集差异表达的铁死亡基因,其中3个下调表达,16个上调表达,见图1B,C。随后对Fe-DEGs进行相关性分析,发现Fe-DEGs之间以正相关性为主,负相关性为辅,见图2。GO富集分析发现,Fe-DEGs在生物过程中主要参与细胞的迁移和细胞对氧化应激与化学应激的反应,见图3A;在细胞组分方面主要在激酶复合物、氨基酸复合体和细胞质膜方面富集;在分子功能中主要以激酶活性、受体活性和蛋白结合为主。KEGG富集分析发现,Fe-DEGs主要在FoxO信号通路、血管内皮生长因子信号通路和FcγR介导的吞噬作用中富集,涉及细胞代谢、增殖,血管新生、血管通透性及免疫炎症反应等,见图3B。"
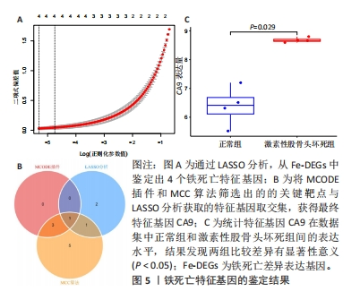
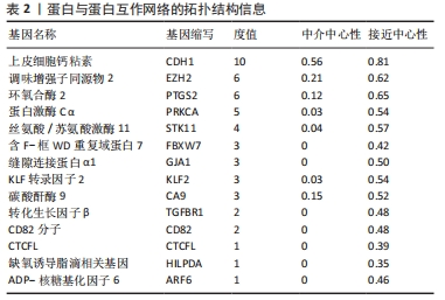
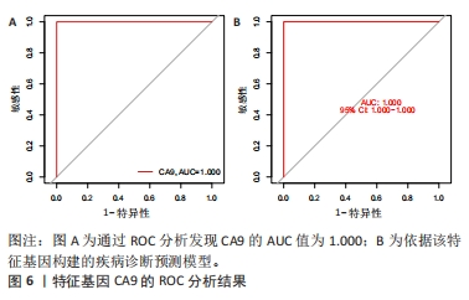
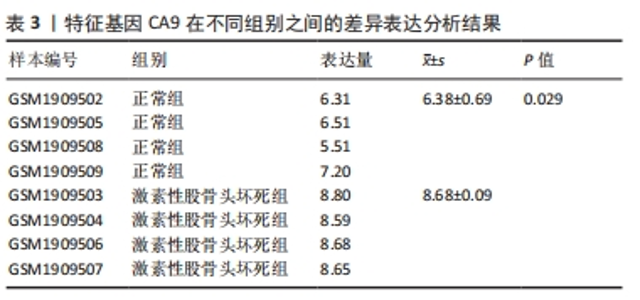
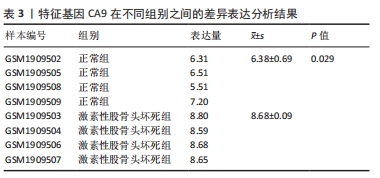
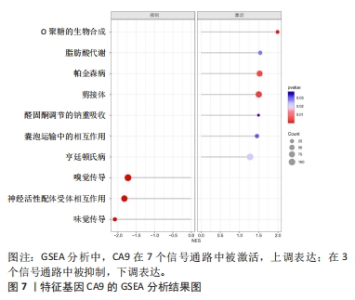
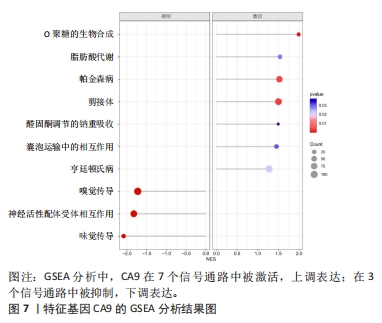
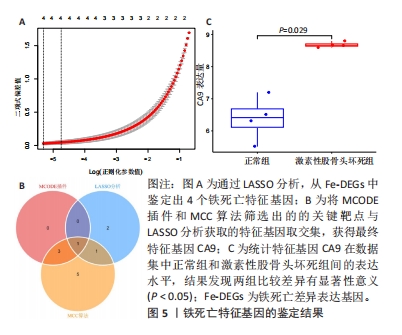
2.1.3 筛选铁死亡特征基因 在LASSO分析中二项分布模型的偏差度(Binomial deviance)越小,则模型的拟合程度越好,通过glmnet函数分析,取二项分布模型的偏差度最小的4个基因为疾病特征基因,分别为HILPDA、H19、TGFBR1和CA9,见图5A。将蛋白互作网络中通过MCODE插件和cytoHubba插件中MCC算法各自筛选出的聚类模块基因和10个核心节点基因与LASSO分析获取的4个疾病特征基因取交集,通过Venn图进行展示,获得疾病特征基因CA9,见图5B。同时,统计了特征基因CA9在数据集中不同组别之间的表达量,并进行了统计学分析,与对照组相比,CA9的表达量在激素性股骨头坏死组明显增高(P < 0.05),见图5C和表3,随后对特征基因进行ROC曲线分析,其AUC值为1.000,见图6A,表明筛选特征基因的准确性与可靠性。此外,基于特征基因构建预测模型,AUC值为1.000,95%CI:1.000?1.000,见图6B。说明特征基因对激素性股骨头坏死中软骨铁死亡有较高的诊断价值,有望成为激素性股骨头坏死软骨铁死亡相关的潜在生物标志物。"
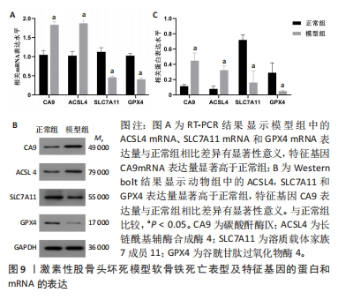
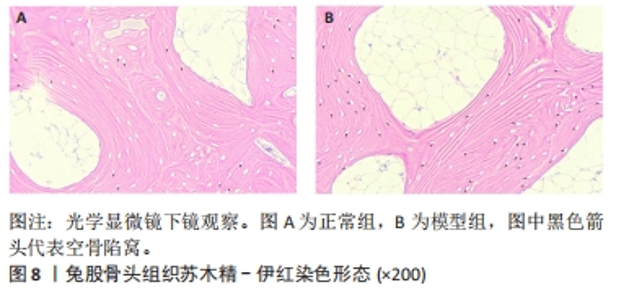
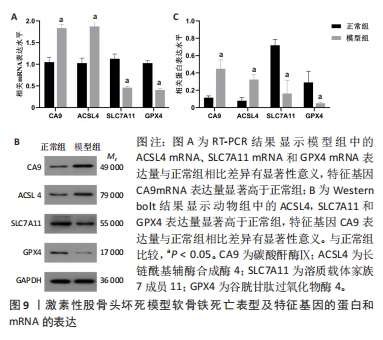
2.2.2 软骨中铁死亡表型和特征基因表达的验证结果 实验通过检测动物模型软骨中ACSL4,SLC7A11和GPX4的表达,验证激素性股骨头坏死软骨中存在由脂质过氧化诱导的铁死亡发生。随后检测CA9的表达量,验证筛选特征基因的准确性与可靠性。通过RT-PCR和Western blot实验结果表明,动物模型中的ACSL4蛋白与mRNA表达量显著高于正常组(P < 0.05),SLC7A11和GPX4蛋白与mRNA表达水平较正常组明显降低(P < 0.05),表明了软骨中存在由脂质过氧化诱导的铁死亡发生;CA9蛋白与mRNA表达水平与正常组相比升高(P < 0.05),表明实验筛选激素性股骨头坏死软骨中铁死亡特征基因的准确性和诊断价值,见图9。"
| [1] ZHAO D, ZHANG F, WANG B, et al. Guidelines for clinical diagnosis and treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head in adults (2019 version). J Orthop Translat. 2020;21:100-110. [2] MOTTA F, TIMILSINA S, GERSHWIN ME, et al. Steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Transl Autoimmun. 2022;5:100168. [3] CHANG C, GREENSPAN A, GERSHWIN ME. The pathogenesis, diagnosis and clinical manifestations of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. J Autoimmun. 2020;110:102460. [4] KANEKO K, CHEN H, KAUFMAN M, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(10):e526. [5] CUI Q, JO WL, KOO KH, et al. ARCO consensus on the pathogenesis of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(10):e65. [6] WANG QR, YANG ZY, ZHANG WL, et al. Abnormal hyperplasia of chondrocytes in a rat model of glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022; 26(18):6536-6549. [7] QIN X, JIN P, JIANG T, et al. A human chondrocyte-derived in vitro model of alcohol-induced and steroid-induced femoral head necrosis. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:539-547. [8] 赵程锦,周煜虎,王坤正.软骨ADAMTS-7基因上调与股骨头坏死发生之间的相关性研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(6):727-733. [9] 史珊,杨学东,方继良,等.股骨头坏死关节软骨损伤MR研究进展[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2023,21(6):172-173. [10] WANG P, WANG C, MENG H, et al. The role of structural deterioration and biomechanical changes of the necrotic lesion in collapse mechanism of osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(5):831-839. [11] SUN F, ZHOU JL, LIU ZL, et al. Dexamethasone induces ferroptosis via P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022;602:149-155. [12] LI W, LI W, ZHANG W, et al. Exogenous melatonin ameliorates steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by modulating ferroptosis through GDF15-mediated signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023;14(1):171. [13] 杜晨阳,李慧英,汪利合,等. “三补一活”方干预兔激素性股骨头坏死作用机制研究[J]时珍国医国药,2021,32(10):2369-2373. [14] 蒋玮,曹林忠,邬明峻,等.激素性股骨头坏死动物模型的建立及评价[J].中国实验动物学报,2019,27(6):799-804. [15] LOCKHART R, TAYLOR J, TIBSHIRANI RJ, et al. A SIGNIFICANCE TEST FOR THE LASSO. Ann Stat. 2014;42(2):413-468. [16] 郭雪峰,于睿,任艳玲.基于“成骨-成血管耦联”理论探讨中医药防治激素性股骨头坏死的科学内涵[J/OL].中华中医药学刊:1-9. [17] 孙懿,赵海燕,成杰,等.激素性股骨头坏死发生机制的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2023,31(1):58-62. [18] MA JX, HE WW, ZHAO J, et al. Bone microarchitecture and biomechanics of the necrotic femoral head. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13345. [19] ŞAHIN N, ÖZDEMIR ÇIÇEK S, PAÇ KISAARSLAN A, et al. The effect of intra-articular steroid injection on the cartilage and tendon thicknesses in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2023. doi: 10.1093/mr/road093. [20] LEMOS SE. Periarticular and intra-articular injections may do the right thing for patients’ pain but may be the wrong thing for their articular cartilage: be careful. Arthroscopy. 2022;38(6):1996-1998. [21] VON MäSSENHAUSEN A, ZAMORA GONZALEZ N, MAREMONTI F, et al. Dexamethasone sensitizes to ferroptosis by glucocorticoid receptor-induced dipeptidase-1 expression and glutathione depletion. Sci Adv. 2022; 8(5):eabl8920. [22] 胡康一,曹林忠,万超超,等.NLRP3炎性小体在激素性股骨头坏死骨代谢及其稳态中的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(5):701-706. [23] LO ACY, YANG M. Lycium barbarum polysaccharides and ferroptosis: jumping into the era of novel regulated cell death. Neural Regen Res. 2022; 17(7):1473-1474. [24] STOCKWELL BR. Ferroptosis turns 10: emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications. Cell. 2022;185(14):2401-2421. [25] JIANG X, STOCKWELL BR, CONRAD M. Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(4):266-282. [26] LIU T, WANG P, YIN H, et al. Rapamycin reverses ferroptosis by increasing autophagy in MPTP/MPP+-induced models of Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(11):2514-2519. [27] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125. [28] KUANG F, LIU J, TANG D, et al. Oxidative damage and antioxidant defense in ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:586578. [29] CHEN Y, FANG ZM, YI X, et al. The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(3):205. [30] ROCHETTE L, DOGON G, RIGAL E, et al. Lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism: two corner stones in the homeostasis control of ferroptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):449. [31] AKASAKI Y, ALVAREZ-GARCIA O, SAITO M, et al. FoxO transcription factors support oxidative stress resistance in human chondrocytes. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(12):3349-3358. [32] HALLETT SA, ONO W, ONO N. The hypertrophic chondrocyte: to be or not to be. Histol Histopathol. 2021;36(10):1021-1036. [33] CHEN L, NI Z, HUANG J, et al. Long term usage of dexamethasone accelerating accelerates the initiation of osteoarthritis via enhancing chondrocyte apoptosis and the extracellular matrix calcification and apoptosis of chondrocytes. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(15):4140-4153. [34] ALDERA AP, GOVENDER D. Carbonic anhydrase IX: a regulator of pH and participant in carcinogenesis. J Clin Pathol. 2021. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath- 2020-207073. [35] MOOKERJEE SA, GONCALVES RLS, GERENCSER AA, et al. The contributions of respiration and glycolysis to extracellular acid production. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1847(2):171-181. [36] JOHNSTON SN, MADHU V, SHAPIRO IM, et al. Conditional deletion of hif-2α in mouse nucleus pulposus reduces fibrosis and provides mild and transient protection from age-dependent structural changes in intervertebral disc. J Bone Miner Res. 2022;37(12):2512-2530. [37] QUEEN A, BHUTTO HN, YOUSUF M, et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX: a tumor acidification switch in heterogeneity and chemokine regulation. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022;86(Pt 3):899-913. [38] SILAGI ES, SCHIPANI E, SHAPIRO IM, et al. The role of HIF proteins in maintaining the metabolic health of the intervertebral disc. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(7):426-439. [39] AN Y, LI S, HUANG X, et al. The role of copper homeostasis in brain disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22):13850. [40] LI Y, WANG H, TU C, et al. Role of hypoxia and EGF on expression, activity, localization and phosphorylation of carbonic anhydrase IX in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1813(1):159-167. [41] GALARIS D, BARBOUTI A, PANTOPOULOS K. Iron homeostasis and oxidative stress: an intimate relationship. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019; 1866(12):118535. [42] 章家皓,刘予豪,周驰,等.氧化应激促进成骨细胞铁死亡介导激素性股骨头坏死的病理过程[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(20):3202-3208. [43] YAN Y, LU A, DOU Y, et al. Nanomedicines reprogram synovial macrophages by scavenging nitric oxide and silencing ca9 in progressive osteoarthritis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(11):e2207490. [44] STOCKWELL BR, FRIEDMANN ANGELI JP, BAYIR H, et al. Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 2017;171(2):273-285. [45] ZHANG H, ZHANG J, DONG H, et al. Emerging field: o-glcnacylation in ferroptosis. Front Mol Biosci. 2023;10:1203269. [46] LIU GB, LI R, LU Q, et al. Three-dimensional distribution of cystic lesions in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. J Orthop Translat. 2020;22:109-115. [47] 黄艺轩,陈浩,薛鹏,等.组织工程治疗股骨头坏死软骨下分离的适用技术[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(21):3385-3392. [48] 张聪敏,任凯迪,张绮雯,等.激素性股骨头坏死易感基因的研究进展[J].中国药学杂志,2022,57(2):85-89. [49] 田心保,林瑞珠,朱宁.激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的发病机制[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(10):915-919. [50] ZHANG Q, YANG J, YANG C, et al. Eucommia ulmoides oliver-tribulus terrestris l. drug pair regulates ferroptosis by mediating the neurovascular-related ligand-receptor interaction pathway- a potential drug pair for treatment hypertension and prevention ischemic stroke. Front Neurol. 2022;13:833922. [51] CHEN X, LI J, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 2021;17(9):2054-2081. [52] CHEN F, KANG R, LIU J, et al. The ACSL4 network regulates cell death and autophagy in diseases. Biology (Basel). 2023;12(6):864. [53] ZHANG HL, HU BX, LI ZL, et al. PKCβII phosphorylates ACSL4 to amplify lipid peroxidation to induce ferroptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2022;24(1):88-98. [54] URSINI F, MAIORINO M. Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis:the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;152:175-185. |
| [1] |
Song Jiating, Chen Jianmin, Wang Kewen, Huang Lanying, Xu Senming, Gui Yuchang, Xu Jianwen.
Metabolomics analysis of serum and urine in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury #br#
#br#
[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(在线): 1-6.
|
| [2] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [3] | Shen Jiangyong, He Xi, Tang Yuting, Wang Jianjun, Liu Jinyi, Chen Yuanyuan, Wang Xinyi, Liu Tong, Sun Haoyuan. RAS-selective lethal small molecule 3 inhibits the fibrosis of pathological scar fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1168-1173. |
| [4] | Huang Xiarong, Hu Lizhi, Sun Guanghua, Peng Xinke, Liao Ying, Liao Yuan, Liu Jing, Yin Linwei, Zhong Peirui, Peng Ting, Zhou Jun, Qu Mengjian. Effect of electroacupuncture on the expression of P53 and P21 in articular cartilage and subchondral bone of aged rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1174-1179. |
| [5] | Zhao Garida, Ren Yizhong, Han Changxu, Kong Lingyue, Jia Yanbo. Mechanism of Mongolian Medicine Erden-uril on osteoarthritis in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1193-1199. |
| [6] | Zhang Kefan, Shi Hui. Research status and application prospect of cytokine therapy for osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [7] | Yin Tong, Yang Jilei, Li Yourui, Liu Zhuoran, Jiang Ming. Application of core-shell structured nanofibers in oral tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 766-770. |
| [8] | Bu Xianzhong, Bu Baoxian, Xu Wei, Zhang Chi, Zhang Yisheng, Zhong Yuanming, Li Zhifei, Tang Fubo, Mai Wei, Zhou Jinyan. Analysis of serum differential proteomics in patients with acute cervical spondylotic radiculopathy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 535-541. |
| [9] | Zhang Yaru, Chen Yanjun, Zhang Xiaodong, Chen Shenghua, Huang Wenhua. Effect of ferroptosis mediated by glutathione peroxidase 4 in the occurrence and progression of synovitis in knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 550-555. |
| [10] | Fu Qiangchang, Zheng Liming, Jiang Lifeng. High tibial osteotomy promotes cartilage regeneration in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5243-5248. |
| [11] | Song Jiating, Chen Jianmin, Wang Kewen, Huang Lanying, Xu Senming, Gui Yuchang, Xu Jianwen. Metabolomics analysis of serum and urine in patients with traumatic spinal cord injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5085-5090. |
| [12] | Lu Xiaoling, Liu Bin, Xu Bin. Bioinformatics identification and validation of genes related to fatty acid metabolism in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5116-5121. |
| [13] | Chen Guanting, Zhang Linqi, Wang Xixi, Chen Xu. Autophagy, ferroptosis-related targets and renal function progression in patients with chronic kidney disease: bioinformatics analysis and experimental verification [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(32): 5122-5129. |
| [14] | Zhang Chike, Wang Feiqing, Wu Dan, Yang Bo, Cheng Jinyang, Chen Juan, Tang Dongxin, Liu Yang, Li Yanju. Effects of conditioned medium of acute myeloid leukemia on biology of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(31): 4995-5002. |
| [15] | Chen Ji, Zhang Chen, Zhang Bin, Huang Leitao. Quantitative evaluation of lumbar facet arthritis-induced cartilage injury by MR T2* mapping [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(30): 4866-4870. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||