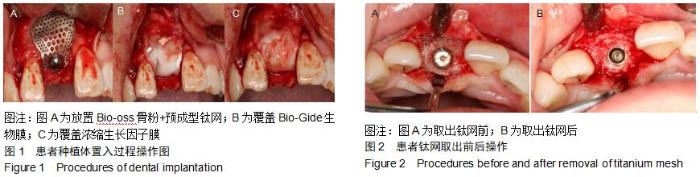
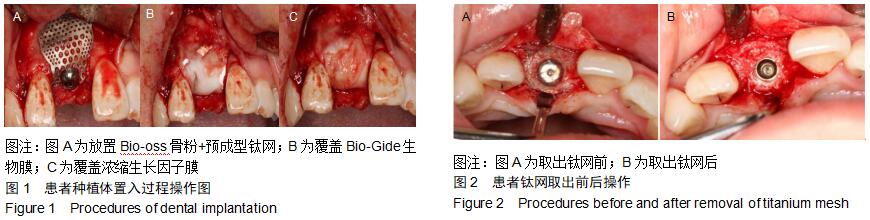
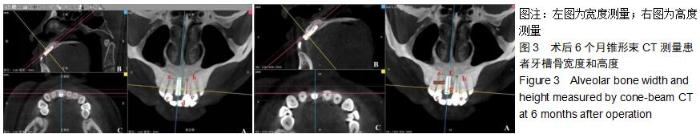
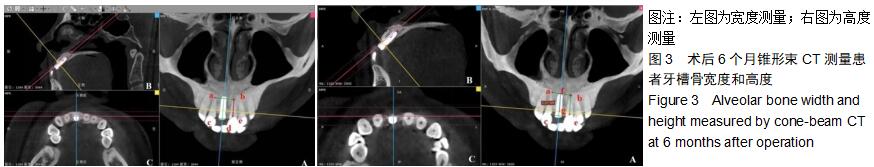
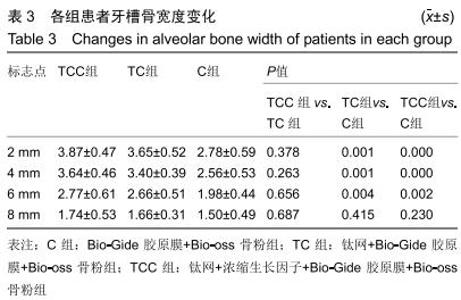
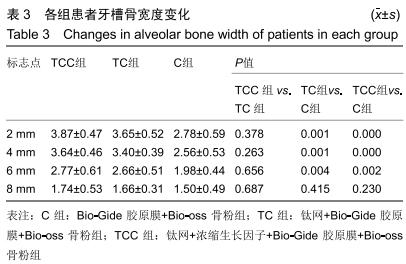
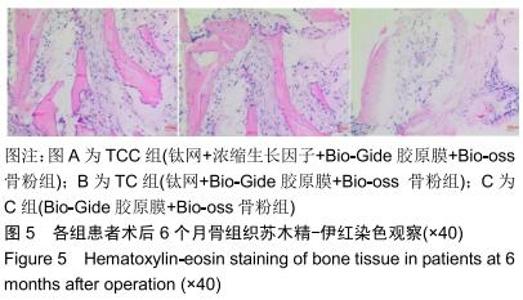
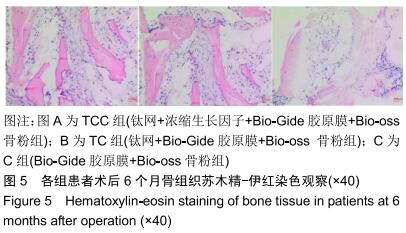
|
[1] ESPOSITO M, GRUSOVIN MG, FELICE P, et al. Interventions for replacing missing teeth: horizontal and vertical bone augmentation techniques for dental implant treatment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2009;(4):CD003607.
[2] BUSER D, DULA K, BELSER U, et al. Localized ridge augmentation using guided bone regeneration. 1.Surgical procedure in the maxilla.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.1993;13(1):29-45.
[3] NIKOLAOS KS, POPI S, VASILIKI PK, et al. Limitations and options using resorbable versus nonresorbable membranes for successful guided boneregeneration.Quintessence Int. 2017;48(2):131-147.
[4] 郭天奇,储顺礼,聂然,等.钛夹板应用于美学区引导骨组织再生1例[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2017,33(6):849-853.
[5] ROBERT A LEVINE, BRADLEY S MCALLISTER. Implant Site Development Using Ti-Mesh and Cellular Allograft in the Esthetic Zone for Restorative-Driven Implant Placement: A Case Report. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2016;36(3): 373-381.
[6] JEGHAM H, MASMOUDI R, OUERTANI H, et al. Ridge augmentation with titanium mesh: A case report.J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;118(3):181-186.
[7] CUCCHI A, SARTORI M, PARRILLI A, et al. Histological and histomorphometric analysis of bone tissue after guided bone regeneration with non-resorbable membranes vs resorbable membranes and titanium mesh.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(4):693-701.
[8] 宿玉成.口腔种植学 [M].2版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2018: 188-194.
[9] LI H, ZHENG J, ZHANG S, et al. Experiment of GBR for repair of peri-implant alveolar defects in beagle dogs.Sci Rep.2018; 8(1):16532.
[10] SIMION M, TRISI P, PIATTELLI A. Vertical ridge augmentation using a membrane technique associated with osseointegratedimplants.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1994;14(6):496-511.
[11] ZHANG T, ZHANG T, CAI X. The application of a newly designed L-shaped titaniummesh for GBR with simultaneous implant placement in theesthetic zone:A retrospective case series study.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2019;21(5): 862-872.
[12] JEYARAJ P. Efficacy and Versatility of the 3-D Titanium Mesh Implant in the Closure of Large Post-Craniectomy Osseous Defects, and its Therapeutic Role in Reversing the Syndrome of the Trephined: Clinical Study of a Case Series and Review of Literature.J Maxillofac Oral Surg.2016;15(1):82-92.
[13] 满毅,王天璐.钛网在口腔种植骨量扩增中的应用[J].口腔颌面外科杂志, 2015, 25(4):241-245.
[14] BRIGUGLIO F, FALCOMATÀ D, MARCONCINI S, et al.The Use of Titanium Mesh in Guided Bone Regeneration:A SystematicReview.Int J Dent.2019;2019:9065423.
[15] CUCCHI A, VIGNUDELLI E, NAPOLITANO A, et al. Evaluation of complication rates and vertical bone gain after guided bone regeneration with non-resorbable membranes versus titanium meshes and resorbable membranes. A randomized clinical trial.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2017; 19(5):821-832.
[16] PROUSSAEFS P, LOZADA J, KLEINMAN A, et al. The use of titanium mesh in conjunction with autogenous bone graft and inorganic bovine bone mineral (bio-oss) for localized alveolar ridge augmentation: a human study.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2003;23(2):185-195.
[17] 白彭,叶平,吴润发,等.两种胶原膜暴露于口腔环境中降解作用的对照研究[J].中国口腔种植学杂志, 2011,16(1):56-57.
[18] EDMUNDS RK, MEALEY BL, MILLS MP, et al. Maxillary anteriorridge augmentation with recombinant human bonemorphogenetic protein 2.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2014;34(4):551-557.
[19] AGARWAL A, GUPTA ND. Platelet-rich plasma combined withdecalcified freeze-dried bone allograft for the treatment ofnoncontained human intrabony periodontal defects: a randomizedcontrolled split-mouth study.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2014;34(5):705-711
[20] 谢永林,陈一,萧雅一,等.CGF对种植修复中骨组织再生和牙龈修复的临床研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2018,34(10):608-612.
[21] 杨惠,王敏,夏海斌.CGF在上颌窦底提升种植修复中的应用[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 2018,259(5):37-40.
[22] 林海燕,张维丹,于艳春,等.钛网联合浓缩生长因子重建上前牙唇侧骨板重度缺损的临床疗效评价[J].上海口腔医学,2016,25(3): 352-356.
[23] 翁涛.CGF在骨组织再生工程中的应用研究进展[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2017, 22(2):97-100.
[24] SCULEAN A, SCHWARZ F, CHIANTELLA GC, et al. Five-year results of a prospective,randomized, controlled study evaluating treatment of intra-bony defects with anatural bone mineral and GTR. J Clin Periodontol.2007;34(1):72-77.
[25] JONKER BP, WOLVIUS EB, VAN DER TAS JT, et al. The effectof resorbable membranes on one-stageridge augmentation in anterior single-toothreplacement: Arandomized, controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Impl Res. 2017;29(1):1–13.
[26] 徐丽娜,王琛.GBR技术与种植相关的研究进展[J].口腔医学, 2017,37(9):829-832.
[27] 李晨琳,徐光宙.口腔种植中骨增量技术的应用进展[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2018,16(6):78-83.
[28] 李慧萍,孙守福,甄锦泽,等.钛网+膜联合使用修复种植体周围牙槽骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国口腔颌面外科杂志, 2017,15(2): 127-130.
[29] CORINALDESI G, PIERI F, SAPIGNI L, et al. Evaluation of survival and success rates of dental implants placed at the time of or after alveolar ridge augmentation with an autogenous mandibular bone graft and titanium mesh: a 3- to 8-year retrospective study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24(6):1119-1128.
|