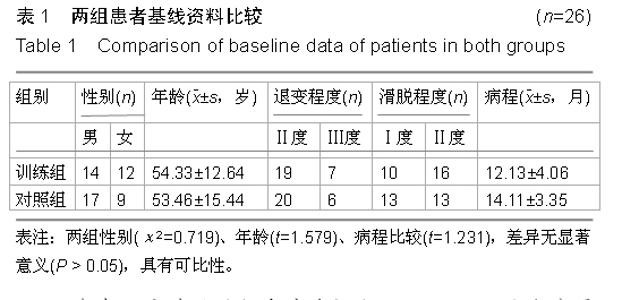
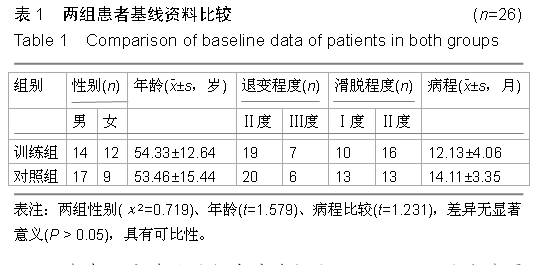
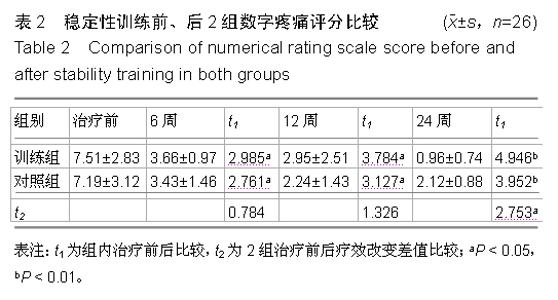
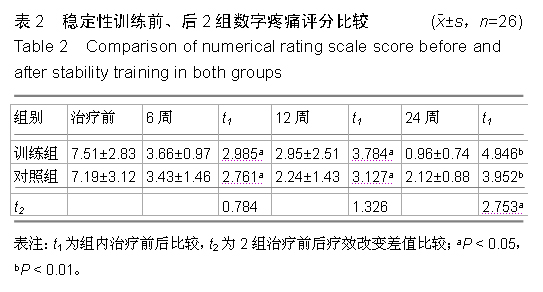
| [1] 徐杰,刘春华,黄惠梅,等.后路单枚Cage植骨融合联合椎弓根钉棒系统治疗腰椎滑脱症[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2012, 26(7):891-892.
[2] Watters WC3rd, Bono CM, Gilbert TJ, et al. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis. Spine J. 2009;7: 609-614.
[3] 颜国城,严照明,陈开明.开窗中枚椎间融合器结合提拉复位系统治疗腰椎滑脱症[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,26(3): 238-239.
[4] Fujiwara A, Tamai K, Yamato M, et al. The relationship between facet joint osteoarthritis and disc degeneration of the lumbar spine: an MRI study. Eur Spine J. 1999;8(5):396-401.
[5] 潘明荣,陈岚岚,韩晓鸣.基于腰椎稳定性理论的慢性腰痛运动疗法研究进展[J].健康研究,2009 (1):75-79.
[6] 任天平.脊柱保健操联合椎间孔电针刺激治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2013,35(6): 473-474.
[7] Fairbank JC, Pynsent PB. The Oswestry disability index. Spine. 2000;25(22): 2940-2953.
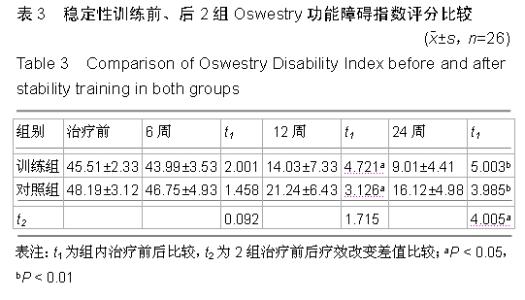
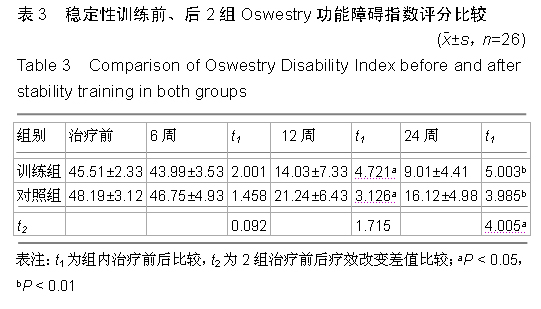
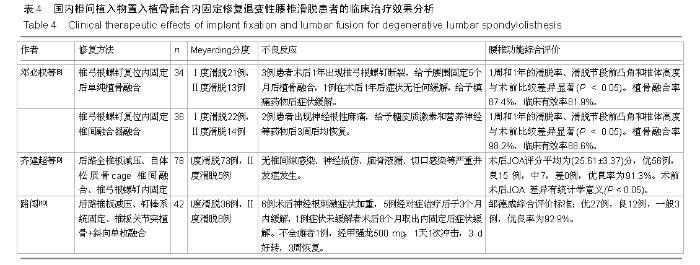
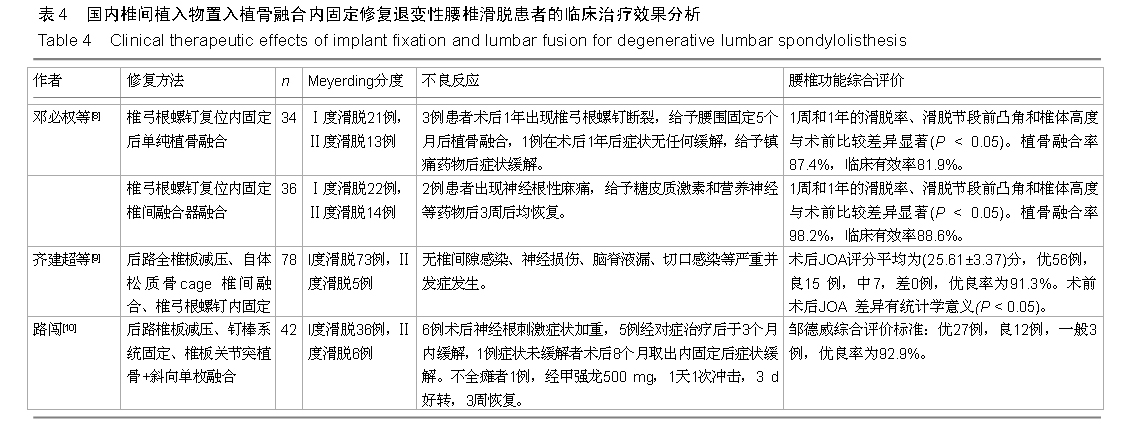
[8] 邓必权,胡华,滕宇,等.椎弓根螺钉复位内固定后单纯植骨融合与椎间融合器融合治疗腰椎滑脱症的疗效比较[J].中国老年学杂志, 2015;35(7):1823-1825.
[9] 齐建超.韩德韬.后路椎间cage置入融合内固定术治疗退行性腰椎滑脱的疗效分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(1):
[10] 路闯,袁宏伟,代振动,等.退变性腰椎滑脱的手术治疗[J]. 中国实用医刊,2014,41(8):77-79.
[11] 李吴祯,周学儒,白瑞霞.医学影像在诊疗脊椎滑脱中的临床价值J].当代医学,2011,17(19):84-85.
[12] Anderson K, Behm DG. The impact of instability resistance training on balance and stability. Sports Med. 2005;35(1): 43-53.
[13] Wang G, Karki SB, Xu S, et al. Quantitative MRI and X-ray analysis of disc degeneration and paraspinal muscle changes in degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2015;28(2):277-285.
[14] Panjabi MM. Clinical spinal instability and low back pain. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2003;13(4):371-379.
[15] 乔志恒,华桂茹主编.理疗学[M].北京:华夏出版社,2005.
[16] MacDonald DA, Moseley GL, Hodges PW. The lumbar multifidus: does the evidence support clinical beliefs? Man Ther. 2006;11(4):254-263.
[17] Boyle, M. Functional Training for Sports.Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics, 2004.
[18] 黎涌明,于洪军,资薇等.论核心力量及其在竞技体育中的训练[J]. 体育科学,2008,28(4):19-29.
[19] Von Korff M, Balderson BH, Saunders K, et al. A trial of an activating intervention for chronic back pain in primary care and physical therapy settings. Pain. 2005;113(3):323-330.
[20] O’Sullivan PB, Phyty GD, Twomey LT, et al. Evaluation of specific stabilizing exercise in the treatment of chronic low back pain with radiologic diagnosis of spondylolysis or spondylolisthesis. Spine.1997;22 (24):2959-2967.
[21] Tarantino U, Fanucci E, Iundusi R, et al. Lumbar spine MRI in upright position for diagnosing acute and chronic low back pain: statistical analysis of morphological changes. J Orthopaed Traumatol. 2013;14:15-22.
[22] 朱康,孙根文,乔培柳,等.椎旁肌横截面积变化可导致退行性腰椎滑脱[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(9):1392-1397.
[23] Gramse R R, Sinaki M, Ilstrup D M. Lumbar spondylolisthesis: a rational approach to conservative treatment[C]//Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 1980;55(11):681-686.
[24] 角南昌三,鈴木康三,黒木裕士,等.京都大学医療技術短期大学部理学療法学科, *大川整形外科,理学療法学,1990,17(3): 264-269.
[25] Radebold A, Cholewicki J, Polzhofer GK, et al. Impaired postural control of the lumbar spine is associated with delayed muscle response times in patients with chronic idiopathic low back pain. Spine. 2001;26:724-730.
[26] Nava-Bringas TI, Hernández-López M, Ramírez-Mora I, et al. Effects of a stabilization exercise program in functionality and pain in patients with degenerative spondylolisthesis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2014;27(1):41-46.
[27] MacDonald DA, Dawson AP, Hodges PW. Behavior of the lumbar multifidus during lower extremity movements in people with recurrent low back pain during symptom remission. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41(3):155-164.
[28] Huang KY, Lin R M, Lee YL, et al. Factors affecting disability and physical function in degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis of L4–5: evaluation with axially loaded MRI. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(12):1851-1857. |