Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (20): 3209-3216.doi: 10.12307/2024.345
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlations between brain function and olfactory function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease and Parkinson’s disease based on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging
Huang Zhongxia1, Wang Yu1, Liu Yawen1, Zhang Xiaoxu2, Xu Dandan2, Yang Yanping2, Huang Mingming1, Yu Hui1
- 1School of Medical Imaging, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-29Accepted:2023-05-22Online:2024-07-18Published:2023-09-11 -
Contact:Yu Hui, MD, Associate professor, Chief physician, School of Medical Imaging, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Huang Zhongxia, Master candidate, School of Medical Imaging, Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:National Foundation Incubation Project of Affiliated Hospital of Guizhou Medical University, No. 8206070224 (to YH)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Huang Zhongxia, Wang Yu, Liu Yawen, Zhang Xiaoxu, Xu Dandan, Yang Yanping, Huang Mingming, Yu Hui. Correlations between brain function and olfactory function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease and Parkinson’s disease based on resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3209-3216.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
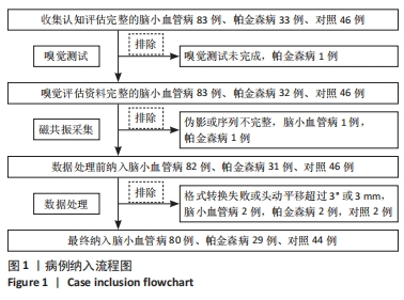
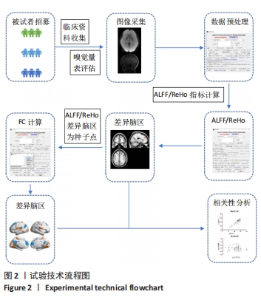
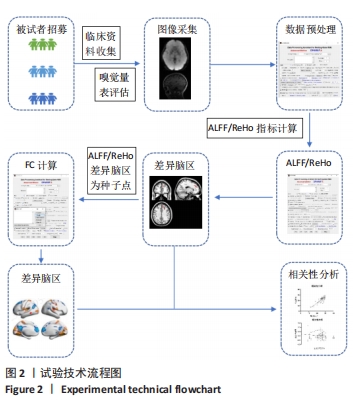
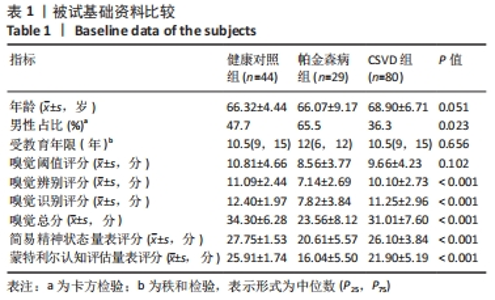
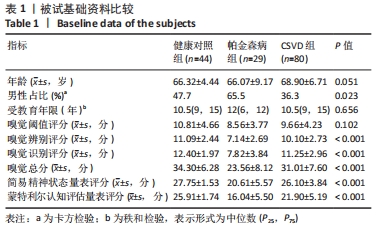
2.1 参与者数量分析 于贵州医科大学附属医院神经内科门诊及住院部收集认知评估资料完整的被试者,根据就诊期间影像及临床资料和病史分为健康对照组(46 例)、CSVD组(83例)及帕金森病组(33 例),影像资料包括全部常规磁共振T1、T2、T2Flair、SagT2、DWI、SWI/ESWAN、MRA、MRV。随后在1 周内对被试者进行嗅觉测试,其中1 例帕金森病患者未完成嗅觉测试从而排除。 嗅觉测试完成之后立即进行高分辨率结构磁共振及静息态功能磁共振扫描,其中1 例CSVD及1 例帕金森病患者磁共振序列存在伪影或者扫描序列不完整进而排除。在数据处理过程中,健康对照组、CSVD组及帕金森病组各存在2 例格式转换失败或者扫描途中头动平移超过3°或3 mm。最终纳入健康对照组44 例、CSVD组80 例、帕金森病组29 例 (图1)。"
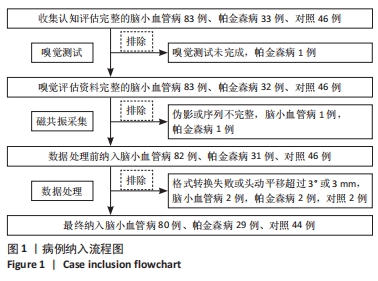
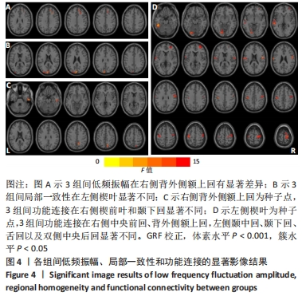
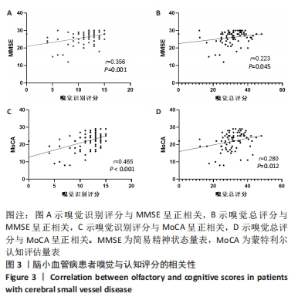
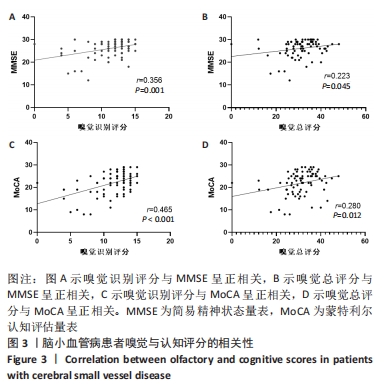
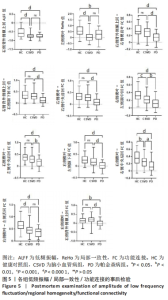
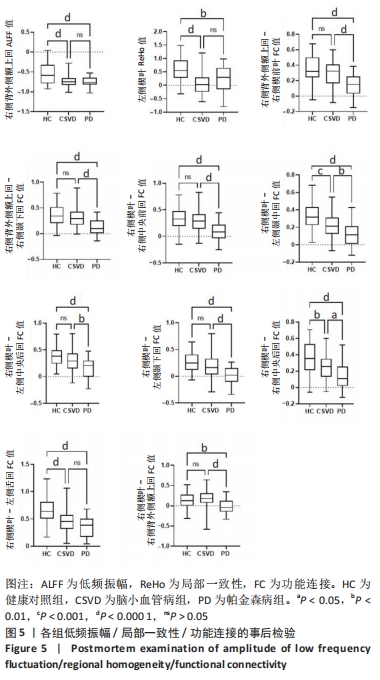
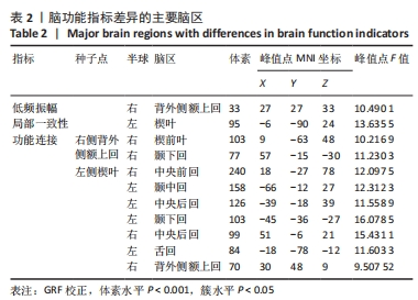
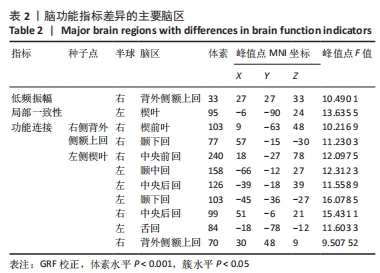
2.4 静息态功能磁共振成像指标异常脑区 组间低频振幅、局部一致性和功能连接显著差异如图4所示,位置如表2所示。与健康对照组相比,CSVD组、帕金森病组右侧背外侧额上回低频振幅及左侧楔叶局部一致性显著降低。以右侧背外侧额上回为种子点的功能连接结果显示,与帕金森病患者相比,右侧楔前叶及颞下回功能连接在健康对照组、CSVD组中显著增强。以左侧楔叶为种子点的功能连接结果显示,与帕金森病患者相比,右侧中央前回及背外侧额上回、左侧中央后回及颞下回的功能连接在健康对照组、CSVD组显著增强;与健康对照组相比,左侧舌回功能连接在CSVD、帕金森病患者中明显减弱;左侧颞中回及右侧中央后回功能连接在健康对照组较CSVD组、帕金森病组增强,CSVD组较帕金森病组增强(图5)。"
| [1] WARDLAW JM, SMITH EE, BIESSELS GJ, et al. Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12(8):822. [2] IADECOLA C, DUERING M, HACHINSKI V, et al. Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia: JACC Scientific Expert Panel. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(25):3326. [3] BOGOLEPOVA AN. Sosudistye kognitivnye narusheniya [Vascular cognitive impairment]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2022; 122(10):17-23. [4] ROSENBERG GA, WALLIN A, WARDLAW JM, et al. Consensus statement for diagnosis of subcortical small vessel disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2016;36(1):6-25. [5] PENG D; Geriatric Neurology Group, Chinese Society of Geriatrics; Clinical Practice Guideline for Cognitive Impairment of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Writing Group. Clinical practice guideline for cognitive impairment of cerebral small vessel disease. Aging Med (Milton). 2019;2(2):64-73. [6] LAU AYL, IP BYM, KO H, et al. Pandemic of the aging society - sporadic cerebral small vessel disease. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(2):143-150. [7] MURPHY C. Olfactory and other sensory impairments in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(1):11-24. [8] SLABIK D, GARASCHUK O. Olfactory dysfunction as a common biomarker for neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(5):1029-1030. [9] TOLOSA E, GARRIDO A, SCHOLZ SW, et al. Challenges in the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2021;20(5):385-397. [10] CAMARGO CHF, JOBBINS VA, SERPA RA, et al. Association between olfactory loss and cognitive deficits in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018;173:120-123. [11] SUI X, ZHOU C, LI J, et al. Hyposmia as a Predictive Marker of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:3753786. [12] SU M, WANG S, FANG W, et al. Alterations in the limbic/paralimbic cortices of Parkinson’s disease patients with hyposmia under resting-state functional MRI by regional homogeneity and functional connectivity analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2015;21(7):698-703. [13] ROH H, KANG J, KOH SB, et al. Hippocampal volume is related to olfactory impairment in Parkinson’s disease. J Neuroimaging. 2021; 31(6):1176-1183. [14] GEORGIOPOULOS C, WITT ST, HALLER S, et al. A study of neural activity and functional connectivity within the olfactory brain network in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2019;23:101946. [15] WALKER IM, FULLARD ME, MORLEY JF, et al. Olfaction as an early marker of Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Handb Clin Neurol. 2021;182:317-329. [16] BARRETT MJ, MURPHY JM, ZHANG J, et al. Olfaction, cholinergic basal forebrain degeneration, and cognition in early Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021;90:27-32. [17] GOLDSTEIN DS, HOLMES C, BENTHO O, et al. Biomarkers to detect central dopamine deficiency and distinguish Parkinson disease from multiple system atrophy. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2008;14(8):600-607. [18] PAOLINI PAOLETTI F, SIMONI S, PARNETTI L, et al. The Contribution of Small Vessel Disease to Neurodegeneration: Focus on Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease and Multiple Sclerosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(9):4958. [19] VISHNEVETSKY A, INCA-MARTINEZ M, MILLA-NEYRA K, et al. The First Report of CADASIL in Peru: Olfactory Dysfunction on Initial Presentation. eNeurologicalSci. 2016;5:15-19. [20] SUH KD, KIM SM, HAN DH, et al. Olfactory Function Test for Early Diagnosis of Vascular Dementia. Korean J Fam Med. 2020;41(3):202-204. [21] 高文鑫,刘华琼,许昌. 静息态功能磁共振在CSVD认知障碍中的研究进展[J]. 影像技术,2022,34(6):61-65. [22] 中国研究型医院学会脑小血管病专业委员会,《中国脑小血管病诊治专家共识》编写组, 胡文立,等. 中国脑小血管病诊治专家共识2021[J]. 中国卒中杂志,2021,16(7):716-726. [23] 周雯,毋愚力,陈科璞. 一种气味呈现工具及其嗅觉测试与训练工具[P]. CN211131007U, 2020-07-31. [24] CHAO-GAN Y, YU-FENG Z. DPARSF: A MATLAB Toolbox for “Pipeline” Data Analysis of Resting-State fMRI. Front Syst Neurosci. 2010;4:13. [25] BATHINI P, BRAI E, AUBER LA. Olfactory dysfunction in the pathophysiological continuum of dementia. Ageing Res Rev. 2019;55: 100956. [26] CHEN B, WANG Q, ZHONG X, et al. Structural and Functional Abnormalities of Olfactory-Related Regions in Subjective Cognitive Decline, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022;25(5):361-374. [27] DU BOISGUEHENEUC F, LEVY R, VOLLE E, et al. Functions of the left superior frontal gyrus in humans: a lesion study. Brain. 2006;129(Pt 12): 3315-3328. [28] FENG M, WEN H, XIN H, et al. Altered Spontaneous Brain Activity Related to Neurologic Dysfunction in Patients With Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021;13:731585. [29] 刘婷, 郭晓鹏, 李丽娟, 等. 卒中后早期认知下降患者默认模式网络和执行控制网络改变的功能磁共振成像研究[J]. 中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2022,24(11):1164-1168. [30] SUN Y, HU Y, QIU Y, et al. Characterization of white matter over 1-2 years in small vessel disease using MR-based quantitative susceptibility mapping and free-water mapping. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:998051. [31] DISBROW EA, SIGVARDT KA, FRANZ EA, et al. Movement activation and inhibition in Parkinson’s disease: a functional imaging study. J Parkinsons Dis. 2013;3(2):181-192. [32] ZHU H, ZHU H, LIU X, et al. Alterations of Regional Homogeneity in Parkinson’s Disease: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) Study. Cureus. 2022;14(7):e26797. [33] AZAMAT S, BETUL ARSLAN D, ERDOGDU E, et al. Detection of visual and frontoparietal network perfusion deficits in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Eur J Radiol. 2021;144:109985. [34] YUAN X, HAN Y, WEI Y, et al. Regional homogeneity changes in amnestic mild cognitive impairment patients. Neurosci Lett. 2016;629:1-8. [35] FAN W, LI H, LI H, et al. Association between Functional Connectivity of Entorhinal Cortex and Olfactory Performance in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2022;12(8):963. [36] YONEYAMA N, WATANABE H, KAWABATA K, et al. Severe hyposmia and aberrant functional connectivity in cognitively normal Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190072. [37] DINTICA CS, MARSEGLIA A, RIZZUTO D, et al. Impaired olfaction is associated with cognitive decline and neurodegeneration in the brain. Neurology. 2019;92(7):e700-e709. [38] TAN Z, WANG Y, LU H, et al. The Effects of Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging Indices in the Association of Olfactory Identification and Cognition in Chinese Older Adults. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14: 873032. [39] TIAN Q, AN Y, KITNER-TRIOLO MH, et al. Associations of Olfaction With Longitudinal Trajectories of Brain Volumes and Neuropsychological Function in Older Adults. Neurology. 2023;100(9):e964-e974. [40] TIAN Q, BILGEL M, MOGHEKAR AR, et al. Olfaction, Cognitive Impairment, and PET Biomarkers in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;86(3):1275-1285. [41] DADAR M, GEE M, SHUAIB A, et al. Cognitive and motor correlates of grey and white matter pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102353. [42] SCAMARCIA PG, AGOSTA F, SPINELLI EG, et al. Longitudinal White Matter Damage Evolution in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov Disord. 2022; 37(2):315-324. [43] MASALA C, CAVAZZANA A, SANNA F, et al. Correlation between olfactory function, age, sex, and cognitive reserve index in the Italian population. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022;279(10):4943-4952. |
| [1] | Shi Jiao, Li Xingjie, Liu Qiqi, Liu Jun, Yuan Xu, Chen Shangjie. Effect of electronic moxibustion on the volume of hippocampal subregion in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(20): 3176-3181. |
| [2] | Xu Kangli, An Lanhua, Zhang Jinsheng, Du Xiaoyan, Yin Lele, Zhang Xixian. Research hotspots and frontiers of functional magnetic resonance imaging in treatment of ischemic stroke by traditional Chinese medicine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(11): 1789-1796. |
| [3] | Bao Wenxia, Zhan Dongge, Wang Nian, Yang Xianjun, Ding Chengbiao. Foot-type recognition algorithm based on plantar pressure images [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(4): 527-533. |
| [4] | Zhang Yeting, Fu Yan, Li Xue, Wei Cuilan, Li Chuikun, Yuan Qiongjia. Effects of aerobic exercise on learning, memory, and hippocampal neuromorphology in mice with Alzheimer’s disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3188-3194. |
| [5] | Liu Yunqin, Lin Li, Xiao Wenhao, Ji Qiuming, Liu Yanqin. Effects of icariin on NRG1-ErbB signaling pathways in hippocampus of schizophrenia rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(20): 3236-3241. |
| [6] | Tang Jiping, Zhang Yeting. Exercise regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease: mechanism and role [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 798-803. |
| [7] | Zhao Yiming, Wang Jie, Zhang Gaowei, Sun Jianjun, Yang Peng. Recognition of human lower limb movement intention based on surface electromyography of lower limb corresponding to five gaits [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(12): 1805-1811. |
| [8] | Zhao Xiang, Wei Cuilan, Zhang Yeting. Neurogenesis and neuroinflammation under exercise: alteration and regulation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 813-820. |
| [9] | Fan Jin, Zeng Luyao, Zhong Dongling, Li Yuxi, Tian Yanping, Huang Yijie, Jin Rongjiang. Development of functional near-infrared spectroscopy in recent 10 years: a visual analysis using CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3711-3717. |
| [10] | Chen Yanlin, Xu Lin, Xu Shengjia. Effects of physical activity on hippocampal plasticity and cognition [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 773-779. |
| [11] | Li Huijun, Wei Cuilan, Li Chuikun, Zhang Yeting. Sports and cognition: a visual analysis using Citespace software [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2277-2283. |
| [12] | Guo Xiaozheng, Wang Xing. Improvement of cognitive function in older adults based on near-infrared spectroscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1790-1796. |
| [13] | Zhang Lin1, Liu Jinjie1, Zhao Yan2, Liu Yi1, Lin Jianwen1. N-butylphthalide affects cognitive function of APP/PS1 transgenic mice (Alzheimer’s disease model) [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(在线): 1-6. |
| [14] | Chen Lingling, Yang Zekun, Sun Jianjun, Zhang Cun. Motion compatibility recognition of walk-aid robot based on multi-scale permutation entropy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(34): 5473-5478. |
| [15] | Hao Jinghan, Yang Peng, Chen Lingling, Geng Yanli. A gait recognition approach based on surface electromyography and triaxial acceleration signals [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5164-5169. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||