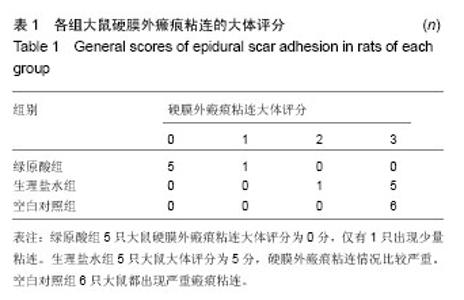
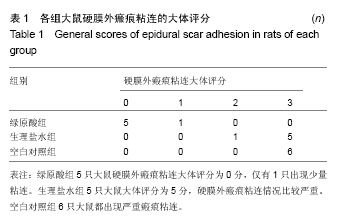
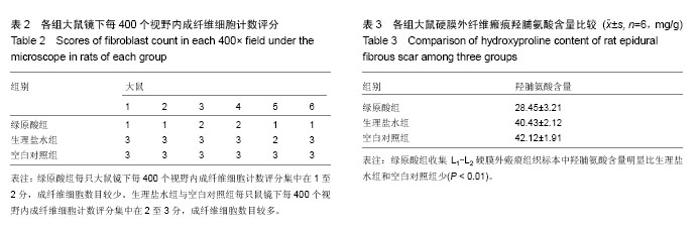
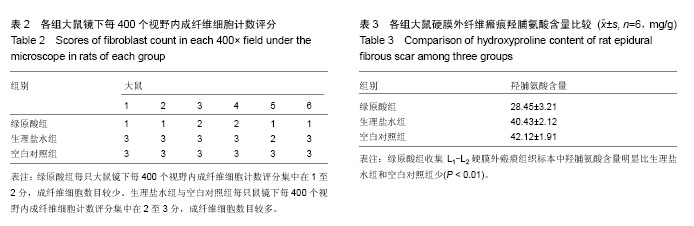
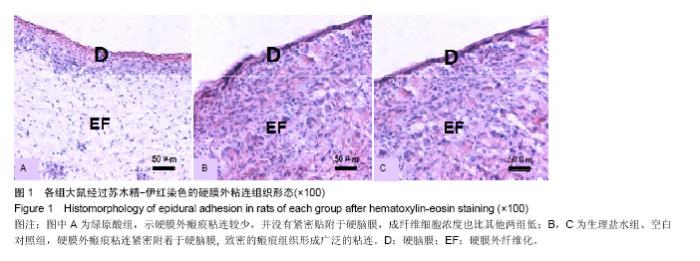
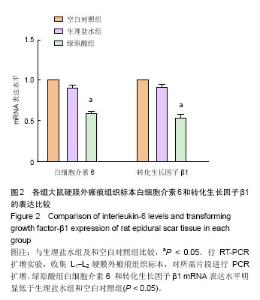
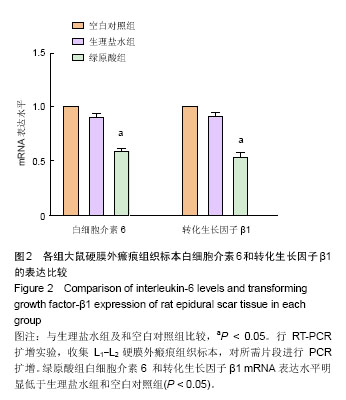
| [1] Kelly GA, Blake C, Power CK, et al. The impact of spinal cord stimulation on physical function and sleep quality in individuals with failed back surgery syndrome: a systematic review. Eur J Pain.2012; 16(6): 793-802.
[2] 陈昌伟,幸永明,王坚,等.半棘突翻转造盖术预防椎板间开窗术后粘连[J].颈腰痛杂志,2004,25(2):119-120.
[3] Rabb CH. Failed back syndrome and epidural fibrosis. Spine J. 2010;10(5):454-455.
[4] Cokluk C, Aydi K. Experimental rabbit hemilaminotomy model in the evaluation of peridural fibrosis: a minimally inva-sive peridural fibrosis model. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2005;48: 235-239.
[5] Sandoval MA, Hernandez-Vaquero D. Preventing peridural fibrosis with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur Spine J. 2008;17:451-455.
[6] 孙庆仲,李正维,闫红艳,等.预防硬膜外瘢痕粘连脂肪移植体大小的筛选研究[J].骨与关节损伤杂志,2003,18(4):223-226.
[7] 洪笃开,林本丹.硬膜外瘢痕粘连及其防治进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(4):285-286.
[8] 陈绍华,王亚琴,罗立新.天然产物绿原酸的进展研究[D].华南理工大学生物科学与工程学院,2008.
[9] 孙秋艳,刘艳,汪茜,等.绿原酸对Lewis肺癌小鼠及人A549肺癌的实验研究[J].华西药学杂志,2010,25(5):536.
[10] Zhang C, Zhou H, Liu C,et al. An experimental novel study:Angelica sinensis prevents epidural fibrosis in laminectomy rats via downregulation of hydroxyproline, IL-6, and TGF-b 1. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013.
[11] 戚晓渊,史秀灵.绿原酸抗肝纤维化作用的研究[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(15):139-143.
[12] 陈芳艳.肝纤维化发生发展及逆转过程中kupffer细胞表型的研究[D].解放军军事医学科学院, 2013.
[13] 朱跃科,王宝恩,申凤俊,等.实验性肝纤维化基质金属蛋白酶-2基因表达与酶活性的变化[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2005,13(7): 509-512.
[14] 杨斌,丘岳,王柳萍,等.广西山银花绿原酸体外抗炎作用及分子机制研究[J]. 中国药理学通报,2009,25(4):542-545.
[15] Cokluk C, Aydi K. Experimental rabbit hemilaminotomy model in the evaluation of peridural fibrosis: a minimally invasive peridural fibrosis model. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2005;48: 235-239.
[16] Siqueira EB, Kranzler LI, Dharkar DD. Fibrosis of the dura mater.a cause of ‘‘failed back’’ syndrome. Surg Neurol. 1983; 19:168-170.
[17] 钱邦平,唐天驷,杨同其,等.后路椎体间融合治疗严重腰椎管狭窄症初步报告[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(5): 371-373.
[18] Rothkopf DM, Webb S, Szabo RM, et al. An experimental model for the study of canine flexor tendon adhesions. J Hand Surg Am. 1991;16:694-700.
[19] Yildiz KH, Gezen F, Is M, et al. Mitomycin C, 5-fluorouracil, and cyclosporin A prevent epidural fibrosis in an experimental laminectomy model. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(9):1525-1530.
[20] 刘灿,周卫,孔焕宇.三七透明质酸钠凝胶对家兔硬膜外瘢痕中成纤维细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 世界中医药杂志,2010,5(4):100-102.
[21] Zhang C, Kong X, Ning G, et al. All-trans retinoic acid prevents epidural fibrosis through NF-jB signaling pathway in post-laminectomy rats. Neuropharmacology. 2014;79: 275-281.
[22] 刘仕良,杨帆,段祥林,等. 当归加玻璃酸钠关节腔注射对兔膝骨关节炎软骨细胞Bcl-2、Bax表达的影响[J]. 数理医药学杂志, 2009, 22(2):163-165.
[23] Gomez-reino JJ,Sandberg M,Carreira PE,et al.Expression of typesⅠ, Ⅲ and Ⅳcollagens genes in fibrotic skin and nerve lesions of toxic oil syndrome patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993; 93(1):103-107.
[24] Jin R, Huang XL, Li H, et al. Laser Therapy for Prevention and Treatment of Pathologic Excessive Scars. Plastic Rec Surg. 2013;(6):1747-1758.
[25] Honnegowda TM, Kumar P, Udupa P, et al. Effect of limited access dressing on hydroxyproline and enzymatic antioxidant status in nonhealing chronic ulcers. Indian J Plast Surg. 2014; 47(2):216-220.
[26] Ozer AF,Oktenoglu T,Sasani M,et al. Preserving the ligamentum flavum in lumbar discectomy:a new technique that prevents scar tissue formation in the first 6 months postsurgery. Neurosurgery. 2006;59(Suppl 1): 126-133.
[27] Xu L, Kitani A,Fuss I,et al.Cutting edge:regulatory Tcells induce CD4+CD25-Foxp3- Tcells or are self-induced to become Thl7 cells in the absence of exogenous TGF-beta. J Immunol. 2007;178(11):6725-6729.
[28] Liu C, Chang R, Yao X, et al. ISG15 expression in response to double-stranded RNA or LPS in cultured Fetal bovine lung (FBL) cells. Vet Res Commun. 2009;33:723-733.
[29] Chen K, Zhang J, Zhang W, et al. ATP-P2X4 Signaling Mediates NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: A Novel Pathway of Diabetic Nephropathy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013; 45(5): 932-943.
[30] Li YX, Hiroi Y, Ngoy S,et al. Notch1 in Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Mediates Cardiac Repair After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation. 2011;123(8):866-876.
[31] Kovacic JC, Mercader N, Torres M,et al. Epithelial-to- Mesenchymal and Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: From Cardiovascular Development to Disease. Circulation. 2012;(14):1795-1808.
[32] Piera-Velazquez S, Li ZD, Jimenez SA. Role of Endothelial- Mesenchymal Transition (EndoMT) in the Pathogenesis of Fibrotic Disorders. Am J Pathol. 2011;179(3): 1074-1080.
[33] Gruber J, Fong S, Chen CB, et al. Mitochondria-targeted antioxidants and metabolic modulators as pharmacological interventions to slow ageing. Biotechnol Adv. 2013;31(5): 563-592.
[34] Ritchie ND, Baggott AV, Andrew Todd WT. Acetazolamide for the Prevention of Acute Mountain Sickness-A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Travel Med. 2012; 19(5): 298-307.
[35] Liu J, Ni B, Zhu L,et al. Mitomycin C-polyethylene glycol controlled-release film inhibits collagen secretion and induces apoptosis of fibroblasts in the early wound of a postlaminectomy rat model. Spine J. 2010;10:441-447.
[36] Lee JY, Stenzel W, Ebel H,et al. Mitomycin C in preventing spinal epidural fibrosis in a laminectomy model in rats. J Neurosurg. 2004;100:52-55.
[37] Wu M, He J, Ren X, et al. Development of functional biointerfaces by surface modification of polydimethylsiloxane with bioactive chlorogenic acid. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;116:700-706.
[38] Labelle M, Begum S, Hynes RO. Direct Signaling between Platelets and Cancer Cells Induces an Epithelial- Mesenchymal-Like Transition and Promotes Metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(5):576-590.
[39] Hayashi M, Yamaji Y, Nakazato Y, et al. The effects of calcium channel blockers on nuclear factor kappa B activation in the mesangium cells. Hypertens Res. 2000;23:521-525.
[40] Espinosa L, Cathelin S, D’Altri T, et al. The Notch/Hes1 Pathway Sustains NF-κB Activation through CYLD Repression in T Cell Leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(3): 268-281. |