Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (11): 1641-1646.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0156
Application of lower edge of teardrop on restoring anatomical hip center height in total hip arthroplasty
Lu Yu-feng1, Guo Wan-shou2, Sun Wei2, Liu Lin1, Xu Peng1
- 1Osteonecrosis and Joint Reconstruction Surgery Ward of Joint Surgery, Honghui Hospital, Xi'an Jiaotong University Health Science Center, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China; 2Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, China-Japan Friendship Hospital, Beijing 100029, China
-
Online:2018-04-18Published:2018-04-18 -
Contact:Xu Peng, Osteonecrosis and Joint Reconstruction Surgery Ward of Joint Surgery, Honghui Hospital, Xi'an Jiaotong University Health Science Center, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Lu Yu-feng, M.D., Attending physician, Osteonecrosis and Joint Reconstruction Surgery Ward of Joint Surgery, Honghui Hospital, Xi'an Jiaotong University Health Science Center, Xi’an 710054, Shaanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Yu-feng, Guo Wan-shou, Sun Wei, Liu Lin, Xu Peng. Application of lower edge of teardrop on restoring anatomical hip center height in total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(11): 1641-1646.
share this article
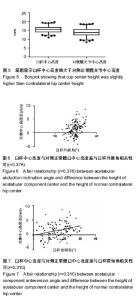
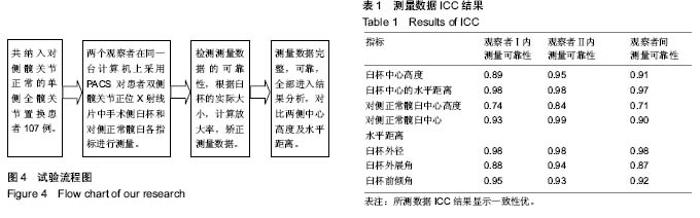
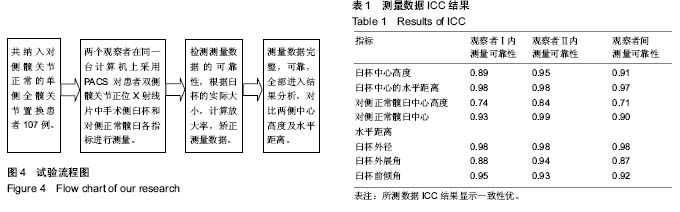
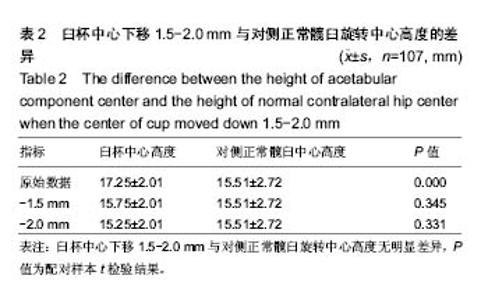
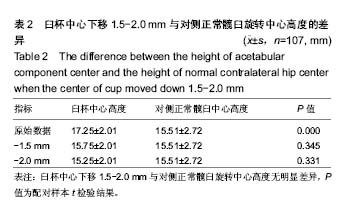
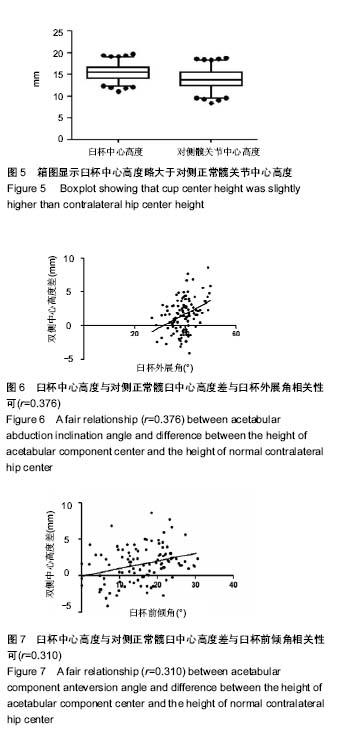
2.3 测量结果分析 臼杯中心平均高度为15.39 mm,对侧正常髋臼中心的高度平均为13.82 mm,臼杯中心高度显著高于正常髋臼中心的高度(P < 0.001,配对样本t 检验),见图5。但是,在所有107例患者中,有100例(93.4%)两者的差距为0-5 mm,7例(6.6%)大于5 mm,两者差距的均值为(1.57±2.44) mm。但是如果臼杯中心高度下移1.5和2.0 mm,与对侧正常髋臼中心的高度差异无显著性意义(P=0.345,0.331),见表2。也就是说,臼杯下缘安放低于泪滴下缘1.5-2.0 mm,能恢复髋臼旋转中心的生理性高度。 2.4 相关性分析 臼杯中心高度与对侧正常髋臼中心高度差与臼杯外展角相关性可(r=0.376,P < 0.001),见图6;与臼杯前倾角相关性可(r=0.310,P < 0.001),见图7。"
| [1] Kiyama T,Naito M, Shitama H,et al. Effect of superior placement of the hip center on abductor muscle strength in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2009;24(2):240-245.[2] Carls J, Wirth CJ, Börner C, et al. Changes of biomechanical parameters in dysplasia of the hip by total hip replacement. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 2002;140(5):527-532. [3] Jerosch J,Steinbeck J,Stechmann J,et al. Influence of a high hip center on abductor muscle function. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1997;116(6-7):385-389.[4] Abolghasemian M, Samiezadeh S, Jafari D,et al. Displacement of the hip center of rotation after arthroplasty of Crowe III and IV dysplasia: a radiological and biomechanical study. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(6):1031-1035.[5] Pagnano W, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG,et al. The effect of superior placement of the acetabular component on the rate of loosening after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(7):1004-1014.[6] Doehring TC, Rubash HE, Shelley FJ, et al. Effect of superior and superolateral relocations of the hip center on hip joint forces. An experimental and analytical analysis. J Arthroplasty. 1996;11(6):693-703.[7] Tanzer M. Role and results of the high hip center. Orthop Clin North Am. 1998;29(2): 241-247.[8] WanZ, BoutaryM, Dorr LD. The influence of acetabular component position on wear in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23(1):51-56.[9] Zhao X, Zhu ZA, Zhao J, et al. The utility of digital templating in total hip arthroplasty with Crowe type II and III dysplastic hips. Int Orthop.2011;35(5):631-638.[10] González Della Valle A,Slullitel G,Piccaluga F,et al. The precision and usefulness of preoperative planning for cemented and hybrid primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(1):51-58.[11] Hossain M, Lewis J, Sinha A. Digital pre-operative templating is more accurate in total hip replacement compared to analogue templating. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2008; 18(8): 577-580.[12] Mast NH, Impellizzeri F, Keller S,et al. Reliability and agreement of measures used in radiographic evaluation of the adult hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(1):188-199. [13] Tannast M, Zheng G, Anderegg C, et al. Tilt and rotation correction of acetabular version on pelvic radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005;438:182-190.[14] Siebenrock KA, Kalbermatten DF, Ganz R. Effect of pelvic tilt on acetabular retroversion:a study of pelves from cadavers. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;407:241-248.[15] Krishnan SP, Carrington RW, Mohiyaddin S,et al. Common misconceptions of normal hip joint relations on pelvic radiographs. J Arthroplasty.2006;21(3):409-412.[16] Lewinnek GE, Lewis JL, Tarr R, et al. Dislocations after total hip replacement arthroplasties. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1978; 60(2):217-220.[17] Merle C,Waldstein W,Pegg E,et al. Femoral offset is underestimated on anteroposterior radiographs of the pelvis but accurately assessed on anteroposterior radiographs of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(4):477-482.[18] Ranawat CS, Dorr LD, Inglis AE. Total hip arthroplasty in protrusio acetabuli of rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1980;62(7):1059-1075.[19] Lewalle J, Hebrant R. Etude multicentrique belge des résultats des arthroplasties totales pour luxation congénitale invétérée de hanche. Acta Orthop Belg.1990;56(1):395-405.[20] Boudriot U, Hilgert J, Hinrichs F. Determination of the rotational center of the hip. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2006; 126(6): 417-420.[21] Fessy MH, N'Diaye A, Carret JP,et al. Locating the center of rotation of the hip. Surg Radiol Anat. 1999;21(4):247-250.[22] RussottiGM, Harris WH. Proximal placement of the acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1991;73(4) :587-592.[23] Pierchon F, Migaud H, Duquennoy A,et al. Radiologic evaluation of the rotation center of the hip. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 1993;79(4):281-284.[24] Nawabi DH, Meftah M, Nam D,et al. Durable fixation achieved with medialized, high hip center cementless THAs for Crowe II and III dysplasia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(2): 630-636.[25] Flecher X, Parratte S, Brassart N,et al. Evaluation of the hip center in total hip arthroplasty for old developmental dysplasia. J arthroplasty. 2008;23(8):1189-1196. [26] Kim DH,Cho SH,Jeong ST,et al. Restoration of the center of rotation in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25(7):1041-1046.[27] Traina F, De Fine M, Biondi F, et al. The influence of the centre of rotation on implant survival using a modular stem hip prosthesis. Int Orthop. 2009;33(6):1513-1518.[28] Holzapfel BM,Greimel F,Prodinger PM, et al. Total hip replacement in developmental dysplasia using an oval-shaped cementless press-fit cup. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(7):1355-1361.[29] Bowerman JW, Sena JM, Chang R.The teardrop shadow of the pelvis; anatomy and clinical significance. Radiology. 1982;143(3):659-662.[30] Pagnano W, Hanssen AD, Lewallen DG, et al. The effect of superior placement of the acetabular component on the rate of loosening after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1996;78(7):1004-1014.[31] Shin JK, Son SM, Kim TW, et al. Accuracy and reliability of preoperative on-screen templating using digital radiographs for total hip arthroplasty. Hip Pelvis. 2016;28(4):201-207.[32] Stigler SK, Müller FJ, Pfaud S, et al. Digital templating in total hip arthroplasty: Additional anteroposterior hip view increases the accuracy. World J Orthop. 2017;8(1):30-35. [33] Maruyama M, Wakabayashi S, Ota H, et al. Reconstruction of the shallow acetabulum with a combination of autologous bulk and impaction bone grafting fixed by cement. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2017;475(2):387-395.[34] Bhaskar D, Rajpura A, Board T. Current concepts in acetabular positioning in total hip arthroplasty. Indian J Orthop. 2017; 51(4):386-396.[35] Kim SC, Lim YW, Kwon SY, et al. Level of surgical experience is associated with change in hip center of rotation following cementless total hip arthroplasty: a radiographic assessment. PLoS One. 2017;12(5):e0178300. [36] Takamatsu T, Shishido T, Takahashi Y, et al. Radiographic determination of hip rotation center and femoral offset in Japanese adults: a preliminary investigation toward the preoperative implications in total hip arthroplasty. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:610763. [37] Lazennec JY, Brusson A, Folinais D, et al. Measuring extension of the lumbar-pelvic-femoral complex with the EOS® system. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol.2015;25(6): 1061-1068. [38] Rousseau MA, Brusson A, Lazennec JY. Assessment of the axial rotation of the pelvis with the EOS® imaging system: intra- and inter-observer reproducibility and accuracy study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014;24(6):891-895.[39] Murphy WS, Klingenstein G, Murphy SB, et al. Pelvic tilt is minimally changed by total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013;471(2):417-421. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [3] | Li Dadi, Zhu Liang, Zheng Li, Zhao Fengchao. Correlation of total knee arthroplasty efficacy with satisfaction and personality characteristics [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1346-1350. |
| [4] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [5] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [6] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [7] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [8] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [9] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [10] | Zhang Chao, Lü Xin. Heterotopic ossification after acetabular fracture fixation: risk factors, prevention and treatment progress [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1434-1439. |
| [11] | Wang Debin, Bi Zhenggang. Related problems in anatomy mechanics, injury characteristics, fixed repair and three-dimensional technology application for olecranon fracture-dislocations [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [12] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [13] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [14] | Zhao Zhongyi, Li Yongzhen, Chen Feng, Ji Aiyu. Comparison of total knee arthroplasty and unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in treatment of traumatic osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 854-859. |
| [15] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||