Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (2): 322-328.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2957
Gingival retraction: application profiles and hot spotlights
Li Rong1, Zuo Enjun2
- 1School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China; 2Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2020-01-14Revised:2020-01-16Accepted:2020-03-18Online:2021-01-18Published:2020-11-14 -
Contact:Zuo Enjun, MD, Associate chief physician, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116044, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Li Rong, Master candidate, School of Stomatology, Dalian Medical University, Dalian 116023, Liaoning Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Rong, Zuo Enjun. Gingival retraction: application profiles and hot spotlights[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 322-328.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
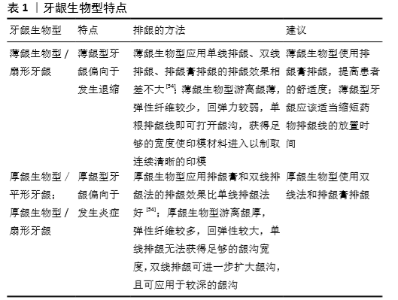
2.1 排龈的目的和意义 排龈技术的原理是利用牙龈软组织的黏弹性特征,通过某种方法将牙龈有效推离开牙面,获得一定的龈沟宽度,要求排龈后游离龈有至少0.2 mm的侧向移位,以减少在牙体修复时车针对牙龈的损伤,控制出血,容纳足够的印模材进入龈沟,取得清晰的印模,达到最佳的治疗效果。良好的排龈不仅要求获得清晰的视野、清晰的印模,减少出血量及龈沟液渗出,更要求保护龈沟底部的结合上皮,保护生物学宽度不被侵犯。排龈技术可以较好的改进临床操作条件,在临床上应用于多种情况。 2.1.1 牙体预备前排龈 在牙体预备前进行排龈可以使牙龈与牙面之间获得一定的间隙,在有一定宽度的龈沟内操作较安全,减少车针对游离龈内侧上皮的损伤,保护沟内上皮和结合上皮,可使生物学宽度在一定程度上不受侵犯;排龈后减少软组织损伤,可以控制出血,控制龈沟液量,从而为医师创造一个清晰的操作视野,此时再预备肩台更能保证肩台的连续、光滑及宽度适宜。 2.1.2 印模前排龈 龈沟必须具有一定的宽度印模材料才能进入其内,使最终印模获得清晰准确的牙体及牙颈部肩台形态,同时排龈也可以控制出血,血迹过多会影响印模的精确度,加大修复体与基牙之间的间隙,使密合度欠佳,引起微渗漏,增加继发龋的发生率。 2.1.3 粘接前排龈 固定义齿粘接时若不进行排龈直接粘接容易导致牙龈边缘卷入龈沟[1],造成龈缘损伤,若粘接剂进入龈沟深部,无法完全去净,则残留的多余粘接剂会直接刺激牙龈,粗糙的表面也容易堆积菌斑,导致牙龈炎,形成的悬突也会对牙周组织造成损害。固定义齿粘接前进行排龈使基牙颈部的肩台得以暴露,可以帮助彻底清除龈沟内残留的粘接剂,减少刺激牙龈的机会,也在一定程度上减少了龈沟液对粘接剂的污染,提高了修复体的粘接强度,避免边缘微渗漏。研究表明,全瓷冠在粘接前进行排龈可减少牙周损伤,减少术后龈沟出血,有效预防牙周病[2]。 2.1.4 修复楔状缺损时排龈 楔状缺损常发生于颈部釉牙骨质的交界,大多平齐牙龈或位于龈下,直接充填修复无法直视缺损的边缘,很容易形成龈下悬突,对牙龈产生机械性刺激,修形抛光时也会损伤牙龈;或充填体与缺损区洞壁接触不密合,使菌斑聚积造成局部的牙龈炎症;或由于缺损部位受到牙周组织的影响,会被牙周组织的血液、龈沟液污染,使充填体易脱落。对位于龈下的楔状缺损应在修复前进行排龈,充分暴露缺损的边缘,防止预备及抛光时损伤牙龈,避免牙龈卷压、损伤,对多余的充填材料较容易去除,避免形成悬突;同时可控制龈沟液及血液渗出,减少洞缘的污染,提高粘接效能,减少微渗漏。吴丽娜等[3]研究表明,楔状缺损修复总疗效的主要影响因素是修复体的边缘密合性、磨损、着色以及脱落率,而排龈后再修复可有效控制龈沟液渗出,避免龈沟液对操作及充填体边缘密合性的影响,降低修复体脱落率,减少微渗漏;还有研究表明,修复楔状缺损前排龈的患者天冬氨酸转氨酶升高较不排龈的患者少,牙龈炎症反应轻,悬突、边缘不密合及充填体脱落的发生率均较不排龈患者少[4-5]。 2.1.5 种植体周围排龈 种植体周围软组织的解剖结构与天然牙齿的牙周组织有不同之处[6],天然牙牙龈结缔组织中的胶原纤维附着于牙骨质,与牙面呈垂直或水平交叉,利于游离龈附着于牙齿表面,种植体周围牙龈中胶原纤维与种植体无附着,且排列方向平行于种植体或环绕种植体表面,无垂直于种植体表面的纤维,这种排列方式不利于游离龈贴附在种植体表面;种植义齿的结合上皮增殖能力弱而渗透性强,与种植体表面的半桥粒附着强度不如天然牙。这些解剖特点使种植体周围软组织抵御口腔中生物和机械性侵袭的能力不如天然牙。对种植体周围炎患者的统计分析表明粘接剂残留是造成种植体周围炎不容忽视的原因之一,靠粘接固位的修复体粘接时残余的粘接剂会引起口腔微生物堆积[7],增加种植体周围炎的发生率[8],研究发现残留的粘接剂未去净会造成龈沟探诊出血和脓肿形成,明显增加了炎症的发生[9]。目前种植体周围炎发生率高但疗效欠佳[10],因此应以预防为主,去除种植体周围的菌斑滞留因素,粘接时对种植体周围组织进行排龈去除多余粘接剂是必要的。 鉴于这些原因,以及种植体的特殊性,在种植体周围进行排龈时应小心谨慎,确保施加的排龈力是温和的[11],适用于种植体周围的排龈方法很少。种植体周围黏膜的再生能力不如牙周黏膜,龈沟底部没有角化龈,使用牙龈旋转刮除术会加深龈沟或使其严重衰退,使用电刀可能会通过金属种植体结构向骨传导电流,引起骨性或黏膜坏死,所以牙龈旋转刮除术、电刀都不适用于种植体周围;排龈线排龈法只适用于龈沟较浅、牙龈较厚的情况;CO2激光在种植体印模时很有用,但它是侵入性的,无法满足保守治疗的原则,所以激光排龈法也应选择性应用,须小心谨慎,以防牙龈边缘产生凹槽影响患者的外观美。排龈膏排龈法适合于多个种植体距离较近时,因为它可以避免牙龈乳头炎[11],但是牙龈回缩过程不仅要自然地暴露基牙的边缘,而且不能改变种植体的表面,有研究表明Expasyl会使种植体的最初表面发生改变,其中种植体的领圈变化最大[12],所以对于种植体而言,排龈膏是瑕瑜互见的,其对种植体的明确影响有待进一步研究。种植体支持的牙冠修复最常遇到的问题是咬合力分布不均匀和种植体各部分承受的不适当的扭力,研究报告采用一种新的牙龈收缩系统(G型袖口G-Cuff)直接印模种植基台,获得基台水平的印模,修复完成后的种植体支持的牙冠达到了更好的长期效果[13];G-Cuff主要是支持种植体基台周围的软组织,不会损伤种植体周围组织,不会使粘接剂残留,且印模可靠度高,适合任何的固定桥和单冠修复。 最新研究表明,排龈线排龈法对种植体周围软组织的损伤也是可逆的[6],在损伤龈沟沟内上皮,破坏结合上皮的封闭后,骨水平种植义齿周围软组织的龈沟液量会明显增多,这种情况是有利的,因为龈沟液中肿瘤坏死因子α含量升高可使大量炎症细胞浸润以吞噬细菌,增多的龈沟液还可以冲洗龈沟以排出细菌及炎症渗出物,这些防御机制可以促进软组织损伤的恢复,之后牙龈的GI、龈沟液量、肿瘤坏死因子α约在排龈后第14天恢复至排龈前水平。此外,较厚的牙龈是更有弹力的,不容易退缩而是倾向于形成袋,因此对于种植体周围排龈来说,厚的牙龈生物型是更有益的[11]。 2.2 各种排龈方法及优缺点 2.2.1 机械排龈 机械排龈法是将排龈线置于龈沟来达到推开牙龈的目的,排龈线有不同的形状和粗细型号,使用时根据龈沟深度和游离龈的松紧度选择合适的排龈线,保持排龈器的尖端与牙体呈45°角,在干燥环境中按顺序轻轻地将排龈线压入龈沟内,使排龈线不高出龈缘,排龈完成取出排龈线时应湿润排龈部位,以防排龈线与牙龈或血凝块粘连,引起出血。排龈线需放置在龈沟内足够的时间才能有效排开游离龈,因为游离龈由多种弹性纤维组成,其弹性形变在一定限度内与时间有关。数字化模型分析研究显示排龈对不同部位的龈沟扩大程度不同,时间从5-10 min可明显增加牙龈各部位的龈沟宽度,而从10-15 min主要有助于轴角部位龈沟宽度的扩大与维持,3个时间下颊侧中部的龈沟宽度均显著大于轴角部位,因此使用单线机械法排龈至少需要10 min[14]。而最大时间的研究结果不很一致,有研究报道单线排龈法排龈时间应在15 min以内,也有学者认为最大排龈时间不超过30 min。 机械排龈法分为单线排龈法和双线排龈法,单线排龈法适用于较薄的游离龈、较浅龈沟,双线排龈法适用于较厚的游离龈、较深的龈沟。双线排龈法先在龈沟内置入一根排龈线,精修肩台,再选一根排龈线置入,10 min后取出上层龈线取模,取模后立即取出底部龈线,研究发现虽然在预备肩台及印模时有底部龈线存在于龈沟内,但对牙周组织的影响较单线排龈法小,修复体边缘密合程度好[15]。相关文献资料表明,患者利用双线排龈法之后,其排龈效果显著,游离牙龈、基牙肩台的边界、牙龈出血情况以及印模清晰度明显优于利用单线排龈法的患者,且不良反应少,修复效果好[16-17]。但若牙龈出现轻度炎症时,牙龈组织内炎症细胞增多,毛细血管充血,纤维成分减少,结合上皮易遭受损害,排龈线排龈产生的机械压力会损伤结合上皮,造成龈沟内出血增多。排龈线排龈对牙周组织造成的急性机械损伤最大,包括龈沟上皮和结合上皮的损伤,不涉及上皮下结缔组织,但其恢复较快,约在14 d后恢复至排龈前水平。 海绵状排龈条是一种新型排龈材料,属于机械压迫排龈法。常用的Merocel可伸缩材料是一种合成的多孔化学材料,从一种产生网状结构的生物相容性聚合材料中提取的,易弯曲成形放入龈沟中,这个海绵状材料吸收龈沟液膨胀,从而对周围牙龈组织产生适当的压力,保证牙龈移位[18],Merocel相较于排龈线和排龈硅橡胶来说可产生较大的侧向和垂直向位移,产生所需位移的时间较排龈线短,且出血少,易放置。 排龈硅橡胶(Magic foam cord)是一种加成型硅橡胶排龈材料,固化过程中可以产生大量气泡,5 min可膨胀至原体积的160%,利用其体积的膨胀来达到排龈的目的,所以利用排龈硅橡胶排龈也属于机械压迫排龈法,其不含血管收缩药,不会损伤牙龈和结合上皮,对牙周组织和全身系统也不会有影响;因其不含止血剂,控制牙龈出血、龈沟液渗出的效果不佳,所以主要适用于患者的牙周健康、牙龈无出血、龈沟液渗出不明显时,也用于多个牙齿需一次完成预备时。学者研究发现:排龈硅橡胶可产生足够的牙龈收缩[18-20];排龈线和Merocel在排龈时均会出血,排龈硅橡胶排龈时不会引起出血;排龈硅橡胶产生牙龈足够位移所需的平均时间更少;排龈硅橡胶使用时用自动手枪注射到龈沟周围,容易放置。MFC也有其适用的有限性[21],对于边缘位于龈上或龈下2 mm以上者排龈效果较好,边缘位于龈下深度大于2 mm时,排龈效果不如排龈线。 2.2.2 机械化学联合排龈 即将排龈线与化学药物联合应用,排龈用的药物一般为血管收缩或收敛剂,如硫酸亚铁、氯化铝、硫酸铁、盐酸四氢唑啉等。最常用的为含肾上腺素的药物排龈线,使用时医师必须考虑患者的用药史、口腔卫生情况、排龈数量和所需的时间等,在严重损伤的龈沟内使用肾上腺素时会使心率加快及血压升高,这种情况下建议使用其他的止血药物如5%硫酸铝替代肾上腺素进行排龈[22],肾上腺素也不能用于血压或血糖高、有心血管疾病、甲亢等疾病的患者。研究发现盐酸四氢唑啉类药物较其他药物有更好的排龈效果,比盐酸肾上腺素对血液循环系统的影响更小[23];硫酸铁等收敛剂为酸性物质[23],其在酸性条件下促进牙龈组织形成蛋白沉淀物,堵塞毛细血管口,可以止血和减少龈沟液渗出,同时其细胞渗透性较低,可影响龈沟内环境的渗透压,使牙龈组织暂时性收缩,实现排龈的目的。研究显示排龈药物随着其酸性越强,对细胞造成的损伤越大,15.5%硫酸铁溶液会引起明显的牙龈炎,对细胞的毒性最大,使用时应适当减小浓度,而盐酸肾上腺素对细胞的毒性最小[24]。排龈线经过长时间的化学浸提液浸泡后可抑制牙龈成纤维细胞增殖[25],诱导其凋亡,适当缩短排龈时间可以增加细胞活性,降低细胞凋亡率,提高牙周组织的健康,建议肾上腺素排龈线不超10 min,硫酸铝排龈线不超15 min;化学浸堤液的稀释浓度越高,细胞毒性越大[26],排龈后用水冲洗可移除残留的药物,减少牙龈损伤。 糊剂型排龈材料也是常用的机械化学联合排龈材料,具有操作简单、高效省时、疼痛感较小,排龈效果好等优点。研究发现,在相同的时间内排龈膏可产生足够的牙龈移位,止血效果好,牙龈损伤小,在保护牙周组织健康方面优于排龈线[27-29]。排龈线的牙龈推移效果较排龈膏明显,但排龈膏的GI、BI值变化比排龈线小[30],也有研究发现排龈膏可较排龈线产生更大的水平位移[31]。排龈膏对牙周组织的机械损伤较轻微,主要在龈沟上皮,结合上皮损伤小;其对牙周组织存在一定化学损伤,使龈沟上皮下结缔组织内大量炎症细胞浸润,恢复较慢。常用的排龈膏是Expasyl排龈膏,有以下优势:膏体中含有15%氯化铝,可显著控制牙龈出血及龈沟液渗出过量;无需麻醉;牙周组织损伤较小;操作时间短,在不超过2.5 min的时间里就能使牙颈部充分露出;可与其他技术合用;适应证广,可用于种植体周围排龈及粘接排龈,无绝对禁忌证。有研究表明,由于Expasyl独特的假弹性特征,随着施加压力的增大,材料内部的剪切应力也增加,Expasyl的黏性降低[29,32],同时放置后的任何操作都会降低黏度,以帮助其进入龈沟,排龈膏进入龈沟产生的压力比置入排龈线时少37.7倍,比置入排龈线后少10倍;排龈膏也有其不足之处,一是有牙周袋时Expasyl可能会注射到袋底等不易清洁的部位,二是Expasyl对牙龈产生的急性损伤较小但恢复较慢[33]。研究还发现,Expasyl的残留对poly(vinyl siloxane)(PVS)、polyether(Monophase)、polyether(Impregum)三种弹性印模材料的聚合有明显的抑制作用[34];印模时必须彻底的清除Expasyl,随后用3%H2O2清洗可显著降低这种对聚合反应的抑制作用;并且Expasyl不能与单相聚醚材料一起使用。 此外,对于排龈过程中出血问题的解决,有一些效果较好的止血剂。止血剂ViscoStat Clear的成分为25%氯化铝,排龈线经其浸泡后使用,可使蛋白质凝固从而抑制出血,对牙周组织的损伤可在后期恢复且不会明显影响树脂水门汀的粘接强度[35];Racegel 是一种新型止血药,含有25%的氯化铝,因其热力学性质,与组织接触时会变得黏稠,用水冲洗时其热效应是可逆的,不会刺激周围组织,可联合排龈线或单独使用[36],但是Racegel 呈流动胶体样,对牙龈的挤压作用较弱[37]。然而,有相关外文资料表明,止血剂可以改变牙本质表面的性质增强其抗酸蚀的能力,因此与全酸蚀系统相比,自酸蚀系统的酸性相对较低,可能不足以充分酸蚀更具抵抗力的牙本质表面,而导致粘接剂的粘接强度变低[38],建议止血剂应被冲洗干净,然后结合使用全酸蚀系统[39]。 2.2.3 激光排龈 近年来在口腔领域广泛应用的激光具有无痛、精准、损失小的优点,激光排龈后牙龈退缩量更接近于沟内上皮的厚度,远大于0.2 mm[40],有研究表明激光排龈是很有效的,可产生约0.48 mm的龈沟宽度[41]。半导体激光的光波将牙龈组织内的血红蛋白和黑色素等特异性吸收,通过热效应将其分解,主要作用于软组织,疼痛较轻,对软组织的保护优于排龈线[42]。 Er:YAG激光的波长(2940 nm)与水的主吸收峰重叠[43],口腔软硬组织中的水分子可以吸收其携带的能量,并聚集于光斑能量照射区,发生烧蚀作用,使水的体积膨胀产生巨大能量,发生微爆破,准确地切削牙龈龈沟上皮;铒激光有杀菌、对组织热损伤小、疼痛小、选择性去除牙体组织等特点[44];研究表明,铒激光排龈时间短,痛感轻,排龈后炎症反应轻,龈沟出血少,减少了止血药物的使用,有益于牙龈健康,较排龈线更适合于有轻度牙龈炎的患者[45]。Nd:YAG激光排龈和二极管激光排龈均比排龈线排龈法时间短、无痛率高[46-47]。但激光也有其缺点,激光不适合止血,不能提供触觉反馈,有损伤结合上皮的危险[36],且激光价格较高,临床无法普遍运用。 2.2.4 高频电刀排龈法 利用高频电刀头产热直接作用于牙龈组织,切除部分沟内上皮,使游离龈与预备体边缘之间呈现出足够间隙,操作简便,排龈效果好;电刀作用于周围组织无特异性,但可破坏牙体硬组织[48]。高频电刀切割准确,止血效果好,可充分暴露牙齿颈部,能够获得更清晰的治疗操作空间和较好的牙体龈方形态,利于楔缺的充填、牙体预备、印模等操作[49];使用高频电刀时应注意以下几点[49]:①尽量不要让电针工作端接触牙体,减少牙髓敏感及不适;②禁止在同一位点频繁切割,以防大量的热损伤造成牙龈坏死,延长恢复时间;③切龈的量为露出龋损便可,尽可能远离结合上皮,避免破坏生物学宽度后加剧牙龈、牙周的损伤。电刀排龈不适合用于种植体周围[11],电极可通过金属种植体向骨传导电流,而不是通过更分散的牙龈组织通路,电极尖端的集中电流可产热引起骨性或黏膜坏死。 2.2.5 临时冠排龈 在传统的二次排龈法中,鉴于颈部肩台的影响及弹性纤维收缩使游离龈塌向颈部,排龈线常常难以就位,排龈效果及印模清晰度欠佳。临时冠的颈部1/3突度可扩展牙龈,防止游离龈向颈部塌陷,牙体预备后制作临时冠来辅助第二次排龈,可以帮助排龈线完全、准确地就位,获得显著的牙龈退缩效果,有效扩大龈沟,使印模边缘清晰,保证工作模型的精确[50]。设计为龈下边缘的冠桥修复体在粘接前利用临时冠辅助排龈可减小排龈难度,提高排龈效果。 2.2.6 牙龈旋转切割法 旋转切割术是使用高速涡轮机快速切除牙龈组织,在边缘处创建一个槽,对于健康、无病的天然牙齿周围组织,如果存在足够的角化龈,旋转刮除术会导致牙龈沟的轻微加深,对牙龈边缘高度的影响很小[11]。但种植体周围龈沟的底部没有角化龈,可能会对旋转刮除术反应过度,加深牙龈沟或使其严重衰退,且在切割软组织时不能提供触觉反馈,可能会导致种植体表面的接触损伤和过度压迫,所以牙龈旋转切割法不适合在种植体周围使用。 2.2.7 推龈器 推龈器用于设计为龈下肩台的基牙预备时,学者根据需求研发了一种可以在高速手机头上使用的推龈器,由固位卡片、固位旋转环、主杆和推龈工作尖组成;固位卡片为宽叶,卡在高速手机头上,固位旋转环放在高速手机转轴出口处,起稳定作用,推龈工作尖为圆弧形、扁平状,设有刻度标记,可精准定位肩台的位置。研究表明,推龈技术优于排龈线排龈,能有效控制肩台的位置,减少牙龈损伤,提升基牙边缘完成线的质量[51]。传统的排龈技术对医师的操作要求较高,初学者不好掌握,同时存在较多不易控制的因素,进行龈下肩台的制备时容易损伤牙龈,推龈器将推龈和龈下肩台精准定位结合起来,再加上其牙龈保护作用,使其得到重视。但个体的牙齿外形差异大,推龈器并不能与之完全匹配,有报告将排龈线与推龈器联合应用于龈下楔状缺损[52],较两者单独使用时成功率高。 2.3 排龈效果的影响因素 2.3.1 牙龈生物型 不同生物型及牙龈形态对排龈的预后是不同的,牙龈生物型可分为薄龈生物型/扇形牙龈、厚龈生物型/平形牙龈、厚龈生物型/扇形牙龈3种[53],见表1。Expasyl排龈膏借助本身的重力推开牙龈,力量仅为0.1 N/mm2[55],较均匀持续,操作过程无痛无创,对薄龈生物型和厚龈生物型均有较好的效果。牙龈生物型也会影响药物排龈线的排龈效果,肾上腺素排龈线排龈后薄龈型牙龈的退缩量大于厚龈型牙龈[56],薄龈型牙龈应该适当缩短药物排龈线的放置时间;研究发现药物排龈线排龈后,薄龈生物型/扇形牙龈较其他2种牙龈型更易发生永久性牙龈退缩[53]。临床上应重视薄龈型牙龈,在排龈前先进行预后评估并于术前告知患者,尽可能操作规范以最大程度地减小牙龈损伤。 2.3.2 排龈时间 排龈线必须在龈沟内放置足够的时间才能扩展龈沟至所需宽度并维持一段时间,排龈膏也需要一定的时间才能控制出血、控制龈沟液的渗出,所以充足的排龈时间才能保证良好的排龈效果,但为了避免造成牙周组织不可逆的损伤,排龈时间也不宜过长。在一定时间内随着排龈线排龈时间的延长,排龈效果的满意率会逐渐增加,使用单线排龈法排龈至少需10 min;关于应用排龈线排龈的最大时间,有人认为超过15 min会增加牙龈退缩的概率,薄龈生物型排龈线的使用不要超过15 min[57],厚龈生物型排龈时间可适当延长,有人认为不超30 min即可[25]。排龈线经化学浸堤液浸泡过长时间后会抑制牙龈成纤维细胞增殖[25],诱导其凋亡,故应适当缩短其排龈时间,保护牙周组织的健康,建议肾上腺素排龈线不超10 min,硫酸铝排龈线不超15 min。 2.3.3 基牙形态 基牙形态也会明显影响基牙的排龈效果,有文献资料表明,没有龈下缺损,临床牙冠高度正常的基牙使用双线排龈、临时冠辅助排龈、排龈膏等的排龈效果都较单线排龈好,残根、短冠基牙会影响排龈线的放置,使用临时冠辅助排龈和排龈膏均比双线排龈效果更佳,说明基牙形态会影响双线排龈法的排龈效果,临床建议最好对残根、短冠基牙做术前评估以选择适合的排龈方式。"
| [1] 杨晓彤,杨永进. 排龈技术在固定修复中的进展研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2015,16(4):253-256. [2] 何嘉菁,钱洁蕾,王德芳. 前牙氧化锆全瓷冠粘固前排龈对牙周组织的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(2):106-108. [3] 吴丽娜,王一霖,刘美瑜.排龈术在龈下楔状缺损修复中的临床应用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2014,30(6):859-861. [4] 刘继乐,苏鑫,毕良佳,等. 排龈线对牙体楔状缺损患者炎症反应及悬突的预防效果[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2016,16(11):2148-2150. [5] 刘玉秀,周瑾. 排龈术在龈下楔状缺损修复中的应用价值分析[J].全科口腔医学杂志,2017,4(5):26-27. [6] 高旭,刘梅,刘翠玲.种植义齿排龈后种植体周围软组织损伤预后的动物实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(3):287-290. [7] 林曦,徐淑兰,郑相淮,等. 粘接剂残留致种植体周围炎[J].实用医学杂志, 2017,33(24):4077-4081. [8] 程磊,于海洋,吴尧,等.牙种植体周围微生物研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2019,37(1):7-12. [9] KORSCH M, ROBRA BP, WALTHER W. Cement-associated signs of inflammation: retrospective analysis of the effect of excess cement on peri-implant tissue. Int J Prosthodont.2015;(1):11-18. [10] 巫佩瑶,周陶,曹志炜,等.种植体周围炎与牙周炎的比较[J].医学综述, 2019,25(17):3333-3337. [11] BENNANI V, SCHWASS D, CHANDLER N.Gingival retraction techniques for implants versus teeth.J Am Dent Assoc. 2008;139(10):1354-1363. [12] CHANG YS, BENNANI V, TAWSE-SMITH A, et al. Effect of a cordless retraction paste material on implant surfaces:an in vitro study.Braz Oral Res. 2011;25(6):492-499. [13] DEOGADE SC, MANTRI SS, DUBE G, et al. A new trend in recording subgingival tissue around an implant while making a direct abutment impression.Case Rep Dent. 2014;2014:847408. [14] 张津京,刘玉华,吕培军,等. 三维模型分析法评价不同排龈时间下的龈沟宽度[J]. 北京大学学报,2011,43(1):73-76. [15] 孙艳燕,匡斌. 双线排龈法和单线排龈法对基牙龈沟液含量和成分的影响[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013,23(1):41-43. [16] 刘思言,牟雁东. 选择性双线排龈技术在前牙全瓷冠修复中的应用研究[J]. 实用医院临床杂志,2016,13(4):141-143. [17] 陈晓峰,熊莉,汤春波. 双线排龈技术在前牙固定修复中的临床应用[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2017,18(5):270-272. [18] THIMMAPPA M, BHATIA M, SOMANI P, et al. Comparative evaluation of three noninvasive gingival displacement systems:An in vivo study. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2018;18(2):122-130. [19] SHRIVASTAVA KJ, BHOYAR A, AGARWAL S,et al. Comparative clinical efficacy evaluation of three gingival displacement syetems.J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2015; 6(Suppl 1):S53-7. [20] GUPTA A, PRITHVIRAJ DR, GUPTA D, et al. Clinical Evaluation of Three New Gingival Retraction Systems: A Research Report.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2013; 13(1):36-42. [21] 王聪.排龈硅橡胶与排龈线应用效果比较[J]. 现代临床医学,2013,39(2): 121-122. [22] 刘健,张晓明,郝鹏杰. 排龈药物对体外培养人牙龈成纤维细胞的毒性比较[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(2):202-205. [23] 冯云枝,曾晓华. 不同排龈药物的排龈效果观察[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2011, 29(1):53-56. [24] 张晓明,慧敏,刘健. 排龈时间与药物对牙龈成纤维细胞的毒性比较研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2011,27(2):248-251. [25] 倪莹,邱振伟,孙霞,等. 3种排龈线不同时间浸堤液的细胞毒性研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2015,31(4):547-550. [26] 倪莹,张晓明,慧敏,等. 三种排龈线对体外培养人牙龈成纤维细胞毒性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5396-5400. [27] HUANG C, SOMAR M, LI K, et al. To cord or not to cord? That is still a question. SUMMARY REVIEW/RESTORATIVE DENTISTRY. 2017;18(1):21-22. [28] WANG Y, FAN F, LI X, et al. Influence of gingival retraction paste versus cord on periodontal health: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Quintessence Int. 2019;50(3):234-244. [29] HUANG C, SOMAR M, LI K, et al.Effificiency of Cordless Versus Cord Techniques of Gingival Retraction: A Systematic Review.J Prosthodont. 2017;26(3):177-185. [30] CHANDRA S, SINGH A, GUPTA KK, et al. Effect of gingival displacement cord and cordless systems on the closure,displacement, and inflammation of the gingival crevice. J Prosthet Dent. 2016;115(2):177-182. [31] PRASANNA GS, REDDY K, KUMAR PK,et al. Evaluation of efficacy of different gingival displacement materials on gingival sulcus width.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013;14(2):217-221. [32] Bennani V, Aarts JM, He LH. A comparison of pressure generated by cordless gingival displacement techniques.J Prosthet Dent. 2012;107(6):388-392. [33] AL HAMAD KQ, AZAR WZ, ALWAELI HA, et al. A clinical study on the effects of cordless and conventional retraction techniques on the gingival and periodontal health. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35(12):1053-1058. [34] ABDULJABBAR TS, AL AMRI MD, AL RIFAIY MQ, et al. Effects of Gingival Retraction Paste and Subsequent Cleaning with Hydrogen Peroxide on the Polymerization of Three Elastomeric Impression Materials:An In Vitro Study.J Prosthodont. 2019; 28(6):709-714. [35] 姜德志,屈波. ViscoStat Clear止血剂联合压线排龈法的临床疗效观察[J]. 黑龙江医药,2016,29(5):828-831. [36] RAJAMBIGAI MA, RAJA SR, SOUNDAR SI,et al. Quick,painless,and atraumatic gingival retraction:An overview of advanced materials. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016;8(Suppl 1):S5-S7. [37] 欧阳罡,周欢,赵三军.不同排龈方法对排龈效果影响的对比研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2018,34(2):202-205. [38] MAISCHBERGER C, STAWARCZYK B, VON HAJMASY A,et al. Hemostatic gingival retraction agents and their impact on prosthodontic treatment steps: A narrative review. Quintessence Int. 2018;49(9):719-732. [39] TARIGHI P, KHOROUSHI M. A review on common chemical hemostatic agents in restorative dentistry. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2014;11(4):423-428. [40] KRISHNA CH V, GUPTA N, REDDY KM, et al. Laser gingival retraction: a quantitative assessment. J Clin Diagn Res.2013,7(8);1787-1788. [41] GOUTHAM GB, JAYANTI I, JALALUDDIN M, et al. Clinical Assessment of Gingival Sulcus Width using Various Gingival Displacement Materials. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018;19(5):502-506. [42] 张新媛,董海涛,吴效民,等.半导体激光排龈法与排龈线排龈法的临床效果对比研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2018,32(1):23-24. [43] 王婕,陈亚明. Er:YAG激光在口腔医学领域的应用及研究进展[J].激光杂志, 2015,36(9):5-9. [44] 罗瑞,王道春. 铒激光治疗口腔疾病的应用进展[J].医学综述, 2018,24(7): 1364-1373. [45] 杨炼,蒲高成,段少宇,等. 激光排龈法与排龈线排龈法排龈效果的临床比较研究[J].激光杂志,2015,36(5):56-60. [46] 杨晓彤,杨永进,李超. 双线排龈法与Nd:YAG激光排龈法的临床效果比较[J].中国激光,2015,42(10):1004001-1 - 1004001-6. [47] MELILLI D, MAUCERI R, ALBANESE A, et al. Gingival displacement using diode laser or retraction cords:A comparative clinical study.Am J Dent. 2018;31(3):131-134. [48] 许志强,姚江武.数字化口腔修复(21)—半导体激光排龈效果的数字化分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2016,32(11):687-690. [49] 刘玉凤,李玉增,沈银环,等.高频电刀结合排龈线修复老年人龈下楔状缺损的疗效观察[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2015,13(5):275-278. [50] 闫改霞.临时冠在二次排龈法中的临床应用[J].求医问药下半月刊,2011, 9(12): 208-209. [51] 许晓波,谭晓蕾,边华琴等.推龈技术在前牙美学修复中的临床应用[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2018,28(4):233-236. [52] 游跃华. 排龈线结合推龈器排龈修复龈下楔状缺损的临床疗效[J].口腔医学, 2014,34(4):285-287. [53] 程婧,姚江武.数字化口腔修复(34)-药物排龈线排龈对于不同牙龈生物型和牙龈形态的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(6):368-371. [54] 何光伟,张萍.三种不同排龈方法在固定义齿修复中的应用比较[J].黑龙江医药科学,2018,41(5):81-83. [55] 冯传翠,张晓明.3种排龈方法对排龈效果影响的对比研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(1):127-128. [56] 宋元英,赵强. 基于牙龈生物型探究肾上腺素对牙龈的影响[J].中国医药导报,2017,14(18):125-129. [57] 林璐,宗娟娟.牙龈生物型[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25 (9):568-572. [58] DALIAH SALEM, ABDULMONEM ALSHIHRI, LIRAN LEVIN, 等.排龈线残留诱发种植体周围炎[J].中国口腔医学继续教育杂志, 2014,17(6):344-346. [59] Tabassum S, Adnan S, Khan FR.Gingival Retraction Methods:A Systematic Review.J Prosthodont. 2017;26(8):637-643. [60] 沈银环,李雅娟,刘玉凤.不同排龈方法在老年人前牙龈下根面龋充填中的临床效果评价[J].北京口腔医学,2019,27(2):109-111. |
| [1] | Zhang Mi, Wu Saixuan, Dong Ming, Lu Ying, Niu Weidong. Expression of interleukin-24 in a mouse model of periapical periodontitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 679-684. |
| [2] | Zhang Bin, Sun Lihua, Zhang Junhua, Liu Yusan, Cui Caiyun. A modified flap immediate implant is beneficial to soft tissue reconstruction in maxillary aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 707-712. |
| [3] | Sun Qi, Zhou Yanan, Dong Xin, Li Ning, Yan Jiazhen, Shi Haojiang, Xu Sheng, Zhang Biao. Metal-ceramic interface characteristics of Co-Cr alloy fabricated by selective laser melting [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 521-525. |
| [4] | Zhang Guomei, Zhu Jun, Hu Yang, Jiao Hongwei. Stress of three-dimensional finite element models of E-MAX porcelain inlay [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 537-541. |
| [5] | Ma Qing, Shi Liyan, Huang Sixue, Zheng Zhangbowen, Zhang Aihua, Zhan Desong, Fu Jiale. Research status and prospect of zirconia ceramics in dental prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3597-3602. |
| [6] | Nie Jianhua, Cheng Jiang, Mo Jiaqi. Analysis of liquid-solid interaction during three-dimensional printing of medical amorphous calcium phosphate [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2548-2553. |
| [7] | Long Qian, Guan Xiaoyan, Wang Qian, Hu Huan, Liu Jianguo. Transcriptome sequencing technology and its application in oral diseases, dental implants and regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1791-1798. |
| [8] | Jiang Nan, Wang Nan, Zhang Yifan, Chen Jingsi, Yao Ziyan, Zhan Desong, Fu Jiale. Clinical application and prospects of zirconia bonding agent [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1635-1640. |
| [9] | Feng Xiaoxia, Hou Weiwei, Jin Xiaoting, Wang Xinhua. Construction of periodontal biomimetic membrane with electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers and electrosprayed chitosan microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 511-516. |
| [10] | Yao Lu, Hu Peixin, Liu Wu, Lü Qitao, Nie Zilin, He Zhengdi. Application and prospects of 3D printing technology in dental manufacturing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 637-642. |
| [11] | Li Zheng, Wang Yuan, Tian Mengting, He Huiyu. Effect of different retentive grooves and adhesives on the retentive force between crown and post and core [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5508-5513. |
| [12] | Wang Xiuting, Li Sisheng, Sun Jian, Zhang Genyuan, Liu Fayin, Zhang Jintao. Effectiveness of artificial intelligent laser location system in reducing the location time and radiation dose of vertebroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(33): 5295-5299. |
| [13] | Yang Liuqing, Xie Lili, Liang Jianmei. The use of epigallocatechin gallate prevents white spot lesions during orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(26): 4141-4145. |
| [14] |
Li Junqing, Wu Jiayuan.
Effect of mechanical stimulation on dental pulp stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(25): 4054-4059. |
| [15] | Ding Jie, Li Xinying, Li Peng. Stress relaxation and creep test of modified glass ionomer cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(22): 3515-3520. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||