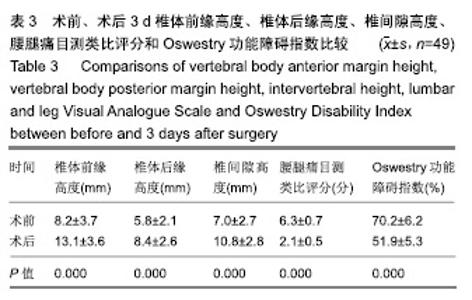
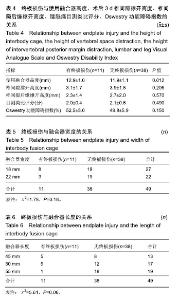
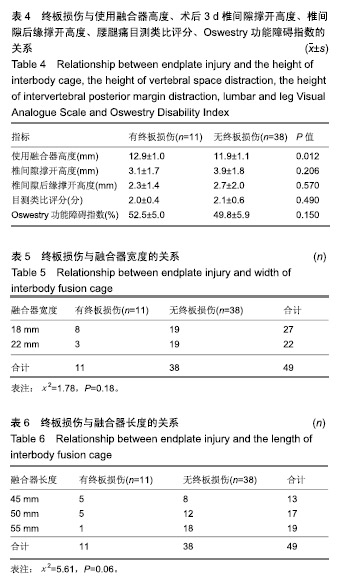
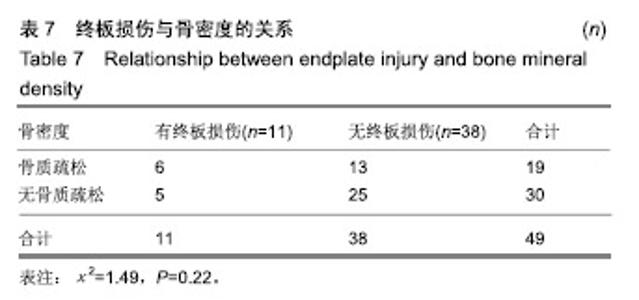
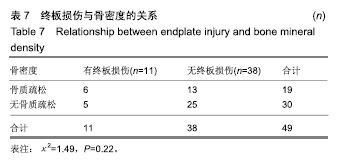
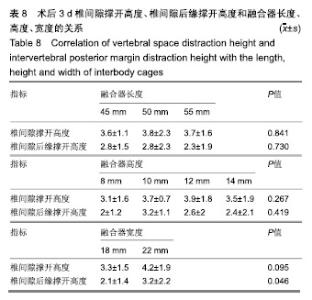
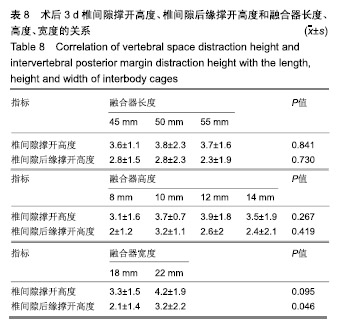
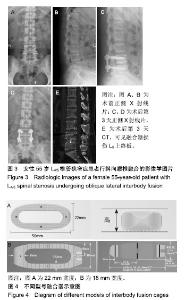
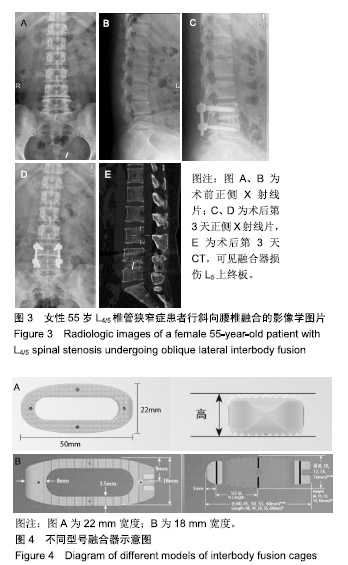
| [1]Mayer HM. A new microsurgical technique for minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1997;22(6):691-699,700.[2]Silvestre C, Mac-Thiong JM, Hilmi R, et al. Complications and morbidities of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lumbar interbody fusion in 179 patients. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(2):89-97.[3]张建锋,范顺武,方向前,等.斜外侧椎间融合术在单节段腰椎间盘退行性疾病中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(2):80-88.[4]刘进平,冯海龙.斜外侧入路腰椎间融合术在腰椎退行性疾病中的应用[J].中华神经外科杂志,2016,32(9):918-922.[5]Abe K, Orita S, Mannoji C, et al. Perioperative complications in 155 patients who underwent oblique lateral interbody fusion surgery: perspectives and indications from a retrospective, multicenter survey. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017;42(1):55-62.[6]Fujibayashi S, Hynes RA, Otsuki B, et al. Effect of indirect neural decompression through oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2015; 40(3):E175-E182.[7]Ohtori S, Orita S, Yamauchi K, et al. Change of lumbar ligamentum flavum after indirect decompression using anterior lumbar interbody fusion. Asian Spine J. 2017;11(1):105-112.[8]Oliveira L, Marchi L, Coutinho E, et al. A radiographic assessment of the ability of the extreme lateral interbody fusion procedure to indirectly decompress the neural elements. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(26 Suppl):S331-S337.[9]丁凌志,范顺武,胡志军,等. 斜外侧腰椎椎间融合术间接减压治疗退行性腰椎管狭窄症[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017,37(16):965-971.[10]范顺武,胡志军.如何严格把握适应证,发挥最大技术优势——斜外侧腰椎椎间融合术临床应用的思考与体会[J].中华骨科杂志,2017, 37(16):961-964.[11]Le TV, Baaj AA, Dakwar E, et al. Subsidence of polyetheretherketone intervertebral cages in minimally invasive lateral retroperitoneal transpsoas lumbar interbody fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(14):1268-1273.[12]原发性骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2017)[J].中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2017,10(5):413-444.[13]Cloward RB. The treatment of ruptured lumbar intervertebral discs by vertebral body fusion. I. Indications, operative technique, after care. J Neurosurg.1953;10(2):154-168.[14]Matge G. Anterior interbody fusion with the BAK-cage in cervical spondylosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien).1998;140(1):1-8.[15]Soriano-Baron H, Newcomb A, Malhotra D, et al. Biomechanical Effects of an Oblique Lumbar PEEK Cage and Posterior Augmentation. World Neurosurg, 2019.[16]Weiner BK, Fraser RD. Spine update lumbar interbody cages. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998;23(5):634-640.[17]钟华璋,田大胜,周云,等.斜外侧椎间融合技术的研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(1):46-52.[18]郑召民,章健,刘辉,等.微创小切口侧前方腰椎间融合术治疗腰椎退变性疾病的近期疗效和围手术期并发症[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2018,28(5):410-417.[19]Nemani VM, Aichmair A, Taher F, et al. Rate of revision surgery after stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(5):E326-E331.[20]Closkey RF, Parsons JR, Lee CK, et al. Mechanics of interbody spinal fusion. Analysis of critical bone graft area. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18(8):1011-1015.[21]Tohmeh AG, Khorsand D, Watson B, et al. Radiographical and clinical evaluation of extreme lateral interbody fusion: effects of cage size and instrumentation type with a minimum of 1-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(26):E1582-E1591.[22]Kozak JA, Heilman AE, O'Brien JP. Anterior lumbar fusion options. Technique and graft materials. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994;(300):45-51.[23]Marchi L, Abdala N, Oliveira L, et al. Radiographic and clinical evaluation of cage subsidence after stand-alone lateral interbody fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;19(1):110-118.[24]Lang G, Navarro-Ramirez R, Gandevia L, et al. Elimination of subsidence with 26-mm-wide cages in extreme lateral interbody fusion. World Neurosurg. 2017;104:644-652.[25]Grant JP, Oxland TR, Dvorak MF. Mapping the structural properties of the lumbosacral vertebral endplates. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(8):889-896.[26]Tempel ZJ, Gandhoke GS, Okonkwo DO, et al. Impaired bone mineral density as a predictor of graft subsidence following minimally invasive transpsoas lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Eur Spine J. 2015;24 Suppl 3:414-419.[27]沈俊宏,王建,刘超,等. 斜外侧腰椎间融合术治疗退变性腰椎疾病的并发症和早期临床结果[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2018,28(5): 397-404.[28]Kim SJ, Lee YS, Kim YB, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of a new cage for direct lateral lumbar interbody fusion. Korean J Spine. 2014;11(3):145-151.[29]Anderson PA, Polly DW, Binkley NC, et al. Clinical Use of Opportunistic Computed Tomography Screening for Osteoporosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(23):2073-2081.[30]Gilbert SG, Johns PC, Chow DC, et al. Relation of vertebral bone screw axial pullout strength to quantitative computed tomographic trabecular bone mineral content. J Spinal Disord. 1993;6(6):513-521.[31]Roberts S, McCall IW, Menage J, et al. Does the thickness of the vertebral subchondral bone reflect the composition of the intervertebral disc? Eur Spine J. 1997;6(6):385-389.[32]Jayasinghe JA, Jones SJ, Boyde A. Three-dimensional photographic study of cancellous bone in human fourth lumbar vertebral bodies. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1994;189(3):259-274.[33]Sato J, Ohtori S, Orita S, et al. Radiographic evaluation of indirect decompression of mini-open anterior retroperitoneal lumbar interbody fusion: oblique lateral interbody fusion for degenerated lumbar spondylolisthesis. Eur Spine J. 2017;26(3):671-678.[34]Alimi M, Lang G, Navarro-Ramirez R, et al. The Impact of Cage Dimensions, Positioning, and Side of Approach in Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion. Clin Spine Surg. 2018;31(1):E42-E49. |