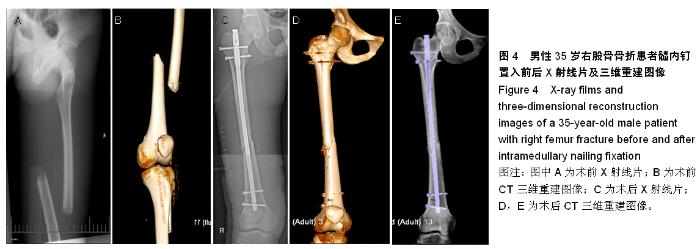
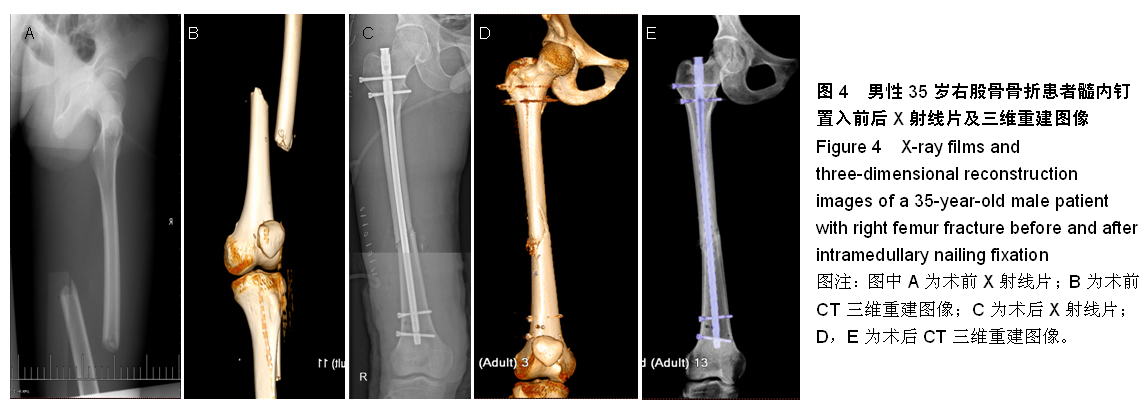
| [1] Campochiaro G, Baudi P, Loschi R,et al.Complex fractures of the humeral shaft treated with antegrade locked intramedullary nail: clinical experience and long-term results.Acta Biomed. 2015;86(1):69-76.
[2] Kurup H, Hossain M, Andrew JG.Dynamic compression plating versus locked intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011; (6): CD005959.
[3] Li WY, Zhang BS, Zhang L, et al.Comparative study of antegrade and retrograde intramedullary nailing for the treatment of humeral shaft fractures.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2009; 22(3):199-201.
[4] Ma TH, Xiang M, Deng YZ, et al.Retrograde locked intramedullary nail for the treatment of middle or distal fractures of humeral shaft].Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2010; 23(9): 657-859.
[5] 刘江银,邓贵生.交锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折154例术后并发症分析[J].中国保健营养(下旬刊),2013,23(4):1787-1787.
[6] 李志刚.带锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折53例并发症原因分析[J].陕西医学杂志,2012,41(9):1198-1199,1211.
[7] 刘岩,陈庆泉,侯春林,等.交锁髓内钉治疗股骨干粉碎性骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2004,6(4):382-385.
[8] Togawa D, Kayanja MM, Reinhardt MK,et al.Bone-mounted miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw and translaminar facet screw placement: part 2--Evaluation of system accuracy.Neurosurgery. 2007;60(2 Suppl 1):ONS129-139.
[9] Tian W, Han X, Liu B, et al.A robot-assisted surgical system using a force-image control method for pedicle screw insertion. PLoS One. 2014; 9(1):e86346.
[10] Lieberman IH, Togawa D, Kayanja MM, et al.Bone-mounted miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw and translaminar facet screw placement: Part I--Technical development and a test case result.Neurosurgery. 2006;59(3):641-650.
[11] Hu X, Lieberman IH.What is the learning curve for robotic-assisted pedicle screw placement in spine surgery?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014; 472(6):1839-1844.
[12] Pechlivanis I, Kiriyanthan G, Engelhardt M, et al. Percutaneous placement of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine using a bone mounted miniature robotic system: first experiences and accuracy of screw placement.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009; 34(4):392-398.
[13] Rosenthal R, Gantert WA, Scheidegger D,et al.Can skills assessment on a virtual reality trainer predict a surgical trainee's talent in laparoscopic surgery?Surg Endosc. 2006; 20(8):1286-1290.
[14] Sugimoto Y, Tanaka M, Nakanishi K, et al.Safety of atlantoaxial fusion using laminar and transarticular screws combined with an atlas hook in a patient with unilateral vertebral artery occlusion (case report).Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009;129(1):25-27.
[15] Reinhold M, Knop C, Beisse R, et al.Operative treatment of traumatic fractures of the thorax and lumbar spine. Part II: surgical treatment and radiological findings].Unfallchirurg. 2009;112(2):149-167.
[16] Shawky A, Al-Sabrout AM, El-Meshtawy M, et al. Thoracoscopically assisted corpectomy and percutaneous transpedicular instrumentation in management of burst thoracic and thoracolumbar fractures.Eur Spine J. 2013; 22(10):2211-2218.
[17] 尹知训,丁红梅,白波,等.经皮椎弓根植骨计算机辅助术前计划与模拟手术[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(17): 3247-3250.
[18] 贺锦阳,张云鹏,任龙韬.肱骨近端四部分骨折的数字化术前模拟手术规划[J].中国现代医生,2011,49(22):24-25.
[19] 蒋协远,王大伟.骨科临床疗效评价标准[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2005:260.
[20] 钟世镇.我国数字医学发展史概要[J].中国数字医学,2011,6(12): 12-14.
[21] 钟世镇.转化医学理念对数字医学的启迪[J].中华消化外科杂志, 2012,11(2):99-100.
[22] Levi D, Rampa F, Barbieri C,et al.True 3D reconstruction for planning of surgery on malformed skulls.Childs Nerv Syst. 2002;18(12):705-706.
[23] Metzger MC, Hohlweg-Majert B, Schön R, et al.Verification of clinical precision after computer-aided reconstruction in craniomaxillofacial surgery.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 104(4):e1-10.
[24] Rodt T, Schlesinger A, Schramm A, et al.3D visualization and simulation of frontoorbital advancement in metopic synostosis. Childs Nerv Syst. 2007; 23(11):1313-1317
[25] Lu J, Ni H, Wang Z, et al.Validation study on precision of digitized custom-made radial head prosthesis by three-dimensional visualization of virtual surgery.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(9):1065-1069.
[26] Bain GI, Ashwood N, Baird R, et al.Management of Mason type-III radial head fractures with a titanium prosthesis, ligament repair, and early mobilization. Surgical technique.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87 Suppl 1(Pt 1):136-147.
[27] Jiang-Jun Z, Min Z, Ya-Bo Y, et al.Finite element analysis of a bone healing model: 1-year follow-up after internal fixation surgery for femoral fracture.Pak J Med Sci. 2014;30(2): 343-347.
[28] Rohlmann A, Boustani HN, Bergmann G, et al.A probabilistic finite element analysis of the stresses in the augmented vertebral body after vertebroplasty.Eur Spine J. 2010; 19(9): 1585-1595.
[29] He Q, Jiang W, Luo J.Investigation on biomechanics behavior using three-dimensional finite element analysis for femur shaft fracture treated with locking compression plate].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2014; 31(4):777-81, 792.
[30] 刘长贵,张保中.带锁髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折并发症及防治[J].中华骨科杂志,1998,27(12):725-727.
[31] 赵宝成,马宝通,刘林涛,等.带锁髓内钉治疗526例长骨骨折疗效分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(3):136-142. |