Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (12): 1829-1836.doi: 10.12307/2024.017
Previous Articles Next Articles
Mechanical analysis and finite element modeling of rabbit patellar tendon and tendon insertion under different mechanical conditions
Wang Li, Wang Bo
- Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Received:2022-12-06Accepted:2023-03-02Online:2024-04-28Published:2023-08-22 -
Contact:Wang Bo, PhD, Lecturer, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Wang Li, Master, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
Supported by:Special Fund for Basic Scientific Research Business Expenses in Central Universities, No. 2017QN009 (to WB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Li, Wang Bo. Mechanical analysis and finite element modeling of rabbit patellar tendon and tendon insertion under different mechanical conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(12): 1829-1836.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
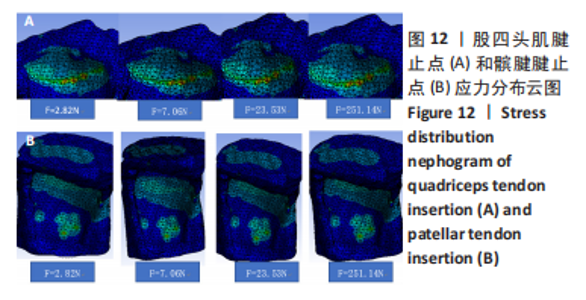
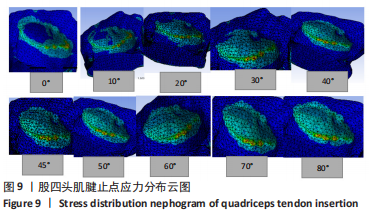
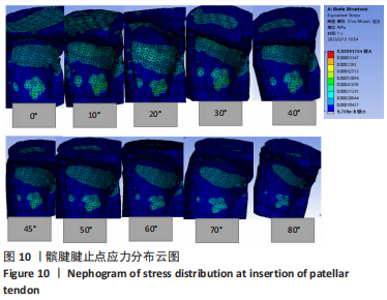
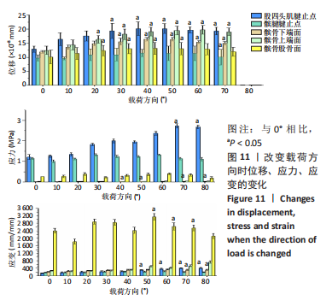
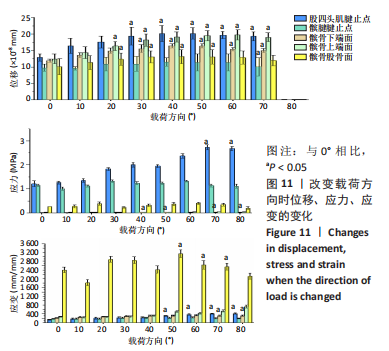
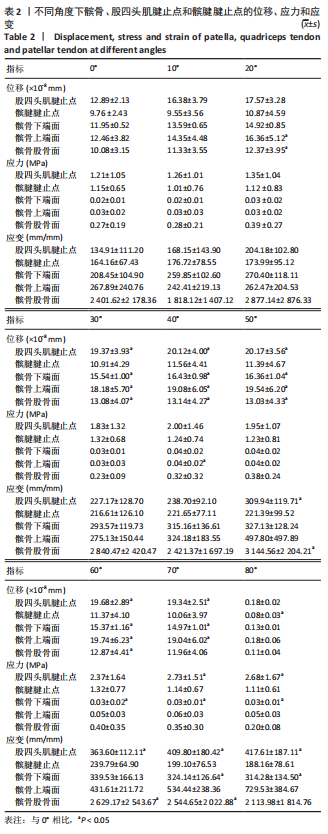
从应力上看,整个变化过程中股四头肌腱止点承受的应力最大,髌腱次之,髌骨上与各部位接触区域的应力则远小于股四头肌腱止点和髌腱腱止点。且随着角度增加,股四头肌腱止点和髌腱腱止点两部分应力差距逐渐增大。与0°位置相比,股四头肌腱止点在70°,80°时有显著性差异,髌腱腱止点无显著性差异,髌骨下端面在60°,70°,80°时差异有显著性意义,髌骨上端面在40°时差异有显著性意义,髌骨股骨面无显著性差异(图11,表2)。 从应变来看,髌腱腱止点承受的应变最小,髌骨上与股骨接触的区域应变最大。与0°位置相比,股四头肌腱止点在50°,60°,70°,80°时差异有显著性意义,髌腱腱止点无显著性差异,髌骨下端面在70°,80°时差异有显著性意义,髌骨上端面无显著性差异,髌骨股骨面50°,60°,70°时差异有显著性意义(图11,表2)。 2.3 相同方向不同载荷下的比较结果 从分布趋势来看,载荷大小的改变在位移、应力、应变方面对髌骨、股四头肌腱止点、髌腱腱止点等部位均无影响(图12)。"
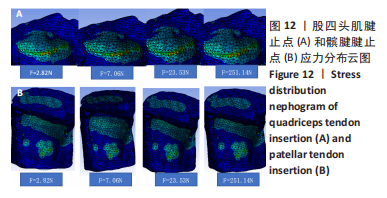
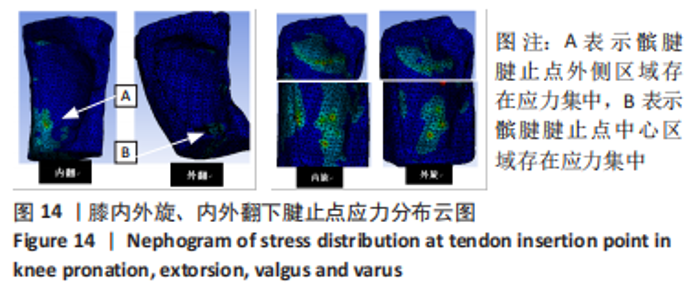
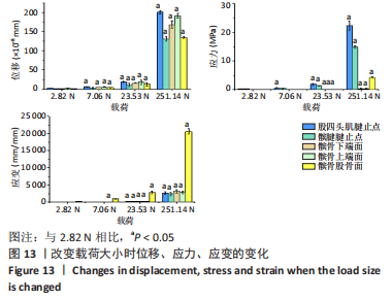
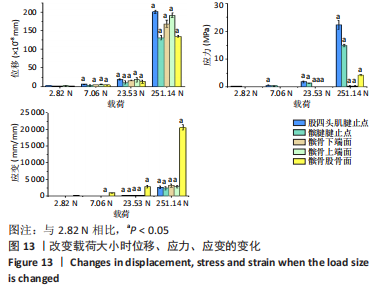
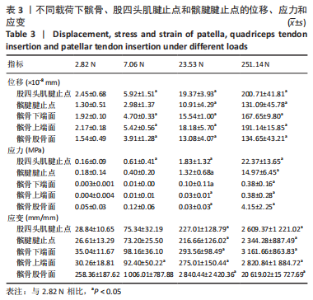
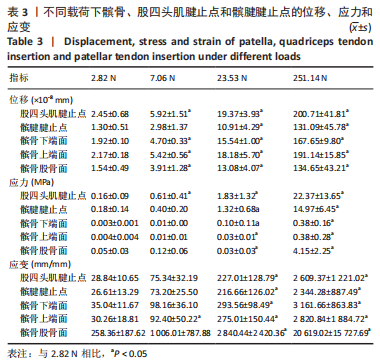
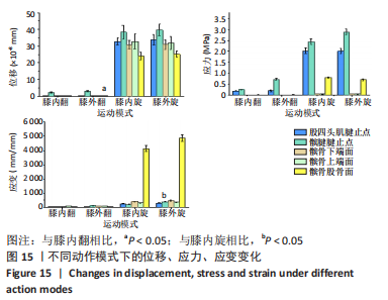
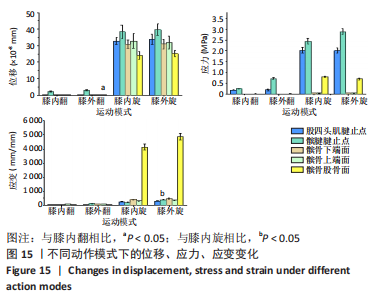
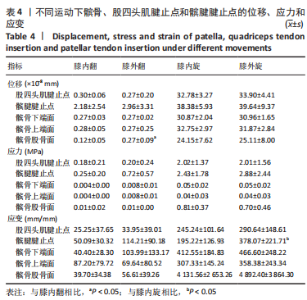
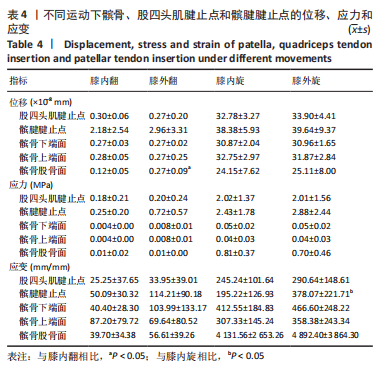
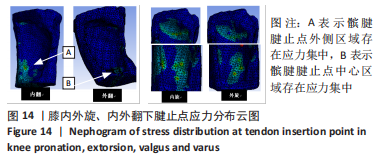
从应力来看,载荷变化过程中股四头肌腱止点的应力始终大于髌腱腱止点,髌骨上各区域承受的应力小于两端腱止点。与2.82 N相比,股四头肌腱止点在3种不同载荷下差异均有显著性意义,髌腱腱止点、髌骨上端面、髌骨下端面、髌骨股骨面均在23.53 N和25.14 N时差异有显著性意义(图13,表3)。 从应变来看,髌腱腱止点始终是最低的应变区域,且始终低于股四头肌腱止点,髌骨上与股骨接触的区域应变最高。与2.82 N相比,髌骨上端面在3种不同载荷下差异均有显著性意义,髌腱腱止点、股四头肌腱止点、髌骨下端面、髌骨股骨面均在23.53 N和25.14 N时差异有显著性意义(图13,表3)。 2.4 膝内外翻与内外旋模式下的结果 从图像趋势分布来看,在内外翻模式下髌腱腱止点处有应力集中,同时股四腱止点处也存在少许的应力集中现象,外翻模式下髌腱腱止点应力集中的区域更集中于髌腱插入髌骨的部分。在内外旋的模式下,股四头肌腱止点和髌腱腱止点都有应力集中的现象,且髌腱腱止点产生应力集中的面积、程度大于股四头肌腱止点。内旋与外旋从图示直观比较可发现内旋模式下髌腱腱止点应力集中区域较大,而外旋模式下应力集中范围较小(图14)。"
| [1] GOMEZ-FLORIT M, LABRADOR-RACHED CJ, DOMINGUES RMA, et al. The tendon microenvironment: Engineered in vitro models to study cellular crosstalk. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;185:114299. [2] ANDARAWIS-PURI N, FLATOW EL, SOSLOWSKY LJ. Tendon basic science: Development, repair, regeneration, and healing. J Orthop Res. 2015;33(6):780-784. [3] SCHWARTZ A, WATSON JN, HUTCHINSON MR. Patellar Tendinopathy. Sports Health. 2015;7(5):415-420. [4] FAIRLEY J, TOPPI J, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Association between obesity and magnetic resonance imaging defined patellar tendinopathy in community-based adults: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:266. [5] TOPPI J, FAIRLEY J, CICUTTINI FM, et al. Factors associated with magnetic resonance imaging defined patellar tendinopathy in community-based middle-aged women: a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:184. [6] LIAN OB, ENGEBRETSEN L, BAHR R. Prevalence of jumper’s knee among elite athletes from different sports: a cross-sectional study. Am J Sports Med. 2005; 33(4):561-567. [7] HäGGLUND M, ZWERVER J, EKSTRAND J. Epidemiology of patellar tendinopathy in elite male soccer players. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(9):1906-1911. [8] HEMS T, TILLMANN B. Tendon entheses of the human masticatory muscles. Anat Embryol (Berl). 2000;202(3):201-208. [9] ALMEKINDERS LC, VELLEMA JH, WEINHOLD PS. Strain patterns in the patellar tendon and the implications for patellar tendinopathy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2002;10(1):2-5. [10] 李海伟,刘志宇,陈振,等. 过度使用性肌腱病在体动物模型及诊断标准研究进展[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(12):1105-1111. [11] WANG L, XIONG K, WANG B, et al. Effects of Time to Start Training After Acute Patellar Tendon Enthesis Injuries on Healing of the Injury in a Rabbit Model. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(10):2405-2410. [12] 王博, 白胜超, 李文博, 等. 高强度跳跃肌腱损伤即刻冷水浸没干预模型兔髌腱组织内的炎症反应和胶原重塑[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(29): 4619-4625. [13] WILLIAMSON PM, FREEDMAN BR, KWOK N, et al. Tendinopathy and tendon material response to load: What we can learn from small animal studies. Acta Biomater. 2021;134:43-56. [14] 王琳. 髌骨骨腱结合部损伤延迟愈合模型建立及冲击波治疗效果的研究[D]. 北京:北京体育大学,2007. [15] 王博. 显微CT在骨腱结合部损伤中的应用与低强度循环载荷对损伤的影响[D]. 北京:北京体育大学,2012. [16] 刘波. 不同性别的兔髌腱、跟腱及屈趾肌腱生物力学特性测试[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志,1996,13(2):113-118+122. [17] ERDEMIR A, GUESS TM, HALLORAN J, et al. Considerations for reporting finite element analysis studies in biomechanics. J Biomech. 2012;45(4):625-633. [18] BURKHART TA, ANDREWS DM, DUNNING CE. Finite element modeling mesh quality, energy balance and validation methods: a review with recommendations associated with the modeling of bone tissue. J Biomech. 2013;46(9):1477-1488. [19] 张太良. 兔膝关节有限元模型的建立及前交叉韧带重建后力学分析[D]. 乌鲁木齐:新疆医科大学,2017. [20] KOT BC, ZHANG ZJ, LEE AW, et al. Elastic modulus of muscle and tendon with shear wave ultrasound elastography: variations with different technical settings. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e44348. [21] LIU H, GAO F, LIANG X, et al. Pathogenesis and Development of Patellar Tendon Fibrosis in a Rabbit Overuse Model. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(5):1141-1150. [22] 赵怡淇, 黄桂武, 李文昌, 等. 中国南方人股骨干形态特征及其对股骨外翻角的影响[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2022,40(1):4-9. [23] SPRAGUE AL, SMITH AH, KNOX P, et al. Modifiable risk factors for patellar tendinopathy in athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(24):1575-1585. [24] MAGANARIS CN, NARICI MV, ALMEKINDERS LC, et al. Biomechanics and pathophysiology of overuse tendon injuries: ideas on insertional tendinopathy. Sports Med. 2004;34(14):1005-1017. [25] IKOMA K, KIDO M, NAGAE M, et al. Effects of stress-shielding on the dynamic viscoelasticity and ordering of the collagen fibers in rabbit Achilles tendon. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(11):1708-1712. [26] SU W, QI W, LI X, et al. Effect of Suture Absorbability on Rotator Cuff Healing in a Rabbit Rotator Cuff Repair Model. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(11):2743-2754. [27] UNSAL SS, YILDIRIM T, KAYALAR M. Comparison of two coracoid process transfer techniques on stress shielding using three-dimensional finite-element model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):371. [28] KAGE T, SANADA T, IWASO H, et al. Morphology of Acute Achilles Tendon Rupture by Intraoperative Evaluation. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2021;60(6):1198-1203. [29] PASSINI FS, JAEGER PK, SAAB AS, et al. Shear-stress sensing by PIEZO1 regulates tendon stiffness in rodents and influences jumping performance in humans. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5(12):1457-1471. [30] YIN NH, MCCARTHY I, BIRCH HL. An equine tendon model for studying intra-tendinous shear in tendons that have more than one muscle contribution. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:205-212. [31] LINDERMAN SW, GOLMAN M, GARDNER TR, et al. Enhanced tendon-to-bone repair through adhesive films. Acta Biomater. 2018;70:165-176. [32] BEKENY JC, ZOLPER EG, DEKKER PK, et al. Long Term Follow-up of Composite Flaps for Single-stage Reconstruction of Concomitant Tendon and Soft Tissue Defects. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022;10(1):e4023. |
| [1] | Yang Yifeng, Ye Nan, Wang Lin, Guo Shuaicheng, Huang Jian. Signaling pathway of dexmedetomidine against ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1464-1469. |
| [2] | Li Zhifei, Yang Yin, Chen Hualong, Liang Qinqiu, Zhong Yuanming, Zhang Yisheng. Finite element analysis of the correlation between tilt angle of titanium cage and postoperative subsidence of titanium cage after anterior subtotal cervical corpectomy, decompression and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1313-1319. |
| [3] | Liang Cheng, Zhang Linqi, Wang Guan, Li Wen, Duan Ke, Li Zhong, Lu Xiaobo, Zhuo Naiqiang. Finite element and biomechanical analysis of different implants in repair for unilateral unstable pelvic posterior ring injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1336-1341. |
| [4] | Guo Sutong, Feng Dehong, Guo Yu, Wang Ling, Ding Yujian, Liu Yi, Qian Zhengying, Li Mingyang. Construction and finite element analysis of normal and osteoporotic hip models [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1342-1346. |
| [5] | Yang Junliang, Lu Tan, Xu Biao, Jiang Yaqiong, Wang Fucheng. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of effects of partial anterior cruciate ligament rupture on knee joint stress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(9): 1347-1353. |
| [6] | Xiaheida·Yilaerjiang, Nijiati·Tuerxun, Reyila·Kuerban, Baibujiafu·Yelisi, Chen Xin. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the distribution pattern of stress in bone tissues with different characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1277-1282. |
| [7] | Lou Guo, Zhang Yan, Fu Changxi. Role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in exercise preconditioning-induced improvement of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1283-1288. |
| [8] | Li Rui, Zhang Guihong, Wang Tao, Fan Ping. Effect of ginseng polysaccharide on the expression of prostaglandin E2/6-keto-prostaglandin 1alpha in traumatic osteoarthritis model rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(8): 1235-1240. |
| [9] | Pan Xiaolong, Fan Feiyan, Ying Chunmiao, Liu Feixiang, Zhang Yunke. Effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on inhibiting the aging of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(7): 1091-1098. |
| [10] | Wang Qiang, Li Shiyun, Xiong Ying, Li Tiantian. Biomechanical changes of the cervical spine in internal fixation with different anterior cervical interbody fusion systems [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 821-826. |
| [11] | Wei Yuanbiao, Lin Zhan, Chen Yanmei, Yang Tenghui, Zhao Xiao, Chen Yangsheng, Zhou Yanhui, Yang Minchao, Huang Feiqi. Finite element analysis of effects of sagittal cervical manipulation on intervertebral disc and facet joints [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 827-832. |
| [12] | Zhang Rui, Wang Kun, Shen Zicong, Mao Lu, Wu Xiaotao. Effects of endoscopic foraminoplasty and laminoplasty on biomechanical properties of intervertebral disc and isthmus [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 833-839. |
| [13] | Kang Zhijie, Cao Zhenhua, Xu Yangyang, Zhang Yunfeng, Jin Feng, Su Baoke, Wang Lidong, Tong Ling, Liu Qinghua, Fang Yuan, Sha Lirong, Liang Liang, Li Mengmeng, Du Yifei, Lin Lin, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe, Li Zhijun. Finite element model establishment and stress analysis of lumbar-sacral intervertebral disc in ankylosing spondylitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 840-846. |
| [14] | Huang Peizhen, Dong Hang, Cai Qunbin, Lin Ziling, Huang Feng. Finite element analysis of anterograde and retrograde intramedullary nail for different areas of femoral shaft fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 868-872. |
| [15] | Tan Nengxian, Wu Wenzheng, Zheng Churong, Luo Lieliang, Gu Peng, Ouyang Chongzhi, Zheng Xiaohui. Finite element analysis of different fixation methods of partially threaded cannulated screws for treating vertical femoral neck fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(6): 873-878. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||