Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (27): 4336-4341.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.27.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Magnetic navigation META-NAIL interlocking intramedullary nailing for tibial shaft fractures via the supra-patellar approach
Zhang Jing, Ma Jiang-wei
- Department of Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Yulin, Yulin 610802, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Online:2017-09-28Published:2017-10-24 -
Contact:Ma Jiang-wei, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Yulin, Yulin 610802, Shaanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhang Jing, Master, Physician, Department of Orthopedics, the First Hospital of Yulin, Yulin 610802, Shaanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Jing, Ma Jiang-wei. Magnetic navigation META-NAIL interlocking intramedullary nailing for tibial shaft fractures via the supra-patellar approach [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(27): 4336-4341.
share this article
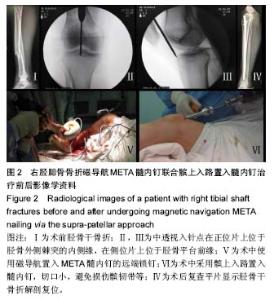
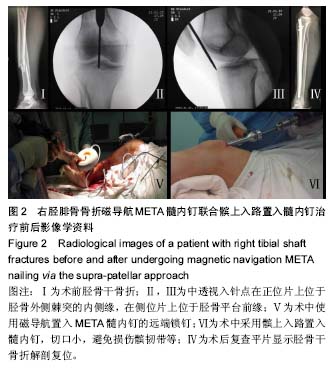
2.2 Lysholm评分 患者术前Lysholm评分平均50分,术后24周Lysholm评分为83-95分,平均90分。用Johner-Wruh标准评价患者术后功能恢复情况,临床优良率约为95%。 2.3 患者手术时间、出血量及住院时间 患者的手术时间为55-80 min,平均为65 min;出血量为10-80 mL,平均为30 mL;术后住院时间为3-10 d,平均7.2 d。 2.4 骨折愈合时间及疼痛情况 患者骨折平均愈合时间为85 d,术后随访中无患者出现患肢膝前疼痛。 2.5 并发症 所有患者术后14 d伤口拆线,未出现伤口不愈合、感染等情况;未出现骨折不愈合、延迟愈合、骨髓炎、畸形愈合等并发症。 2.6 典型病例 患者,男,43岁,因车祸导致右闭合型胫腓骨骨折,患处皮肤肿胀,小腿畸形明显,有反常活动,形成假关节。入院后给予患者跟骨牵引、消肿止痛、抬高患肢、患处冷敷等对症处理。待患肢肿胀消退产生皮纹后行手术治疗。患者在硬膜外麻醉下行磁导航META髓内钉髌上入路置入髓内钉治疗,手术过程顺利(见图2)。患者的手术时间约为60 min,出血量约为35 mL。术后复查平片显示胫骨干骨折解剖复位,术后鼓励患者行早期功能锻炼,预防深静脉血栓形成,患者对手术效果满意,术后3 d患者遵医嘱出院。 患者出院后前3个月每个月门诊复查1次,3个月后约2个月复查1次。术后2个月开始行部分负重功能锻炼,术后3个月开始行完全负重功能锻炼。术后6个月胫骨干骨折断端完全愈合,患者康复过程中未出现膝前疼痛、切口感染、下肢深静脉血栓及骨髓炎等并发症。 "
| [1] Yamamoto N, Ogawa K, Terada C, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis using posterolateral approach for distal tibial and tibial shaft fractures. Injury. 2016; 47(8): 1862-1866.[2] Larsen P, Lund H, Laessoe U, et al. Restrictions in quality of life after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fracture: a retrospective follow-up study of 223 cases. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(9): 507-512.[3] Sadighi A, Elmi A, Jafari M A, et al. Comparison study of therapeutic results of closed tibial shaft fracture with intramedullary nails inserted with and without reaming. Pak J Biol Sci. 2011;14(20): 950-953.[4] Obremskey WT, Cutrera N, Kidd CM.A prospective multi-center study of intramedullary nailing vs casting of stable tibial shaft fractures. J Orthop Traumatol.2017;18(1): 69-76.[5] Saied A, Ostovar M, Mousavi AA, et al. Comparison of intramedullary nail and plating in treatment of diaphyseal tibial fractures with intact fibulae: A randomized controlled trial. Indian J Orthop. 2016;50(3): 277-282.[6] Meena RC, Meena UK, Gupta GL, et al.Intramedullary nailing versus proximal plating in the management of closed extra-articular proximal tibial fracture: a randomized controlled trial. J Orthop Traumatol.2015;16(3):203-208.[7] Zelle BA. Intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures in the semi-extended position using a suprapatellar portal technique. Int Orthop. 2017.[8] Lowenberg DW, Githens M, Boone C. Principles of tibial fracture management with circular external fixation. Orthop Clin North Am. 2014;45(2):191-206.[9] Mukherjee S, Arambam MS, Waikhom S, et al. Interlocking Nailing Versus Plating in Tibial Shaft Fractures in Adults: A Comparative Study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(4): C8-C13. [10] Borrelli J J, Prickett W, Song E, et al. Extraosseous blood supply of the tibia and the effects of different plating techniques: a human cadaveric study. J Orthop Trauma. 2002; 16(10) : 691-695. [11] Auston DA, Meiss J, Serrano R, et al. Percutaneous or Open Reduction of Closed Tibial Shaft Fractures During Intramedullary Nailing Does Not Increase Wound Complications, Infection or Nonunion Rates. J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(4): 215-219.[12] Song SY, Chang HG, Byun JC, et al.Anterior knee pain after tibial intramedullary nailing using a medial paratendinous approach. J Orthop Trauma.2012;26(3):172-177.[13] Yalcinkaya M, Yavuz U, Sokucu S. Influence of nail prominence and insertion point on anterior knee pain after tibial intramedullary nailing. Orthopedics. 2014;37(6): 364.[14] Vaisto O, Toivanen J, Kannus P, et al. Anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of fractures of the tibial shaft: an eight-year follow-up of a prospective, randomized study comparing two different nail-insertion techniques. J Trauma. 2008; 64(6): 1511-1516.[15] Rodrigues FL, de Abreu LC, Valenti VE, et al.Bone tissue repair in patients with open diaphyseal tibial fracture treated with biplanar external fixation or reamed locked intramedullary nailing. Injury.2014;45 Suppl 5: S32-S35.[16] 陈德明,徐晓阳,王蔚,等.多功能带锁髓内钉和钢板置入内固定修复关节外胫骨创伤性骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(4): 549-553.[17] Yao Q, Ni J, Peng L B, et al. Locked plating with minimally invasive percutaneous plate osteosynthesis versus intramedullary nailing of distal extra-articular tibial fracture: a retrospective study. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013;93(47): 3748-3751.[18] Busse JW, Bhandari M, Einhorn T A, et al. Trial to re-evaluate ultrasound in the treatment of tibial fractures (TRUST): a multicenter randomized pilot study. Trials. 2014;15: 206.[19] Xia L,Zhou J,Zhang Y,et al.A meta analysis of reamed versus undreamed intramedullary nailing for the treatment of closed tibial fractures.Orthopedics.2014;37(4):e332-338.[20] Franke J, Hohendorff B, Alt V, et al. Suprapatellar nailing of tibial fractures-Indications and technique. Injury. 2016, 47(2): 495-501.[21] Eastman J,Tseng S,Lo E,et al. Retropatellar technique for intramedullary nailing of proximal tibia fractures:a cadaveric assessment. J Orthop Trauma.2010;24(11):672-676.[22] Polonet DMD. Suprapatellar nailing technique for tibial fracture. Orthopaedics.2014;29(3):145-149.[23] Hannah A, Aboelmagd T, Yip G, et al. A novel technique for accurate Poller (blocking) screw placement. Injury. 2014; 45(6):1011-1014.[24] 孙竞群,纪瑞耿. 阻挡螺钉矫正胫骨骨折髓内钉内固定残余移位及加强稳定性的疗效观察[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015, 30(12):1331-1332.[25] Kulkarni SG,Varshneya A,Kulkarni S,et al. Intramedullary nailing supplemented with Poller screws for proximal tibial fractures. J Orthop Surg(Hong Kong).2012;20(3):307-311.[26] Fu B. Locked META intramedullary nailing fixation for tibial fractures via a suprapatellar approach. Indian J Orthop. 2016, 50(3): 283-289.[27] Zelle BA, Boni G. Safe surgical technique: intramedullary nail fixation of tibial shaft fractures. Patient Saf Surg.2015;9: 40.[28] Tahririan M A, Ziaei E, Osanloo R. Significance of the position of the proximal tip of the tibial nail: An important factor related to anterior knee pain. Adv Biomed Res. 2014; 3: 119[29] Seyhan M,Unay k,Sener N. Intramedullary nailing versus percutaneous locked plating of distal extra-articular tibial fractures:a retrospective study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2013;23(5):595-601.[30] 徐德世. 不同手术方法治疗胫骨骨折的临床疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2016(S1): 99.[31] 郭远武,曾志刚,李剑辉,等.三种髓内钉置入固定治疗胫骨骨折79例比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,3(4):756-758.[32] Kreb DL, Blokhuis TJ, van Wessem KJ, et al. Intramedullary nailing without interlocking screws for femoral and tibial shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2013; 133(8):1109-1113.[33] Durakbasa O, Haklar U, Tuygun H, et al. [Intramedullary nailing of adult femoral fractures]. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2002;36(4): 316-321.[34] Negrin LL, Vecsei V. Is a magnetic-manual targeting device an appealing alternative for distal locking of tibial intramedullary nails?. Arch Trauma Res. 2013;2(1):16-20.[35] Rueger JM, Rucker AH, Hoffmann M. Suprapatellar approach to tibial medullary nailing with electromagnetic field-guided distal locking. Unfallchirurg. 2015;118(4): 302-310.[36] 张浩,张立海,黄睿,等. 可视化磁力导航在胫骨髓内钉远端锁钉中的应用[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2014,3(3):20-223.[37] Moreschini O, Petrucci V, Cannata R.Insertion of distal locking screws of tibial intramedullary nails: a comparison between the free-hand technique and the SURESHOT Distal Targeting System. Injury. 2014;45(2): 405-407.[38] 钟健,刘欣伟,周大鹏,等. 应用Meta髓内钉结合髌上入路治疗胫骨中上段骨折20例早期疗效分析[J].临床军医杂志, 2016,44(2): 202-204.[39] Xu X,Li X,Liu L,et al.A meta-analysis of external fixator versus intramedullary nails for open tibial fracture fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9: 75.[40] Katsoulis E, Court-Brown C, Giannoudis P V. Incidence and aetiology of anterior knee pain after intramedullary nailing of the femur and tibia. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(5): 576-580.[41] Cartwright-Terry M,Snow M,Nalwad H. The severity and prediction of anterior knee pain post tibial nail insertion. J Orthop Trauma.2007;21(6):381-385.[42] Metsna V,Vorobjov S,Martson A,et al. Prevalence of anterior knee pain among patients following total knee arthroplasty with nonreplaced patella: a retrospective study of 1778 knees. Medicina (Kaunas). 2014; 50(2): 82-86.[43] Sanders RW, Dipasquale TG, Jordan CJ, et al. Semiextended intramedullary nailing of the tibia using a suprapatellar approach: radiographic results and clinical outcomes at a minimum of 12 months follow-up. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28 Suppl 8: S29-S39.[44] Gaines RJ, Rockwood J, Garland J, et al.Comparison of insertional trauma between suprapatellar and infrapatellar portals for tibial nailing. Orthopedics. 2013, 36(9): e1155-e1158.[45] Gelbke MK,Coombs D,Powell S,et al. Suprapatellar versus infrapatellar intramedullary nail insertion of the tibia:a cadaveric model for comparison of patellofemoral contact pressures and forces. J Orthop Trauma.2010;24(11):665-671.[46] Sanders RW,DiPasquale TG,Jordan CJ,et al. Semiextended intramedullary nailing of the tibia using a suprapatellar approach:radiographic results and clinical outcomes at a minimum of 12 months follow up.J Orthop Trauma.2014; 28(5):245-255.[47] Labronici PJ, Santos PR, Franco JS, et al. Recommendations for avoiding knee pain after intramedullary nailing of tibial shaft fractures. Patient Saf Surg. 2011; 5(1): 31.[48] Morandi M, Rose KM, Mangano S. Update in tibia intramedullary nailing: percutaneous suprapatellar access route with the knee in semi-extended position for intramedullary stabilization of tibia fractures. Techniques in Orthopaedics. 2014; 29(2): 56-61.[49] Jones M,Parry M,Whitehouse M,et al.Radiologic outcome and patient reported function after intramedullary nailing: a comparison of the retropatellar and infrapatellar approach. J Orthop Trauma.2014;28(5):256-262.[50] 付备刚,王秀会,蔡攀,等. 髌上入路锁定型胫骨Meta髓内钉内固定治疗复杂胫骨骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志. 2017,32(2): 152-155. |
| [1] | Li Shengkai, Li Tao, Wei Chao, Shi Ming. Comparison of biomechanical properties of calcium phosphate/polymethyl methacrylate composite bone cement and polymethyl methacrylate bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2581-2586. |
| [2] | Yang Xue, Wang Baoqun, Jiang Xiaowen, Zou Shengcan, Ming Jinfa, Lin Shasha. Preparation and properties of biodegradable plant polysaccharide hemostatic microspheres [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2607-2611. |
| [3] | Liu Jiali, Suo Hairui, Yang Han, Wang Ling, Xu Mingen. Influence of lay-down angles on mechanical properties of three-dimensional printed polycaprolactone scaffolds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2612-2617. |
| [4] | Liu Xiaojun, Xu Yuyin, Liu Kangbo, Zhou Jing, Han Ying, Xiong Yue, Tian Yuan. Preparation and properties of carboxymethylated cotton linters hemostatic gauze [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2593-2599. |
| [5] | Huang Bo, Chen Mingxue, Peng Liqing, Luo Xujiang, Li Huo, Wang Hao, Tian Qinyu, Lu Xiaobo, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . Fabrication and biocompatibility of injectable gelatin-methacryloyl/cartilage-derived matrix particles composite hydrogel scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 10(16): 2600-2606. |
| [6] | Luo Di, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Li Jiacheng, Yan Bozhao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Difference in osteogenesis- and angiogenesis-related protein expression in femoral head samples from patients with femoral head necrosis of different etiologies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1641-1647. |
| [7] | Zhu Chunhui, Zhang Yi, Song Huanghe, Liang Wenwei. Protective effect of astaxanthin on tert-butyl hydrogen peroxide-induced chondrocyte damage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1648-1655. |
| [8] | Zhao Tianyu, Jin Song, Zhang Di, Liu Xiaoxiao, Ma Jiang, Wang Ju. Baduanjin training for patellar tendinopathy in a randomized controlled trial: improving pain, muscle flexibility and lower limb balance stability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1662-1668. |
| [9] | Zhang Lei, Xiu Chunmei, Ni Li, Chen Jianquan. Identification and expression analysis of mouse nucleus pulposus specific markers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1669-1674. |
| [10] | Yu Dong, Liu Kan, Shi Zongting, Yang Xiaoxia, Liu Hengping, Zhang Qingfeng. Pathological changes of the cervical intervertebral discs and rules of migration and apoptosis in endplate chondrocytes in a rabbit model of dynamic disequilibrium [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1675-1679. |
| [11] | Tian Zhuang, Wang Diaodiao, Zhang Chu, Li Hanchen, Zhou Jian, Yao Qi. The mechanism by which bone morphogenetic protein 2 indirectly regulates sclerostin expression in osteocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1686-1691. |
| [12] | Li Jingyu, Su Yingying, Bai Ding. Morphological characteristics of subchondral bone in a mouse model of early osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1692-1698. |
| [13] | Bao Hongyu Lü Dongmei, He Yun, Xia Delin, Chen Junliang. Incidence of osteonecrosis in rats with jaw versus femoral defects following zoledronic acid injection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1699-1704. |
| [14] | Tan Qian, Li Bocun, Li Jing, Li Jia, Xiang Hongchun, Cai Guowei. Acupuncture combined with moxibustion regulates the expression of circadian clock protein in the synovium of rats with osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1714-1719. |
| [15] | Fei Jing, Tao Meihui, Li Leiji. Electroacupuncture promotes facial nerve regeneration in a rat model of facial nerve crush [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1728-1733. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||