Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (22): 3581-3586.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.22.023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Orthopedic treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: implant fixation and bony fusion
Chen Bin1, Wang Wen-ji2, Li Wang-li3
- 1First Clinical Medical College, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2Department of Spine Surgery, First Hospital, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 3Department of Pathology, Yulin Municipal Second Hospital, Yulin 719000, Shaanxi Province, China
-
Revised:2014-04-25Online:2014-05-28Published:2014-05-28 -
Contact:Wang Wen-ji, Chief physician, Professor, Department of Spine Surgery, First Hospital, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China -
About author:Chen Bin, Studying for master’s degree, Attending physician, First Clinical Medical College, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Bin, Wang Wen-ji, Li Wang-li. Orthopedic treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: implant fixation and bony fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(22): 3581-3586.
share this article
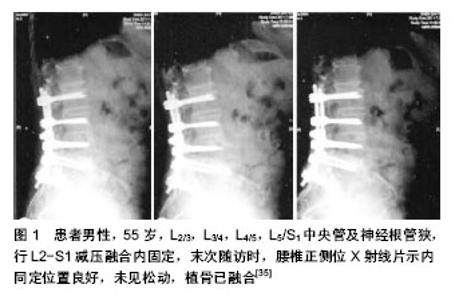
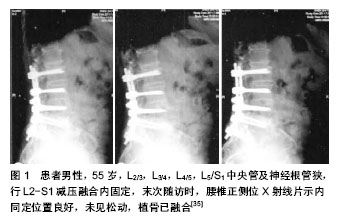
2.1 外科治疗指南 目前腰椎管狭窄症的外科治疗指征尚存在争议,退行性腰椎管狭窄症是一种慢性疾病,一般不会危及患者的生命,部分患者的症状可以自行中止发展或到改善。因此,发病后应首先选择保守治疗。如保守治疗无效且症状加剧,并出现以下症状、体征时,才考虑外科治疗。①自觉症状明显且持续性加重,活动后腰痛及双下肢麻痹、疼痛,肌肉萎缩,严重影响正常生活和工作。②明显的神经损害,进行性神经功能缺失。③进行性加重的腰椎滑脱、侧凸伴相应的临床症状和体征[13]。即使出现上述症状,亦有保守治疗好转的报道。有些调查显示,腰椎管狭窄症手术后1,2,5,10年的再手术率分别是2%,5%,8%和11%[14]。但大部分学者认为,对于腰椎管狭窄严重,下肢疼痛、间歇性跛行、马尾综合征等症状明显,严重影响患者日常生活、工作,经保守治疗3-6个月无明显缓解,全身情况可耐受手术者,均应行手术治疗。 2.2 外科治疗方法 腰椎管狭窄症的手术治疗的主要目的是为了对“责任节段”彻底减压,松解受压迫的神经根和(或)马尾神经,同时尽量保证脊柱的稳定性,以达到改善症状,提高生活质量的目的[15],并非治愈。对于责任节段的确定,必须结合临床症状、神经定位体征及影像学检查结果,以获得准确定位[16]。手术方式主要包括以下几种。 2.2.1 椎板减压优势与不足 全椎板切除减压:全椎板切除减压一直被认为是退变性腰椎管狭窄症的传统经典治疗方式。全椎板减压具有视野宽,显露好,相对好操作,神经减压彻底的优点。据Wiltse报道,第1例椎板减压是在1893年,由Lane医生主刀治疗1例马尾神经综合征的患者[17]。Sachs和Fraenkel于1900年首次报告临床应用此术式并获得较好临床效果。对于严重的退变性腰椎管狭窄症,在选择手术治疗时主要是以全椎板切除为主的后路减压。 全椎板切除主要适用于:①多种原因造成单一平面的严重椎管狭窄,硬膜囊需要充分的减压。②多节段的、多平面的严重椎管狭窄。③狭窄节段腰椎不稳定,需要行植骨融合内固定。外科治疗应针对椎间盘、增生的黄韧带及小关节引起的中央管、侧隐窝及神经根管进行逐步减压。减压治疗时维持脊柱的稳定性、彻底减压、恢复椎管容积是外科治疗的主要目的[18]。外科治疗的关键是解决所有狭窄因素,彻底切除导致硬膜囊及神经根受压的病理结构,减压的彻底与否是影响疗效的主要原因。 Guigui等[19]研究发现在近期外科治疗失败的病例中,56%是因为减压不充分引起的。Gelalis等[20]通过全椎板切除术治疗54例腰椎管狭窄症患者,平均随访11.6年,效果满意,优良率达72%。然而,全椎板切除破坏了腰椎后部结构,影响了脊柱的稳定性,手术形成硬膜外瘢痕粘连致神经根和硬膜受牵拉而产生疼痛、麻木、无力等症状。瘢痕挛缩可引起再次狭窄,出现临床症状,远期疗效常下降,且有腰椎不稳、滑脱等并发症[21-22]。Johasson报道全椎板切除治疗腰椎管狭窄,术后发生腰椎滑脱约20%[23],于是,越来越多的医师倾向于用有限减压的方法进行治疗,以维持脊柱的稳定。 改良的全椎板减压:近年来人们通过改良的全椎板减压手治疗腰椎管狭窄症,也叫保留棘突的全椎板切除,治疗适应证与全椎板切除一样,是从病变较重一侧的腰椎暴露一侧椎板,将狭窄椎体相邻下一阶段的棘突从根部及棘突矢状位正中切断,将狭窄椎管上一阶段的棘突同样的方法切断,使狭窄椎管相对应的棘突能够相对侧移动(移动的棘突阶段应略大于狭窄的椎管),将棘突及另一侧骶棘肌向一边牵开,再行减压。 改良的全椎板减压相当于半椎板对椎体的破坏,有效的保护了骶棘肌小关节、棘突、棘上韧带、棘间韧带及腰背筋膜。在没有进行植骨融合内固定等措施的情况下未发现有椎体不稳及复发情况。改良的全椎板切除术是治疗腰椎管狭窄中对传统手术的有效补充,脊柱的长期稳定性依赖于脊柱的软组织稳定与骨组织稳定的协调平衡。改良手术不仅仅是减小骨组织的破坏而是更注重对这一平衡机制的重视。卢宁、汤光荣等[24]在对25例腰椎管狭窄患者行改良减压手术后,随访5年,症状较术前缓解在90%以上。 半椎板切除减压:该术式主要用于单节段或双节段椎管狭窄,不合并腰椎不稳,减压过程中关节突关节基本完整保留者。即骨膜下剥离骶棘肌并显露椎板、关节突,切除棘突、椎板、内聚的小关节内侧缘,行半椎板切除者仅切除一侧椎板及内聚小关节突内侧缘而保留棘突、棘问及棘上韧带,充分显露硬脊膜,扩大侧隐窝及神经根管,使神经根充分减压、松弛。1997年Spetzger等[25]报道了单侧椎板切除两侧减压的手术方法。吴叶等[26]对38 例轻或中度单侧腿疼的退变性腰椎管狭窄症患者分别行单椎板切除两侧减压和保守治疗,随访2 年,单椎板切除有效率达68%,而保守治疗组有效率仅33%,认为对于轻或中度单侧腿痛的退变性腰椎管狭窄症,单椎板切除治疗的效果较保守治疗要好,而且可以避免因为全椎板切除而产生的并发症。 开窗减压:长期以来,全椎板切除一直是标准的减压术式,广泛椎板切除脊柱后柱,可引起腰椎术后不稳,使远期疗效下降。椎板开窗减压不仅有效保留了腰椎后部结构,还最大限度解除神经根压迫、保持了脊柱的稳定性,也有效避免了椎板切除术后形成瘢痕和萎缩的椎旁肌肉神经对硬膜和神经根的刺激,防止了腰椎的不稳和滑脱。在外科治疗时要注意椎管及神经根的致压物,特别是椎间盘组织要清除干净,使椎管扩大,神经根得到彻底松解,从而为神经恢复创造有利条件。在实施外科治疗时要注意:确定开窗的范围,保留棘突、棘间棘上韧带及腰背筋膜的连续性,从而保留腰椎后部张力结构,保持脊柱的稳定性[27]。Fu等[28]的前瞻性研究表明,开窗术长期疗效优于全椎板切除术,优良率89%,且并发症及费用均较少。 2.2.2 植骨融合 以融合的方式治疗退行性腰椎管狭窄症的主要目的是预防因为减压带来的医源性失稳并改善慢性腰痛的症状,全椎板切除造成医源性不稳的报道不少见。Nair等[29]报道其所做的全椎板切除后患者不稳定发生率为10%-15%,其中17%患者需再次手术解决新形成的狭窄或不稳治疗。而内固定仅仅起到辅助融合的作用。获得骨性融合是最终目的。 近20年来,随着脊柱内固定器械的发展。融合术越来越多的应用于腰椎退行性疾病的外科治疗[30]。最常用的植骨方法有椎体间植骨、横突间植骨及小关节突植骨等,横突间植骨,暴露面积相对较大,出血量较多,加之横突周围有小关节突的关节囊、筋膜及肌肉等软组织的影响,很难做出良好的植骨床[31],而且横突间植骨远离脊柱后柱中心,并不完全符合脊柱生物力学要求,部分病例术后出现植骨吸收、骨愈合不良、假关节形成,甚至引起断棒断钉、内固定失败等。 横突间植骨的假关节发生率较高,同时缺乏椎板的有效保护,使硬膜囊及神经根发生黏连,加重骨质增生而产生再次狭窄,从而影响手术效果。椎间植骨能够恢复椎体间高度、腰椎生理前凸及腰椎生物力学特性,为其提供纵向支撑,椎体间融合因具有较高的融合率以及能够提供术后即刻稳定性已被广泛采用。植骨是纠正原有腰椎不稳和减压后可能出现不稳的重要措施,尤其对广泛的减压术后,有利于改善临床症状[32]。 融合的具体指征主要有:①全椎板切除后,伴有50%以上的小关节突切除者。②双侧50%以上关节突切除或单侧全关节突切除者。③融合前行腰椎过伸、过屈位摄片提示有腰椎不稳者( 椎体平移超过4 mm,成角大于10°)。④相同节段再次手术者。⑤严重的下腰痛。 1991年Herkowitz和Kurz对50例退行性腰椎滑脱伴椎管狭窄症的患者进行了单纯减压与减压加原位融合的前瞻性对比研究,平均3年的随访结果表明减压加融合组的腰痛缓解率要明显高于单纯减压组。Lombardi等对47名神经减压的患者2-7年随访,结果表明:全关节切除,临床优良率33%;关节保留,临床优良率80%;加有后外侧融合,临床优良率90%。建议椎管减压应保留关节突,植骨融合能提高临床疗效。Breen等[33]结合临床文献认为,存在明显的下腰痛、椎体滑脱、行广泛椎管探查减压以及相对年轻爱好体育运动退变性腰椎管狭窄症患者,行椎管减压时需行融合。 2.2.3 植骨融合与内固定 如有腰椎失稳、腰椎滑脱及广泛减压小关节破坏者,在减压的同时还需行内固定和植骨融合。在以下情况时可考虑放置内固定器:①退行性腰椎管狭窄合并腰椎滑脱或腰椎侧凸和旋转畸形,负重行走下腰痛明显加重者。②腰椎管狭窄症减压范围较广,有可能致脊柱节段不稳者。③合并腰椎间盘突出。④腰椎管狭窄术后发生假关节需要再次手术,同一节段反复多次减压致腰椎不稳者。⑤部分年龄较大、肥胖女性、不宜长期卧床的患者,并且患者明确表示术后需早期活动者。但是有骨质疏松者应慎用。 国外研究认为腰椎管狭窄症外科治疗后远期疗效的优良率为40%-80%[34],国内目前对其远期疗效的研究缺乏大样本量报道。朱迪、李危石等[35]对腰椎管狭窄症患者行减压固定融合后经平均7年以上的随访,整体优良率仍然达74.6%。且治疗后各种评分较治疗前均有明显改善(图1)。提示腰椎管狭窄症减压固定融合后中远期疗效较满意。杨晋才,海摇涌,藏摇磊等[36]回顾性随访分析了53例双节段腰椎椎管狭窄症行后路减压椎间加压植骨联合单枚cage置入椎体间融合的临床疗效,认为该术式效果肯定,外科治疗方式安全,治疗后恢复快,出现下腰疼痛病例少,融合率高。 2.2.4 非融合性内固定 坚强固定引起的邻近节段退变逐渐引起临床医生的高度关注。腰椎融合后邻近节段出现退变的比例高达52.5%[37]。Mulholland等[38]综合多篇文献后,提出了动力性固定的概念。所谓动力固定也称软固定或弹性固定,即通过内固定装置既固定脊柱节段,又允许其在限制的范围内活动,从而增加相应水平椎管横截面积和椎间孔高度,降低椎间盘内负荷和关节突关节负荷以缓解疼痛,达到增加载荷分享,减少应力遮挡和应力集中的作用,控制异常活动,保持运动功能来预防邻近节段退变,使失稳的腰椎达到接近正常状态的活动特性,实现动态重建腰椎序列[39],对腰椎只固定而不是融合。 祝明浩等[40]应用Dynesys系统治疗腰椎退变性疾病患者24例,治疗后ODl评分较术时明显下降,日本骨科协会(JOA)评分治疗后较治疗前明显提高,效果满意。Fayyazi等[41]报道采用Dynesys系统治疗椎管狭窄、椎间盘退变、退变性滑脱等腰椎病变及再次修复手术患者83例,平均随访38.1个月。治疗后腰腿痛评分及Oswestry评分较治疗前都有明显的改善。 非融合固定技术改变了脊柱运动节段的负载模式,减少后部终板、纤维环承受的应力,分散小关节承受的应力,不影响邻近节段椎间盘内应力和运动;对脊柱生理结构的破坏小,增强了腰椎稳定性,保留了腰椎正常解剖结构,相应节段的运动功能对相邻节段的影响明显小于融合术;限制腰椎异常活动,保留正常活动度,并且在外科治疗过程中操作简单、安全性高。这些都充分展现了非融合技术的优势。其动态固定的理念已为众多脊柱外科医生所接受,非融合技术无疑为腰椎退行性疾病的治疗增加了一种全新的选择。"
| [1] Siebert E, Prtiss H, Klingebiel R, et al .Lumbar spinal stenosis syndrome diagnostics and treatment.Nat Rev Neurol. 2009; 5(7): 392-403.
[2] Haig AJ, Tong HC, Yamakawa KS, et al. spinal stenosis,back pain,or no symptoms at all A masked study comparing radiologic and electrodiagnostic diagnoses to the clinical impression. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.2006;8(7):897-903.
[3] 蔡维山,鞠洪斌,郭东明.腰椎管狭窄症诊断新进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2008,29(3): 177-186.
[4] Amundsen T, Weber H,Lilleas F, et al.Lumbar spinal stenosis: clinical and radiologic features. Spine.1995;20(10):1178-1186.
[5] 赵太茂,邱贵兴,仉建国,等.291例腰椎管狭窄症患者的临床特点分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2006,16(1l): 812-814.
[6] Azimi P, Mohammadi HR, Montazeri A.An outcome measure of functionality in patients with lumber spinal stenosis: a validation study of the Iranian version of Neurogenic Claudication Outcome Score. BMC Neurol.2012;9(12): 101.
[7] Airaksinen O, Hemo A, Turunen V, et al. SurgicaI outcome of 438 patients treated surgically for lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine.1997;22(19):2278-2282.
[8] 赵慧毅,梅芳瑞,叶欣,等.腰椎管狭窄症的手术减压与内固定选择(259例临床分析)[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2003,13(1):18-21.
[9] Shabat S, Arinzon Z,Folman Y. Long-term outcome of decompressive surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis in octogenarians.Eur Spine.2008;17(2):193-198.
[10] Weinstein JN.Surgical versus nonsurgical therapy for lumbar spinal stenosis.NEnglJMed.2008;358:794-810.
[11] Malmivaara A.Surgical or nonoperative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis A randomized controlled trial. Spine. 2007; 32:1-8.
[12] Siebert E,Pruss H,Klingebiel R,et al.Lumbar spinal stenosin: syndrome,diagnostics and treatment.Nat Rev Neurol. 2009; 5(7):392-403.
[13] Cakir B, Schmidt R, Reichel H, et al.Lumbar disk hemiation: what are reliable criterions indicative for suigery. Orthpedics. 2009;32 :589.
[14] Jansson AK, Nemeth G, Granath F, et al.Spinal stenosis reoperation rate in Sweden is 11% at 10 years a-national analysis of 9664 operations. Eur Spinal J.2005;14 (1): 659-633.
[15] Kaptan H, Kasin O, Cakiroglu K, et al. Lumber spinal stenosis in elderly patients.Amm N Y Acad Sci.2007;4(2):173.
[16] 刘付明.退行性多节段腰椎管狭窄症定位诊断[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(9): 651-653.
[17] Szpalski M,Gunzburg R.Lumbar spinal stenosis in the elderly:an overview. Eur Spine J.2003;12 Suppl 2:S170-175.
[18] Tetsuhiro I, Akira K, Junichi N, et al. Minimum 10years outcome of decompressive laminectomy for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis.Spine.2000;25(14):754-756.
[19] Guigui P,Ulivieri JM,Lassale B,et al.Reoperations after surgical treatment of lumbar stenosis.Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot.1995;81:663-671.
[20] Gelalis ID,Stafilas KS,Korompilias AV,et al.Decompressive surgery for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis:long-term results.Int Orthop(SICOT).2006,30(1):59-63.
[21] 赵延胜,王文军.腰椎管狭窄症手术治疗进展[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2009,13(1):70-73.
[22] Yucesoy K,Crawford NR.Increase in spinal canal area after inverse laminoplasty:an anatomical study.Spine.2000; 25(21): 2771-2776.
[23] Johnsson KE,Willner S,Johnsson K.Postopertive instability after decompression for lumbar spina stenosis. Spine. 1986; 11:107.
[24] 卢宁,汤荣光,陈国强,等.改良全椎板切除术治疗腰椎管狭窄的疗效评价[J].中国伤残医学,2006,14(3):1-3.
[25] Spetzger U, Bertalanffy H, Reinges MH, et al. Unilateral laminotomyfor bilateral decompression of lumbar spinal stenosis. PartII:Clinical experiences.ActaNeuroc hir(Wien). 1997;139(5):397-403.
[26] 吴叶,李家顺,贾连顺.单椎板切除双侧减压和保守治疗腰椎管狭窄疗效的比较[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2003, 24(4): 210-213.
[27] Gelalis ID,Stafilas KS,Korompilias AV,et al.Decompressire surgery for degenerative Lumbar spinal stenosisLong-term results.Int Orthop.2006;30(3):59-63.
[28] Fu YS,Zeng BF,Xu JG.Long-term outcomes of two different decompressive techniques for lumbar spinal stenosis.Spine. 2008;33(5):524-518.
[29] Nair GM,Nery PB,Diwakaramenon S,et al.A systematic review of randomized trials comparing radiofrequency ablation with antiarrhythmic medications in patients with atrial fibrillation.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol.2009;20(2):138-144.
[30] Chou R,Baisden J,Carragee EJ,et al.Surgery for low back paln:a review of the evidence for an American Pain Society Clinical Practice Guideline.Spine.2009;34(10):1094-1109.
[31] 张贵林,荣国威,丁古云,等.脊柱胸腰段骨折术后椎弓根螺钉断裂及弯曲松动的原因分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(8):470-472.
[32] 贾连顺,扬立利.退变性腰椎管狭窄症的现代外科学概念[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,2(8):509 -512.
[33] Breen A, Muggleton J, Mellor F, et al. Lumbar intervertebralmotion in asymptomatic and postfusion subjects. J Bone JointSurg Br. 2005,87-B(SUPP_I): 35.
[34] Airaksinen O,Herno A.Turunen V,et al.Surgical outcome of 438 patients treated surgically for lumbar spinal stcnosis. Spine. 1997;22(19):2278-2282.
[35] 朱迪,李危石,陈仲强,等. 腰椎管狭窄症减压定融合术后远期疗效及其影响因素分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(10): 865-871.
[36] 杨晋才,海摇涌,藏摇磊,等.加压植骨联合单枚cage的椎体间融合与后外侧融合治疗双节段腰椎椎管狭窄症临床效果的回顾性研究[J].脊柱外科杂志,2011,9(4):216-219.
[37] Yu CH,Lee JE,Yang JJ,et al.Adjacent segment Degeneration after Single-Level PLIF:Comparison between Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis,Degenerative Spondylolisthesisand spinal stenosis.Asian spine J.2011;5(2):82-90.
[38] Mulholland RC, Sengupta DK. Rationale, principles and experimental evaluation of the conceptofsoftstabilization. Eur Spine J.2002;11 Suppl2: S198-S205.
[39] 王洪立,姜建元.腰椎棘突间分离装置研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008;18(8):631-634.
[40] 祝明浩,夏茂凤.Dynesys系统内固定联合椎板开窗减压术治疗腰椎退变性疾病[J].中医正骨,2011,23(12):53-55.
[41] Fayyazi AH, Ordway NR, Park SA, et al. Radiostereometric analysis of postoperative motion after application of dynesys dynamic posterior stabilization system for treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis. J spinal Disord Tech.2010; 23(4):236-241.
[42] Alimi M, Njoku I Jr, Cong GT, et al.Minimally Invasive Foraminotomy Through Tubular Retractors Via a Contralateral Approach in Patients With Unilateral Radiculopathy.Neurosurgery. 2014 Mar 27. [Epub ahead of print].
[43] Aleem IS, Rampersaud YR.Elderly Patients Have Similar Outcomes Compared to Younger Patients After Minimally Invasive Surgery for Spinal Stenosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Dec 4. [Epub ahead of print].
[44] Nandyala SV, Fineberg SJ, Pelton M, et al.Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: one surgeon's learning curve.Spine J. 2013 Oct 3. pii: S1529-9430(13) 01493-9.
[45] Anand N, Baron EM, Khandehroo B.Does Minimally Invasive Transsacral Fixation Provide Anterior Column Support in Adult Scoliosis?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2013 Nov 6. [Epub ahead of print].
[46] Zou S, Wang J, Pan W, et al.Comparison of traumatic related index in serum between minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for tissue injury.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013; 27(8):960-964.
[47] Perez-Cruet MJ, Hussain NS, White GZ,et al.Quality-of-life outcomes with minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion based on long-term analysis of 304 consecutive patients.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2014;39(3): E191-198.
[48] Hironaka Y, Morimoto T, Motoyama Y,et al.Surgical management of minimally invasive anterior lumbar interbody fusion with stand-alone interbody cage for L4-5 degenerative disorders: clinical and radiographic findings.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo).2013;53(12):861-869.
[49] Ang CL, Phak-Boon Tow B, Fook S,et al.Minimally invasive compared with open lumbar laminotomy: no functional benefits at 6 or 24 months after surgery.Spine J. 2013 Oct 4. pii: S1529-9430(13)01382-X.
[50] Chen KS, Than KD, Lamarca F, et al.Minimally invasive unilateral approach for bilateral decompression of spinal stenosis and modified transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative spondylolisthesis.Neurosurg Focus.2013; 35(2 Suppl):Video 4.
[51] Ding Y, He S, Zhang H.Minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis stenosis.Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.2013;27(4):404-408.
[52] Toyoda H,Nakamura H,Konishi S,et al.Clinical outcomeof microsurgical bilateral decompression via unilateral approach for lumbar canal stenosis:minimum five-year follow-up. Spine. 2011;36(5):410-415. |
| [1] | Lu Yao-jia, Xiong Chuan-zhi, Li Xiao-lei, Hu Han-sheng, Chen Gang, Wang Qiang, Lu Zhi-hua. Comparison of two methods for reducing blood loss during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(7): 1004-1008. |
| [2] | Jiang Wei, Yuan Feng. Unilateral pedicle screw fixation combined with translaminar facet screw fixation versus bilateral pedicle screw fixation for lower lumbar degenerative diseases: a 2-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(19): 2973-2979. |
| [3] | Zhang Song, Zhang Tao, Yang Jian-wen, An Min, Tang Ben-sen. Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid on blood loss in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus during total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017, 21(11): 1681-1687. |
| [4] | A Jian-cuo, Wang Xi-min, Li Zhan-yin, Xu Zhi-hua. Biocompatibility of anatomic porous titanium fusion cage [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7185-7191. |
| [5] | Liang Lei, Liu Wen-de, Wu Yi-fan, Sun Xiao-hang, Ding Jun-jie . Posterior percutaneous pedicle screw fixation for acute thoracolumbar vertebral fractures with simple anterior spinal column injury: study protocol for a retrospective, self-controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7267-7272. |
| [6] | Zhang En-ze, Liao Zhen-hua, Liu Wei-qiang. Research method and progresses of biomechanical properties of human spine [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7273-7279. |
| [7] | Chen Qun-qun, Chen Jian-fa, Zhou Chi, Dong Lu-jue, Huo Shao-chuan, Wang Hai-bin. Blood loss in primary total knee replacement with intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid and presurization [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6564-6569. |
| [8] | Liu Hong-bin, Zhao Han-qing, Shi Yue, Hou Li-jun, Wang Zhong-xun. Establishment and volume estimation of three-dimensional digital model of osteoarthrosis of the femoral head [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6629-6635. |
| [9] | Wu Tao, Zhang Guo-qiu. Minimally invasive treatment of proximal humerus fractures with locking compression plate improves shoulder function in older patients: study protocol for a prospective randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(44): 6655-6660. |
| [10] | Zhou Li, Yang Hong-lin, Cao Xiao-jian. Selective decompression of lumbar root canal and pedicle screw fixation after laminectomy for the treatment of elderly lumbar spinal stenosis: indications and prognosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5195-5202. |
| [11] | Wan Sheng-yu1, Yang Bo2, Lin Xu1. Influences of BioFlex dynamic stabilization system fixation on the stress of adjacent segments of intervertebral disc at different decompression ranges [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5203-5209. |
| [12] | Zhai Peng-fei, Liu Wei, Sun Zhi-ming, Zhang Xue-li. Adjacent segment degeneration after anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5216-5223. |
| [13] | Hao Ting, Wang Xing-guo, Li Xiao-he. Finite element analysis of distal femoral locking plate and minimally invasive internal fixation system in different motion states [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5237-5243. |
| [14] | Huang Jia-gu, Zhang Ke, Tian Hua, Wang Xiao-yong, Cai Hong, Li Zi-jian, Li Feng. Influential factors for hidden blood loss after primary unilateral total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3823-3829. |
| [15] | Wang Shao-gang, Tao Zhong-liang, Wang Sheng, Tang Ji-ying. Correlation of free fatty acids and hidden blood loss after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3830-3836. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||