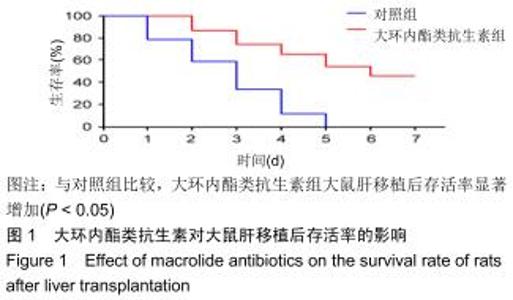
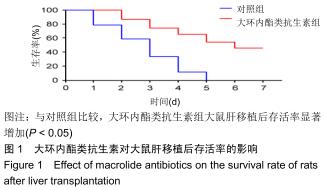
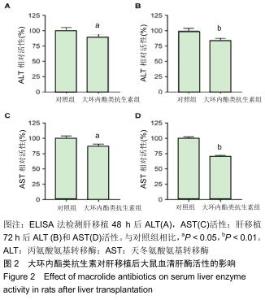
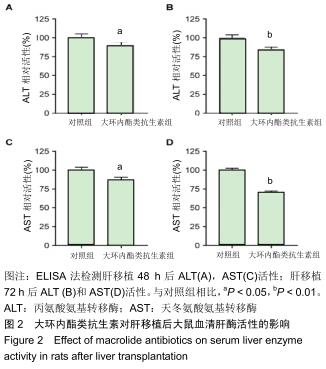
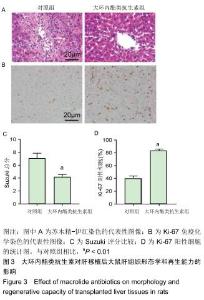
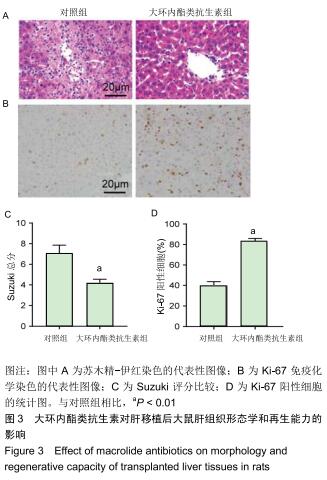
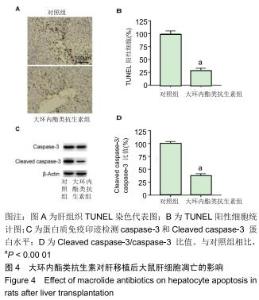
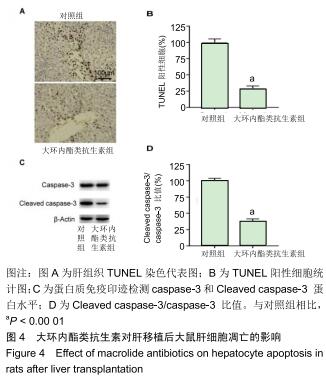
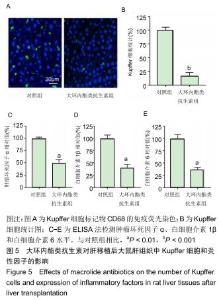
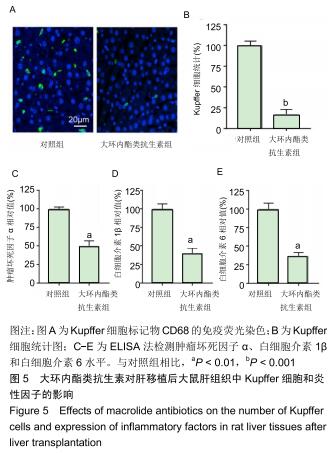
|
[1] THORSEN T, SOLHEIM JM, LABORI KJ, et al. Liver transplantation as a lifesaving procedure for posthepatectomy liver failure and iatrogenic liver injuries.Langenbecks Arch Surg.2019;404(3):301-308.
[2] SHI S, VERSTEGEN MMA, MEZZANOTTE L, et al. Necroptotic cell death in liver transplantation and underlying diseases: mechanisms and clinical perspective. Liver Transpl. 2019;25(7):1091-1104.
[3] TEOH NC. Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: contemporary perspectives on pathogenic mechanisms and basis for hepatoprotection-the good, bad and deadly. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.2011; 26 Suppl 1:180-187.
[4] BHOGAL RH, WESTON CJ, VELDUIS S, et al. The reactive oxygen species-mitophagy signaling pathway regulates liver endothelial cell survival during ischemia/reperfusion injury. Liver Transpl.2018; 24(10):1437-1452.
[5] VAN GOLEN RF, REINIERS MJ, OLTHOF PB, et al. Sterile inflammation in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury: present concepts and potential therapeutics. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(3):394-400.
[6] KUYVENHOVEN JP, MOLENAAR IQ, VERSPAGET HW, et al. Plasma MMP-2 and MMP-9 and their inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 during human orthotopic liver transplantation. The effect of aprotinin and the relation to ischemia/reperfusion injury. Thromb Haemost.2004;91(3):506-513.
[7] BUSUTTIL RW, TANAKA K. The utility of marginal donors in liver transplantation. Liver Transpl.2003;9:651-663.
[8] 陈峰,王建,张雅敏.FK506抑制HMGB1的释放减轻肝移植大鼠肝脏缺血再灌注损伤[J].世界华人消化杂志, 2017,25(4): 326-333.
[9] CANNISTRÀ M, RUGGIERO M, ZULLO A, et al. Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury: A systematic review of literature and the role of current drugs and biomarkers. Int J Surg.2016; 33 Suppl 1:S57-S70.
[10] DE VRIES Y, BERENDSEN TA, FUJIYOSHI M, et al. Transplantation of high-risk donor livers after resuscitation and viability assessment using a combined protocol of oxygenated hypothermic, rewarming and normothermic machine perfusion: study protocol for a prospective, single-arm study (DHOPE-COR-NMP trial). BMJ Open.2019; 9(8):e028596.
[11] LIN SD, LEE KRISHNAMOORTHY T, KUMAR R, et al. Tacrolimus monotherapy in recipients of liver transplant: A single-center experience. Transplant Proc.2019;51(6): 1920-1922.
[12] HUBER R, KASISCHKE K, LUDOLPH AC, et al. Increase of cellular hypoxic tolerance by erythromycin and other antibiotics. NeuroReport.1999;10(7):1543-1546.
[13] KOUTSOGIANNIDIS C-PC, JOHNSON EO. Pharmacological neuroprotection in cardiac surgery: effectiveness of pharmacologic-preconditioning with erythromycin. Curr Vasc Pharmacol.2018; 16(4):329-335.
[14] TROTTER JF, LIZARDO-SANCHEZ L. Everolimus in liver transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2014;19(6): 578-582.
[15] NARUMI S, WATARAI Y, GOTO N, et al. Everolimus-based immunosuppression possibly suppresses mean fluorescence intensity values of de novo donor-specific antibodies after primary kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc.2019; 51(5): 1378-1381.
[16] CZIGANY Z, SCHERER MN, PRATSCHKE J, et al. Technical aspects of orthotopic liver transplantation-a survey-based study within the eurotransplant, swisstransplant, scandiatransplant, and british transplantation society networks. J Gastrointest Surg.2019;23(3):529-537.
[17] CZIGÁNY Z, IWASAKI J, YAGI S, et al. Improving research practice in rat orthotopic and partial orthotopic liver transplantation: a review, recommendation, and publication guide. Eur Surg Res.2015; 55(1-2):119-138.
[18] SCAFFIDI P, MISTELI T, BIANCHI ME. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature. 2002;418(6894):191-195.
[19] 常琦,王琴.吡格列酮对肝脏缺血再灌注损伤模型大鼠的保护作用[J].解放军药学学报,2018,34(5):401-404.
[20] THOMSEN KL, ROBERTSON FP, HOLLAND-FISCHER P, et al. The macrophage activation marker soluble CD163 is associated with early allograft dysfunction after liver transplantation. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2019;9(3):302-311.
[21] ELTZSCHIG HK, ECKLE T. Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17(11):1391-1401.
[22] MENDES-BRAZ M, ELIAS-MIRÓ M, JIMÉNEZ-CASTRO MB, et al. The current state of knowledge of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury based on its study in experimental models. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:298657.
[23] ABU-AMARA M, YANG SY, TAPURIA N, et al. Liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: processes in inflammatory networks--a review. Liver Transpl.2010;16(9):1016-1032.
[24] GRIGG SE, SARRI GL, GOW PJ, et al. Systematic review with meta-analysis: sirolimus- or everolimus-based immunosuppression following liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment Pharmacol Ther.2019; 49(10):1260-1273.
[25] LI Z, ZHANG J, MULHOLLAND M, et al. mTOR activation protects liver from ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury through NF-κB pathway. FASEB J.2017;31(7):3018-3026.
[26] LI Z, GU J, ZHU Q, LIU J, et al. Obese donor mice splenocytes aggravated the pathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease via regulating differentiation of Tregs and CD4+ T cell induced-type I inflammation. Oncotarget.2017;8(43):74880-74896.
[27] WU Y, WANG W, PENG XM, et al. Rapamycin upregulates connective tissue growth factor expression in hepatic progenitor cells through TGF-β-Smad2 dependent signaling. Front Pharmacol.2018;9:877.
[28] LIM EJ, CHIN R, NACHBUR U, et al. Effect of immunosuppressive agents on hepatocyte apoptosis post-liver transplantation. PLoS One.2015;10(9):e0138522.
[29] CHAUDHRY S, EMOND J, GRIESEMER A. Immune cell trafficking to the liver. Transplantation. 2019;103(7): 1323-1337.
[30] BAI H, WEN J, GONG JP, et al. Blockade of the Notch1/ Jagged1 pathway in Kupffer cells aggravates ischemia-reperfusion injury of orthotopic liver transplantation in mice. Autoimmunity.2019;52(4):176-184.
[31] AL-SAEEDI M, LIANG R, SCHULTZE DP, et al. Glycine protects partial liver grafts from Kupffer cell-dependent ischemia-reperfusion injury without negative effect on regeneration. Amino Acids.2019; 51(6):903-911.
[32] TAMURA T, KONDO T, PAK S, et al. Interaction between Kupffer cells and platelets in the early period of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury--an in vivo study. J Surg Res. 2012;178(1):443-451.
[33] YUAN DD, CHI XJ, JIN Y, et al. Intestinal injury following liver transplantation was mediated by TLR4/NF-κB activation-induced cell apoptosis. Mol Med Rep.2016;13(2): 1525-1532.
|