Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (29): 4726-4733.doi: 10.12307/2024.561
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioactive glass: different application forms and functions by adjusting preparation process and doping elements
Gao Hua, Che Hui, Hu Dan, Hao Yuefeng
- Affiliated Suzhou Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2023-10-25Accepted:2023-11-29Online:2024-10-18Published:2024-03-23 -
Contact:Hao Yuefeng, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Affiliated Suzhou Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Gao Hua, Master candidate, Affiliated Suzhou Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Suzhou 215000, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation Project of Jiangsu Provincial Department of Science and Technology, No. BK20211083 (to HYF); Key Disease Project of Suzhou Municipal Health Commission, No. LCZX202110 (to HD); Young Backbone Research and Cultivation Project of Gusu College of Nanjing Medical University, No. GSKY20220527 (to CH); Graduate Practical Innovation Program, No. SJCX23-0684 (to GH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Hua, Che Hui, Hu Dan, Hao Yuefeng. Bioactive glass: different application forms and functions by adjusting preparation process and doping elements[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(29): 4726-4733.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
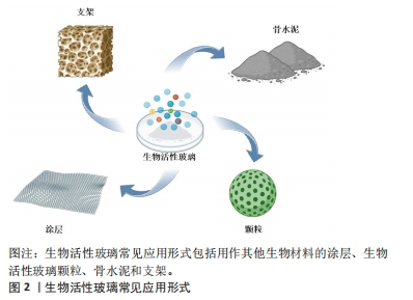
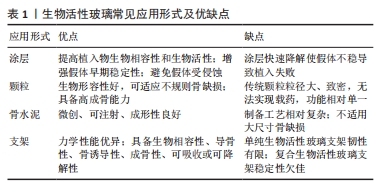
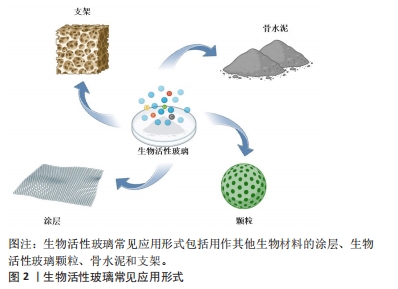
2.1 生物活性玻璃的不同应用形式 生物活性玻璃自研发以来,经过持续的基础实验研究与临床试验,不断揭示出新的性能特点,包括骨导电性、骨诱导性、血管生成能力和抗菌作用等。由于这些优异的生物学性能,其应用领域从最初的硬组织再生逐渐扩大到软组织再生、药物递送,甚至癌症治疗。为满足不同的临床需求,研究者采用不同的制备工艺,创造了各种形式的生物活性玻璃产品,目前主要的形式包括涂层、颗粒、支架和骨水泥。 2.1.1 涂层 金属植入物以因卓越的机械性能,在过去几十年一直被视作承重植入材料的良好选择,然而,金属材料并不具备出色的生物活性和其他生物功能。为提高生物材料生物相容性和生物活性,传统的方式之一是应用表面涂层技术[8]。目前,生物活性玻璃已广泛用于制作金属植入物的表面涂层,常见涂层技术包括溶胶凝胶技术、搪瓷技术、电泳沉积技术、热喷涂技术和激光熔覆技术[9]。这些涂层可以在植入初期与宿主组织形成化学键,从而使植入物获得早期的稳定性。此外,生物活性玻璃涂层还能够保护植入物基质免受腐蚀,并防止有毒金属离子的释放[10]。生物活性玻璃涂层可以增强底物的矿化、表面(纳米级)粗糙度、细胞行为(如生长、增殖和分化等),以改善骨整合、骨组织生成、血管生成、抗菌和抗炎活性。然而,由于生物活性玻璃涂层与基体之间存在热膨胀和弹性不匹配,因此界面结合强度相对较弱,这对其应用前景构成挑战。此外,目前生物活性玻璃涂层的快速降解可能导致植入物的不稳定,进而引发植入失败[11],因此,目前通过对生物活性玻璃涂层合适组分的研究,从而实现适当的降解速率,并获得与植入物基体相匹配的热膨胀系数,将显著增加生物活性玻璃涂层的临床使用。 2.1.2 颗粒 生物活性玻璃可通过挤压方式制备成不同颗粒形态,以适用于填充不同类型的骨缺损。这些颗粒一旦植入,可以在局部快速刺激骨组织生长,促进骨再生。目前,通常采用熔融法制备生物活性玻璃颗粒,然而,这种方法制备的生物活性玻璃颗粒通常具有较大的粒径和致密的结构,不太适用于承载药物或离子等多功能应用。研究表明,采用溶胶-凝胶法制备的介孔生物活性玻璃颗粒具有出色的生物相容性,其高比表面积更有助于形成羟基磷灰石表层,而有序排列的介孔结构则便于药物负载。体外研究结果也证实了介孔生物活性玻璃颗粒在促进成骨和药物递送方面具备卓越性能[7]。并有研究人员利用介孔生物活性玻璃颗粒的此性能,制备了可生物降解的聚合物复合支架,从而进一步优化了支架性能[12]。 2.1.3 骨水泥 与金属植入物和颗粒不同,骨水泥具有微创、可注射、成形性良好等优势,这使得它更容易适应不规则的骨缺损,避免了植入物与骨之间形成间隙,从而缩短愈合时间并降低感染风险[13]。在临床上,商用骨水泥,如聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯水泥、硫酸钙水泥和磷酸钙水泥已得到广泛应用[14]。生物活性玻璃骨水泥是通过将生物活性玻璃粉末与液相混合制备,然后通过微创方法注射到骨缺损部位,它在固化后提供了早期的机械支撑,并释放功能离子,有效促进骨组织再生。此外,生物活性玻璃骨水泥仍具备载药功能。例如,CUI等[15]在生物活性玻璃粉末中掺入万古霉素粉末,制备出既具有抗菌作用、又具备生物相容性和良好降解性的可注射型生物活性玻璃骨水泥,将这种骨水泥植入到兔慢性骨髓炎模型后,观察到了令人满意的抗感染及骨修复效果。另有研究者将含有不同比例锶的生物活性玻璃颗粒与聚甲基丙烯酸酯粉末混合,制备出了不同配比的复合骨水泥,这些复合骨水泥与纯聚甲基丙烯酸酯相比,具有更低的放热温度、更短的凝固时间、更高的可注射性,同时锶的掺入增强了复合骨水泥的成骨特性[16]。因此,新型的生物活性玻璃复合骨水泥有望成为传统骨水泥的出色替代品。 2.1.4 支架 自体骨移植一直被视为治疗骨缺损的金标准。然而,当骨缺损达到一定尺寸时,自体骨移植可能面临挑战。使用生物活性玻璃颗粒填充或注射骨水泥同样不适用于这种情况。在这种背景下,骨组织工程提供了一种新的替代方法,即使用支架。由于生物活性玻璃具备多种特性,包括生物相容性、导骨性、骨诱导性、成骨性、可吸收或可降解性,同时具备与植入部位骨组织相似的力学性能,能够提供临时的机械支持,因此成为新一代备受欢迎的支架候选材料[17]。研究者将生物活性玻璃纤维制成多孔支架,用于修复兔胫骨缺损,并与颗粒型材料(例如PerioGlas?)进行了对比,组织学观察表明,在促进新骨形成和骨结构改造方面,生物活性玻璃支架更具优势[18]。然而生物活性玻璃的断裂韧性有限,因此无法满足力学要求较高、需要承受周期性应力的部位,例如股骨和胫骨。为此,研究人员将聚合物与生物活性玻璃结合,制备复合材料。有研究者进行了聚乳酸涂层的生物活性玻璃支架与无涂层生物活性玻璃支架的比较研究,发现尽管两者有相似的屈服强度,但涂层支架具有更大的伸长率和更佳的韧性[19]。然而,涉及生物活性玻璃与聚合物的降解能力的不同的问题仍需进一步研究,以解决支架的稳定性,同时还需要研究如何有效地将生物活性玻璃与聚合物稳定结合以提高支架性能。 生物活性玻璃常见应用形式示意图见图2,优缺点总结见表1。"
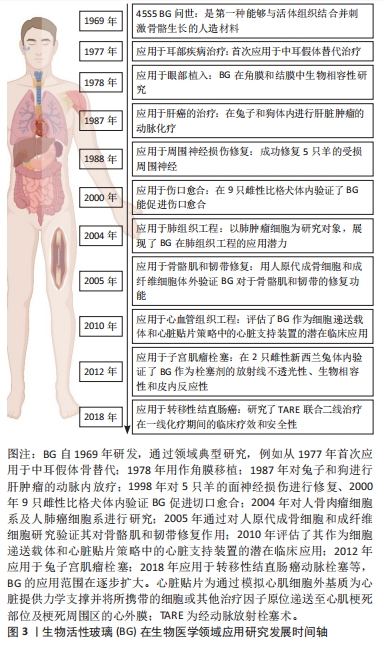
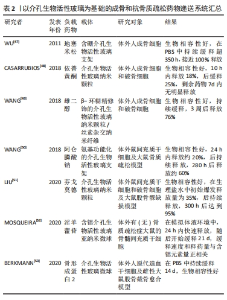
2.2 生物活性玻璃在生物医学领域的应用 无论是天然的还是合成的生物材料,在组织修复再生、感染治疗等生物医学领域都有广泛的应用,可用于替代受损组织或恢复其生物功能。当一种生物材料具备以下特征时,即易获取、成本低廉、生物惰性、无毒性、可塑性、容易植入和不干扰医疗检查,那么可以被视为优秀的临床应用生物材料[20]。自从1969年生物活性玻璃诞生以来,通过不断的研究和发展,凭借其卓越的生物相容性和生物学活性,在生物医学领域得到了广泛的应用。得益于制备工艺的进步以及功能性离子的掺入,生物活性玻璃的应用范围已经从最初的中耳假体骨替代,扩展到了包括口腔科、骨组织工程、软组织工程甚至癌症治疗等领域,见图3。"
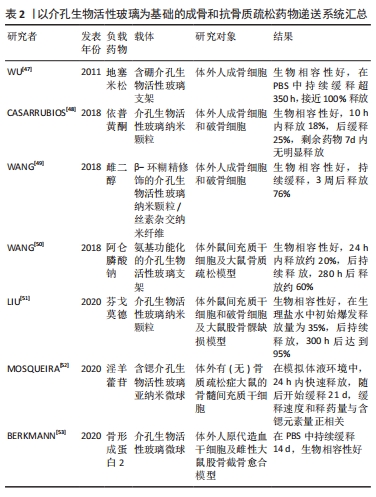
2.2.1 口腔科 生物活性玻璃在口腔科领域具有多重应用。首先,生物活性玻璃在口腔护理产品中发挥关键作用,尤其在牙膏中的应用引起了广泛关注。最新获得美国食品药品监督管理局批准的一款牙膏含有生物活性玻璃和氟化物,它通过在刷牙后数小时内控制释放钙、磷酸盐和氟化物离子,从而改善牙齿表面和牙本质小管的状态[5]。其次,生物活性玻璃广泛用于治疗牙周病和种植牙领域。生物活性玻璃颗粒在治疗牙周缺陷中通过增加骨矿化来实现成骨,同时,生物活性玻璃的抗菌特性可在覆盖植入物时预防感染和炎症的发生,促进钛植入物与骨的结合,减少早期植入失败的风险[21]。再次,生物活性玻璃在正畸治疗中发挥作用。正畸托槽黏附治疗可能会为细菌提供有利的生存条件,导致牙齿脱矿和白斑病变的形成。研究表明,生物活性玻璃能够使白斑病变再矿化,含有生物活性玻璃和氟化物的正畸黏接剂可增强磷灰石结构的强度,有望在预防白斑病变的形成中发挥作用[22]。此外,生物活性玻璃还在根管治疗中被用作局部牙根消毒剂。生物活性玻璃通过表面反应形成碱性环境,减少细菌的生存,同时不影响牙本质的稳定性[23]。最后,生物活性玻璃在口腔颌面外科中还扮演重要角色。多种商用生物活性玻璃产品,如Bioglass 45S5、Biogran、70S30C生物活性玻璃、BonAlive和Strongbone等已被广泛应用于口腔颌面外科手术。其中,生物活性玻璃 45S5作为骨替代物用于唇腭裂患者的二次牙槽骨移植,避免了髂骨采集所带来的并发症,并简化了手术流程,术后骨连续性的恢复也得到了满意的效 果[24]。 2.2.2 骨科 生物活性玻璃在骨骼系统疾病应用中同样具有广泛的潜力。人体骨骼是一种高度动态和高度血管化的组织,能够通过调节成骨细胞和破骨细胞的活性来维持骨代谢平衡,从而实现骨骼的不断重塑。许多骨骼系统疾病与骨代谢密切相关,而骨形成和骨吸收的过程受到多种系统和局部调控因素的调节,包括生长因子、激素和应激作用等[1]。研究表明,单独的无机离子元素如钙(Ca)、硅(Si)、磷(P)、锶(Sr)、锌(Zn)以及硼(B)、钒(V)、钴(Co)和镁(Mg)参与了骨代谢过程[25-33],并在骨组织的血管生成、生长和矿化中发挥了重要的生理作用,而这些离子在生物活性玻璃降解过程中广泛存在。例如,Ca2+通过影响成骨细胞表面钙敏感受体,激活细胞内相关信号通路,在骨重塑中发挥重要作用,研究发现Ca2+能够促进谷氨酸释放,增加成骨细胞、破骨细胞和骨细胞对机械刺激的敏感性[25];Si作为骨组织形成和钙化的基本元素,在骨形成中发挥重要作用,特别是正硅酸,它可通过促进Ⅰ型胶原的生成和成骨细胞的分化,从而加速骨组织形成[26],此外,它也可通过诱导羟基磷灰石的沉淀促进骨骼钙化,因此,通过饮食摄入足量的Si可以增加骨密度,预防骨质疏松症;P通过刺激骨形成关键调节因子,如基质Gla蛋白来调节骨代谢[27];Zn可通过增加ATP酶活性,调节Ⅰ型胶原,碱性磷酸酶,骨桥蛋白和骨钙蛋白及Runx2信号通路,促进成骨细胞分化和蛋白分泌,刺激骨形成。此外,Zn也可通过降低破骨细胞活性,抑制骨吸收,在骨代谢中发挥重要作用[29]。 功能性的复合生物活性玻璃材料,含有不同的金属元素,可在人体实现缓释效果,从而有助于促进成骨、血管生成、抗菌、抗肿瘤磁热治疗、冷光标记等作用,这些材料可以通过定向释放功能性微粒的方式,更有针对性地治疗骨科相关疾病[34]。目前,Bioglass?45S5(其组分为46.1SiO2-24.3Na2O-27.0CaO-2.6P2O5)在骨科应用广泛,主要用于修复非承重骨缺损、促进骨折愈合、进行脊柱融合术以及髋关节脱位和髋臼截骨术等[35]。研究者在脊柱侧弯融合术中使用生物活性玻璃替代自体髂骨移植,结果表明两者具有相同的临床效果,且生物活性玻璃有效减少了自体髂骨移植可能引起的附加损伤。尽管生物活性玻璃产品在骨修复中发挥了重要作用,但仍存在多个局限性需要克服:首先,这些产品多为颗粒型,力学强度低,限制了它们在承重骨缺损和大段骨缺损的修复应用;其次,产品颗粒组分普遍存在析晶趋势,这使得通过热烧结法制备具有三维网络结构的支架,以应对承重骨修复的需求变得复杂;另外,产品颗粒组分中SiO2含量较高,导致生物活性较低,体内降解过慢,与新骨生成速度不匹配;最后,这些产品缺乏其他功能成分,无法在骨修复的同时实现其他治疗效果。为了克服这些限制,需要在生物活性玻璃骨修复材料的研发过程中寻求解决方案[36]。 此外,生物活性玻璃在骨质疏松领域的临床应用也在不断扩展。一些研究者已经开始尝试将生物活性玻璃颗粒与抗骨质疏松药物结合,例如:通过声化学方法,将市售产品Biogran?(与Bioglass?45S5具有相似成分)和雷洛昔芬结合,可用于修复大鼠颅骨中的关键骨缺损,这证明了在生物活性玻璃复合支架中加载抗骨质疏松药物、离子、抗生素、促血管生成物质和促成骨疗法是促进骨再生的有效策略[37]。关于生物活性玻璃在骨质疏松中的作用机制,研究者使用生物活性玻璃纳米颗粒诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分泌异质细胞外囊泡,并测试了生物活性玻璃纳米颗粒刺激骨髓间充质干细胞产生异质细胞外囊泡与否,以及这些异质细胞外囊泡对抑制破骨细胞分化的影响。研究结果表明,生物活性玻璃能够诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分泌异质细胞外囊泡,并具有抑制破骨细胞分化的作用,这可能因为异质细胞外囊泡中的lncRNA NRON能够抑制破骨细胞NFATc1核易位,从而抑制破骨细胞分化[38]。 2.2.3 创面愈合 组织工程技术现已成为促进伤口修复的重要手段之一。近年来,生物活性玻璃在软组织修复,尤其是伤口愈合中的应用日益引起关注。在创面局部应用不同成分的生物活性材料可以抗炎、促进血管生成和加速伤口愈合。早在1981年,WILSON等[39]就发现了生物活性玻璃与软组织结合的特性。随后,研究者发现了生物活性玻璃与胶原蛋白的结合能力,胶原蛋白通过促进成纤维细胞的增殖来控制细胞迁移、增殖和分化的周期,在软组织修复过程中起到必不可少的作用[40]。然而,胶原蛋白具有高降解率和较低的力学强度,这在一定程度上限制了其应用。通过将胶原蛋白与生物活性玻璃结合,不仅可以增强其力学强度,还可以实现抗炎抗菌效果,从而更好地满足临床需求。研究表明,生物活性玻璃可以通过上调软组织修复相关基因的表达,如血管内皮生长因子、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和血管细胞黏附分子等,促进上皮细胞增殖,减轻损伤部位的炎症,从而促进伤口愈合[41]。此外,生物活性玻璃还可与一些功能性离子结合,例如:Ag+具有优异的抗菌和抗炎效果,尤其对革兰阴性菌的作用优于革兰阳性菌[42];Cu2+能够促进血管化,并具有一定的抗菌作用,已有研究证明其还能促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖[43];Zn2+同样具有一定的抗菌和促进血管生成的特性[44],从生物活性玻璃中释放的Zn2+通过产生活性氧并在细胞质或细菌外膜积累而具有抑菌作用[45]。值得一提的是,美国ETS伤口护理公司的硼酸盐生物活性玻璃敷料产品(MIRRAGEN)已于2016年获得美国食品药品监督管理局批准,用于一度和二度烧伤、创伤性伤口、手术切口以及糖尿病溃疡等疾病的治疗[46]。然而,伤口愈合是一个复杂而漫长的过程,涉及多种细胞因子和生长因子的分泌,以及不同类型的细胞相互作用[47-53],见表2。因此,生物活性玻璃在这个长期过程中的持效性和如何实现长期效应仍需进一步探究。"

2.2.4 癌症 采用熔融凝胶法制备的介孔生物活性玻璃相较于传统生物活性玻璃通常表现出更优异的成骨性能和载药性能,这使其成为包括癌症诊断及治疗在内的生物医学应用中的理想材料[54]。功能化的介孔生物活性玻璃可以通过增强降钙素原的诊断信号来辅助癌症诊断,特别是针对表现为发热和C-反应蛋白水平升高为主的癌症病例[55]。同时,介孔生物活性玻璃通过其有序的结构,可以将亲水和疏水抗癌药物通过外表面吸附或(非)共价结合等方式有效封装在其中,充分利用其更大的表面积,提高药物的负载能力[56]。 此外,各种不同类型的刺激响应型介孔生物活性玻璃,如pH响应、磁响应性、光响应性等,可以实现药物的脉冲释放或时空控制,以满足药物按需释放的需求[57],这使其在癌症治疗中,可制造成具有持续或可控药物释放特性的先进药物传递系统。介孔生物活性玻璃不仅能传递治疗离子和药物,还可以将一些具有抗癌和再生特性的离子整合到其框架中,以实现协同治疗效果[58]。然而,这些材料在实现可靠的癌症治疗方面仍存在一些未解决的生物学问题,包括治疗分子(如离子和药物)在介孔生物活性玻璃中的最佳剂量以及长期不良反应等,需要进一步的研究来解决。 2.3 各种生物活性玻璃缓释离子的生物学功能 人体必需元素在生命代谢中发挥着重要的作用,而人体非必需元素也已广泛用于药物治疗。将特定元素掺入生物活性玻璃,不仅能提升其机械性能,还赋予了它特殊生物学功能,如生物活性、可降解性和抗菌性[59],使其适用于更丰富的临床场景。生物活性玻璃的“经典”元素成分包括硅(Si)、磷(P)、钙(Ca)、钠(Na)和钾(K)。此外,生物活性玻璃中还可添加其他具有生物活性的元素,如铜(Cu)、锌(Zn)、镁(Mg)、银(Ag)、锰(Mn)、锂(Li)、铕(Eu)、钬(Ho)、钆(Gd)、钇(Y)、镧(La)和锆(Zr)等。 2.3.1 常见元素 Si:是人体必需的微量元素之一。研究表明,Si2+能够刺激人体主动脉内皮细胞的增殖,特别是在浓度为0.6-2.0 μg/mL时可表现出明显的刺激效果[60]。增加Si2+浓度有助于提高局部Ca/P值,促进矿化过程,并刺激细胞新陈代谢。这可进一步激发促创伤愈合因子的自分泌反应,从而加速创伤修复。此过程中Si2+聚集于羟基磷灰石层表面,促进新生组织在创面迅速生长和覆盖[61]。此外,适量的SiO2在体外对破骨细胞有明显的抑制作用,并同时激活成骨细胞活性,其主要机制涉及对抗核转录因子κB的激活,从而加强了破骨细胞的吸收,和促进成骨细胞的形成[26]。 P:是构成人类骨骼无机磷灰石[Ca10(PO4,CO3)6OH2]的主要成分之一,无机磷酸盐在细胞外基质的矿化过程中发挥至关重要的作用。体外研究表明,无机磷酸盐还能够诱导Ca沉积。进一步研究还揭示了,无机磷酸盐和基质Gla蛋白在骨形成中是关键的调节因子,P通过ERK1/2-Fra-1信号通路调控成骨细胞内基质Gla蛋白的表达,从而影响骨代谢[62]。 Ca:同样作为人类骨骼无机相Ca10(PO4,CO3)6OH2的主要成分之一,在骨骼形成和吸收中起着重要的作用。研究表明,Ca2+在体外影响成骨细胞。低浓度钙(2-4 mmol)和中浓度钙(6-8 mmol)分别有利于成骨细胞增殖、分化和细胞外基质矿化。然而,较高浓度的钙(> 10 mmol)则具有细胞毒性[63]。此外,Ca2+还能促进胰岛素样生长因子1/2(IGF-1/2)表达,从而调节成骨细胞的增殖[64]。 Cu:是一种常见的金属元素,具有优异的生物学性能,广泛应用于生物医学领域。Cu掺杂的生物活性玻璃在生理环境中逐渐释放Cu2+,可发挥多种重要作用。首先,Cu2+可诱导成骨细胞分化,抑制破骨细胞活性,刺激胶原蛋白生成和聚集,对于骨和软骨形成及愈合至关重要[65]。然后,Cu2+可增强成纤维细胞生长因子的能力,通过上调缺氧诱导因子、血管内皮生长因子和内皮型一氧化氮合酶表达,促进内皮细胞增殖和迁移,从而加速血管生成。Cu2+还可与巯基、咪唑、羧基和胺等成键,改变细胞膜结构,导致膜转运功能障碍,从而发挥一定的抗菌作用。Cu2+也可通过促进抗炎性白细胞介素10的表达,抑制促炎性白细胞介素1β实现抗炎作用。此外,Cu2+还在肿瘤酸性环境中参与类芬顿反应,从而导致氧化应激反应的产生。这会导致线粒体损伤和细胞膜通透性的改变,诱导癌细胞凋亡。因此,Cu掺杂生物活性玻璃也作为癌症治疗中的小分子及药物的递送和控释平台,减轻了高剂量药物治疗所带来的高成本和全身毒副作用。然而,Cu的添加会对生物活性玻璃的结晶度、溶解度、稳定性和形态等多个性质产生影响[66-67],因此需要进一步研究以深入了解其在各种应用中的利与弊。 Zn:最新研究已经深刻认识到Zn在骨代谢中扮演的关键角色。Zn可以刺激骨细胞内相关蛋白质表达和增强相关酶的活性,从而诱导骨形成,并具有优异的抗菌和抗炎性能。HOPPE等[59]的研究表明,当Zn掺杂的生物活性玻璃溶解后,可通过提高ATP活性提升细胞活性,同时,碱性磷酸酶的活性显著上升,显著促进了成骨细胞的增殖。另一方面,Zn2+还可抑制破骨细胞形成,降低骨吸收。此外,实验还证明了Zn2+在促进新血管的生成方面表现出卓越的潜力,进一步增加了其在生物医学领域的吸引力[44,67]。 Mg:可与骨细胞相互作用,促进新骨的形成。当体内Mg含量不足时,可能导致骨生成减少,骨吸收增加,最终引发骨质疏松。研究者在对CaO-SiO2-P2O5-MgO网络研究时发现,将Mg添加到生物活性玻璃结构中,根据其在生物模拟体液中的浸泡数据,可以明显观察到生物活性的提高,其机制在于,Mg的加入改变了生物活性玻璃的网络结构,进而导致表面羟基磷灰石结晶降低[68]。至于Mg2+是否能够促进细胞增殖和分化,目前尚无明确结论。 Ag:是人体组织的微量元素之一,以其著名的抗菌特性而广为人知。有研究者采用纳米多孔膜的生物活性玻璃(n-BGs)并在其中掺入Ag,结果证实了含Ag的生物活性玻璃(Ag-BG)在止血和抗菌作用方面表现出了卓越的性能[42]。此外,研究者还发现Ag+能够通过下调转化生长因子β,进而促进成骨的发生[69]。 Mn:是人体骨骼和牙齿所必需的金属离子。研究表明,在生物活性玻璃中加入Mn能够显著提高其生物活性并加速骨矿化的过程。此外,Mn缺乏可能会导致蛋白聚糖水平下降和糖基化的质变,从而影响成骨和破骨细胞活性[70]。Mn还可以通过调节多糖聚合酶及半乳糖转移酶活性,催化二磷酸尿苷-N-乙酰-半乳糖胺与二磷酸尿核苷-葡萄糖醛酸结合,促进黏多糖形成,而黏多糖是软骨和骨的重要成分。因此,Mn的缺乏也会导致软骨组织功能异常及骨骼异常[71]。 2.3.2 非常见元素 Li:是人体必需微量元素之一。研究发现,口服Li可通过抑制Wnt信号通路的负性调节因子糖原合成激酶,从而激活Wnt信号通路,促进软骨下骨生成[72]。此外,在骨折愈合过程中,Li可以通过激活Wnt信号通路中的关键传导蛋白β-链蛋白调节的T细胞因子(TCF)的转录,促进间充质干细胞成骨分化。同时,Li通过激活自噬保护软骨细胞。有Li掺杂的磷酸盐生物涂层能够促进细胞黏附和增殖[73-74]。 Eu:是一种稀土元素,通常不会自然存在于人体内,它的Eu3+具有发光特性。因此,Eu掺杂的生物活性玻璃(Eu-BGs)在紫外线照射下可发出红光,且强度会随Eu3+浓度增加而增强[75],这种性质使Eu-BG成为药物输送系统、细胞成像、光学设备以及骨骼和皮肤再生等领域的理想选择[76-80]。研究发现,在成分为60SiO2-(36-x)CaO-xEu2O3-4P2O5的介孔生物活性玻璃纳米球中,通过增加Eu浓度(x=0.5、1和2 mol%),可以改变中孔二氧化硅的大小、形态和孔隙结构,实现了对抗癌药物阿霉素的可控释放[76]。此外,Eu掺杂的中孔二氧化硅纳米球已被证明可显著上调间充质干细胞成骨标志物(ALP、OPN、OCN、COL1和Runx2)的表达水平,并增强人脐静脉内皮细胞的血管生成因子(CD31、PDGFR-α/β、VEGFR-1/2)的表达水平。这表明Eu-MSNs具有促进成骨分化和血管生成的能力[79]。 Ho:同样作为稀土元素,Ho逐渐引起研究人员的兴趣。有研究表明,Ho可能对加速人体新陈代谢产生影响。在生物活性玻璃领域,其主要应用于硅酸盐基体系。例如,采用58SiO2-33CaO-9P2O5-xHo2O3(x=1.25、质量分数2.5%,5.0%)的溶胶凝胶制备的掺Ho的58 S生物活性玻璃(Ho-BGs)已被证实可促进MC3T3-E1细胞增殖。此外,由于生物活性玻璃网络中存在Si-O-Ho共价键,Ho的加入显著降低了玻璃的降解速度,但并没有减缓其生物活性[81]。目前相关研究还相对较少,针对Ho-BGs在组织工程应用中的潜力仍有待进一步开发和研究。 Gd:其在临床上广泛用作磁共振成像的造影剂。近年来,由于其在近距离放射治疗、发光成像及磁共振成像领域的卓越特性,Gd掺杂的生物活性玻璃(Gd-BGs)的研究和开发逐渐引起关注。有研究者证明壳聚糖支架中的Gd-BG介孔微球可以通过激活人间充质干细胞的 Akt/GSK3β通路,提高碱性磷酸酶活性和骨钙素的表达。类似地,Gd-BGs也可以通过激活Wnt/-catenin信号通路,增强鼠间充质干细胞的成骨潜 力[82-83]。这些发现都表明Gd-BGs在组织工程和骨科应用中的价值。 Y:其已在临床癌症治疗中得到应用[84],而掺杂Y的生物活性玻璃(Y-BGs)也在放射治疗、口腔科和骨组织工程等不同领域中展现出了广泛的潜力。研究表明,Y-BGs在体内放射治疗中具有良好的化学耐久性和稳定性[67]。此外,研究者观察到含Y的58 S生物活性玻璃在模拟体液中6 h后可快速形成羟基磷灰石表层,这表明Y-BGs也具有优异的生物活性[85]。 La:作为一种稀土元素,La已用于改良硅酸盐和磷酸盐生物活性玻璃。相对于与未掺杂La的支架,La掺杂的含壳聚糖复合生物活性玻璃(La-BGs)支架可通过上调成骨标志物的表达水平,明显提高成骨细胞的增殖和成骨分化能力。此外,当La-BGs支架与人脐静脉内皮细胞接触时,能够显著诱导碱性成纤维生长因子、血管内皮生长因子和血小板衍生生长因子的表达水平,从而起到促血管生成的作用[67]。 Zr:ZrO2因其出色的力学性能和细胞相容性而被广泛用于口腔和骨植入物领域[86]。Zr的添加可以增强硅酸盐、硼酸盐和磷酸盐生物活性玻璃的机械稳定性并促进羟基磷灰石层形成。研究表明,ZrO2纳米颗粒的含量增加时,如在56SiO2-34CaO-10P2O5 mol/%的生物活性玻璃支架中,会引发ZrSiO、ZrSiO4、Zr2O(PO4)和Ca(ZrO3)结晶相形成,从而提高支架的抗压强度。此外,研究者还发现Zr-BGs支架对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、铜绿假单胞菌都具有抗菌特性,尽管对枯草芽孢杆菌的抑制作用较弱[87-88]。 文章最后总结了生物活性玻璃中不同元素的生物学作用,见表3。"

| [1] Kaou MH, Furkó M, Balázsi K, et al. Advanced bioactive glasses: the newest achievements and breakthroughs in the area. Nanomaterials. 2023;13(16):2287. [2] Fiume E, Migneco C, Verné E, et al. Comparison between bioactive sol-gel and melt-derived glasses/glass-ceramics based on the multicomponent SiO2-P2O5-CaO-MgO-Na2O-K2O system. Materials. 2020;13(3):540. [3] Kuzmenka D, Sewohl C, König A, et al. Sustained Calcium (II)-release to impart bioactivity in hybrid glass scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(12):1192. [4] Hench LL. The story of bioglass. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(11):967-978. [5] Dai LL, Mei ML, Chu CH, et al. Effect of strontium-doped bioactive glass-ceramic containing toothpaste on prevention of artificial dentine caries formation: an in vitro study. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):288. [6] Maillard M, Bandiaky ON, Maunoury S, et al. The effectiveness of calcium phosphates in the treatment of dentinal hypersensitivity: a systematic review. Bioengineering. 2023;10(4):447. [7] Yao H, Luo J, Deng Y, et al. Alginate-modified mesoporous bioactive glass and its drug delivery, bioactivity, and osteogenic properties. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:994925. [8] Marchenko ES, Baigonakova GA, Dubovikov KM, et al. Properties of coatings based on calcium phosphate and their effect on cytocompatibility and bioactivity of titanium Nickelide. Materials. 2023;16(7):2581. [9] Nikolova MP, Apostolova MD. Advances in multifunctional bioactive coatings for metallic bone implants. Mater Basel Switz. 2022;16(1):183. [10] Amirtharaj Mosas KK, Chandrasekar AR, Dasan A, et al. Recent advancements in materials and coatings for biomedical implants. Gels. 2022;8(5):323. [11] Montesissa M, Borciani G, Rubini K, et al. Ionized jet deposition of calcium phosphates-based nanocoatings: tuning coating properties and cell behavior by target composition and substrate heating. Nanomaterials. 2023;13(11):1758. [12] Pant S, Thomas S, Loganathan S, et al. 3D bioprinted poly(lactic acid)/mesoporous bioactive glass based biomimetic scaffold with rapid apatite crystallization and in-vitro Cytocompatability for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;217:979-997. [13] Olov N, Bagheri-Khoulenjani S, Mirzadeh H. Injectable hydrogels for bone and cartilage tissue engineering: a review. Prog Biomater. 2022;11(2): 113-135. [14] Tan QC. Bioactive graphene oxide-functionalized self-expandable hydrophilic and osteogenic nanocomposite for orthopaedic applications. Mater Today Bio. 2022;23:18:100500. [15] Cui X, Zhao C, Gu Y, et al. A novel injectable borate bioactive glass cement for local delivery of vancomycin to cure osteomyelitis and regenerate bone. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(3):733-745. [16] Goñi I, Rodríguez R, García-Arnáez I, et al. Preparation and characterization of injectable PMMA-strontium-substituted bioactive glass bone cement composites. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(3): 1245-1257. [17] Martelli A, Bellucci D, Cannillo V. Additive manufacturing of polymer/bioactive glass scaffolds for regenerative medicine: a review. Polymers. 2023; 15(11):2473. [18] Moimas L, Biasotto M, Di Lenarda R, et al. Rabbit pilot study on the resorbability of three-dimensional bioactive glass fibre scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2006;2(2):191-199. [19] Eriksson E, Björkenheim R, Strömberg G, et al. S53P4 bioactive glass scaffolds induce BMP expression and integrative bone formation in a critical-sized diaphysis defect treated with a single-staged induced membrane technique. Acta Biomater. 2021;126:463-476. [20] Cannio M, Bellucci D, Roether JA, et al. Bioactive glass applications: a literature review of human clinical trials. Materials. 2021;14(18):5440. [21] Al-Harbi N, Mohammed H, Al-Hadeethi Y, et al. Silica-based bioactive glasses and their applications in hard tissue regeneration: a review. Pharm Basel Switz. 2021;14(2):75. [22] Skallevold HE, Rokaya D, Khurshid Z, et al. Bioactive glass applications in dentistry. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(23):5960. [23] Alambiaga-Caravaca AM, López-Castellano A, Chou YF, et al. Release kinetics of monomers from dental composites containing fluoride-doped calcium phosphates. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(7):1948. [24] Graillon N, Degardin N, Foletti JM, et al. Bioactive glass 45S5 ceramic for alveolar cleft reconstruction, about 58 cases. J Cranio-Maxillo-fac Surg Off Publ Eur Assoc Cranio-Maxillo-fac Surg. 2018;46(10):1772-1776. [25] Nasser Atia GA, Barai HR, Shalaby HK, et al. Baghdadite: a novel and promising calcium silicate in regenerative dentistry and medicine. ACS Omega. 2022;7(49):44532-44541. [26] Shie MY, Ding SJ. Integrin binding and MAPK signal pathways in primary cell responses to surface chemistry of calcium silicate cements. Biomaterials. 2013;34(28):6589-6606. [27] Hou X, Zhang L, Zhou Z, et al. Calcium phosphate-based biomaterials for bone repair. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):187. [28] Anand A, Sengupta S, Kaňková H, et al. Influence of copper-strontium co-doping on bioactivity, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activity of mesoporous bioactive glass. Gels Basel Switz. 2022;8(11):743. [29] Roesner M, Zankovic S, Kovacs A, et al. Biocompatibility assessment of zinc alloys as a new potential material for bioabsorbable implants for osteosynthesis. Mater Basel Switz. 2023;16(15):5224. [30] Sharma A, Mani V, Pal RP, et al. Boron supplementation in peripartum Murrah buffaloes: The effect on calcium homeostasis, bone metabolism, endocrine and antioxidant status. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020;62:126623. [31] Ak A. Fibroblast Cell Responses to vanadium and niobium titanium alloys: a biocompatibility study. ACS Omega. 2023;8(37):33802-33808. [32] Lei J, Zhang W, Ma L, et al. Sonodynamic amplification of cGAS-STING activation by cobalt-based nanoagonist against bone and metastatic tumor. Biomaterials. 2023;302:122295. [33] He M, Chen L, Yin M, et al. Review on magnesium and magnesium-based alloys as biomaterials for bone immobilization. J Mater Res Technol. 2023;23:4396-4419. [34] 王青,王德平,黄文旵,等.复合功能性金属离子生物活性玻璃特征、功能及应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30):4882-4887. [35] Ilharreborde B, Morel E, Fitoussi F, et al. Bioactive glass as a bone substitute for spinal fusion in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a comparative study with iliac crest autograft. J Pediatr Orthop. 2008;28(3):347-351. [36] 黄勇华,李理,石展英,等.生物活性玻璃在骨修复中的应用和研究现状[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(5):660-666. [37] Lisboa-Filho PN, Gomes-Ferreira PHS, Batista FRS, et al. Bone repair with raloxifene and bioglass nanoceramic composite in animal experiment. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(sup1):97-101. [38] Yang Z, Liu X, Zhao F, et al. Bioactive glass nanoparticles inhibit osteoclast differentiation and osteoporotic bone loss by activating lncRNA NRON expression in the extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials. 2022;283:121438. [39] Wilson J, Pigott GH, Schoen FJ, et al. Toxicology and biocompatibility of bioglasses. J Biomed Mater Res. 1981;15(6):805-817. [40] Merwin GE, Atkins JS, Wilson J, et al. Comparison of ossicular replacement materials in a mouse ear model. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1982;90(4):461-469. [41] Kargozar S, Hamzehlou S, Baino F. Can bioactive glasses be useful to accelerate the healing of epithelial tissues? Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;97:1009-1020. [42] Hu G, Xiao L, Tong P, et al. Antibacterial hemostatic dressings with nanoporous bioglass containing silver. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:2613-2620. [43] Liu Y, Zhu J, Xu L, et al. Copper regulation of immune response and potential implications for treating orthopedic disorders. Front Mol Biosci. 2022;9:1065265. [44] Hassan A, Elebeedy D, Matar ER, et al. Investigation of angiogenesis and wound healing potential mechanisms of zinc oxide nanorods. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:661217. [45] Sergi R, Bellucci D, Salvatori R, et al. Zinc containing bioactive glasses with ultra-high crystallization temperature, good biological performance and antibacterial effects. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109910. [46] Zheng K, Niu W, Lei B, et al. Immunomodulatory bioactive glasses for tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2021;133:168-186. [47] Wu C, Miron R, Sculean A, et al. Proliferation, differentiation and gene expression of osteoblasts in boron-containing associated with dexamethasone deliver from mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2011;32(29):7068-7078. [48] Casarrubios L, Gómez-Cerezo N, Feito MJ, et al. Incorporation and effects of mesoporous SiO2-CaO nanospheres loaded with ipriflavone on osteoblast/osteoclast cocultures. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018;133:258-268. [49] Wang D, Steffi C, Wang Z, et al. Beta-cyclodextrin modified mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles/silk fibroin hybrid nanofibers as an implantable estradiol delivery system for the potential treatment of osteoporosis. Nanoscale. 2018;10(38):18341-18353. [50] Wang X, Zeng D, Weng W, et al. Alendronate delivery on amino modified mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds to enhance bone regeneration in osteoporosis rats. Artif Cells Nanomedicine Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup2):171-181. [51] Liu L, Zhao F, Chen X, et al. Local delivery of FTY720 in mesoporous bioactive glass improves bone regeneration by synergistically immunomodulating osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(28):6148-6158. [52] Mosqueira L, Barrioni BR, Martins T, et al. In vitro effects of the co-release of icariin and strontium from bioactive glass submicron spheres on the reduced osteogenic potential of rat osteoporotic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomed Mater. 2020;15(5):055023. [53] Berkmann JC, Herrera Martin AX, Pontremoli C, et al. In vivo validation of spray-dried mesoporous bioactive glass microspheres acting as prolonged local release systems for BMP-2 to support bone regeneration. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(9):823. [54] Anand A, Lalzawmliana V, Kumar V, et al. Preparation and in vivo biocompatibility studies of different mesoporous bioactive glasses. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;89:89-98. [55] Vincenzi B, Fioroni I, Pantano F, et al. Procalcitonin as diagnostic marker of infection in solid tumors patients with fever. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28090. [56] Vallet-Regí M, Colilla M, Izquierdo-Barba I, et al. Achievements in mesoporous bioactive glasses for biomedical applications. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2636. [57] Ashrafizadeh M, Mirzaei S, Gholami MH, et al. Hyaluronic acid-based nanoplatforms for doxorubicin: a review of stimuli-responsive carriers, co-delivery and resistance suppression. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;272:118491. [58] Sharifi E, Bigham A, Yousefiasl S, et al. Mesoporous bioactive glasses in cancer diagnosis and therapy: stimuli‐responsive, toxicity, immunogenicity, and clinical translation. Adv Sci. 2022;9(2):2102678. [59] Hoppe A, Güldal NS, Boccaccini AR. A review of the biological response to ionic dissolution products from bioactive glasses and glass-ceramics. Biomaterials. 2011;32(11):2757-2774. [60] Zhai W, Lu H, Chen L, et al. Silicate bioceramics induce angiogenesis during bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(1):341-349. [61] Barrak FN, Li S, Mohammed AA, et al. Anti-inflammatory properties of S53P4 bioactive glass implant material. J Dent. 2022;127:104296. [62] Xiao D, Zhang J, Zhang C, et al. The role of calcium phosphate surface structure in osteogenesis and the mechanisms involved. Acta Biomater. 2020; 106:22-33. [63] Yang L, Perez-Amodio S, Barrère-de Groot FYF, et al. The effects of inorganic additives to calcium phosphate on in vitro behavior of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Biomaterials. 2010;31(11):2976-2989. [64] Marie PJ. The calcium-sensing receptor in bone cells: a potential therapeutic target in osteoporosis. Bone. 2010;46(3):571-576. [65] Bernhardt A, Bacova J, Gbureck U, et al. Influence of Cu2+ on Osteoclast Formation and Activity In Vitro. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2451. [66] Ke W, Li J, Mohammed F, et al. Therapeutic polymersome nanoreactors with tumor-specific activable cascade reactions for cooperative cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 2019;13(2):2357-2369. [67] Pantulap U, Arango-Ospina M, Boccaccini AR. Bioactive glasses incorporating less-common ions to improve biological and physical properties. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2021;33(1):3. [68] Kargozar S, Milan PB, Amoupour M, et al. Osteogenic potential of magnesium (Mg)-doped multicomponent bioactive glass: in vitro and in vivo animal studies. Mater Basel Switz. 2022;15(1):318. [69] Sharifi E, Sadati SA, Yousefiasl S, et al. Cell loaded hydrogel containing Ag-doped bioactive glass-ceramic nanoparticles as skin substitute: Antibacterial properties, immune response, and scarless cutaneous wound regeneration. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022;7(3):e10386. [70] Wei L, Qin S, Ye Y, et al. Chondrogenic potential of manganese-loaded composite scaffold combined with chondrocytes for articular cartilage defect. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(10):74. [71] Westhauser F, Wilkesmann S, Nawaz Q, et al. Effect of manganese, zinc, and copper on the biological and osteogenic properties of mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(8):1457-1467. [72] Houschyar KS, Tapking C, Borrelli MR, et al. Wnt pathway in bone repair and regeneration - what do we know so far. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:170. [73] HAN P, WU C, CHANG J, et al. The cementogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament cells via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway by Li+ ions released from bioactive scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2012;33(27):6370-6379. [74] Simila HO, Boccaccini AR. Sol-gel synthesis of lithium doped mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles and tricalcium silicate for restorative dentistry: comparative investigation of physico-chemical structure, antibacterial susceptibility and biocompatibility. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1065597. [75] Wu L, Yang F, Xue Y, et al. The biological functions of europium-containing biomaterials: a systematic review. Mater Today Bio. 2023;19:100595. [76] Zhang Y, Hu M, Wang X, et al. Design and evaluation of europium containing mesoporous bioactive glass nanospheres: doxorubicin release kinetics and inhibitory effect on osteosarcoma MG 63 cells. Nanomater Basel Switz. 2018; 8(11):961. [77] Chen M, Wang M, Niu W, et al. Multifunctional protein-decorated bioactive glass nanoparticles for tumor-specific therapy and bioimaging in vitro and in vivo. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(13):14985-14994. [78] Su X, Wang T, Guo S. Applications of 3D printed bone tissue engineering scaffolds in the stem cell field. Regen Ther. 2021;16:63-72. [79] Shi M, Xia L, Chen Z, et al. Europium-doped mesoporous silica nanosphere as an immune-modulating osteogenesis/angiogenesis agent. Biomaterials. 2017; 144:176-187. [80] Wang G, Lv Z, Wang T, et al. Surface functionalization of hydroxyapatite scaffolds with MgAlEu-LDH nanosheets for high-performance bone regeneration. Adv Sci Weinh Baden-Wurtt Ger. 2022;10(1):e2204234. [81] Delpino GP, Borges R, Zambanini T, et al. Sol-gel-derived 58S bioactive glass containing holmium aiming brachytherapy applications: a dissolution, bioactivity, and cytotoxicity study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;119:111595. [82] Zhu DY, Lu B, Yin JH, et al. Gadolinium-doped bioglass scaffolds promote osteogenic differentiation of hBMSC via the Akt/GSK3β pathway and facilitate bone repair in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:1085-1100. [83] Liao F, Peng XY, Yang F, et al. Gadolinium-doped mesoporous calcium silicate/chitosan scaffolds enhanced bone regeneration ability. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109999. [84] Chellan P, Sadler PJ. The elements of life and medicines. Philos Trans R Soc Math Phys Eng Sci. 2015;373(2037):20140182. [85] Hadush Tesfay A, Chou YJ, Tan CY, et al. Control of dopant distribution in yttrium-doped bioactive glass for selective internal radiotherapy applications using spray pyrolysis. Mater Basel Switz. 2019;12(6):986. [86] Barros SA de L, Soares DG, Leite ML, et al. Influence of zirconia-coated bioactive glass on gingival fibroblast behavior. Braz Dent J. 2019;30(4):333-341. [87] Kumar P, Kumar V, Kumar R, et al. Fabrication and characterization of ZrO2 incorporated SiO2-CaO-P2O5 bioactive glass scaffolds. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;109:103854. [88] MEHRABI T, MESGAR AS, MOHAMMADI Z. Bioactive glasses: a promising therapeutic ion release strategy for enhancing wound healing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(10):5399-5430. |
| [1] | Yang Yufang, Yang Zhishan, Duan Mianmian, Liu Yiheng, Tang Zhenglong, Wang Yu. Application and prospects of erythropoietin in bone tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1443-1449. |
| [2] | Chen Kaijia, Liu Jingyun, Cao Ning, Sun Jianbo, Zhou Yan, Mei Jianguo, Ren Qiang. Application and prospect of tissue engineering in treatment of osteonecrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1450-1456. |
| [3] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [4] | Zhong Jun, Wang Wen. Network meta-analysis of different anatomical repair strategies to improve chronic lateral ankle instability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1470-1476. |
| [5] | Li Zhifei, Yang Yin, Chen Hualong, Liang Qinqiu, Zhong Yuanming, Zhang Yisheng. Finite element analysis of the correlation between tilt angle of titanium cage and postoperative subsidence of titanium cage after anterior subtotal cervical corpectomy, decompression and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1313-1319. |
| [6] | Ouyang Beiping, Ma Xiangyang, Luo Chunshan, Zou Xiaobao, Lu Tingsheng, Chen Qiling. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of a new horizontal screw-screw crosslink in posterior atlantoaxial internal fixation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1320-1324. |
| [7] | Chen Mengmeng, Bao Li, Chen Hao, Jia Pu, Feng Fei, Shi Guan, Tang Hai. Biomechanical characteristics of a novel interspinous distraction fusion device BacFuse for the repair of lumbar degenerative disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1325-1329. |
| [8] | Liang Cheng, Zhang Linqi, Wang Guan, Li Wen, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang. Finite element and biomechanical analysis of different implants in repair for unilateral unstable pelvic posterior ring injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1336-1341. |
| [9] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [10] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [11] | Wu Jing, Yao Yingce, Yang Xiaowei, Xue Boshi, Zhao Jianbin, Yang Chen, Luan Tianfeng, Zhou Zhipeng. Intervention of muscle strength training combined with neuromuscular electrical stimulation on lower limb function and biomechanical changes in patients with patellofemoral pain [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1365-1371. |
| [12] | Min Meipeng, Wu Jin, URBA RAFI, Zhang Wenjie, Gao Jia, Wang Yunhua, He Bin, Fan Lei. Role and significance of artificial intelligence preoperative planning in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1372-1377. |
| [13] | Qi Haodong, Lu Chao, Xu Hanbo, Wang Mengfei, Hao Yangquan. Effect of diabetes mellitus on perioperative blood loss and pain after primary total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1383-1387. |
| [14] | Li Xiaoqiang, Chen Wei, Li Mingyue, Shan Tianchi, Shen Wen. Value of preoperative quantitative ultrasound analysis of quadriceps femoris in predicting chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1388-1393. |
| [15] | Xi Jintao, Lu Qilin, Wang Yang, Wang Xiaojuan, Lyu Peng, Chen Long, Shi Zhen, Xie Wei, Zhu Yiliang, Li Xugui. Risk factors for cage retropulsion following transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1394-1398. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||