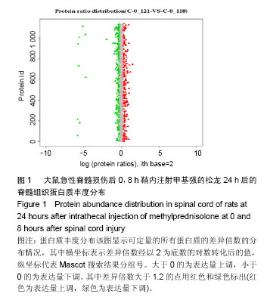
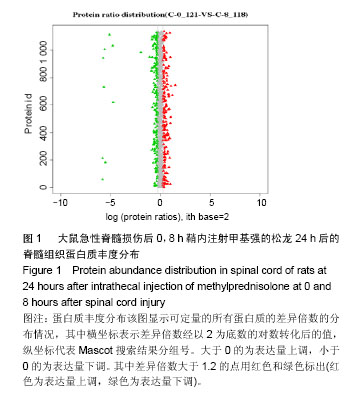
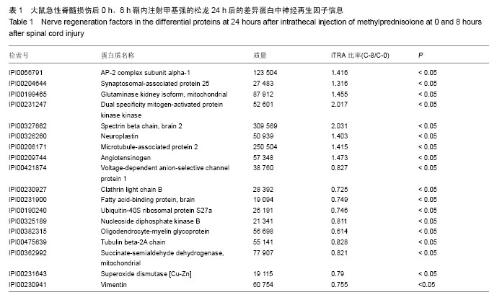
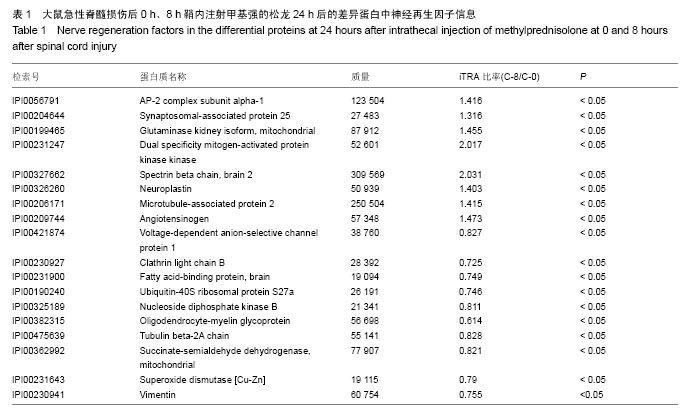
| [1] Fehlings MG,Perrin RG.The timing of surgical intervention in the treatment of spinal cord injury:a systematic review of recent clinical evident.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(11):28-35.
[2] 郑启新,汪健,郭晓东.急性脊髓损伤后神经保护的研究现状与展望[J].中华实验外科杂志,2012,29(7):1213-1216.
[3] Harel NY, Strittmatter SM.Can regenerating axons recapitulate developmental guidance during recovery from spinal cord injury?Nat Rev Neurosci.2006;7(8):603-616.
[4] WiseYong,胥少汀,苟三怀.大剂量甲基强的松龙治疗急性脊髓损伤[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2000,10(5):304-305.
[5] 郑力恒,林宏生,李锦聪.脊髓损伤后急性期甲基强的松龙干预对脊髓神经细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(5): 452-458.
[6] Tsutsumi S,Ueta T,Shiba K, et al.Effects of the second national acute spinal cord injury study of hish-dose methylprednisolone therapy on acute cervical spinal cord injury-results in spinal injuries center. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006; 31(26):2992-2996.
[7] Suberviola B, Gonzalez-Castro A, Llorca J, et al. Early complications of high-dose methylprednisolone in acute in acute spinal cord injury patients. Injury.2008; 39(7):748-752.
[8] 孙强,徐杰,王黎明,等.大剂量甲基强的松龙冲击治疗急性脊髓损伤的疗效观察[J].中国伤残医学,2009,17(6):5-7.
[9] Lee HC, Cho DY, Lee WY, et al. Pitfalls in treatment of acute cervical spinal cord injury using high-dose , methylprednisolone: a retrospect audit of 111 patients. Surg Neurol.2007; 68:37-42.
[10] 周红英,戚观树,侯群.脊髓损伤的发病机制及治疗进展[J].中华中医药学刊,2012,30(4):769-771.
[11] Park D,Joo SS,Lee HJ,et al.Microtubule-associated protein 2, an early blood marker of ischemic brain injury.J Neurosci Res.2012;90(2):461-467.
[12] Rozet I.Methylprednisolone in acute spinal cord injury is there any other ethical choice.J Neurosurg Anesth.2008;20(2): 137-139.
[13] Ito Y, Sugimoto Y, Tomioka M, et al. Does high dose methylprednisolone sodium succinate really improve neurological status in patient with acute cervical cord injury?: a prospective study about neurological recovery and early complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009; 34(20):2121- 2124.
[14] 孙天胜.甲基强的松龙对急性脊髓损伤的治疗效果与存在的问题[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2005,15(7):389-390.
[15] Pettiford JN,Bikhchandani J,Ostlie DJ,et al.A review: the role of high dose methylprednisolone in spinal cord trauma in children.Pediatr Surg Int.2012;28(3):287-294.
[16] 李青,王春庆,支钢,等.甲基强的松龙冲击治疗急性脊髓损伤的早期并发症[J].中国现代医学杂志,2012,22(6):65-68.
[17] 王凯丰,刘海鹰,王波.甲泼尼龙琥珀酸钠鞘内注射治疗急性脊髓损伤的实验研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,51(5):426-430.
[18] 柏亮杰,梅晰凡,袁亚江.甲基强的松龙对大鼠脊髓损伤节段炎性细胞因子和自噬因子表达的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2014, 30(1):13-18.
[19] 宗少晖,方晔,彭金珍,等.急性不完全脊髓损伤模型大鼠相关炎症因子的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(18):2806-2811.
[20] Li Q, Wong JH, Lu G,et al.Gene expression of synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (SNAP-25) in the prefrontal cortex of the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR).Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792(8):766-776.
[21] 杨朝鲜,李雷激,高小青.Neuroplastin在培养的神经元的表达及对小脑颗粒细胞神经突起生长与神经元存活的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2009,25(5):546-552.
[22] Sarto-Jackson I, Milenkovic I, Smalla KH,et al.The cell adhesion molecule neuroplastin-65 is a novel interaction partner of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors.J Biol Chem. 2012;287:14201-14214.
[23] 梁新华,焦炎,高彩荣.大鼠闭合性脑损伤后MAP-2的时序性表达[J].中国法医学杂志,2011,26(2):32-34.
[24] Yiu G,He Z.Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration.Nat Rev Neurosci.2006;7:617-627.
[25] Yuan YM, He C.The glial scar in spinal cord injury and repair. Neurosci Bull. 2013;29(4):421-435.
[26] Mehta NR,Lopez PH,Vyas AA,et al.Gangliosides and Nogo receptors independently mediate myelin-associated glycoprotein inhibition of neurite outgrowth in different nerve cells.J Biol Chem.2007;282(38):27875-27886.
[27] Chivatakarn O,Kaneko S,He Z,et al.The Nogo-66 receptor NgR1 is required only for the acute growth cone-collapsing but not the chronic growth-inhibitory actions of myelin inhibitors. J Neurosci.2007;27(27):7117-7124.
[28] 许华燕,王俊娟,翟月.少突胶质细胞核脊髓损伤[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012,29(6):1226-1229.
[29] Huang JY,Wang YX,Gu WL,et al.Expression and function of myelin-associated proteins and their common receptor NgR on oligodendrocyte progenitor cells. Brain Res.2012; 1437: 1-15.
[30] 张亮,冯世庆.轴突生长抑制因子的实验研究进展[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(2):121-124.
[31] Ji B,Case LC,Liu K,et al.Assessment of functional recovery and axonal sprouting in oligodendrocyte-mrelin glycoprotein (OMgp)null mice after spinal cord injury.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2008;39(2):258-267. |