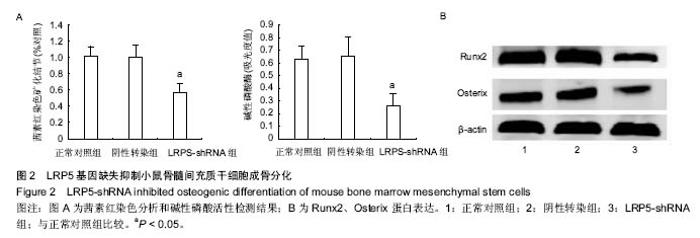
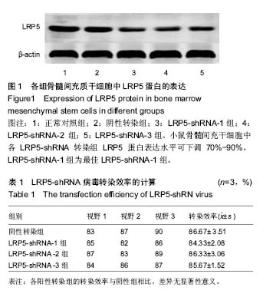
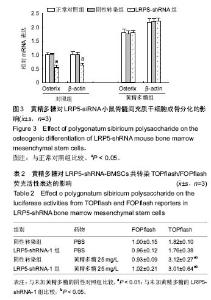
| [1] Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, et al. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1-34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis.N Engl J Med. 2001;344(19):1434-1441.[2] Tanaka Y, Nakayamada S, Okada Y.Osteoblasts and osteoclasts in bone remodeling and inflammation.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy.2005;4(3):325-328.[3] Black DM, Delmas PD, Eastell R, et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatmentof postmenopausal osteoporosis.N Engl J Med. 2007;356(18):1809-1822.[4] Bock O, Boerst H, Thomasius F E, et al. Common musculoskeletal adverse effects of oral treatment with once weekly alendronate and risedronate in patients with osteoporosis and ways for their prevention.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact.2007;7(2):144-148.[5] Mchorney CA, Schousboe JT, Cline RR, et al.The impact of osteoporosis medication beliefs and side-effect experiences on non-adherence to oral bisphosphonates.Current Medical Research & Opinion.2007;23(12):3137-3152.[6] Inderjeeth CA, Lee S, Glendenning P. Efficacy, side-effects and route of administration are more important than frequency of dosing of anti-osteoporosis treatments in determining patient preference and compliance: A critical review of published articles from 1970-2009. Bone. 2010;47(Suppl 1):S206.[7] 雷震,杨光义,叶方,等.黄精多糖药理作用及临床应用研究概述[J].中国药师,2012,(01):114-116.[8] 何才通,李文.黄精多糖药理功效研究进展[J].新中医,2014(03): 196-199.[9] 胡敏,王琴,周晓东,等.黄精药理作用研究进展及其临床应用[J].广东药学, 2005,(05):68-71.[10] 曾高峰,宗少晖,邹斌,等.黄精多糖对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化中ALP和BGP表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,(7):779-783.[11] 农梦妮,曾高峰,宗少晖,等.黄精多糖调控骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(15):2133-2139.[12] Hadjidakis DJ, Androulakis II. Bone Remodeling.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1092:385-96.[13] Ferron M,Wei J,Yoshizawa T,et al.Insulin Signaling in Osteoblasts Integrates Bone Remodeling and Energy Metabolism. Cell.2010; 142(2):296-308.[14] Pluskiewicz W, Adamczyk PE, Leszczynski P, et al. Ten-year probability of osteoporotic fracture in 2012 Polish women assessed by FRAX and nomogram by Nguyen et al.- Conformity between methods and their clinical utility. Bone. 2010;46(46):1661-1667.[15] Bliuc D,Nguyen ND,Milch VE, et al. Mortality risk associated with low-trauma osteoporotic fracture and subsequent fracture in men and women.JAMA.2009;301(5):513-521.[16] Lippuner K, Johansson H, Kanis J A, et al. Remaining lifetime and absolute 10-year probabilities of osteoporotic fracture in Swiss men and women. Osteoporos Int. 2009;20(7): 1131-1140.[17] Khang D, Choi J, Im YM, et al. Role of subnano-, nano- and submicron-surface features on osteoblast differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials.2012; 33(26):5997-6007.[18] Kemp KC, Hows J, Donaldso DC. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 2005;46(11): 1531-1544.[19] Fata JE, Kong YY, Li J, et al.The osteoclast differentiation factor osteoprotegerin-ligand is essential for mammary gland development.Cell. 2000;103(1): 41-50.[20] Ponte AL, Marais E, Gallay N, et al. The In Vitro Migration Capacity of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Comparison of Chemokine and Growth Factor Chemotactic Activities.Stem Cells.2007;25(7):1737-1745.[21] Zhou S, Greenberger J, Epperly M, et al. Age-related intrinsic changes in human bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and their differentiation to osteoblasts.Aging Cell.2008;7(3):335-343.[22] Darnay BG, Ni J, Moore PA, et al. Activation of NF-kappaB by RANK requires tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase.J Biol Chem. 1999;274(12):7724-7731. .[23] Jarrett H,Soles E,Sirna S,et al. Risk Factor Predominance in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Differs by Race: An Observational Study. J Clin Lipidology.2015; 9(3):423. [24] 曾高峰,宗少晖,邹斌,等.黄精多糖对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化中PINP和BMP-2表达的影响[J].天然产物研究与开发,2014,(08): 1188-1192.[25] Natsag J,Kendall MA,Sellmeyer DE,et al. Vitamin D, osteoprotegerin/receptor activator ofnuclear factor-kappaBligand (OPG/RANKL) and inflammation with alendronate treatment in HIV-infected patients with reduced bone mineral density.HIV Med. 2016;17(3):196-205. |