Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (17): 2687-2696.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3138
Previous Articles Next Articles
An exploration on mechanism of Shengyu Decoction in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on network pharmacology
Zhou Yi, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lai Yu, Liao Jianzhao, Li Shibin
- Department of Traumatology and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2020-05-06Revised:2020-05-12Accepted:2020-06-03Online:2021-06-18Published:2021-01-08 -
Contact:Chen Yueping, MD, Chief physician, Department of Traumatology and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhou Yi, Master candidate, Department of Traumatology and Hand Surgery, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760796 and 81960803 (both to CYP); Young Teachers’ Basic Ability Improvement Project of Guangxi Colleges and Universities, No. 2019KY0352 (to ZXY); 2019 School-level Scientific Research Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019QN027 (to ZXY); Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, No. 2015GXNSFAA139136 (to CYP); First-class Subject Construction Open Project of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, No. 2019XK029 (to ZXY); Key Project of Guangxi Health Department, No. S201419-05 (to CYP); 2016 National Distinguished Chinese Physician-Huang Yourong Inheritance Studio Construction Project (to ZXY [project participant]); Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine Qihuang Engineering High-level Talents Cultivation Project-Traditional Chinese Medicine Master Wei Guikang's Academic Thought Inheritance and Innovation, No. 2018004 (to ZXY [project participant])
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Yi, Chen Yueping, Zhang Xiaoyun, Lai Yu, Liao Jianzhao, Li Shibin. An exploration on mechanism of Shengyu Decoction in treating osteonecrosis of the femoral head based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2687-2696.
share this article
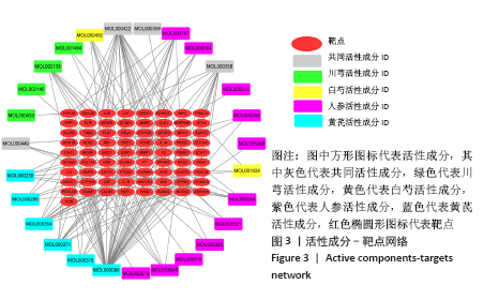
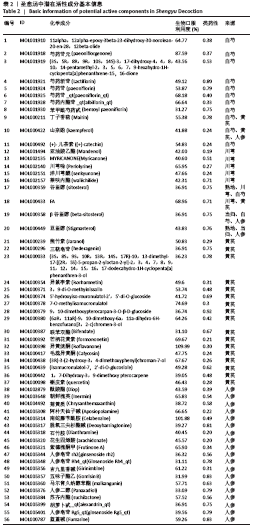
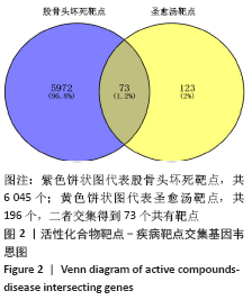
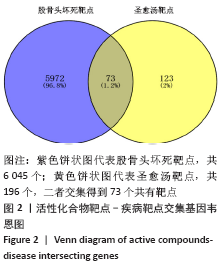
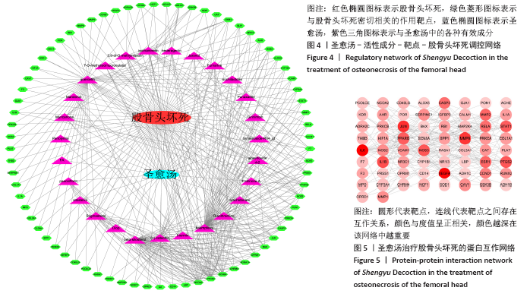
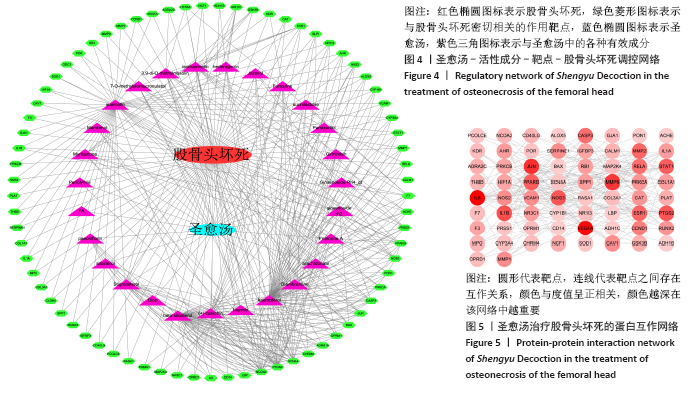
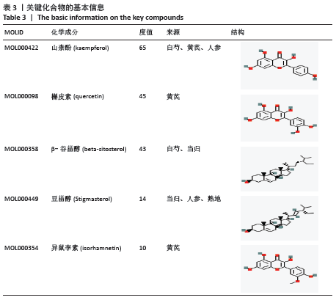
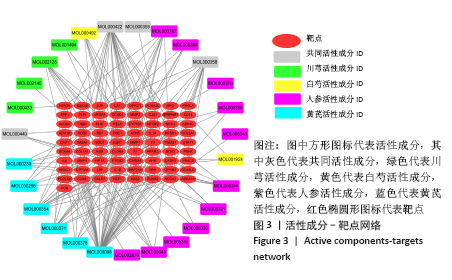
2.4 构建“活性成分-靶点”和“疾病-药物-活性成分-靶点”网络 运用Cytoscape软件构建“活性成分-靶点”网络,见图3,共包括100个节点(27个活性成分节点和73个靶点节点)和182条边。同时构建“疾病-药物-活性成分-靶点”,见图4。使用Network analyze功能对网络进行拓扑属性分析,其中度值是衡量1个节点在网络中关键性的重要参数。该网络中度值排名前5位的化合物分别是山柰酚 (kaempferol)、槲皮素(quercetin)、β-谷甾醇(beta-sitosterol)、豆甾醇(Stigmasterol)和异鼠李素(isorhamnetin)、分别能与65,45,43,14,10个靶点连接,对治疗股骨头坏死具有重要的意义,其基本信息见表3。 2.4 构建“活性成分-靶点”和“疾病-药物-活性成分-靶点”网络 运用Cytoscape软件构建“活性成分-靶点”网络,见图3,共包括100个节点(27个活性成分节点和73个靶点节点)和182条边。同时构建“疾病-药物-活性成分-靶点”,见图4。使用Network analyze功能对网络进行拓扑属性分析,其中度值是衡量1个节点在网络中关键性的重要参数。该网络中度值排名前5位的化合物分别是山柰酚 (kaempferol)、槲皮素(quercetin)、β-谷甾醇(beta-sitosterol)、豆甾醇(Stigmasterol)和异鼠李素(isorhamnetin)、分别能与65,45,43,14,10个靶点连接,对治疗股骨头坏死具有重要的意义,其基本信息见表3。 2.5 PPI网络及网络拓扑分析结果 通过STRING数据库以最低要求互动得分(minimum required interaction score)为0.7为筛选参数分析共得到233对蛋白互作关系,涉及73个蛋白靶点。采用Cytoscape软件构建蛋白互作网络,见图5。 "
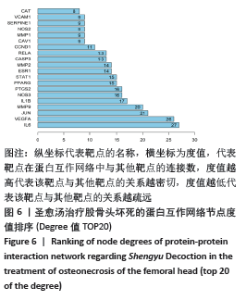
文章通过Network Analyzer工具分析网络中节点的度值,将度值≥8(均值)的靶点由高到低排序,见图6。度值排名前5的蛋白基因是炎性细胞因子白细胞介素6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)、血管内皮生长因子A(Vascular endothelial growth factor A,VEGFA)、原癌基因蛋白(Proto-oncogene proteins,jun)、基质金属肽酶9(Matrix metalloproteinase-9,MMP9)及炎性细胞因子白细胞介素1β(Interleukin-1 beta,IL-1β)。这些蛋白在整个网络中起着关键的作用,蛋白所对应的靶点在圣愈汤治疗治疗股骨头坏死中具有重要作用,认为是圣愈汤治疗股骨头坏死的关键靶点。"
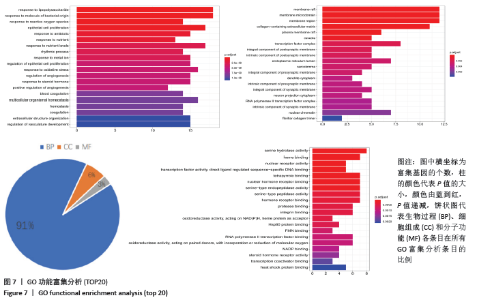
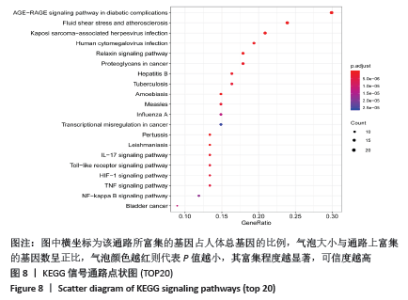
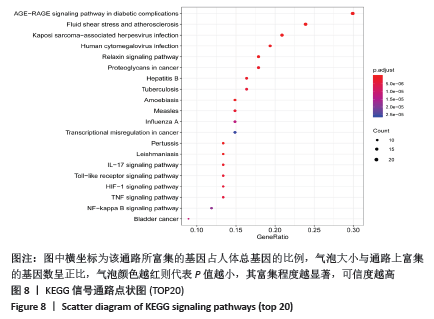
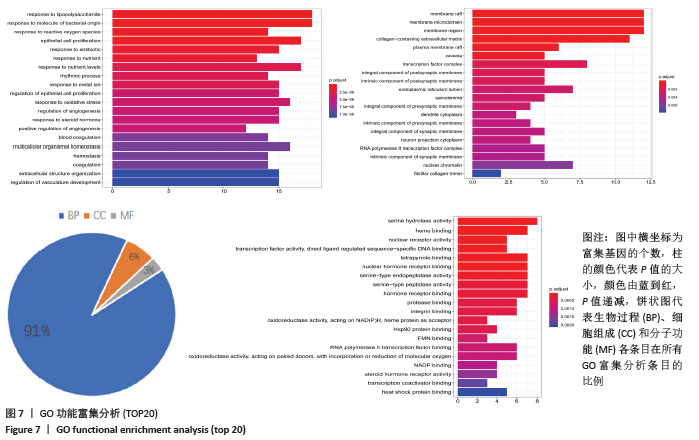
2.6 GO富集分析结果 GO富集分析得到GO条目共804个(P < 0.01),其中生物过程(BP)、细胞组成(CC)和分子功能(MF)条目分别为732,23,49个。 从生物过程的相关条目分析,圣愈汤治疗股骨头坏死的靶点主要参与对炎症反应(Inflammatory reaction)、氧化应激反应(response to oxidative stress)和血管生成调节(regulation of angiogenesis)等过程;从细胞组成的相关条目分析,治疗靶点主要包括转录因子复合体(transcription factor complex)、内质网腔(intrinsic component of postsynaptic)及核染色质(RNA polymerase II transcription factor)等区域;从分子功能的相关条目分子,治疗靶点主要与丝氨酸水解酶活性(serine hydrolase activity)、调节核受体活性(nuclear receptor activity)和蛋白酶结合(protease binding)等方面相关。根据P值排序,每个模块前20位的条目见图7。 "
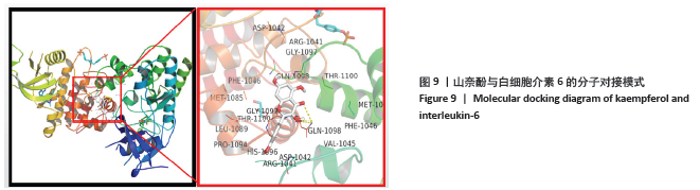
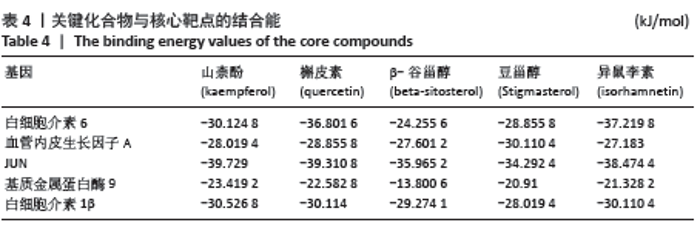
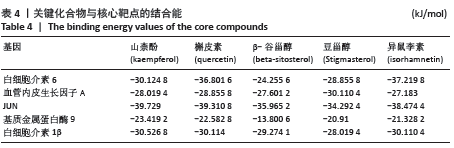
2.8 分子对接验证 将“2.4”项筛选出的关键化合物和“2.5”项的关键靶蛋白进行分子对接验证。分子对接结果显示圣愈汤关键活性化合物与靶蛋白的分子对接亲和力均远小于-5.0 kJ/mol,结果表明圣愈汤中关键化合物与关键靶蛋白有较好的结合活性,结果见表4。山奈酚为预测靶点最多的活性成分,白细胞介素6为PPI网络中degree值最大的靶点,以山奈酚和白细胞介素6蛋白结构对接模式为例,结果显示山柰酚能稳定地对接到白细胞介素6蛋白结构的活性口袋中,见图9;山奈酚与白细胞介素6蛋白结合关键疏水氨基酸残基是ASP-1042,ARG-01041,GLY-1097,GLN-1098,THR-1100,PHE-1046, MET-1085,VAL-1045和HIS-1096。 "
| [1] 赵德伟,胡永成.成人股骨头坏死诊疗标准专家共识(2012年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2012,6(3):479-484 [2] ZHAO DW, YU M, HU K, et al. Prevalence of nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head and its associated risk factors in the chinese population: results from a nationally representative survey. Chin Med J (Engl). 2015;128(21):2843-2850. [3] 周明旺,陈彦同,李盛华,等.股骨头坏死保髋治疗[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019, 25(9):1351-1356. [4] 陈卫衡,何伟,童培建,等.股骨头坏死中医辨证标准(2019年版)[J].中医正骨, 2019,31(6):1-2. [5] 王晨,施杞.施杞辨治股骨头坏死经验撷菁[J].上海中医药杂志,2015,49(11):1-3. [6] 刘粉叶,沙其朋,王娓娓.益气养血法对骨髓抑制小鼠骨髓造血的促增殖作用及机制[J].中华中医药学刊,2019,37(10): 2328-2331. [7] HAI YX, YAN QZ, ZHEN ML, et al. ETCM: an encyclopaedia of traditional Chinese medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1): D976-D982. [8] EDGAR R, DOMRACHEV M, LASH AE. Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(1):207-210. [9] TROTT O, OLSON AJ. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading[J]. J Comput Chem. 2010;31(2):455-461. [10] 徐森楠,庄莉,翟园园,等.基于网络药理学研究二至丸防治骨质疏松症的物质基础与作用机制[J].中国药学杂志,2018, 53(22):1913-1920. [11] YU X, ZHANG D, CHEN X, et al. Effectiveness of various hip preservation treatments for non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Sci. 2018;23(2):356-364. [12] PISANI LP, ESTADELLA D, RIBEIRO DA. The role of toll like receptors (TLRs) in oral carcinogenesis. Anticancer Res. 2017; 37(10):5389-5394. [13] GÜLER-YÜKSEL M, HOES JN, BULTINK IEM, et al. Glucocorticoids, Inflammation and Bone. Calcif Tissue Int. 2018;102(5): 592-606. [14] JOHNSON RW, MCGREGOR NE, BRENNAN HJ, et al. Glycoprotein130 (Gp130)/interleukin-6 (IL-6) signalling in osteoclasts promotes bone formation in periosteal and trabecular bone. Bone. 2015;2015(81): 343-351. [15] TANAKA Y, TAKEUCHI T, AMANO K, et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor, tocilizumab, in preventing joint destruction in patients with rheumatoid arthritis showing inadequate response to TNF inhibitors. Modern Rheumatol. 2014;24(3): 399-404. [16] LANGE J, SAPOZHNIKOVA A, LU C, et al. Action of IL-1beta during fracture healing. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(6):778-784. [17] CZEKANSKA EM, RALPHS JR, ALINI M, et al. Enhancing inflammatory and chemotactic signals to regulate bone regeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;28:320-334. [18] VOSS JO, LOEBEL C, BARA JJ, et al. Effect of short-term stimulation with interleukin-1β and differentiation medium on human mesenchymal stromal cell paracrine activity in coculture with osteoblasts. BioMed Res Int. 2015;2015:714230. [19] 郭成龙,魏玉娇,何玲,等.生骨再造丸对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠骨代谢及炎症细胞因子表达的影响[J].中药药理与临床,2019,35(4):170-174. [20] 帅波,沈霖,杨艳萍,等.古方青娥丸加味干预早期非创伤性股骨头缺血性坏死骨转换标志物、血流变及炎症相关因子的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(46):6907-6914. [21] SODHI CP, NEAL MD, SIGGERS R, et al. Intestinal epithelial Toll-like receptor 4 regulates goblet cell development and is required for necrotizing enterocolitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3): 708-718. [22] YAMAGUCHI M, WEITZMANN MN. Quercetin,a potent suppressor of NF-κB and Smad activation in osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 2011;28(4):521-525. [23] BELLEI B, PITISCI A, IZZO E, et al. Inhibition of melanogenesis by the pyridinyl imidazole class of compounds: possible involvement of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e33021. [24] MENG L, SUN JY. Progression of TLR4 signal pathway in osteoblast. Chinese J Osteop Bone Mineral Res. 2013;6(3):260-265. [25] 李文锋,侯树勋,张伟佳,等.TNF-α-NF-κB对成骨细胞分化过程中BMP-2-Smad1信号通路的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2011,17(1):1-4. [26] 李知玻,李子锋,章莹,等. TNF-α对成骨细胞凋亡作用的探讨[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2012,18(10):892-894. [27] GLASS GE, CHAN JK, FREIDIN A, et al. TNF-alpha promotes fracture repair by augmenting the recruitment and differentiation of muscle-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(4): 1585-1590. [28] LI JK, CHENG L, ZHAO YP, et al. ADAMTS-7 exhibits elevated expression in cartilage of osteonecrosis of femoral head and has a positive correlation with TNF- α and NF- κB P65. Mediators Inflamm. 2015; 2015:196702. [29] CHEN G, DENG C, LI YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8(2): 272-288. [30] ZHANG JR, PANG DD, TONG Q, et al. Different modulatory effects of IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23 on osteoblast differentiation. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:5950395. [31] HUANG H, KIM HJ, CHANG EJ, et al. IL-17 stimulates the proliferation and differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells: implications for bone remodeling. Cell Death Differ. 2009;16(10):1332-1343. [32] ZHAO L, LIU Z, YANG F, et al. Intrabody against prolyl hydroxylase 2 promotes angiogenesis by stabilizing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11861. [33] LI J, FAN L, YU Z, et al. The effect of deferoxamine on angiogenesis and bone repair in steroid-induced osteonecrosis of rabbit femoral heads. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(2):273-280. [34] ZHANG W, YUAN Z, PEI X, et al. In vivo and in vitro characteristic of HIF-1α and relative genes in ischemic femoral head necrosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(6):7210-7216. [35] MA W, XIN K, CHEN K, et al. Relationship of common variants in VEGFA gene with osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a Han Chinese population based association study. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):16221. [36] SONG J, JING Z, HU W, et al. α-linolenic acid inhibits receptor activator of NF-κB ligand induced (RANKL-Induced) osteoclastogenesis and prevents inflammatory bone loss via downregulation of nuclear factor-kappaB-inducible nitric oxide synthases (NF-κB-iNOS) signaling pathways. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23: 5056-5069. [37] 徐涛涛,劳杨骏,廖菲,等.HIF-1α信号通路与激素性股骨头坏死相关性研究进展[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2015,10(5):730-733. [38] WU J, YAO L, WANG B, et al. Tao-Hong-Si-Wu Decoction ameliorates steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head by regulating the HIF-1α pathway and cell apoptosis. Biosci Trends. 2016;10(5): 410-417. [39] CASADO-DÍAZ A, ANTER J, DORADO G, et al. Effects of quercetin, a natural phenolic compound, in the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) into adipocytes and osteoblasts. J Nutr Biochem. 2016;32:151-162. [40] GE YW, FENG K, LIU XL, et al. Quercetin inhibits macrophage polarization through the p-38α/β signalling pathway and regulates OPG/RANKL balance in a mouse skull model. Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(5): 3203-3216. [41] KIM IR, KIM SE, BAEK HS, et al. The role of kaempferol-induced autophagy on differentiation and mineralization of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016;16(1):333. [42] 刘威良,姬昱,黄艾祥.β-谷甾醇的研究及开发进展[J].农产品加工,2019, (1):77-79. [43] DAS N, BHATTACHARYA A, KUMAR MANDAL S, et al. Ichnocarpus frutescens (L.) R. Br. root derived phyto-steroids defends inflammation and algesia by pulling down the pro-inflammatory and nociceptive pain mediators: an in-vitro and in-vivo appraisal. Steroids. 2018;139:18-27. [44] CHAUHAN S, SHARMA A, UPADHYAY NK, et al. In-vitro osteoblast proliferation and in-vivo anti-osteoporotic activity of Bombax ceiba with quantification of Lupeol, gallic acid and β-sitosterol by HPTLC and HPLC. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018;18(1): 233. [45] GABAY O, SANCHEZ C, SALVAT C, et al. Stigmasterol: a phytosterol with potential anti-osteoarthritic properties. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):106-116. [46] YANG L, CHEN Q, WANG F, et al. Antiosteoporotic compounds from seeds of Cuscuta chinensis. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011;135(2):553-560. [47] 谢兴文,徐世红,李宁.中药单味或单体诱导骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化研究概况[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2010, 18(10):65-67. [48] COOK D, GENEVER P. Regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;(786):213-229. [49] XU S, ZHANG L, JIN H, et al. Autologous stem cells combined core decompression for treatment of avascular necrosis of the femoral head: a systematic meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2017;(2017):6136205. [50] KANG JS, MOON KH, KIM BS, et al. Clinical results of auto-iliac cancellous bone grafts combined with implantation of autologous bone marrow cells for osteonecrosis of the femoral head:a minimum 5-year follow-up. Yonsei Med J. 2013;54(2):510-515. [51] 徐凌霄,高俊,张前德.左归丸含药血清对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞骨向分化中碱性磷酸酶含量的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(7):149-152. [52] 廖清船,肖洲生,秦艳芳,等.植物雌激素金雀异黄酮通过p38MAPK通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[J].中国药理学通报,2006,22(6):683-687. |
| [1] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [2] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [11] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [12] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [13] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [14] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| [15] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||